Chemistry Exam 3
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
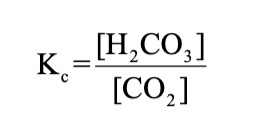
3.2
1.9M
Consider the following reaction: 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2 SO3(g) ; Kc = 1.7 × 108
The concentrations at equilibrium are: [SO2]eq = 0.0034 M, [O2]eq = 0.0018 M.
Determine the equilibrium concentration of SO3(g).
2.6 × 10^-5
The equilibrium constant is given for one of the reactions below. Determine the value of the missing equilibrium constant.
H2(g) + Br2(g) ⇌ 2 HBr(g) K1 = 3.8 × 104
2 HBr(g) ⇌ H2(g) + Br2(g) K2 = ?
5.7 × 10^-7
The reaction below has a Kp value of 3.3 × 10-5. What is the value of Kc for this reaction at 700 K?
2 SO3(g) ⇌ 2 SO2(g) + O2(g)
0.021
2.50 mol NOCl was placed in a 2.50 L reaction vessel at 400ºC. After equilibrium was established, it was found that 28% of the NOCl had dissociated according to the equation
2NOCl(g) →← 2NO(g) + Cl2(g).
Calculate the equilibrium constant, Kc, for the reaction.
17
A reaction mixture A(g) + 2B(g) →← C(g) was allowed to come to equilibrium. The initial amounts of reactants placed into a 5.00 L vessel were 1.0 mol A and 1.8 mol B. After the reaction reached equilibrium, 1.0 mol of B was found. Calculate Kc for this reaction.
7.5
The brown gas NO2 and the colorless gas N2O4 exist in equilibrium, 2NO2 →← N2O4. In an experiment, 0.625 mole of N2O4 was introduced into a 5.00 L vessel and was allowed to decompose until equilibrium was reached. The concentration of N2O4 at equilibrium was 0.0750 M. Calculate Kc for the reaction.
0.152 atm
Pure NO2(g) is placed into a vessel at a pressure of 0.500 atm. At equilibrium, the total pressure inside the reaction vessel is 0.674atm. The reaction that takes place is: 2NO2(g) →← 2NO(g) + O2(g) . Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure of NO2.
2.7M
For this reaction 3H2(g) + N2(g) →← 2NH3(g), Kc = 6.0 ◊ 10–2 at 500°C. The concentrations at equilibrium are: 0.250 M H2 and 0.050 M NH3. What is the equilibrium concentration of N2?
Number 1
For the equilibrium reaction 2SO2(g) + O2(g) →← 2SO3(g), ΔHºrxn = –198 kJ/mol. Which one of these factors would cause the equilibrium constant to increase?
Decreasing the temperature
Increasing the pressure
A catalyst does not change the equilibrium constant because it does not alter the energies of the reactants or products
Explain why addition of a catalyst does not affect the equilibrium constant for a reaction.
17.3
5.00 mol of ammonia are introduced into a 5.00 L reactor vessel at high temperatures. The reaction that takes place is:
2NH3(g) → ← 3H2(g) + N2(g)
At equilibrium, 1.00 mole of ammonia remains. Calculate Kc for the reaction.
7.1g
Calcium carbonate decomposes at high temperatures to give calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
CaCO3(s) →← CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Kp for this reaction is 1.16 atm at 800°C.
A 5.00 L vessel containing 10.0 g of CaCO3(s) was evacuated to remove the air, sealed, and then heated to 800°C. Ignoring the volume occupied by the solid, what will be the mass of the solid in the vessel be once equilibrium is reached?
66.7
Given the reaction PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) → PCl5(g)
An equilibrium mixture at 450 K contains
PCl3 = 0.124 atm,
Cl2= 0.157 atm, and
PCl5= 1.30 atm.
What is the value of Kp at this temperature?
4.0 × 10^-2
The reaction below has a Kc value of 61. What is the value of Kp for this reaction at 200 ᵒC?
N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ⇌ 2 NH3(g)
0.253 M CO2, and 0.053 M H2
For the reaction CO2(g) + H2(g) ⇌ H2O(g) + CO(g) , Kc = 1.6 at 990ºC.
Calculate the concentration of carbon dioxide and hydrogen in the final equilibrium mixture obtained by initially adding 2.00 mol of CO2 , 1.00 mol of H2, to a 5.00 L reactor at 990ºC.
a. 19.5
b. Yes
c. [H2] = 0.250 M, [I2] = 0.041 M, [HI] = 0.746 M)
A reaction mixture of 0.623 M H2, 0.414 M I2 and 2.24 M HI is placed in a steel container. The reaction that takes place is:
H2(g) + I2(g) 2 HI (g) Kc = 54.3 at 430 ºC
Calculate the reaction quotient, Qc, for the initial mixture.
Will the reaction proceed towards making HI?
Calculate the concentration of these species at equilibrium.
0.020
The initial concentration of [CH4] = 0.114 M. At equilibrium, the mixture contains [C2H2] = 0.035 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, Kc, at this temperature?
2CH4(g) →← C2H2(g) + 3H2(g)
interdependent
The concentrations of Hb, O2, and HbO2 are all
the condition wherein the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal
Dynamic equilibrium
equal
At equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are _____ at equilibrium
the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction
Chemical equilibrium
concentration, pressure, volume, temperature
Factors that affect chemical equilibrium:
temperature dependent
Dynamic process is ________
relates the molar concentrations of the products and reactants after the equilibrium has been reached
Equilibrium constant
inverted
When the reaction is written in reverse (i.e., backward), the equilibrium constant, K, is
reaction quotient. predicts in which direction the reaction will proceed from a starting set of concentrations for all of the components of a reaction
Qc
reactants will be converted into products; reaction goes reactants → products
Qc<Kc
the reaction will proceed in the reverse direction. The products will decrease and reactants will increase.
Q>K
the reaction will proceed in the forward direction. The products will increase and reactants will decrease.
Q<K
the reaction is at equilibrium. The products and reactants will not change.
Q=K
Initial concentration
Change in concentration to reach equilibrium
Equilibrium concentration
ICE stands for
If an external stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system will adjust to reduce this stress and will re-establish new concentrations, keeping Kc constant (Kc is temperature dependent)
La Chatelier’s Principle
restored
If the conditions are changed, the concentrations of all the chemicals will change until equilibrium is ______
minimize
It says that if a system at equilibrium is disturbed, the position of equilibrium will shift to _________ the disturbance
favoring
If the temperature is increased, the system will shift to reduce this “added heat” by ______ the endothermic reaction
increases, changing, reducing
The equilibrium will be reached sooner because the catalyst ______ the rate of reaction by ______ the mechanism and ______ the activation energy
do not
Catalysts ______ affect the position of equilibrium
neutralize bases
Acids have the ability to …
hydrochloric acid
HCl
sulfuric acid
H2SO4
Nitric acid
HNO3
Acetic acid
HC2H2O2
Citric acid
H3C6H5O7
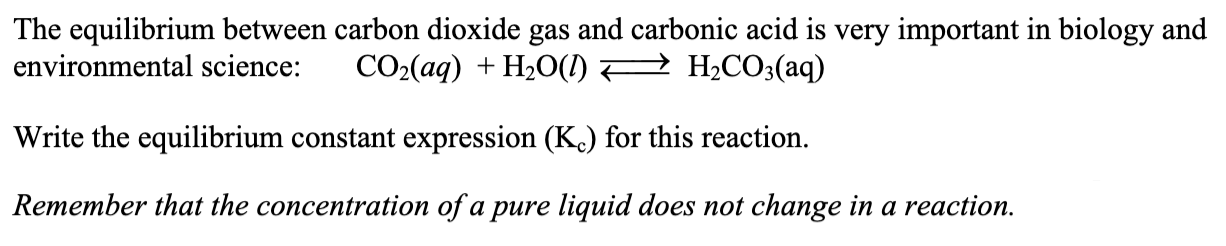
Carbonic acid
H2CO3
Hydroflouric acid
HF
Phosphoric acid
H3PO4
COOH
Carboxylic acids have a _____ group
H
Only the ___ in the (carboxylic acid) group is acidic
neutralize acids
Bases have the ability to …
Sodium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide
Sodium bicarbonate
Sodium carbonate
Ammonia
Name the 5 common bases
Sodium hydroxide
NaOH
Potassium hydroxide
KOH
Sodium bicarbonate
NaHCO3
Sodium carbonate
Na2CO3
Ammonia
NH3
Hydrochloric acid
Sulfuric acid
Nitric acid
Acetic acid
Citric acid
Carbonic acid
Hydroflouric acid
Phosphoric acid
Name the 8 common acids
H3O+
Hydronium ion formula
H+
An arrhenius acid releases ___ into solution
OH-
An arrhenius base releases ___ into solution
an acid that is an electron pair acceptor
Lewis acid
an base that is an electron pair donor
Lewis base
an acid that is a proton donor
Bronsted-Lowry acid
a base that is a proton donor
Bronsted-Lowry acid
an acid that fully dissociates in water
Strong acid
a base that fully dissociates in water
Strong base
an acid that doesn’t fully dissociate in water
Weak acid
a base that doesn’t fully dissociate in water
Weak base
when dissolved in water, they dissociate into ions
Why are acids and bases electrolytes
H2CO3 and HCO3-
In the reaction H2CO3 + H2O ⇌ HCO3 – + H3O+ , the Brønsted acids are
CO32-
Identify the conjugate base of HCO3 – in the reaction: CO3 2– + HSO4 – ⇌ HCO3 – + SO4 2–
H2CO3
Identify the conjugate acid of HCO3 – in the reaction and circle it: HCO3 – + HPO4 2– ⇌ H2CO3 + PO4 3–
-0.40
What is the pH of [H + ] in a 2.5 M HCl solution?
2.0 × 10^-3 M
The [OH– ] in a 1.0 x 10^–3 M Ba(OH)2 solution is
2.0 × 10^-13 M
What is the H+ ion concentration in a 4.8 x 10–2 M KOH solution?
a. 0.0057M
b. 3.4 × 10^-4
A 0.10 M HF solution is 5.7% ionized.
a) Calculate the [H + ]
b) calculate the Ka of HF
5.7%, pH= 2.1
Calculate the percent ionization of HNO2 in a 0.14 M HNO2 solution, knowing that the Ka of HNO2 is Ka = 4.6 x 10-4 . What is the pH of this solution?
a. 0.0025 M
b. 1.4 × 10^-4
If a 0.048 M lactic acid, HA, solution is 5.2% ionized, determine:
a) the [H3O+ ] concentration at equilibrium
b) the acidity constant, Ka, for this acid
12.65
Determine the pH of a KOH solution made by mixing 0.251 g KOH with enough water to make 100.0 mL of solution
0.004M
Calculate the [H + ] in lemon juice that has a pH 2.40.
a. 2.46
b. 0.0158M
a) Calculate the pH of a 3.5 x 10–3 M HNO3 solution
b) What is the [HNO3] if the pH of the solution is pH 1.80?
100
The pH of coffee is approximately pH 5. How many times greater is the [H+ ] in coffee than in pure water, pH 7 ?
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) →← NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
An aqueous solution of ammonia is basic. Write the net ionic equation that explains this observation.
water, aluminum oxide, zinc oxide
List 3 amphoteric species:
2.56 × 10^-11 M
Calculate the [OH⁻] in a solution that contains 3.9 × 10-4 M H3O⁺ at 25°C.
4 × 10^-5 M
The pOH of a solution is 9.60. Calculate the hydronium ion concentration in this solution.
HF because HF is the strongest bond so it ionizes the least in water
Identify the weakest acid and explain how you made the decision: HF HCl HBr HI
A. 2NO2 + H2O → HNO2 + HNO3
B. LiOH → Li+ + OH-
C. K2O + H2O → 2KOH
D. NaCl → Na+ + Cl-
E. Ca(OH)2 → Ca²+ + 2OH-
Reaction A produces an acidic solution that dissolves in water
Write the reaction with water for the following compounds. Which of the following produces an acidic solution when dissolved in water?
A) NO2
B) LiOH
C) K2O
D) NaCl
E) Ca(OH)2
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
N2O5 + H2O → 2HNO3
The oxides SO3 and N2O5 will form acids in water. Write the two reactions.
8.5 × 10^-6
A 0.294 M weak acid, HA, solution has a pH 2.80. Determine the Ka of the acid.
11.26
Determine the pH of a 0.188 M NH3 solution at 25°C. The Kb of NH3 is 1.76 × 10-5
D
Which of the following weak acids has the strongest conjugate base?
A) acetic acid, Ka = 1.8 × 10-5
B) nitrous acid, Ka = 4.5 × 10-4
C) dihydrogen phosphate ion, Ka = 6.2 × 10-8
D) hydrocyanic acid, Ka = 4.0 × 10-10
E) benzoic acid, Ka = 6.3 × 10-5
2.7 × 10^-3 M
pH = 2.57
What is the hydronium ion concentration and the pH of a 0.400 M acetic acid solution with Ka = 1.8 × 10-5? The equation for the dissociation of acetic acid is: CH3CO2H + H20 →← H3O+ + CH3CO2-
9.47
Calculate the pH of a 1.60 M CH3COONa solution. Ka for acetic acid, CH3COOH, is 1.8 × 10-5.
0.056 M
Determine the ammonia concentration of an aqueous solution that has a pH 11.00. The equation for the dissociation of NH3 (Kb = 1.8 × 10-5) is: NH3 + H2O →← NH4+ + OH-
4.03
Calculate the pH of a 0.020 M carbonic acid solution, H2CO3(aq), that has the stepwise dissociation constants Ka1 = 4.3 × 10-7 and Ka2 = 5.6 × 10-11
4.97
What is the pH of a 0.20 M solution of NH4Cl? Kb(NH3) = 1.8 x10–5
9.57
Morphine, C17H19NO3 (or R3N in short notation) is often used to control severe postoperative pain. What is the pH of the solution made by dissolving 25.0 mg of morphine in 100. mL of water? (For morphine, Kb = 1.62 10–6 .)
R3N + H2O →← R3NH+ + HO-
11.40
Calculate the pH of a solution containing 0.20 g of NaOH in 2.00 L solution.