Required Practical 3 - Electrolysis
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
How do you set up a general electrolysis experiment?
Place the positive and negative electrodes in a beaker containing a molten or dissolved ionic compound.
Connect both electrodes to a power supply with wires
How could you investigate what happens when an aqueous solution of CuCl₂ is electrolysed?
Half fill a beaker with aqueous CuCl₂.
Place a lid on the beaker and insert the electrodes into the solution through holes in the lid (electrodes must not touch).
Connect the electrodes to a low voltage power supply.
Switch the power supply on to 4V.
Turn off the power after a few minutes and record any observations
What forms at the cathode and the anode in electrolysis?
Cathode: Metals or hydrogen.
Anode: Non-metals
What would you observe at each electrode when copper chloride solution is electrolysed?
Positive electrode: Bubbles of gas (chlorine). Negative electrode: Electrode coated with a brown solid (copper)
What would you observe at each electrode when sodium chloride solution is electrolysed?
Positive electrode: Bubbles of gas (chlorine). Negative electrode: Bubbles of gas rapidly produced (hydrogen)
Draw a diagram of the apparatus set up when copper chloride solution is electrolysed.
see diagram
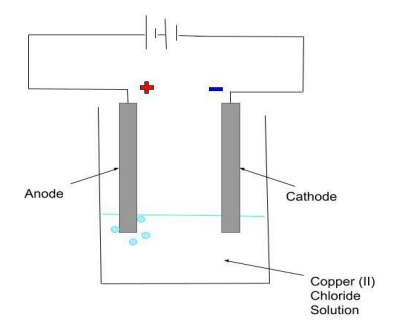
Why must the positive electrode (anode) be regularly replaced?
The positive electrode is made of carbon and will react with oxygen (produced during electrolysis) to produce carbon dioxide
Write half equations for the reactions that occur at the electrodes when aqueous CuCl₂ is electrolysed (Higher only)
Cathode: Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ ⟶ Cu.
Anode: 2Cl⁻ ⟶ Cl₂ + 2e⁻
Write half equations for the reactions that occur at the electrodes when aqueous NaCl is electrolysed (Higher only)
Cathode: 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ ⟶ H₂.
Anode: 2Cl⁻ ⟶ Cl₂ + 2e⁻
In the electrolysis of NaCl, hydrogen is produced at the cathode. Why is sodium not produced?
Hydrogen is produced because sodium is more reactive than hydrogen. Sodium remains in the solution
How could you test that chlorine gas was produced at the anode?
The gas produced will bleach damp litmus paper - it will turn white
How could you test that hydrogen gas was produced at the anode?
The gas produced will make a squeaky pop with a lighted splint
How could you test that oxygen was produced at the anode?
The gas produced will relight a glowing splint