SLP ANAPHY - Unit 2 (Part 2)
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Tissue
a group of cells that usually have a common origin with an embryo and function together to carry out specialized activities
Histology
a branch of science that deals with the study of tissues
Pathologist
a physician who examines cells and tissues to help other physicians make accurate diagnoses
Epithelial Tissue
Connective Tissue
Muscular Tissue
Nervous Tissue
the different types of tissues are:
Epithelial Tissue
this tissue covers body surfaces and lines hollow organs, body cavities, and ducts
Epithelial Tissue
this tissue allows the body to interact with both its internal and external environments
Epithelial Tissue
an avascular tissue that is composed of cells arranged in continuous sheets, in either single or multiple layers
Connective Tissue
this tissue protects and supports the body and its organs
Connective Tissue
this tissue has different functions, such as binding organs together, storing energy reserves as fat, and help provide immunity to disease-causing organisms
Muscular Tissue
this tissue is composed of cells specialized for contraction and generation of force; this tissue also generates heat that warms the body
Muscular Tissue
this tissue produces motion in response to muscle action potentials by contractility, extensibility, elasticity, and excitability
Muscular Tissue
this tissue consists of fibers that provide motion, maintain posture, and generate heat
Nervous Tissue
detects changes in a variety of conditions inside and outside the body and responds by sending action signals (nerve impulses) to the brain (control center) that activates muscular contractions and/or glandular secretions
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: the epithelial tissue contains many cells packed together with little or no extracellular matrix
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: the epithelial tissue has no blood vessels (avascular) and forms surface layers; it is also not covered by another tissue
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: the connective tissue has a few scattered cells surrounded by a large extracellular matrix
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: the connective tissue has a significant network of blood vessels (vascular)
Cell Junction
this is the points of contact between cells
Tight Juctions
Adherens Junctions
Demosomes
Hemidesmosomes
Gap Junctions
the types of cell junctions are:
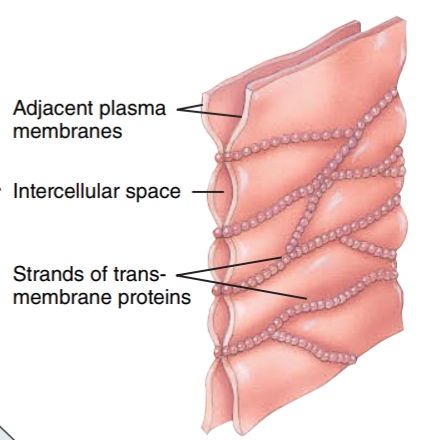
Tight Junctions
these consist of tight, weblike strands of transmembrane proteins that fuse adjacent plasma membranes, which prevent the contents of some organs from leaking into the blood and surrounding tissues
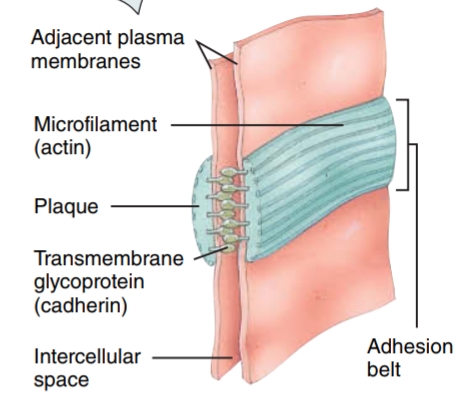
Adherens Junctions
these contain plaque, a dense layer of proteins on the inside of the plasma membrane, and an adhesion belt - this helps the epithelial cells resist separation during contraction
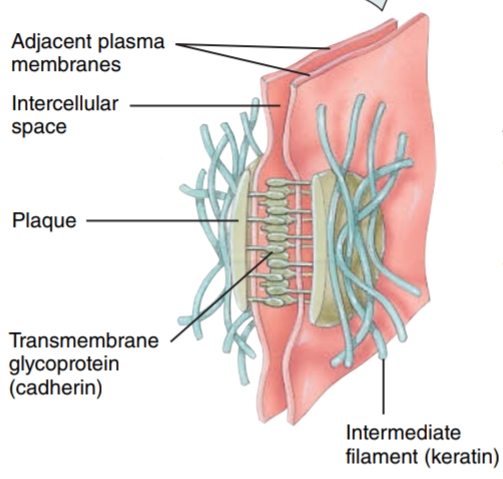
Desmosomes
they consist of intermediate filaments, which contain keratin - these contribute to the stability of the cells and tissues; they prevent epidermal cells from separating during contraction
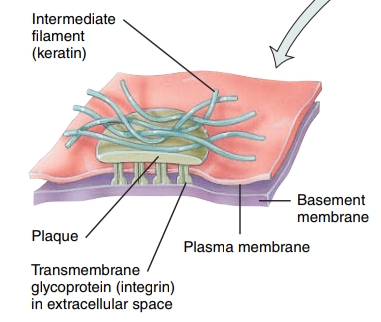
Hemidesmosomes
these resemble desmosomes, but they do not link adjacent cells - they are attached to the basement membrane via laminin
Gap Junctions
these junctions’ plasma membranes are separated by a narrow intercellcular gap - connexons serve as tiny tunnels which allow diffusion of small particles from the cytosol of one cell to another
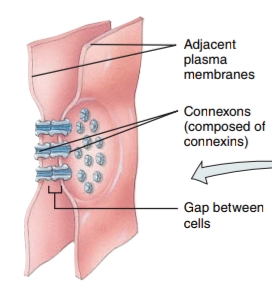
Apical (Free) Surface - faces the body surface
Lateral Surface - face the adjacent cells on either side
Basal Surface - the deepest layer of the epithelial cell
the different surfaces of the epithelial cell are:
Covering and Lining Epithelium
Glandular Epithelium
the types of epithelial cell:
Covering and Lining Epithelium
forms the outer covering of the skin and some internal organs
Covering and Lining Epithelium
forms the inner lining of blood vessels, ducts, body cavities, and interior of respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive system
Glandular Epithelium
makes up the secreting portion of glands (e.g. thyroid gland, adrenal gland, sweat glands, and digestive glands)
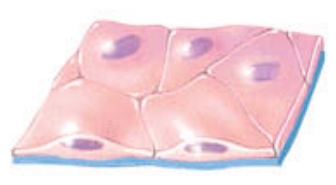
Squamous - squashed flat
Cuboidal - cube-shaped
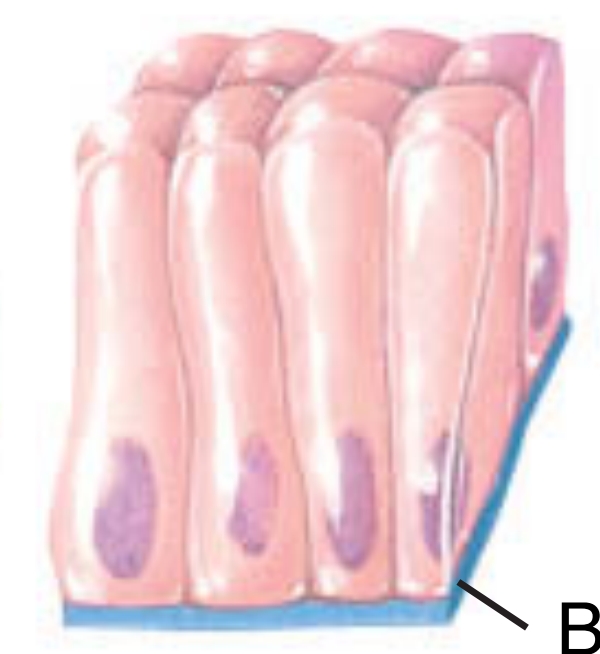
Columnar - column-shaped
the different cell shapes of covering and lining epithelium are:
Squamous
this cell shape is flat and thin; it allows for rapid passage of substances
Cuboidal
this cell shape is cube-shaped and is tall as it is wide; its apical surface have microvilli and function in secretion and absorption

Columnar
this cell shape column-shaped and is much taller than it is wide; it protects underlying tissues and their apical surface have cilia or microvilli
Transitional
this cell “shape” is composed of at least two cell types; they change shape and are found in organs that need to stretch (e.g. the urinary bladder)
Simple
Pseudostratified
Stratified
the different arrangement of cells in layers are:
Simple
this arrangement is composed of a single layer of cells that functions in diffusion, osmosis, filtration, secretion, and absorption

Pseudostratified
this arrangement looks like it has multiple layers because the cells lie at different levels and not all reach the apical surface
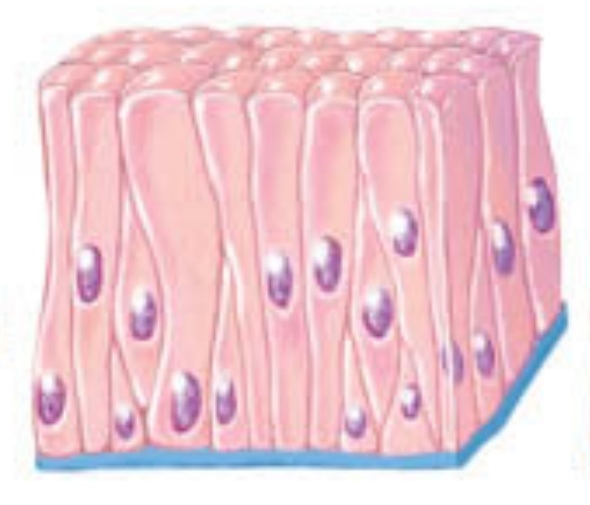
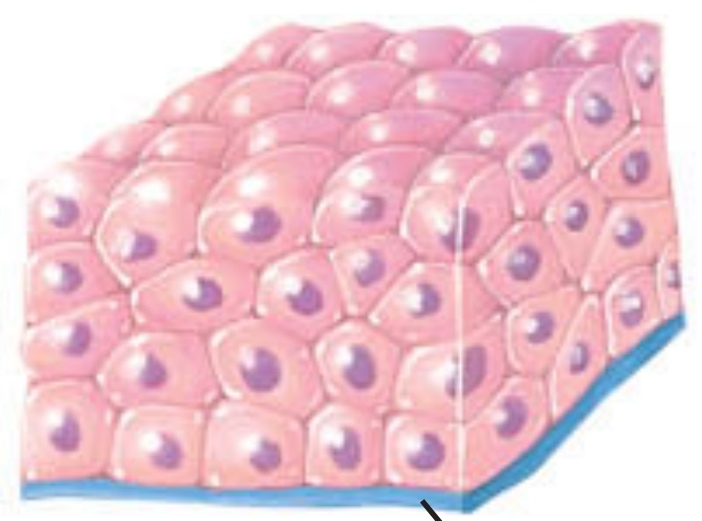
Stratified
this arrangement is composed of multiple layers to protect underlying tissues in locations with considerable wear and tear
Unicellular (single-celled) - goblet cells
Multicellular (multiple cells) - sweat, oil, salivary glands
the different glandular epithelium structures are:
Merocrine Secretion
Apocrine Secretion
Holocrine Secretion
the different glandular functions are:
Merocrine Secretion
secretions are released from the cell in secretory vesicles (e.g., salivary glands and pancreas)
Apocrine Secretion
secretions accumulate at the apical surface of the cell, then a portion of the cell is pinched off during secretion (e.g., mammary glands)
Holocrine Secretion
secretions accumulate in the cytosol - as the cell matures, it ruptures (dies) and becomes the secretory product
Endocrine
Exocrine
the types of glandular epithelium are:
Endocrine
release hormones to the bloodstream that regulate metabolic and physiological activities to maintain homeostasis
Exocrine
produce substances outside the bloodstream onto the skin surface or body cavities to aid in lowering temperature, lubrication, etc.
Ducts are branched (compound) or unbranched (simple)
Shape of the ducts (tubular [tube-shaped], acinar [rounded], coiled, or tubuloacinar [both tube-shaped and rounded])
multicellular glands are categorized into two criteria:
Extracellular Matrix
Cells
the connective tissue is made up of two basic elements, namely:
Extracellular Matrix
the material located between its widely spaced cells
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: the extracellular matrix does not usually occur in body surfaces and is highly vascular (rich in blood vessels), except in the cartilage and tendons
Protein Fibers
Ground Substance
the extracellular matrix is composed of:
Collagen Fibers - strong, flexible bundles of collagen, which are the most abundant in the body (bone, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments)
Elastic Fibers - stretchable but strong fibers that can return to their original shape after being stretched (skin, blood vessel walls, and lung tissue)
Reticular Fibers - provide support in blood vessel walls and form networks around various cells (spleen and lymph nodes)
the different types of fibers are:
Embryonic CT
Mature CT
the two classifications of connective tissue are:
Embryonic Connective Tissue
connective tissue present in an embryo/fetus and develops into mature connective tissue
Mature Connective Tissue
connective tissue that is present at birth and persists throughout life
Mesenchyme
Mucous
the two types of embryonic connective tissue are:
Mesenchyme
this forms almost all other types of connective tissue and is present during cell division
Mucous
this lines the membranes of the different organs
Connective Tissue Proper (Dense and Loose)
Supporting Connective Tissue (Cartilage and Bone)
Liquid Connective Tissue (Blood and Lymph)
the three classifications of mature connective tissue are:
Areolar CT
Adipose CT
Reticular CT
the loose connective tissue is further divided into:
Areolar Connective Tissue
found in and around nearly every part of the body (“packing material” of the body) and functions in strength, elasticity, and support
Adipose Connective Tissue
specialized storage for triglycerides (fats) and functions in reducing heat loss through the skin
Reticular Connective Tissue
a fine interlacing network of reticular fibers and function in forming the stroma (supporting framework) of organs and removing worn-out blood cells in the spleen and microbes in lymph nodes
Dense Regular CT
Dense Irregular CT
Elastic CT
the dense connective tissue is further divided into:
Dense Regular CT
forms tendons (muscle to bone), ligaments (bone to bone), and aponeuroses (sheet-like tendons), and functions in providing a strong attachment to various structures and withstands pulling/tension along the long axis of fibers
Dense Irregular CT
they are irregularly arranged and are often found in the pericardium, periosteum, and perichondrium, and function in providing pulling (tensile) strength in many directions
Elastic CT
contain elastic fibers and are found in organs that expand and contract (e.g., lungs and arteries), and function in allowing various organs to stretch as it is strong and can recoil to their original shape after being stretched
Cartilage
Bones
the supporting connective tissue are further divided into:
Hyaline Cartilage
it is the most abundant type of cartilage in the body, and functions in providing smooth surfaces for the movement of joints, flexibility, and support; yet, it is the weakest type of cartilage and can be fractured
Fibrocartilage
it functions to support and join structures together; it contains thick bundles of collagen fibers, which provide strength and rigidity, making it the strongest type of cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
it provides strength and elasticity and maintains the shape of certain structures
Compact Bone - has osteons
Spongy Bone - has trabeculae
the subdivisions of bone are:
Blood - fluid present in blood vessels which transport oxygen and nutrients to various organs
Lymph - the extracellular fluid present in lymph vessels which functions in immunity and fluid balance
the subdivisions of fluid connective tissue are:
Membranes
these are flat sheets of pliable tissue that cover of line a part of a body
Epithelial Membrane
Synovial Membrane
the two types of membrane are:
Mucous Membrane
Serous Membrane
Cutaneous Membrane
the three types of epithelial membranes are:
Mucous Membrane
lines a body cavity that opens directly to the outside of the body (digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tract); they also contain a layer of epithelium and an underlying layer of connective tissue
Serous Membrane
lines a body cavity that does not open directly to the outside (pleura [lungs], pericardium [heart], peritoneum [abdominal cavity]); it has two parts: parietal layer (outside) and visceral layer (inside)
Cutaneous Membrane
lines the skin, which covers the entire body and is composed of the epidermis (superficial layer) and dermis (deep layer)
Synovial Membrane
line joints and contain connective tissue without epithelium, only connective tissue, and contain synovial fluid
Skeletal MT
Cardiac MT
Smooth MT
the three types of muscular tissue are:
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
they contain long, cylindrical, striated fibers; it is voluntary in nature since it is under conscious control; they attach to the bones via tendons and function in motion, posture, heat production, and protection
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
they are striated with one centrally located nucleus; it is involuntary in nature and it is found in the heart, and function to pump blood throughout the body
Smooth Muscle Tissue
they are not striated and are involuntary in nature; they can be found in irises, hollow organ walls, and airways, and function to provide motion (constriction of blood vessels and airways, propulsion of foods through the gastrointestinal tract, contraction of the urinary bladder and gallbladder)
Neurons
Neuroglia
the nervous tissue is composed of:
Neurons
they can carry sensory or motor information and they can perform integrative functions
Neuroglia
they protect and support neurons
Electrical Excitability
the ability to respond to certain stimuli by producing electrical signals, such as action potentials, which travel along the plasma membrane
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: neurons and muscle fibers are considered excitable cells because they exhibit electrical excitability
Tissue Repair
the process that replaces worn out, damaged, or dead cells
Fibrosis
the formation of scar tissue