Ch 17 and Ch 19: Carboxylic Acids, Esters, Amides, and Amines
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What two groups make up a carboxylic acid?
A carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (–OH)
What is the general formula for a carboxylic acid?
RCOOH or RCO₂H
What does the “R” represent in RCOOH?
The rest of the molecule, usually a carbon chain
What two groups make up an ester?
A carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to an –OR group
What is the general formula for an ester?
RCOOR′ or RCO₂R′
What two main groups make up an amide?
A carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a nitrogen atom (N)
What can the nitrogen in an amide be bonded to?
Hydrogen atoms or carbon atoms
What makes an amide primary (1°)?
The nitrogen is bonded to 1 carbon and 2 hydrogens
What makes an amide secondary (2°)?
The nitrogen is bonded to 2 carbons, 1 hydrogen
What makes an amide tertiary (3°)?
The nitrogen is bonded to 3 carbons, 0 hydrogens
Amides are primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on the number of ______ atoms bonded directly to the nitrogen atom:
Carbon

What is the central structural feature of carboxylic acids, esters, and amides?
The acyl group (RCO)
What is the geometry of the acyl group?
Trigonal Planar
Is the acyl group polar or nonpolar?
Polar
Which group in carboxylic acids allows them to form hydrogen bonds?
The hydroxyl group
Why do carboxylic acids have higher boiling and melting points than similar-sized esters and alcohols?.
Because hydrogen bonds between carboxylic acid molecules create stronger intermolecular forces
Out of carboxylic acids, esters, and alcohols, which has the highest boiling and melting point?
Carboxylic Acids
Which types of amides can form hydrogen bonds?
Primary (1°) and secondary (2°) amides
Why can’t tertiary (3°) amides form hydrogen bonds with each other?
Because they have no N-H group
Out of primary, secondary, and tertiary amides, which have the higher boiling and melting points?
Primary and secondary
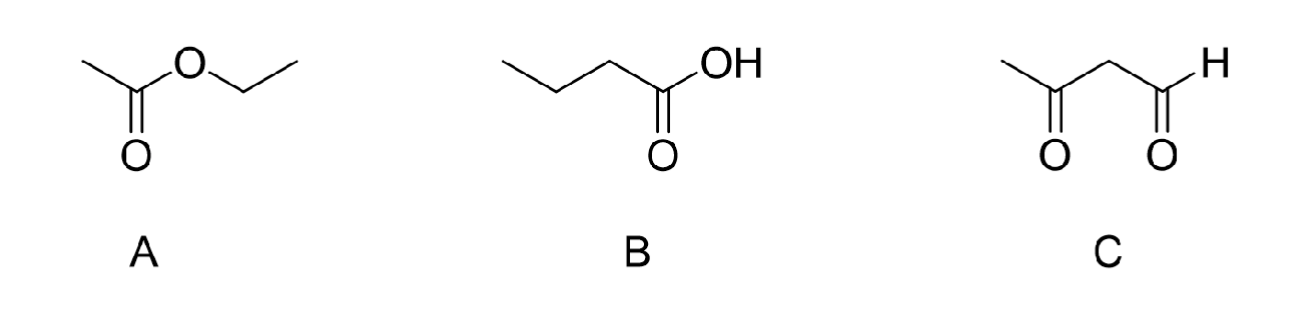
Which molecule will have the higher boiling point?
B
__________ are more soluble in water than most other organic molecules:
Carboxylic Acids
Why can carboxylic acids dissolve better than most other organic molecules in water?
Because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules at their carbonyl and hydroxyl groups
How does hydrogen bonding affect the solubility of carboxylic acids?
It increases their solubility in water
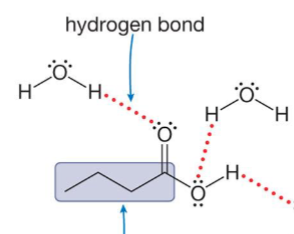
Are short chain acids soluble or not soluble in water?
Soluble
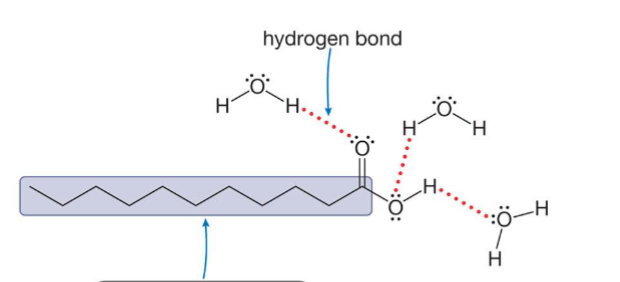
Are long chain acids soluble or not soluble in water?
Not soluble
Are esters and amides soluble in water?
Yes
Why are esters and amides soluble in water?
Because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
Which atoms in esters and amides allow hydrogen bonding with water?
The oxygen in esters and the nitrogen in amides
Compared to carboxylic acids, are esters and amides more or less soluble in water?
Less soluble
Are carboxylic acids strong or weak acids?
They are weak acids
Are carboxylic acids polar?
Yes
Are esters polar?
Yes
Are amides polar?
Yes
Which type of amide(s) cannot for hydrogen bonds with themselves?
Tertiary
Can carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonds with themselves?
Yes
Can Esters form hydrogen bonds with themselves?
No
Can Amides form hydrogen bonds with themselves?
Yes but only primary and secondary
Which can form hydrogen bonds with water?
All- carboxylic acids, esters, and amides
Which are soluble in water?
All- carboxylic acids, esters, and amides
Which types of amides have stronger molecular forces and higher melting/boiling points?
Primary and secondary amides have stronger forces and higher BP than tertiary amides
______________ have very strong intermolecular forces and higher boiling/melting points than similar sized esters and amides":
Carboxylic acids
What reaction type do acyl compounds undergo?
Substitution reactions
What is a substitution reaction?
When the group bonded to the carbonyl carbon gets replaced by another group (hydroxyl groups in carboxylic acids get replaced in this case)
What is esterification?
Substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol to form an ester and water
During esterification, carboxylic acids + _________ = Ester and Water
Alcohol
During esterification, Carboxylic acids + Alcohol = ________ and _______
Ester and water
What group is getting replaced during esterification and What group is replacing it?
The OH of a carboxylic acid gets replaced with OR of an ester
What is usually the catalyst during esterification?
H2SO4
What are amide formation reactions?
Substitution reaction of carboxylic acid with an amine to form an amide and water
During amide-formation reactions, carboxylic acid + _________ = Amide and water
Amine
During amide-formation reactions, carboxylic acid + amine = _______ and _______
Amide and water
What group is getting replaced during an amide-formation reaction and what group is replacing it?
The OH of a carboxylic acid gets replaced with NR’2 of an amide
What is usually the catalyst during an amide-formation reaction?
Heat
Hydrolysis is taking a large molecule (ester or amide) and splitting it back into smaller pieces using _________:
Water (H2O)
Hydrolysis is basically undoing __________ and ___________:
Esterification reactions and amide-forming reactions
During hydrolysis, An ester + water = _______ and _______
Carboxylic acid and Alcohol
During hydrolysis, An amide + water = _______ and _______
Carboxylic Acid and ammonium
An amine is like an amide but doesn’t have a….
Carbonyl group
What is an amine?
A nitrogen atom bonded to a combination of hydrogen atoms and carbon groups
Amines and amides are alike because they both contain…
Nitrogen
To classify whether an amide is primary, secondary, or tertiary, you should count the…
The carbon + the number of R groups attached
To classify whether an amine is primary, secondary, or tertiary, you should count the…
Number of carbs attached to the nitrogen
A primary amine is a nitrogen atom bonded to _____ carbon atom(s):
1
A secondary amine is a nitrogen atom bonded to _____ carbon atom(s):
2
A tertiary amine is a nitrogen atom bonded to _____ carbon atom(s):
3
What are the reactants of esterification? (condensation)
Carboxylic acid and alcohol
What are the products of esterification? (condensation)
Ester and Water
What are the reactants of amide-formation reactions? (condensation)
Carboxylic Acid and Amine
What are the products of amide-formation reactions? (condensation)
Amide and Water
What are the reactants in the hydrolysis of esters?
Ester and Water
What are the products in the hydrolysis of esters?
Carboxylic Acid and Alcohol
What are the reactants in the hydrolysis of amides?
Amide and water
What are the products in the hydrolysis of amides?
Carboxylic Acid and Ammonium
Can amines form hydrogen bonds with each other?
Yes but only primary and secondary
Can tertiary amines form hydrogen bonds with themselves?
No (no N-H bond)
Amines have high boiling points, but they are less than ______:
Alcohols
Can amines form hydrogen bonds with water?
Yes
Are amines soluble?
Yes, but only ones with fewer than 6 carbons
Amines with ______ dissolve better in water:
H-bonds