Chemistry - Ionic Bonding
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Ion
-an atom that losses or gains an electron
-Lower ionisation energy, more likely to lose electrons
=i.e. group 1-3 (lose electrons), group 5-7 (gain electrons)
ionic bonding
-occur by transferring electrons from a metal to non-metal.
-Now the two atoms become oppositely charge and attract becoming stable
ionic Model
-Cations and anions form and will arrange themselves in a continuous 3D lattice
-They bond through electrostatic attraction between the + and - natures of the ion
-They find themselves in fixed position with ‘directional bonds’
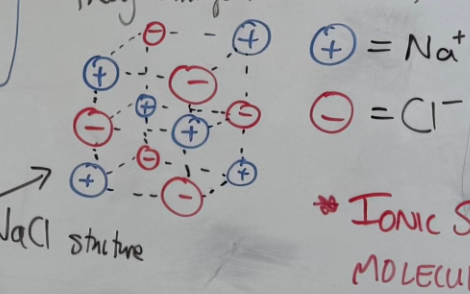
Properties
1.High melting/boiling point
2.Hard and brittle (not malleable or ductile)
3.Conductivity (only in liquid form)
4.Solubility (more will cover in Sem 2)
High melting/boiling point
-Caused by strong attractive forces (more energy to change state)
-attractive forces between + and - ion is relatively strong so high amounts of energy needed to disrupt (to melt)
Hard and brittle (not malleable or ductile)
-Due to strict formation of ions in a lattice, a shift or change in this structure causes bonds to break
-if force is applied, Movement of ions will result in repulsion of like ions, causing lattice to break
-Ionic hardness is due to strength of attraction (particles close) and directional bonds

Conductivity (charged particles must be mobile for electricity to flow)
-As a solid, ions are in rigid formation and unable to move if there was an electric current
-As a liquid or solution- ions are not in a lattice and can move towards electric terminals, allowing electricity to flow
Solubility (more will cover in Sem 2)
-Some compounds dissolve, some don’t
*info in data booklet