3.DIffusion, osmosis, and active transport and photosynthesis and leaf structure
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What is diffusion?
The movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration down a concentration gradient due to random movement
What provides the energy for diffusion?
The kinetic energy of particles from their random movement (Brownian motion)
What is Brownian motion?
The random movement of particles caused by collisions with other particles
What type of membrane is the cell membrane?
Partially permeable
What does partially permeable mean?
Allows some molecules to pass through but restricts others
Why is diffusion important in living organisms?
To obtain substances
How does surface area to volume ratio affect diffusion?
A larger surface area to volume ratio increases the rate of diffusion
Why do root hair cells have a large surface area?
To increase absorption of water and mineral ions
Why are alveoli one cell thick?
To reduce diffusion distance and increase diffusion rate
How does temperature affect diffusion?
Higher temperature increases particle energy and diffusion rate
How does concentration gradient affect diffusion?
A steeper gradient increases diffusion rate
What is water potential?
A measure of the tendency of water to move
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water molecules from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane
What moves during osmosis?
Water molecules only
From where to where does water move in osmosis?
From higher water potential to lower water potential
What happens to plant cells in dilute solutions?
They gain water and become turgid
What is turgor pressure?
Pressure of cell contents pushing against the cell wall
Why don’t plant cells burst in dilute solutions?
The cell wall resists further expansion
What happens to plant cells in concentrated solutions?
They lose water and become flaccid or plasmolysed
What is plasmolysis?
When the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall
What happens to animal cells in concentrated solutions?
They lose water and become crenated
What happens to animal cells in distilled water?
They gain water and may burst (lysis)
What is active transport?
Movement of substances against a concentration gradient using energy from respiration
Does active transport require energy?
Yes
Why is energy needed for active transport?
Particles move against the concentration gradient
What proteins are involved in active transport?
Carrier proteins
What happens first in carrier protein transport?
Substance binds to the carrier protein
What happens second in carrier protein transport?
Energy causes the protein to change shape
What happens last in carrier protein transport?
Substance is released into the cell
What is photosynthesis?
The process by which plants make glucose from carbon dioxide and water using light energy
What are the raw materials for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide and water
What is the waste product of photosynthesis?
Oxygen
What provides energy for photosynthesis?
Light energy
What pigment traps light energy?
Chlorophyll
Where is chlorophyll found?
In chloroplasts
Why do plants appear green?
Chlorophyll reflects green light
State the word equation for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide plus water produces glucose and oxygen
Why is light not a raw material?
It is energy not a substance
How does carbon dioxide enter a plant?
Through stomata by diffusion
How does water enter a plant?
Through roots by osmosis
What is the role of glucose in plants?
Energy source and building material
How is glucose stored in plants?
Converted to starch
How is glucose used to make cell walls?
Converted into cellulose
How is glucose transported in plants?
Converted into sucrose
Why is nectar produced?
To attract pollinators
How are proteins made in plants?
By combining glucose with nitrogen ions
Why are mineral ions needed?
To make proteins and chlorophyll
What is a mineral ion?
An inorganic substance absorbed from the soil
How are mineral ions absorbed?
By active transport in root hair cells
What element is needed for chlorophyll?
Magnesium
What is the effect of magnesium deficiency?
Yellowing leaves
What element is needed for amino acids?
Nitrogen
What happens in nitrate deficiency?
Poor growth
Why test leaves for starch?
Glucose is quickly used or transported
What is the first step in the starch test?
Boil leaf in water
Why is ethanol used in the starch test?
To remove chlorophyll
What plant is used to measure photosynthesis rate?
Pondweed
How is oxygen measured?
Counting bubbles or volume collected
What indicates a higher rate of photosynthesis?
More oxygen produced
How is light intensity changed?
Moving lamp closer or further
How is temperature changed?
Using different water temperatures
What gas exchange occurs during respiration?
Oxygen in carbon dioxide out
What gas exchange occurs during photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide in oxygen out
What happens at night in plants?
Only respiration occurs
What indicator is used for gas exchange?
Hydrogencarbonate indicator
Why does indicator change colour?
Carbon dioxide is acidic
State the balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 plus 6H2O produces C6H12O6 plus 6O2
What form of energy is stored in glucose?
Chemical energy
What is a limiting factor?
A factor in shortest supply limiting a process
Name three limiting factors of photosynthesis
Light intensity temperature carbon dioxide
Why is water not a limiting factor?
Only small amounts are needed
How does temperature affect photosynthesis?
Increases rate until enzymes denature
What happens when enzymes denature?
Reaction rate decreases
How does light intensity affect rate?
Rate increases then levels off
How does CO2 concentration affect rate?
Rate increases until another factor limits
What is the structure of a leaf adapted for?
Efficient photosynthesis
Why are leaves broad?
Large surface area
Why are leaves thin?
Short diffusion distance
What tissue contains most chloroplasts?
Palisade mesophyll
Why are palisade cells near the top?
Receive most light
What is the role of spongy mesophyll?
Gas exchange
Why are air spaces important?
Allow diffusion of gases
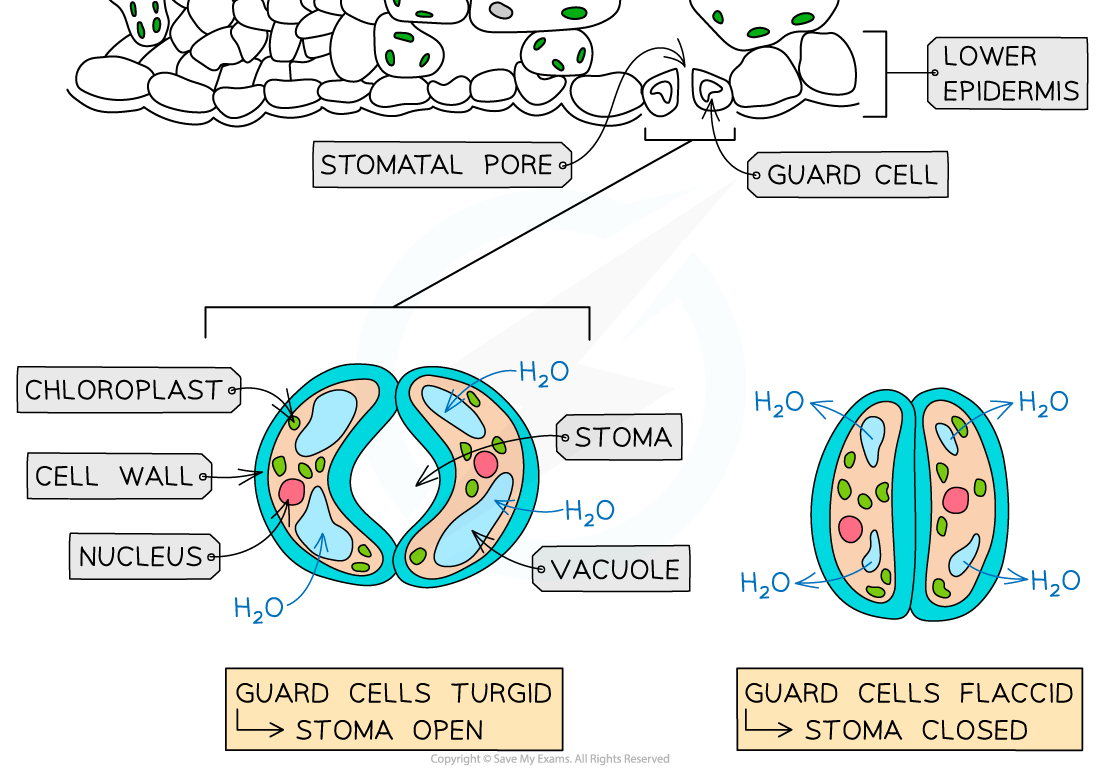
What is the function of stomata?
Allow gas exchange
What controls opening of stomata?
Guard cells
What is the function of xylem?
Transport water and minerals
What is the function of phloem?
Transport sugars
Why are veins important?
Transport substances and support leaf