Mendelian Genetics and Inheritance Patterns
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Mendelian Genetics
Study of heredity and trait inheritance.
Traits
Observable characteristics inherited from parents.

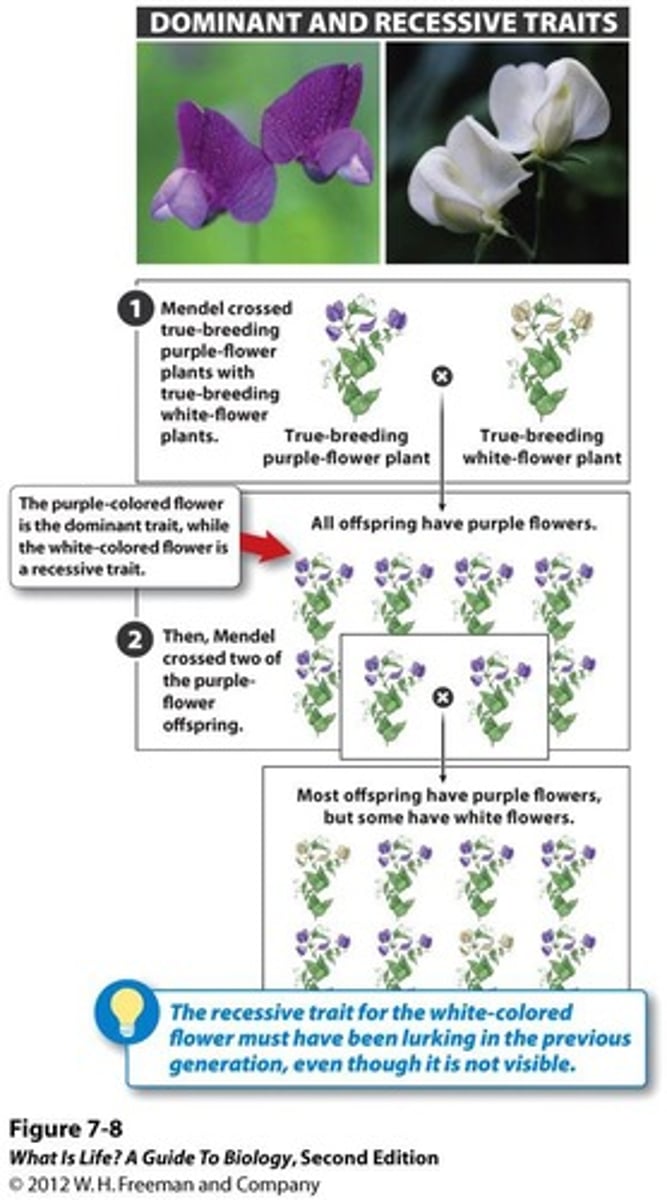
Dominant Traits
More common traits expressed with one allele.
Recessive Traits
Traits expressed only with two recessive alleles.
Hybridization
Mating two true-breeding individuals with different traits.
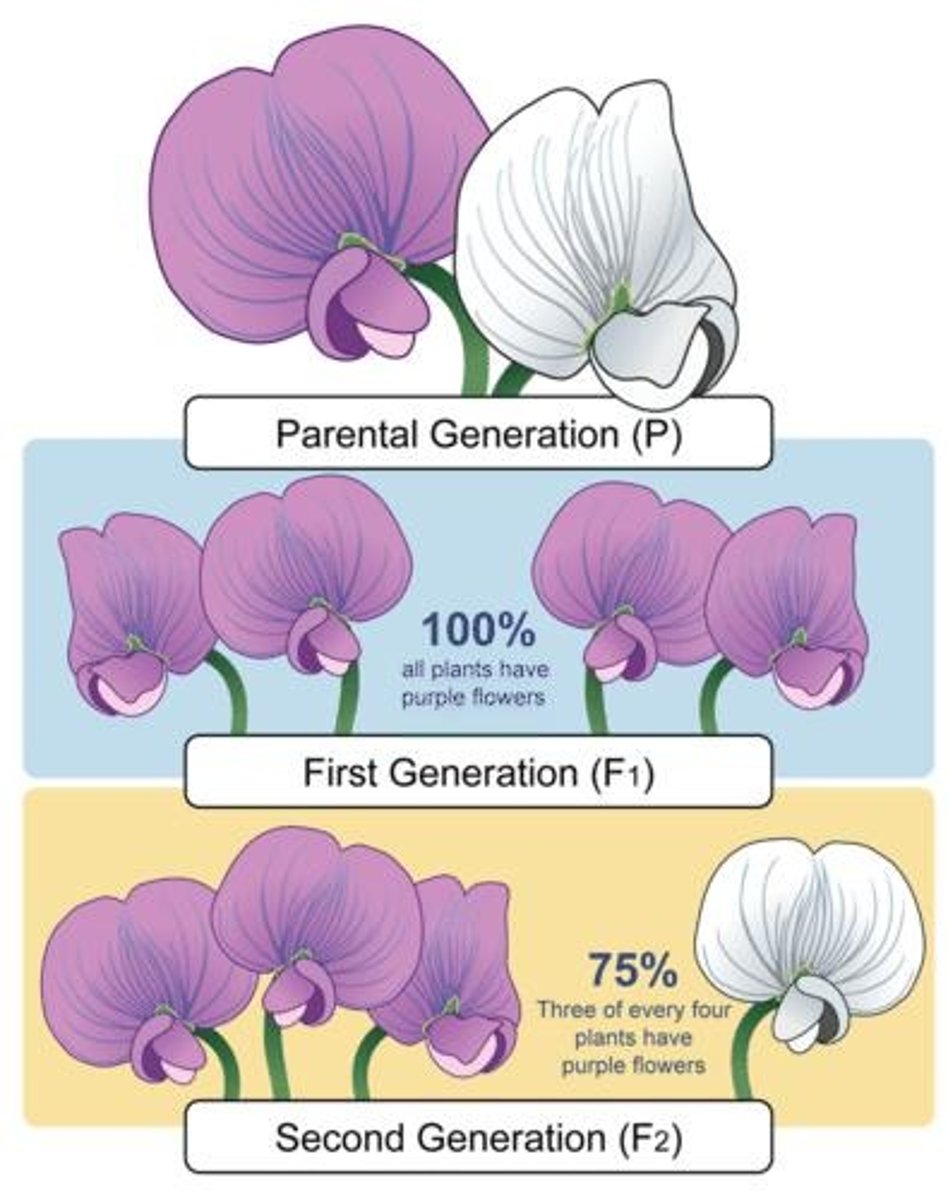
P0 Generation
Parent generation in Mendel's experiments.
F1 Generation
First filial generation from P0 cross.
F2 Generation
Second filial generation from F1 self-fertilization.
Alleles
Alternative versions of a gene causing trait variation.
Law of Segregation
Gene copies separate during meiosis into gametes.
Law of Independent Assortment
Gametes combine independently of their alleles.
True-Breeding Plants
Plants that consistently produce offspring resembling parents.
Continuous Variation
Traits that blend and show a range of phenotypes.
Discontinuous Variation
Distinct traits that remain unchanged across generations.
Mendel's Experiments
Used garden peas for systematic genetic studies.
Self-Fertilization
Process where a plant fertilizes itself naturally.
Phenotype
Observable expression of a genotype in an organism.
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an individual, including alleles.
Mendel's Discoveries
Revealed basic principles of heredity and inheritance.
Quantitative Analyses
Statistical methods used to analyze genetic data.
Scientific Community Rediscovery
Mendel's work revived in 1900 after initial neglect.
Garden Pea Characteristics
Seven traits studied, each with two contrasting forms.
Recessive
Inheritance pattern for certain traits.
Alleles
Different versions of a gene.
Protein Expression
Variation in protein production and activity.
Phenotype
Observable traits expressed by an organism.
Dominant Allele
Allele that expresses its trait in heterozygotes.
Recessive Allele
Allele expressed only in homozygous conditions.
Homozygous Dominant
Two copies of the dominant allele.
Homozygous Recessive
Two copies of the recessive allele.
Heterozygous
One dominant and one recessive allele.
Punnett Square
Tool to predict genetic cross outcomes.
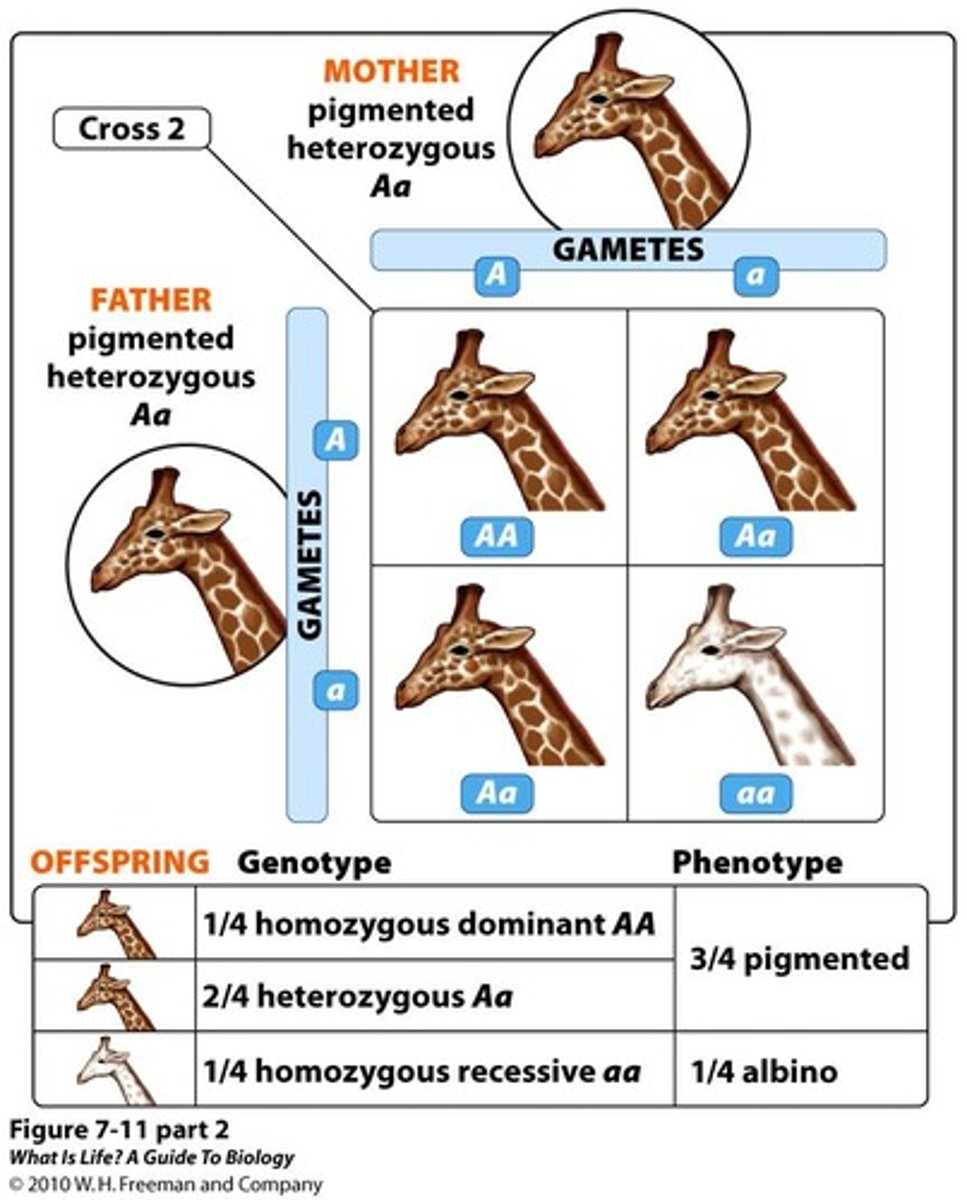
Genotype
Genetic makeup for a specific trait.
Central Dogma
Process: gene → protein → trait.
Incomplete Dominance
Intermediate phenotype in heterozygotes.
Co-dominance
Both alleles expressed equally in phenotype.
Mendelian Genetics
Study of inheritance patterns established by Mendel.
Pleiotropic Genes
Genes affecting multiple traits.
Environmental Influence
External factors altering gene expression.
Dominant Trait Frequency
Not necessarily more common than recessive traits.
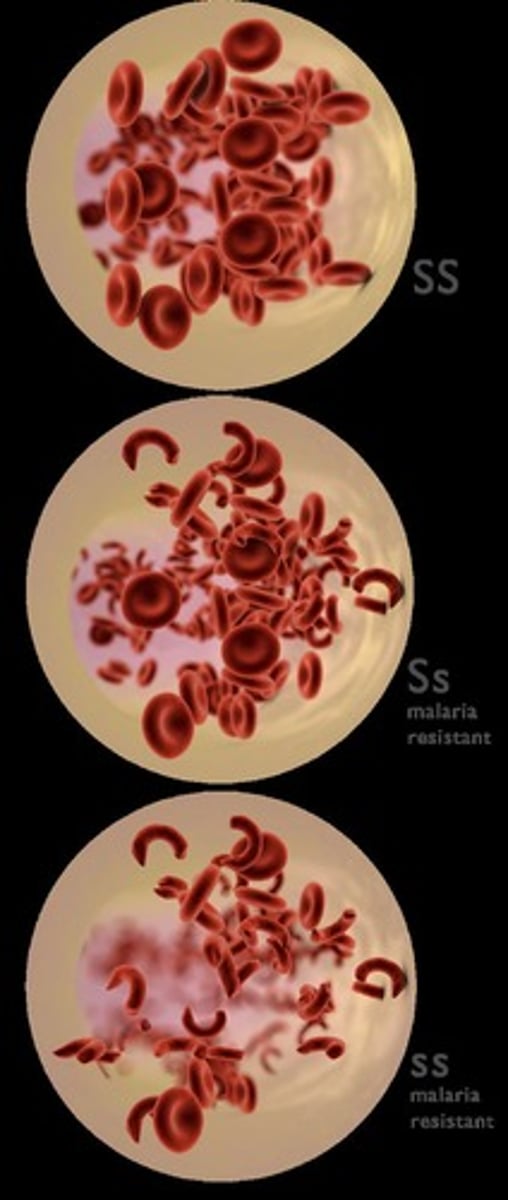
Sickle Cell Allele
Depends on context for dominance classification.
Genetic Cross
Mating of organisms to study inheritance.
Mendel's Pea Plants
Classic experiment demonstrating inheritance patterns.
Trait Survival
Frequency influenced by environmental adaptability.
Incomplete Dominance
Neither allele is dominant; both expressed together.
Punnet Square
Tool for predicting genetic trait inheritance.
Super-scripts
Used in Punnet squares to denote alleles.
Homozygous Dominant
Genotype with two dominant alleles (e.g., CRCR).
Homozygous Recessive
Genotype with two recessive alleles (e.g., CWCW).
Heterozygous Genotype
Genotype with one dominant and one recessive allele (e.g., CRCW).
Co-Dominance
Both alleles fully expressed in phenotype.
Multiple Alleles
Single gene with more than two allele options.
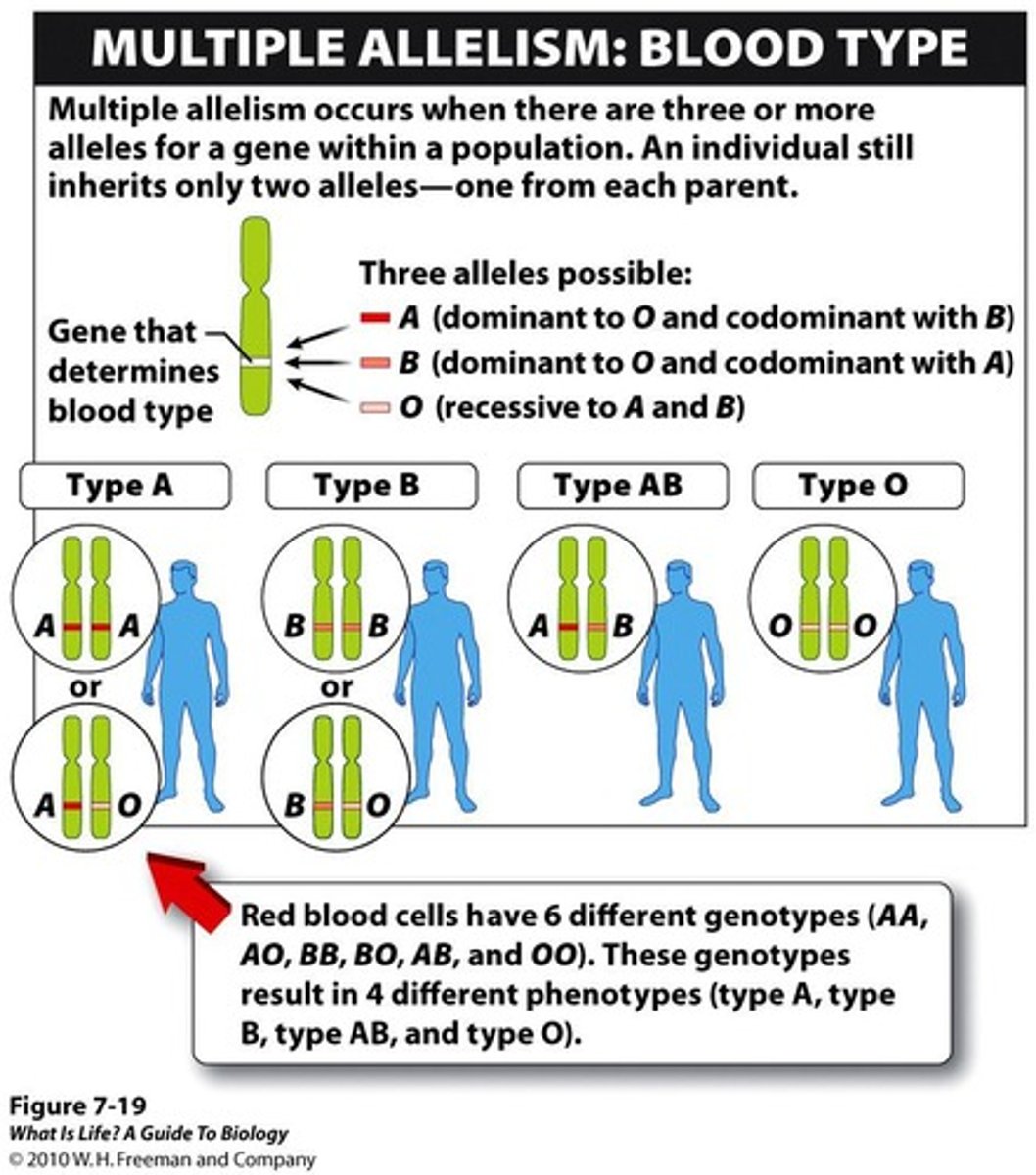
Blood Type
Determined by combinations of A, B, AB, O alleles.
Sex-Linked Traits
Traits expressed differently in males and females.
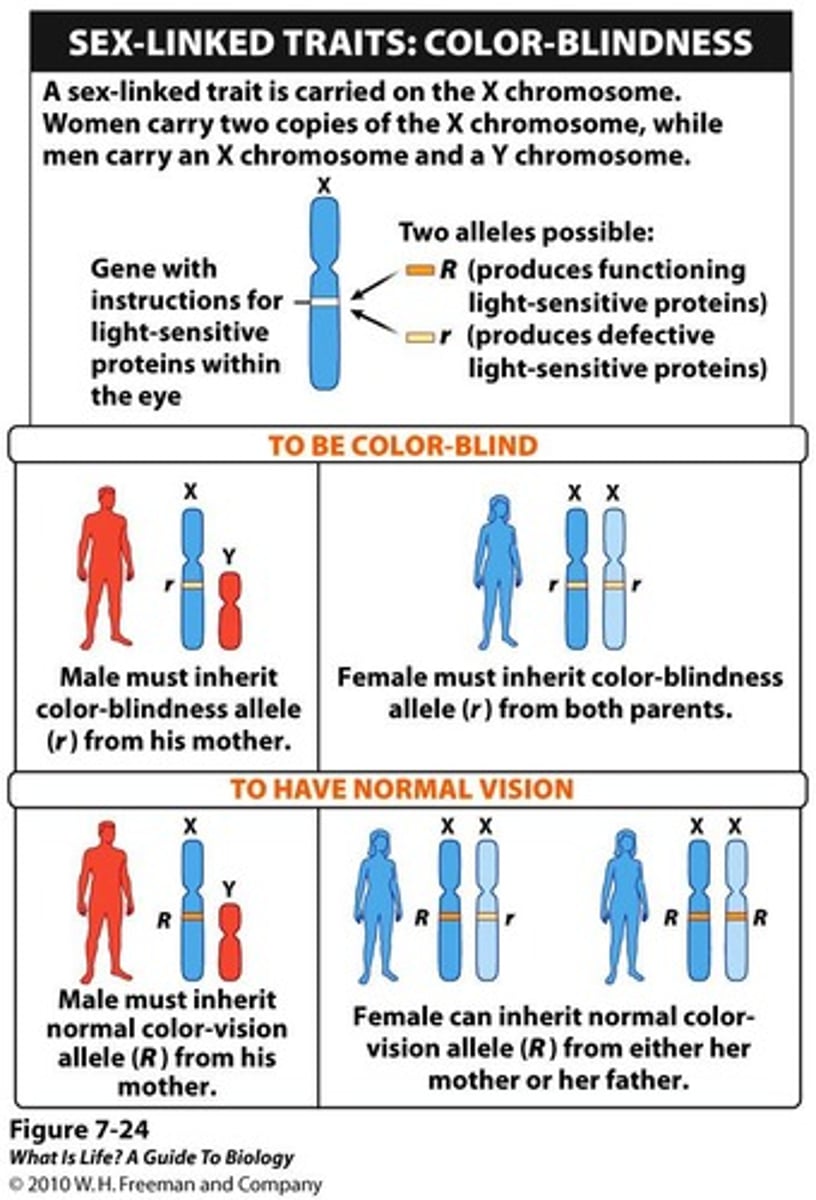
Recessive Allele
Requires two copies for expression in females.
Colorblindness Inheritance
Males inherit colorblindness from their mothers.
Polygenic Trait
Trait influenced by multiple genes.
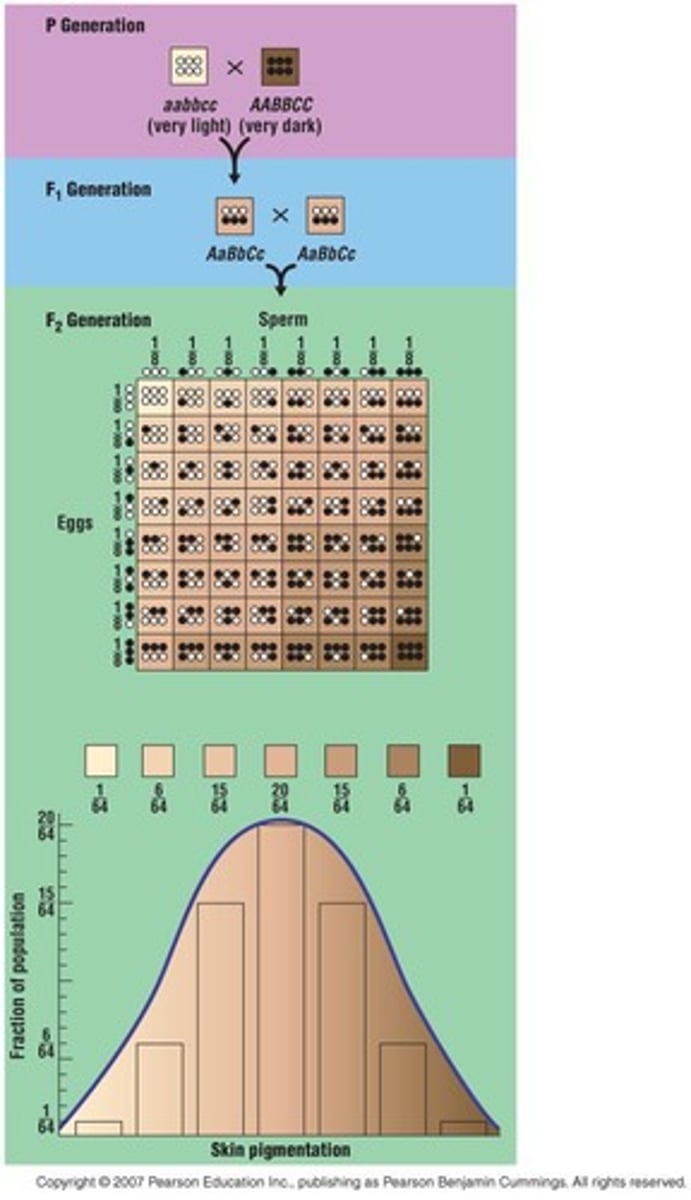
Continual Variation
Gradual changes between two extremes in traits.
Epigenetics
Study of gene expression modifications without DNA changes.
Gene Expression
Activation or silencing of genes in cells.
Environmental Stimuli
External factors influencing gene expression.
Unique Genetic Combinations
Different gene activations lead to individual uniqueness.
Reversible Epigenetics
Potential to reverse gene expression states.
Cancer and Epigenetics
Diseases may involve abnormal gene expression states.
Gene Specialization
Different cells express different genes for function.
Chemical Modifications
Alterations around genes affecting their activity.
Inheritance of Epigenetics
Some epigenetic changes can be passed to offspring.