VSEPER Geometries + d Orbital Shapes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
1
New cards
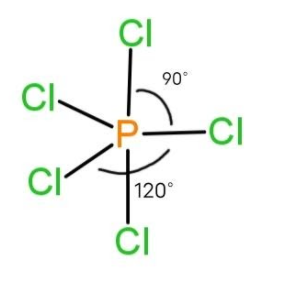
Atomic geometry of Sp3d
trigonal bipyramidal
2
New cards
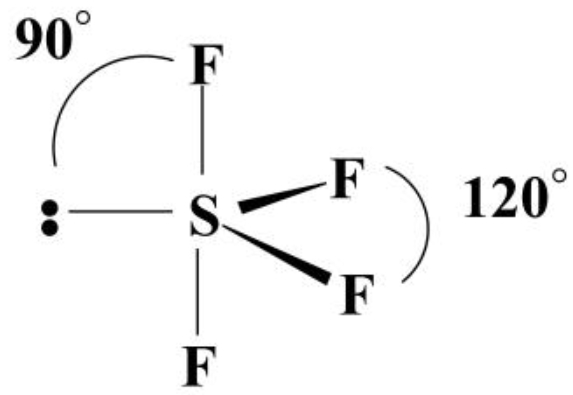
Molecular geometry of Sp3d (1 lone pair)
see-saw
3
New cards
How many lone pars does a see-saw shape have
1
4
New cards
What is the hybridization of a see-saw shape
Sp3d
5
New cards
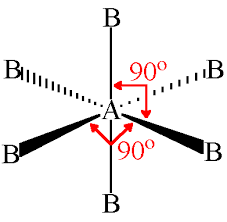
atomic geometry of sp3d2
octahedral
6
New cards
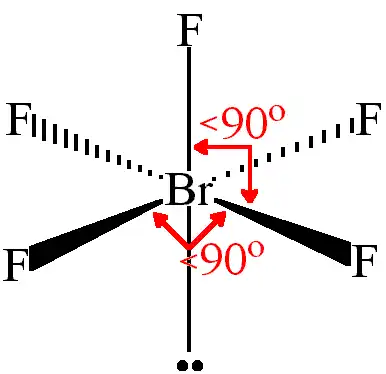
molecular geometry of sp3d2 with 1 lone pair
square pyramid
7
New cards
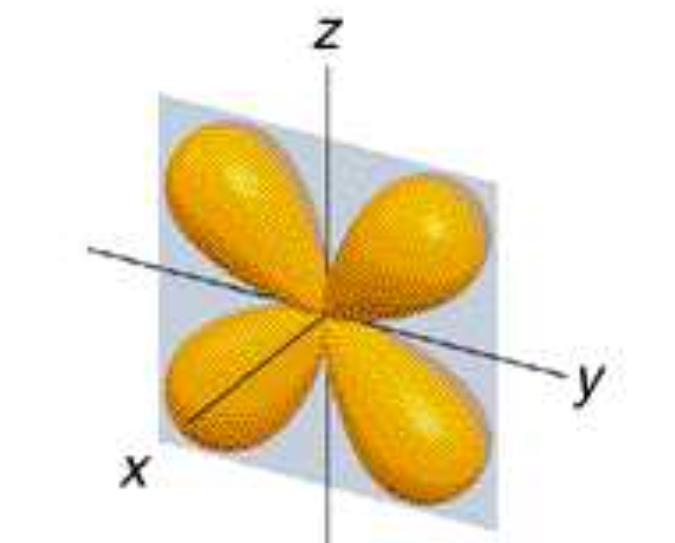
dyz
8
New cards
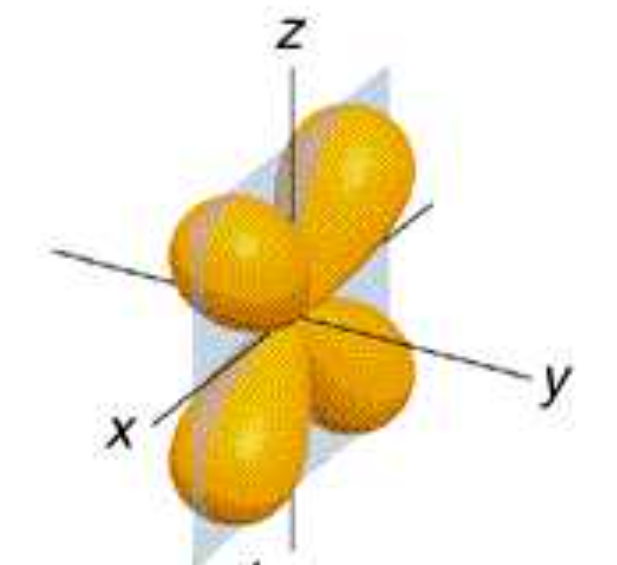
dxy
9
New cards
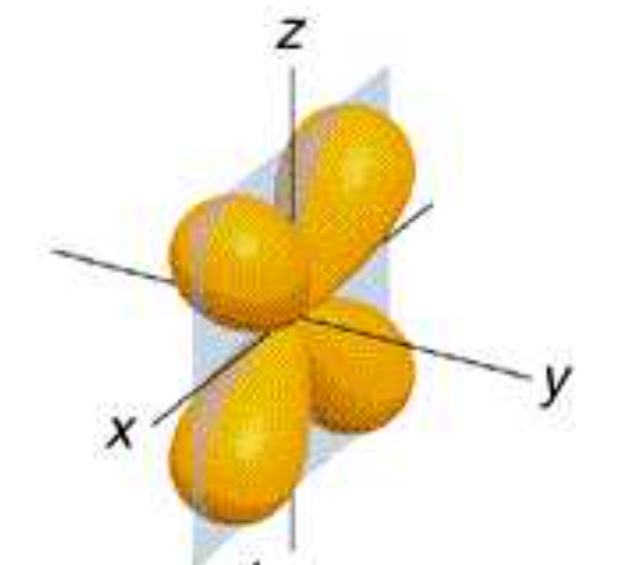
dxz
10
New cards
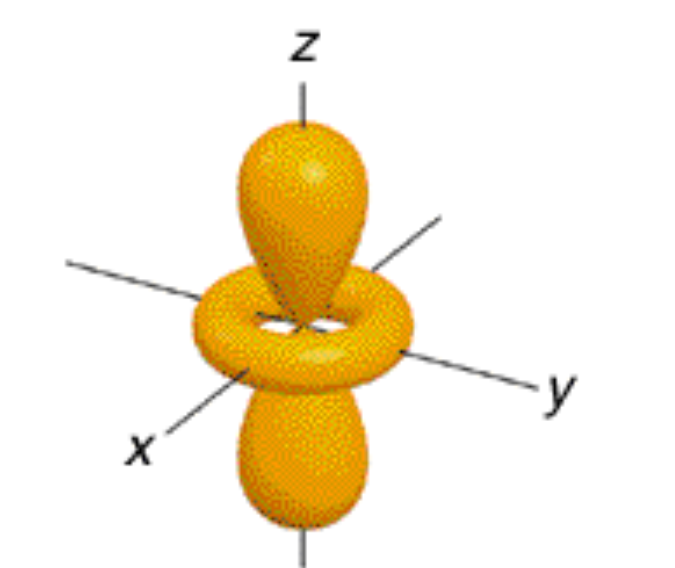
dz^2
11
New cards
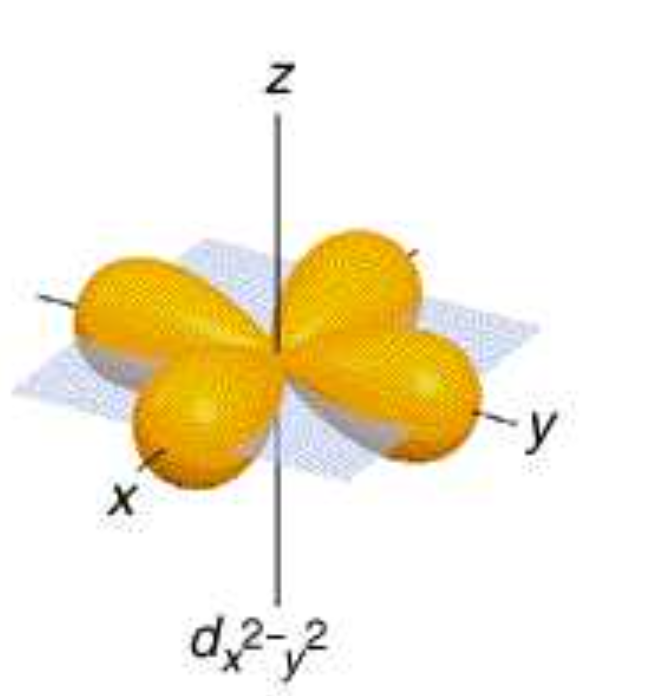
dx^2y^2
12
New cards
Hybridization of sp3d2 with 2 lone pairs
square planar
13
New cards
Angles in see-saw
14
New cards
Angles in square pyramid
15
New cards
Angles in Square planar
90
16
New cards
See-saw is…
The molecular geometry of a center atom with 5 electron domains one of which is a lone pair
17
New cards
How many electron domains are on a central atom with the atomic geometry trigonal bipyramidal
5
18
New cards
How many electron domains are there on a central atom with atomic geometry octahedral
6
19
New cards
Equation for bond order for Lewis Structures
B.O. = \[ number of bonds\] / \[number of "outer things'“\]
20
New cards
sp1 atomic geometry
linear
21
New cards
sp2 atomic geometry
trigonal planar
22
New cards
sp3 atomic geometry
tetrahedral
23
New cards
sp3d1 atomic geometry
trigonal bipyramidal
24
New cards
sp3d2 atomic geometry
octahedral
25
New cards
Equation for bond order for molecular orbitals
B.O. = 1/2 \[bonding electrons - anti-bonding electrons\]
26
New cards
atomic radius
the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electrons
27
New cards
Zeff
( Z - number of inner-shell electrons)
28
New cards
Ionization energy
the removal of one electron. Across a period it **increases** down a group it **decreases**
29
New cards
Planar nodes are characterized by the symbol
L
30
New cards
Formula for radial nodes
n - L - 1
31
New cards
Formula for total nodes
n-1
32
New cards
Writing empirical formula steps
1. g → m
2. divide all moles by smallest mole value
3. round or multiply to get whole numbers
33
New cards
Formula to get molecular formula
AMU (given) / total g/mol (real amu)
34
New cards
The limiting reagent is the value with the lowest x per x ratio
mole x coefficient
35
New cards
Theoretical yield will be
the smallest product from the given mols on the left side of the equation
36
New cards
mL is the ____ or the orbital
orientation
37
New cards
mL will always be __ and __
\-land l
38
New cards
ms is
electron spin, either -1/2 or 1/2
39
New cards
The planar node value determines the
shape of the electron.
s: l=0
p: l=1
d: l=2
f: l=3
s: l=0
p: l=1
d: l=2
f: l=3
40
New cards
Pauli’s principle
no two e’ will have the same 4 quantum numbers
41
New cards
Hund’s rule
electrons will fill up orbitals one at a time and only pair up once they are all half filled
42
New cards
Aufbau’s principle
orbitals will be filled from lowest to highest energy levels
43
New cards
Arrhenius Definition of Acids/Bases
Acid forms H+ ions in an aq solution
Base forms OH- in an aq solution.
Base forms OH- in an aq solution.
44
New cards
Bronsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases
An acid will donate protons to another polar substance
A base will accept protons from another polar substance
A base will accept protons from another polar substance
45
New cards
Lewis’ definition of acids and bases (lone pairs)
Acids: electron pair acceptors
Bases: electron pair donors
Bases: electron pair donors
46
New cards
Vectors will go toward
terminal atoms from the central atom
47
New cards
A sigma bond has a ___ overlap
single
48
New cards
A pi bond has a ___ overlap
double
49
New cards
Bonds ____ an interaction between two atoms
stabilize
50
New cards
Antibonds _____ interactions between two atoms
destabilize
51
New cards
More overlap means more
energy
52
New cards
Name one advantage of the molecular orbital approach over the Lewis Structure approach
The molecular orbital theory predicts the paramagnetism of atoms.
53
New cards
Name 4 generally paramagnetic molecules
B2, O2, Al2, and S2
54
New cards
Molecular orbital diagrams will be abnormal if the atomic umber is ____. These structures are symmetrical in 2p bonding and anti-bonding structure.
less than 8
55
New cards
The conjugate base of a strong acid is a ____ acid
weak
56
New cards
The conjugate base of a week acid is a ___ base
strong
57
New cards
a complex is a
central metal ion surrounded by ligands
58
New cards
a ligand is
an ion or molecule that can donate a lone pair to the central metal ion
59
New cards
coordinate bond
the bond that forms when a ligand donates its pair of electron to the metal ion
60
New cards
Name the 3 combinations that are superimposable
MA4, MA3B, MA2B2, MA2BC
61
New cards
What combination is not superimposable and therefore optically active?
MABCD
62
New cards
Color depends on
1. identity of metal
2. oxidation state of metal
3. identity of ligand
63
New cards
Limitations of VSEPER
you can’t predict where the lone pairs belong