geography gcse - the changing economic world (paper 2)
1/293
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
294 Terms
what is development
an improvement in standard of living, income and quality of life
what is quality of life
access to goods and service (e.g. education, healthcare, clean water)
what are indicators of development important for (2)
measure the level of development in a country
classify countries according to IOD
what are 3 examples of economic IOD
GDP per capita
GNI per capita
% employed in primary/secondary/tertiary sectors
what does GDP stand for
gross domestic product
what is GDP per capita
average income → value of all goods and services produced within a country
what does GNI stand for
gross national income
what is GNI per capita
value of all goods and services produced by a countries’ businesses (globally)
what are 7 examples of social IOD
education/literacy rates
healthcare
% population with access to clean water, electricity, internet etc.
life expectancy
birth/death rate
HDI
infant mortality rate
what does HDI stand for
human development index
what is HDI
summary index of literacy rates, life expectancy and GDP/capita
what is death rates
no. of deaths per 1000 people (per year)
what is infant mortality rates
no. of babies (per 1000 live births) that die before the age of 1
what is birth rates
no. of births per 1000 people (per year)
as GNI increases, the birth rate…
decreases
why does birth rate decrease with increasing GNI? (4)
families don’t need children to work
better family planning
better education and access to contraception
in HIC’s, birth rate is low because children are expensive
as GNI increases, literacy rates…
increase
why do literacy rates increase with increasing GNI? (2)
greater investment in education
greater access to books/education (e.g. libraries, mandatory school systems)
as GNI increases, death rates…
decrease
why do death rates decrease with increasing GNI? (4)
better access to healthcare
better healthcare
more balanced diets
greater access to clean water
as GNI increases, infant mortality rates…
decrease
why do infant mortality rates decrease with increasing GNI? (2)
regular vaccinations for babies in HIC
improved healthcare → more people and babies survive
what is HIC
high income country
what is NEE
newly emerging economy
what is LIC
low income country
what is HDI calculated from (3)
GDP/capita, life expectancy, literacy rate
how is HDI measured
on a scale from 0-1
what is 0
lic
what is 1
hic
what are 3 indicators of development
life expectancy, literacy rate, GNI per head
what type of indicator is life expectancy
social
advantages of life expectancy (+ associated factors) (3)
infant mortality reflects healthcare + quality of life
provides information on healthcare
birth rate reflects on education, contraception, family planning
limitations of life expectancy (3)
accuracy of data can be unreliable in LICs
death rates are poor due to varying ages of population
birth rate can be influenced by gov policies (e.g. China)
what type of indicator is literacy rates
social
advantages of literacy rates (1)
shows no. of educated people/people in school
limitations of literacy rate (1)
other skills (e.g. farming, practical skills) are ignored, which may be more valuable to community
what type of indicator is gni/head
economic
advantages of gni/head as indicator (3)
allows comparison of countries (even if they are vastly different sizes)
takes population into comparison
provides information on education, employment, income
limitations of gni/head (4)
doesn’t talk about individual standard of life, or quality of life
many agricultural/craft products not included
currencies vary, changing value
those with high income affect data
why do HICs have increasing death rates (death rate greater than birth rate) (2)
diseases of wealth (e.g. obesity)
increasing aging populations
why is HDI useful (2)
takes into account a variety of factors (e.g. healthcare, education, income etc)
limitations are limited
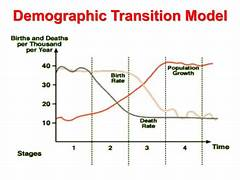
what is demographic transition model used to show
how populations change over time as a country develops
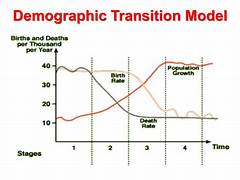
what goes on the x axis of a dtm
time
what goes on the y axis of a dtm
total population + any other factor (e.g. birth rate/death rate)
stage 1 or 2 =
LIC
stage 3 =
NEE
stage 4 =
HIC
what does dtm not take into account (4)
gov policies
pandemics
wars
migration
what is an example of a region that is still in stage 2
sub-saharan africa
how is death rate in sub-saharan africa
low (lower then in UK) due to youthful population
how is birth rate in sub-saharan africa
high
what are 2 examples of regions that are stage 3
india, china
however, there can still be …
variation within a country
e.g. in richer parts of the uk, how is average death rate different to in poorer parts of the Uk
12 years older (due to factors like varied and balanced diet, less stress)
however, what is there in richer areas
higher risk of diseases of wealth (obesity) or heart diseases
what are 2 examples of countries in the world that are stage 5
japan, italy
what are 2 concerns with stage 5 regions
employment, economy
explain how dtm links to stages of economic development (4)
stage 1: BR + DR high → LIC, poor healthcare/family planning
stage 2 + 3: Decline in BR + DR → NEE, better sanitation + vaccinations, better education
stage 4: BR + DR low → HIC
what are 3 main sectors of causes of uneven development (in Africa)
physical
historical
economic
what physical factors have caused uneven development? (3)
location
climate
extreme events
how has location caused uneven development
16/54 countries are landlocked, making trade difficult → have to rely on neighbouring countries for trade (could result in disputes or war if countries don’t agree)
how does climate cause uneven development (3)
monsoon seasons can affect crops
more climate-related diseases (e.g. malaria, ebola)
global warming can affect crops
how do extreme events cause uneven development (2)
events like hurricanes + droughts becoming more frequent → destroy crops, livestock, homes, trade (e.g. ports)
must receive global aid from other countries → could end up in debt for decades
what historical factors cause uneven development
colonialism
how does colonialism cause uneven development (2)
between 1800-1900, many european countries began taking control of Africa → British brought infrastructure (e.g. railways, roads, ports)
however wealth derived went to colonial powers in other countries, leaving the economy poor
how is the economy now in africa
based around raw materials rather then manufacturing
what do these countries still have a lot of
political instability (e.g. Niger)
what economic factors have caused uneven development (4)
health + water quality
education
trade
political factors
how have health and water quality affected uneven development (2)
clean water not always available
water can be infectious (e.g. cholera, bilharzia)
who is particularly susceptible to Bilharzia
children playing in water + adults working in wet fields
is Bilharzia very dangerous
there is treatment if caught in time, but it can cause major problems (even death for adults)
how does education cause uneven development (2)
costs money that some people can’t afford (e.g. In Uganda, uniforms are expensive)
development requires a workforce sufficiently educated to be literate
how does trade cause uneven development (4)
efficient trade requires infrastructure which poorer countries lack
global trading policies dont favour the poor
wealthier countries are part of trade blocs
poorer countries usually export primary goods (which are cheap) → richer countries process these, adding value and making profit
what is a trade bloc
groups of wealthy countries which trade with eachother
how do political factors cause uneven development (2)
corrupt governments may have workers diverting development funds into their own pockets
lack of investment in education and health
assess the significance of factors that have caused uneven development (9 marks)
economic - highly significant → global trade, political corruption
physical - significant → climate + location, there are exceptions (e.g. USA)
historical - significant → its in the past
what is international migration
movement of people from one country to another
what is internal migration
movement of people within a country
what are 3 consequences of uneven development
disparities in wealth
disparities in health
migration
what does disparities in wealth include
money, opportunities, access to resources
disparities in wealth (3)
despite global economic and social progress, bringing millions out of poverty, wealth disparity is growing
within HICs and LICs, rich and poor are moving further apart economically
some families get opportunities due to gov-funded education
disparities in health (3)
life expectancy lower in LICs then HICs → reflects disease and incidences of war
HICs offer better medical facilities, treatment and preventative care (e.g. vaccines)
HICs often better at preventing diseases occurring
people migrate from LIC to
NEE and HIC
what is involuntary migration
migration to seek refuge from war, political unrest or natural disasters
what is an economic migrant
someone who moves to seek a better standard of living - voluntary
what do international migrants include
economic migrants and refugees
why do EU countries try to limit the no. of migrants
economic purposes → may not be enough jobs, could put a strain on services
advantages of migrants
fill jobs, multiplier effect, economic growth
what are the two types of development
bottom up and top down
what is top down development (3)
government-led investment
large scale
may involve global financial institutions (e.g. World Bank)
what is bottom up development (4)
community-led development
involves local people in decision making
low cost
focus on skills (e.g. education, healthcare)
what are 3 top down strategies to reduce the development gap
Large Scale Investment (e.g. dams)
Large Scale Aid
Debt relief
what are advantages of large scale investments (2)
provides jobs for locals
provides Hydroelectric power
why is hydroelectric power good
doesn’t release fossil fuels
guaranteed energy for industry
what are disadvantages of large scale investment (4)
people displaced due to flooding
loss of farmland
costly
noise pollution during construction
what is large scale aid
funding coming into a poorer country from various sources (e.g. world bank) for development purposes
what are advantages of large scale aid (3)
new infrastructure boosts economy
increased quality of life
benefits ‘trickle down’ from top to bottom in economy
disadvantages of large scale aid (3)
often expensive to repay loans
can be lost to corruption in gov
can lead to exploitation
what is debt relief
writing off debts, or making payments lower for a longer period of repayment