Chemistry First Semester
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
How do you determine the number of sig figs?
Count the number of non-zeros (integers)
Count the zeros between non-zeros
Count ending zeros after a decimal
Cross out starting zeros
How many sig figs are in: 0.0120 m
3 sig figs (cross out starting zeros, add non-zeros and ending zero)
How many sig figs? 100.5 mL
4 (count non-zeros and middle zeros)
How many sig figs? 101
3- two non-zeros and one middle zero
How many sig figs? 350
2- two non-zeros, one eliminated ending zero
Round 5,487,129 m to 3 sig figs
5,490,000
0.013479265 mL to 6 sig figs
0.0134793
31,947.972 cm2 to 4 sig figs
31,950.
What is a mixture?
Two or more elements/compounds that can be separated physically
What is a compound?
Two or more elements chemically bonded
What is an element?
One or more atoms of the same type bonded together
macrosopic
observable
submicroscopic
molecular
symbolic
representational
molecules
made from more than one atom
homogenous
appear uniform
heterogenous
can be separated easily, clear separation
Pure substance
element or compound, separated by chemical means
Physical properties
determined witthout changing the chemical structure
chemical properties
measured by changing the chemical makeup
Physical change
physical properties may change, but chemical ones don’t
Chemical change
New physical and chemical properties. New substance and composition
Intesive properties
Do not depend on the amount of matter ex:tempeerrature, boiling point, conncentration, luster
Extensive
Depends on the amount of matter Ex:weight, length, volume, entropy
Density
Mass per amount of volume
How is density different in the states of matter?
Solids are the most dense, gases are the least, liquids in the middle
accuracy
how close to actual value
precision
how close measurements are to each other
How do you use sig figs when calculating?
Round to the amount of sig figs that is lower. Ex: 25×274= 6850 25 has 2 sig figs and 274 has 3, so 6850 is rounded to 6800
How are estimates used?
Take the measurement round to the smallest unit exactly measured. Then, estimate the next digit. Ex: If water is filled between 25mL and 26mL, round to the nearest tenth for the amount, 25.6mL
what do flat lines represent on heating curves
phase changes (ex: melting)
what do slanted lines represnt on a heating curve
states of matter (ex: solid)
triple point
where all states of matter exist in unison
critical point
where a material is indistinguisable between a gas and liquid
Temperautre
The measure of average kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
collisions of particles
Heat
the flow of thermal energy between objects. Caused by differences in temperature. Flows to create equilibrium
Exothermic
releases heat
Endothermic
absorbs heat
Energy
capacity to do work or produce heat
Does adding heat always increase temp?
No, at a certain point, is it used to change phases
Specific Heat
the amount of energy it takes to heat 1g by 1°C
Lower specific heat acts how on a graph?
It is steeper because it takes less heat to increase the temperature
Higher specific heat acts how on a graph?
It is less steep because it requires more heat to change the temperature
Are specific heats the same across states of matter?
No, water, ice, and water vapor all have different specific heats
What is the specific heat formula? (Changing temperature)
q=mc∆T (energy= mass x temperature change x specific heat)
What is the phase change formula?
Q= mHvap or q=mHfus (vap is for vaporization/condensation, fus is for freezing/melting)
What does phase depend on?
Temperature and pressure
How do atrractive forces between particles vary in the phases?
Solid has the highest, then liquid, then gas. Strong is harder to separate
What is Kinetic Molecular Theory?
Molecules and particles that bounce of the wall of a container create pressure and the average kinetic energy is the temperature in Kelvin
What are teh 5 basic gas laws?
Ideal, Charles’, Boyle’s, Gay-Lussac’s, and Avogadro’s. Combined they create Combined Gas Law
What si the ideal gas law?
PV=nRT. It is used when there is no change in the system but a measurment is unknown
What is Boyle’s Law
P1V1=P2V2 V↑P↓, T is constant. Inverse relationship
What is Charles’ Law?
V1/T1=V2/T2 T↑V↑, P is constant, direct relationship
What is Gay-Lussac’s Law?
P1/T1=P2/T2 T↑P↑, V is constant, direct relationship
What is Avogadro’s Law
V1/n1=V2/n2, n↑V↑, T and P are constant, direct relationship
What is Combined Gas Law?
P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2
Democritus
Greek Philosopher who hypothesized about atoms but was not considered a scientist because he did not experiment
John Dalton
Atomic Theory. Elements are made of indivisible atoms
J.J. Thompson
Cathode Ray. Discovered electrons and that like charges repel. Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford
Gold foil experiment. Discovered nucleus, a positively charged, dense core in the middle. Model with ovals or model with dotted line circle
Robert Millikan
Oil drop experiment. Charge and mass of a single electron/different amounts of electrons in each element/ion
Niels Bohr
Electron Energy Levels. Electrons “jump” between levels. Planetary model
Erwin Schrödiger
Electrons move in waves, not paths. Clouds of probability

Dalton’s model
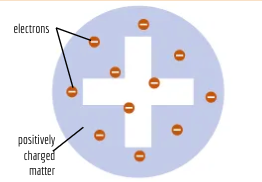
plum pudding
Thomson’s model
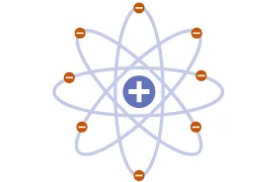
Rutherford one “generic/movie atom”

Rutherford’s model
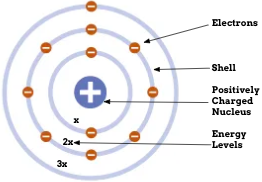
Bohr’s model

Schrödiger’s model
What indetifies an atom?
Proton number and atomic number (same thing)
Where are protons located?
The Nucelus
What makes up the atomic mass?
The average atomic mass of the naturally occuring isotopes, but what makes those is the number of protons+number of neutrons
Where are electrons located?
The electron shells that orbit the nucleus
What are ions?
Charged atoms, they gained or lost electrons
What are cations?
Positive ions that lost electrons
What are anions?
Negative ions that gained electrons
What are isotopes?
Atoms that gained or lost neutrons, changes the atomic mass
what does 14 represent in “ N714 “
mass number
what does 7 represent in “ N714 “
atomic number ( # of protons)
What is average atomic mass?
On periodic table, weighted avergae of the isotope masses
What is isotope mass?
Added masses (both equal 1) of the protons and the neutrons
How do you calculate avergae atomic mass?
(mass of isotope x percentage of abundance) + (mass of isotope x percentage of abundance) added with all isotopes
What is an orbital?
Space in an atom where an electron is likely to be
What are orbital diagrams?
sublevels shown in boxes
What is electron configuration?
Condesned representation
ground state
The lowest energy state of an atom or molecule.
excited state
A state of an atom or molecule where one or more electrons have moved to a higher energy level than their ground state.
Aufbau Principle
Lowest to highest level
Hund’s Rule
Fill each sublevel singly before pairing up
Pauli Exclusion Principle
Each orbital can only hold two electrons, and they must have opposite spins.
Noble Gas Configuration
List the noble gas before the element in brackets, then continue with the electron configuration
What is light?
A form of energy that acts as both a wave and a particle
What are characteristics of waves with shorter wavelengths?
More energy, higher frequency
What are characteritics of longer wavelengths?
Less energy, lower frequency
How is color a thing?
Within the visible light spectrum, the different colors have different wavelengths, therfore have different energies, frequencies, and speeds.
Diffraction Grating
Tiny film with grooves that bends light into different colors.
Line emission spectrum
Lines created by an element’s light emission going through diffraction grating, can indentify an elemtent or the element in a compound/molecule