Non-sterile Compounding Calculations
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Why are amber vials used?
to protect against:
- temperature
- light
- moisture
Typical hazards in a lab
Chemical hazards:
- fire/explosion
- chemical/thermal burns
- absorption of chemicals
- inhalation of chemicals
- ingestion of chemicals
Physical hazards:
- slips, trips and falls
- cuts, scrapes, bruises
Electrical hazards
General routes of exposure
INHALATION of vapors, gasses, mists, or particulates
SKIN CONTACT with chemicals can cause skin or tissue damage or allow absorption into blood
INGESTION through GI tract
INJECTION from skin punctures from contaminated objects
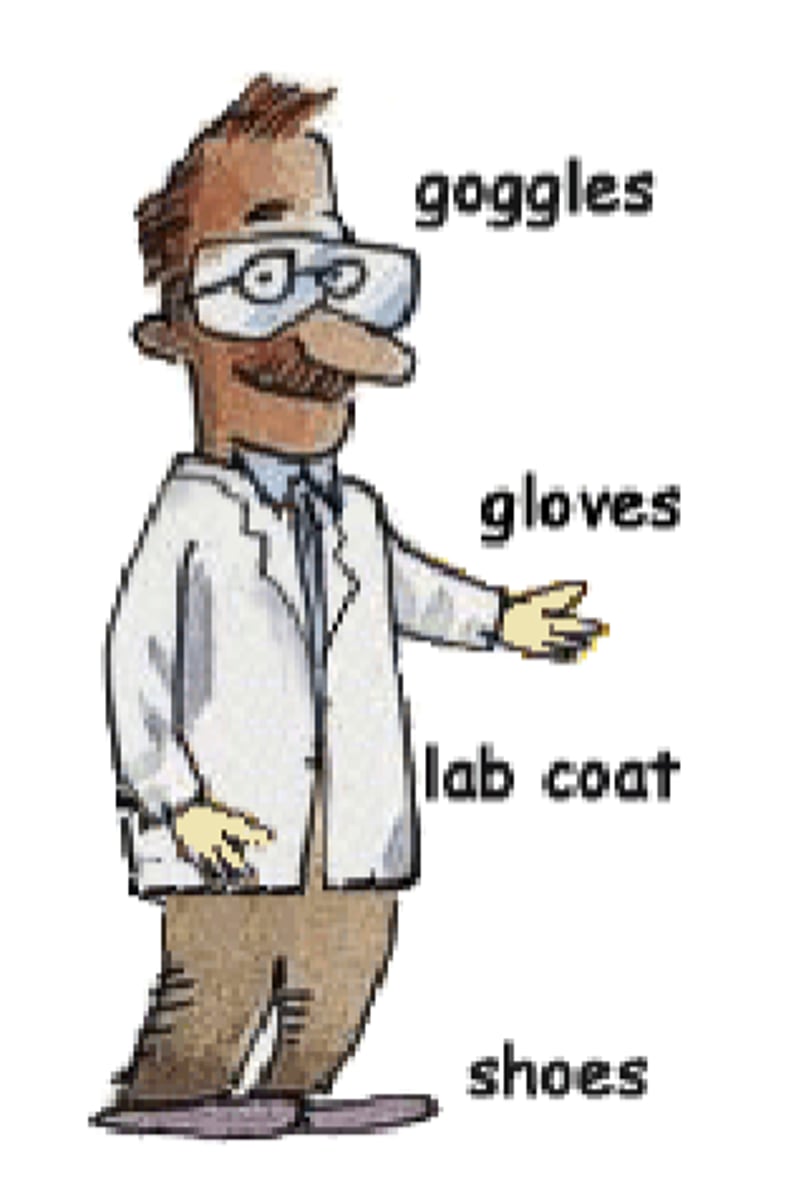
Proper lab dress, PPE
- eye/face protection (safety goggles/glasses)
- lab coat
- chemical resistant gloves
- long pants
- closed toe shoes
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
designed to provide specific info. about chemicals including:
- physical properties
- physical & health hazards
- proper handling procedures
- readily accessible to students/employees
- located in room #610 non-sterile compoudnig lab in designated wood cabinet
MSDS content
• Chemical and manufacturer identity
• Hazardous ingredients
• Physical and chemical characteristics
• Fire, explosion, and reactivity
• Health hazards
- Routes of entry
- Exposure levels
- Symptoms of exposure
- First-Aid and emergency info.
• PPE
• Safe handling and storage
• Spills and leaks
• Compliance issues
What is the importance of labels?
• The identity of the chemical
• Name, address, and emergency phone number of the manufacturer
• Physical and health hazards
• Special handling instructions
• Basic PPE recommendations
• First aid, fire response, spill cleanup
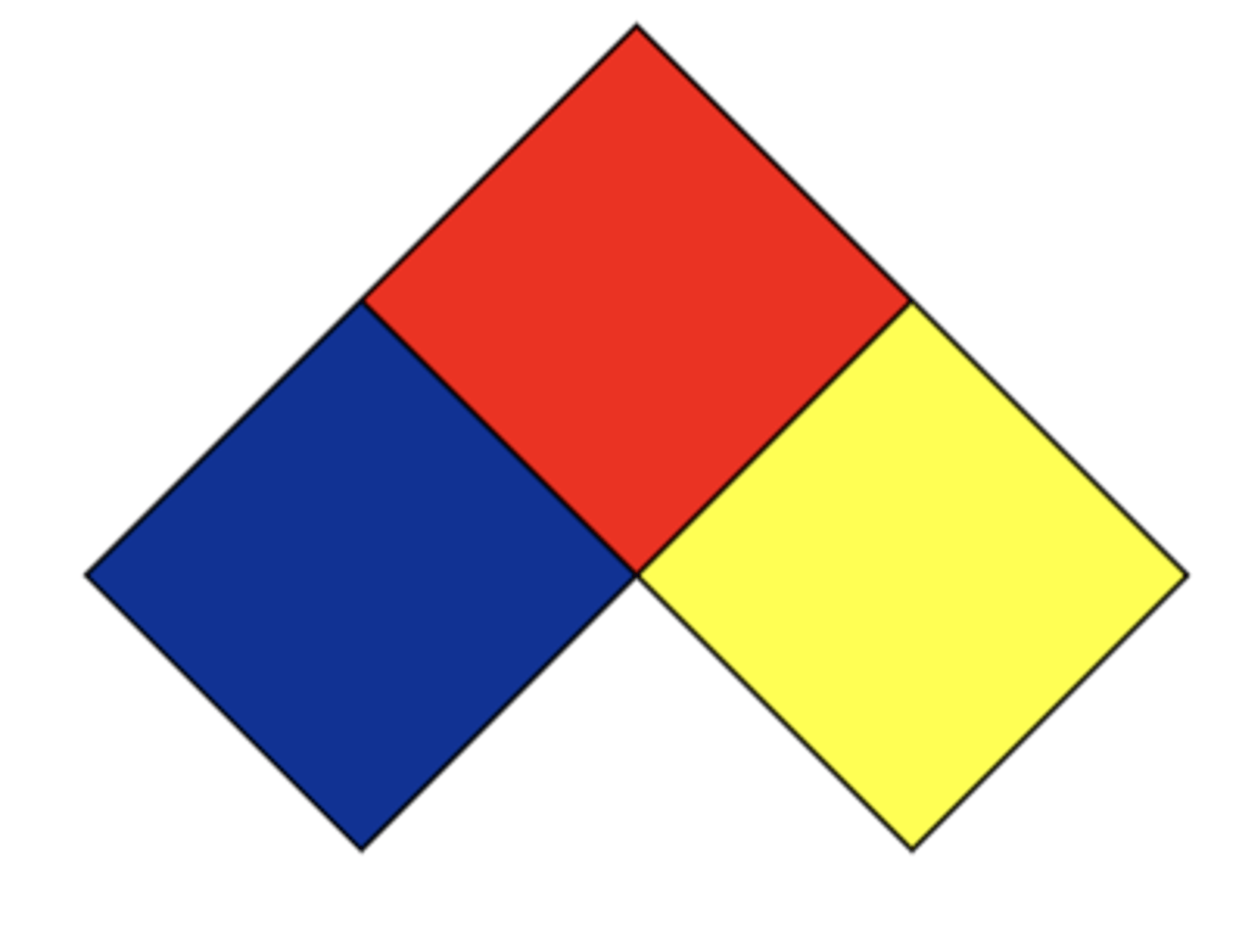
NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) Labeling systems
- Red =
- Blue =
- Yellow =
- White =
• Red = Flammability
• Blue = Health
• Yellow = Reactivity
• White = Other hazards or special handling

NFPA labeling: Scale
0 to 4
0- no hazard
4- extreme hazard
Eye protection
safety glasses/goggles
- students are required to wear safety glasses with side shields
- provide protection against flying particles
- required where impact or hazardous materials exist
- if student requires corrective lenses, safety glasses that fit over typical eyeglasses are available
T/F: you only need to wear safety glasses in the lab while working
FALSE
always wear in lab, not just while working. someone next to you could spill something
If there is a reasonable risk of splash,....
skin surfaces should be protected
- scrub suits (shirts and trousers) plus a mid-thigh to knee length white lab coat
A student found without what while compounding will be asked to leave/receive no credit?
without lab coat, scrubs, close toed shoes, working without gloves and safety glasses/goggles
What can't be done in the lab?
- applying cosmetics
- eating or drinking
- tasting chemicals
- pour from large containers into smaller ones- label all secondary containers
- do not smell any chemicals directly- use hand to fan vapor to your nose (waft)

check glassware for..
stars or cracks

handle hot glassware with...
gloves (special ones)
- the oven is in C, not F so 100 is HOT
Wash your hands with...
soap and water before leaving
_______________________ carefully to make sure that you are using the right chemical
read and reread
Hair
- tie back long hair
- hair bonnets should be worn while compounding and handling hazardous chemicals
Hot plates should be ____________ and ______________ when not using them
turned off and unplugged
Prior to working in the lab identify the nearest ___________ and _________
eyewash and shower
- notify facilities/lab safety if the shower or eyewash is not operational or inaccessible
T/F: first aid kits are available
TRUE
High degree of precaution must always be taken with any sharp itemsused in the laboratory, including....
glass slides, graduated cylinders, beakers, broken glass
Clean up all broken glass ___________________ and dispose broken glass in ________________________ for broken glass
- immediately
- special receptacles labeled
- spilled chemicals should also be cleaned immediately
T/F: it is okay to put broken glass in trash cans
FALSE
do not put broken glass in trash cans
Sharps containers are never placed in the...
normal waste stream or used for any purpose other than sharps disposal
In case you poke yourself with sharps...
• Squeeze out blood
• If necessary, seek medical attention immediately (know what was the contaminants of the sharps)
Compounding
the act of reconstituting, mixing, or preparing a medication into a dosage form usable by the patient
Non-sterile (extemporaneous) compounding
includes all compounding of dosage forms not prepared in a sterile environment
extemporaneous- preparation of drug on demand
Dosage forms compounded in non-sterile environment often include:
- oral preparation
- topical
- vaginal
- rectal
- otic preparations (excludes use in perforated eardrums)
- nasal and sinus preparations intended for local application (nasal sprays & irrigation)
There are a number of reasons for a patient to require a compounded medication, including...
- medication is not commercially available
- when a patient cannot tolerate, or is allergic to a component of the commercially available product (dye or coloring used)
Guidelines for non-sterile compounding are published by...
the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) chapter <795>
The preparation, packaging, and dispensing of most compounded prescriptions involve a number of pharmacy calculations.
These calculations present one of the greatest....
greatest potential sources of error
- ZERO TOLERANCE IS ALLOWED FOR ERRORS
______________________ or ________________ is one of the first steps in preparing any prescription
Weighing or measuring ingredients
T/F: The actual quantity of a formula to be prepared is often the same quantity that is described in a formulation record
FALSE
is often NOT the same quantity described in record. reducing and enlarging is often required
In many cases, the quantity must be _______________ or _____________ to achieve quantity of product
increased or decreased
To ensure that the relative quantities of the ingredients remain consistent, the quantities of all ingredients must be increased or decreased by the....
same factor
If factor is greater than 1....
If factor is less than 1....
create enlargements
create reduction
The amount of PCCA Rapid Dissolve Tablet Powder Base will vary with...
API content
- Displacement of PCCA Rapid Dissolve Tablet Powder Base is made by subtracting 100% of the solid ingredients from the weight of PCCA Rapid Dissolve Tablet Powder Base in this mold
Geometric dilution involves ___________________, typically used when a _________________ needs to be combined with a _______________
- mixing powders
- potent substance
- large amount of diluent
Geometric dilution should be followed when mixing an ingredient of a ____________ with a second ingredient of a _____________
- larger quantity
- smaller quantity
- L is to be mixed into S in small portions
Geometric dilution
1. potent drug is initially placed on a roughly equal volume of diluent in a mortar, and gently mixed through trituration
2. Second portion of diluent, equal in volume to the powder mixture in the mortar is added, trituration is repeated
3. The procedure continues, with additional diluent added in amounts equal to the mixture's volume in the mortar at each step, until all the diluent is fully incorporated
- used for making tablets

T/F: Under NO circumstances should the entire quantity of the larger amount of substance be added at once to the smaller quantity in the expectation that uniform dispersion will be achieved quicker
TRUE
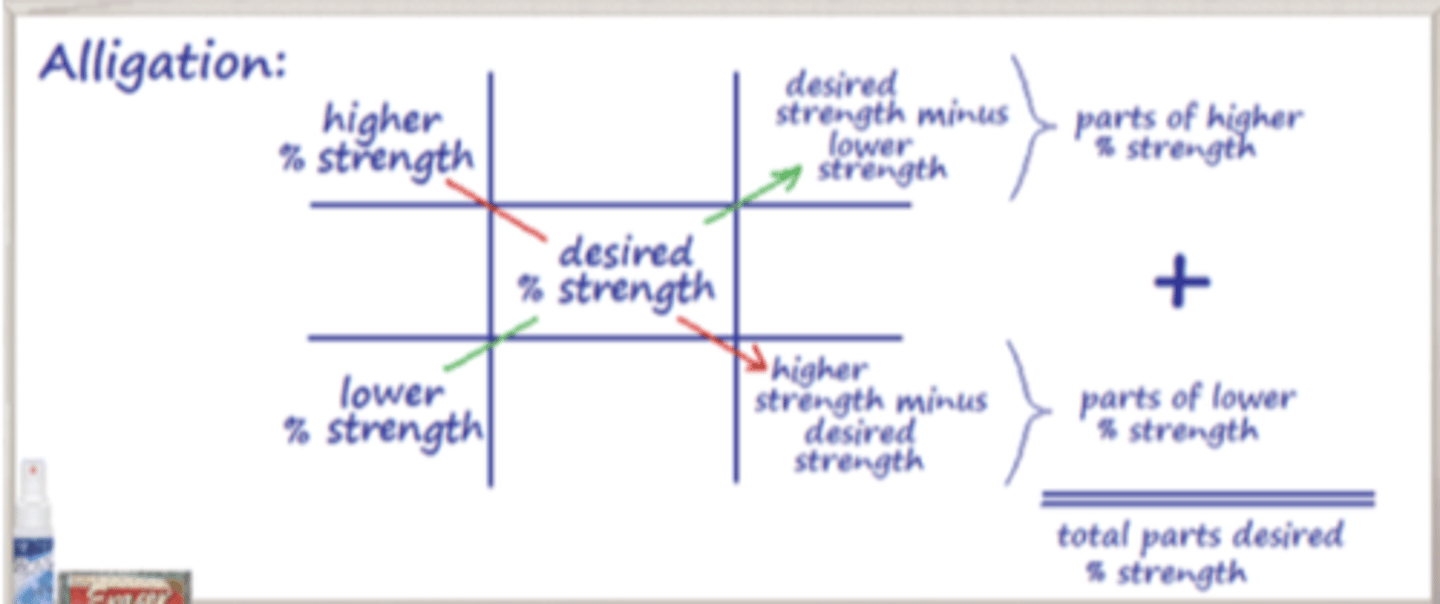
Alligation
a method for calculating proportions of different substances to mix to create a desired concentration or strength
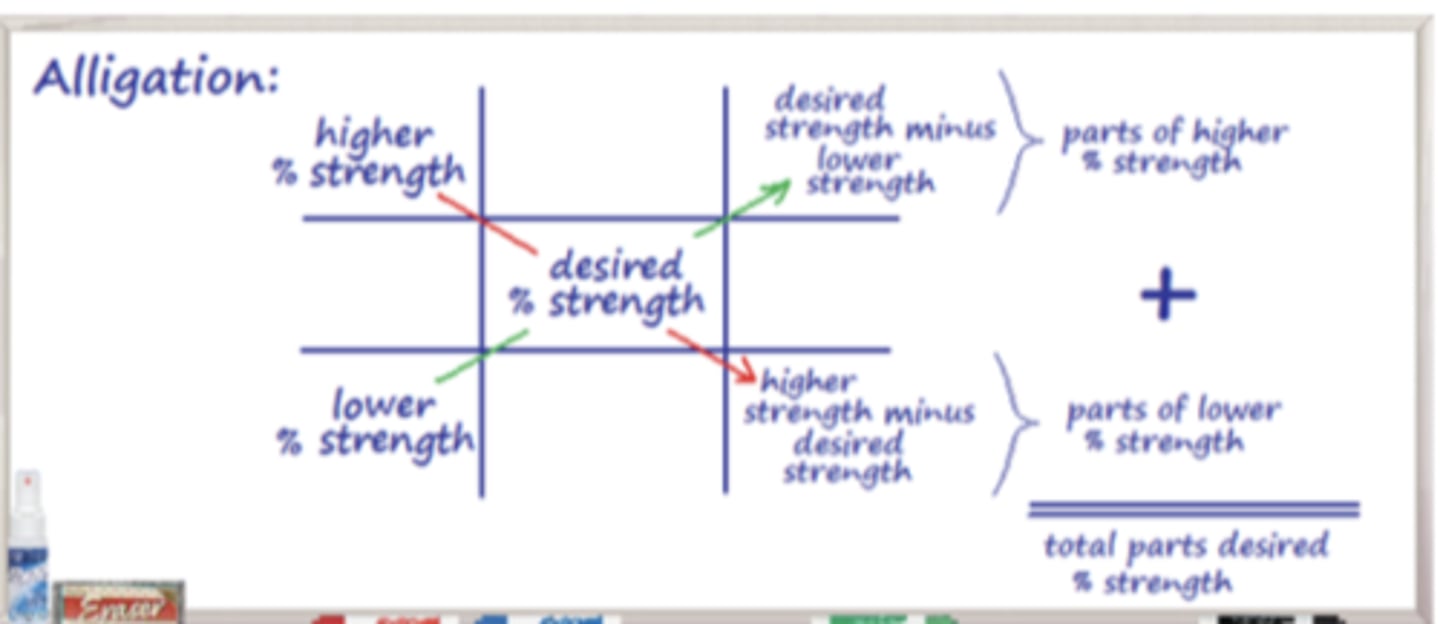
Alligation is to obtain a new ___________ that is between ________________ the pharmacist has in stock
- strength (percentage)
- two strengths
Specific gravity (SG)
a ratio, expressed decimally, of the weight of a substance to the weight of an equal volume of a substance chosen as a standard, both substances at the same temperature
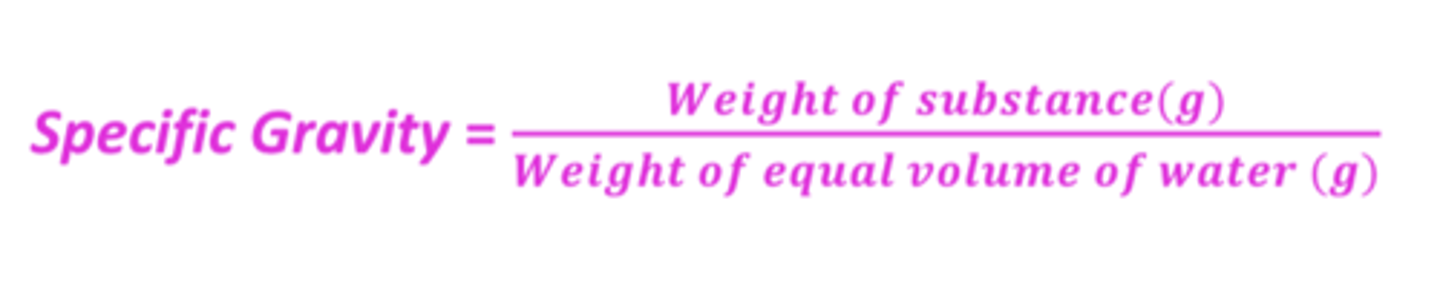
What are the units of specific gravity?
it is UNITLESS!
SG expresses how much ____________ or ____________ a substance is than ____________
- heavier or lighter
- water
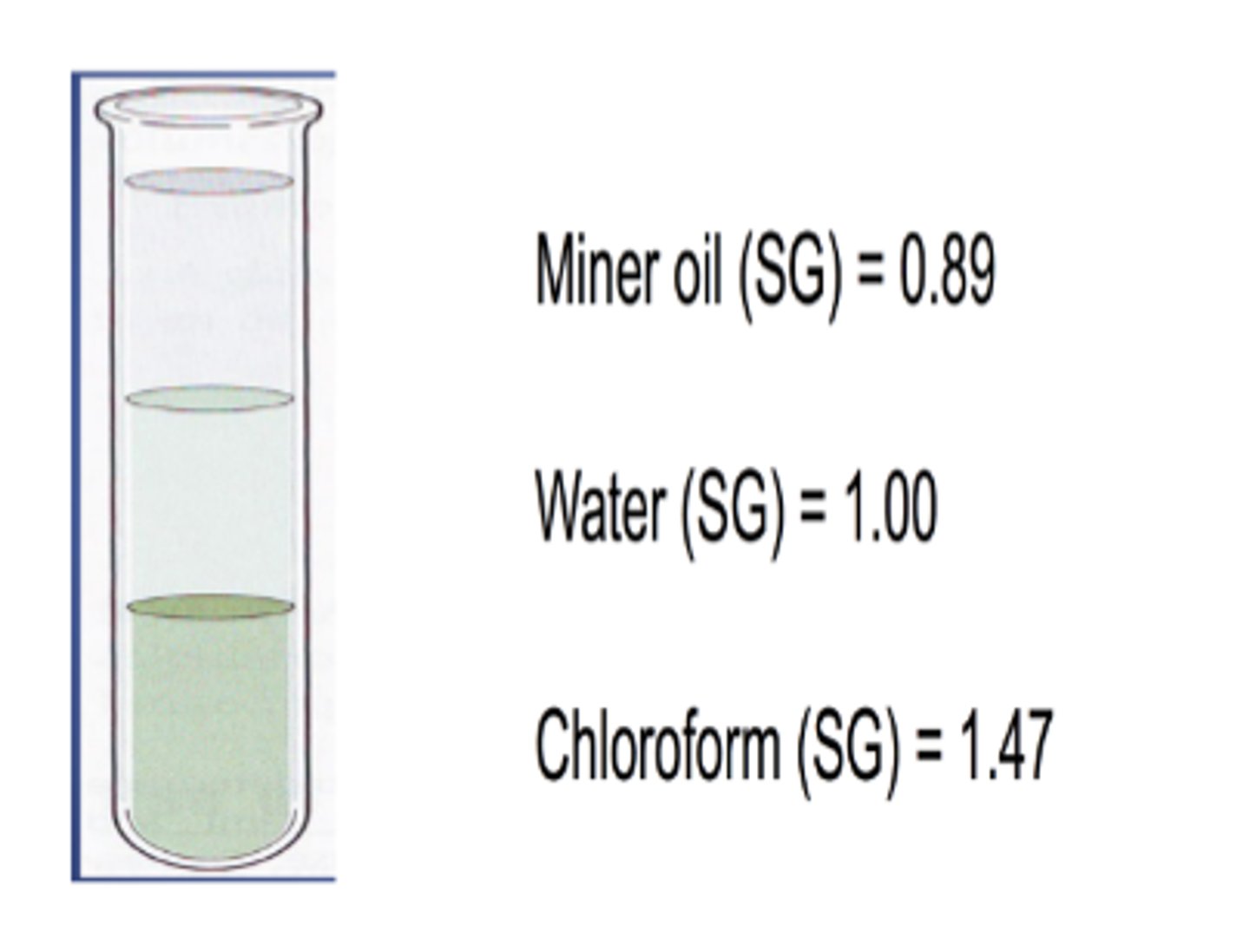
SG: substances with a SG <1, are....
substances with a SG >1, are......
- lighter than water
- heavier than water
When compounding, how much extra do we usually take of all ingredients due to the potential for loss during preparation/dispensing?
10% excess

What is often done to the clear plastic bottles in the lab prior to starting?
calibrating the bottle to the desired volume by using purified water and a marker to mark the bottom of the meniscus
What is used to triturate powders?
mortar and pestle
If the formulation is complete but has not reached the marked line on the bottle, what is done?
add a portion of water (or other substance depending) sufficient to bring the total volume of the preparation (i.e. "qs") to the pre-calibrated line
For tablets, the API used must be stable at a temperature of....
110 degrees C for 30 minutes
What is often done after a formulation is completed and poured into the calibrated bottle?
the mortar is rinsed and emptied into the bottle to collect the most substance possible
After compounding an oral suspension (ex: acetaminophen 500 mg/5 mL) the BUD according to USP <795> is...
estimated to be 14 days
For creams and ointments, some ingredients must be...
melted/mixed on a beaker on hot plate with other ingredients
(ex: cold cream and camphor/menthol ointment)
For creams and ointments the products have to....
cool
ointments are passed through an ointment mill to....
- reduce particle size of the active ingredients
- eliminate any grittiness of the final preparation
For lip balms, ensure that lip balm tubes are....
twisted all the way down to ensure they will not overflow when pouring in