1.2 Essential Review – Chemical Reactions
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Synthesis
Decomposition
Single Displacement
Double Displacement
Combustion
Acid-Base Neutralization
What are the 6 main reactions?
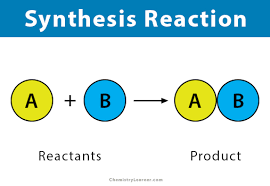
Two or more species react to produce a new reagent (or reagents).
How does Synthesis work?
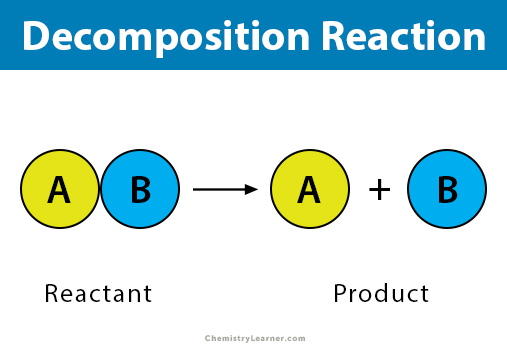
A single reactant breaks down into two or more simple products.
How does Decomposition work?
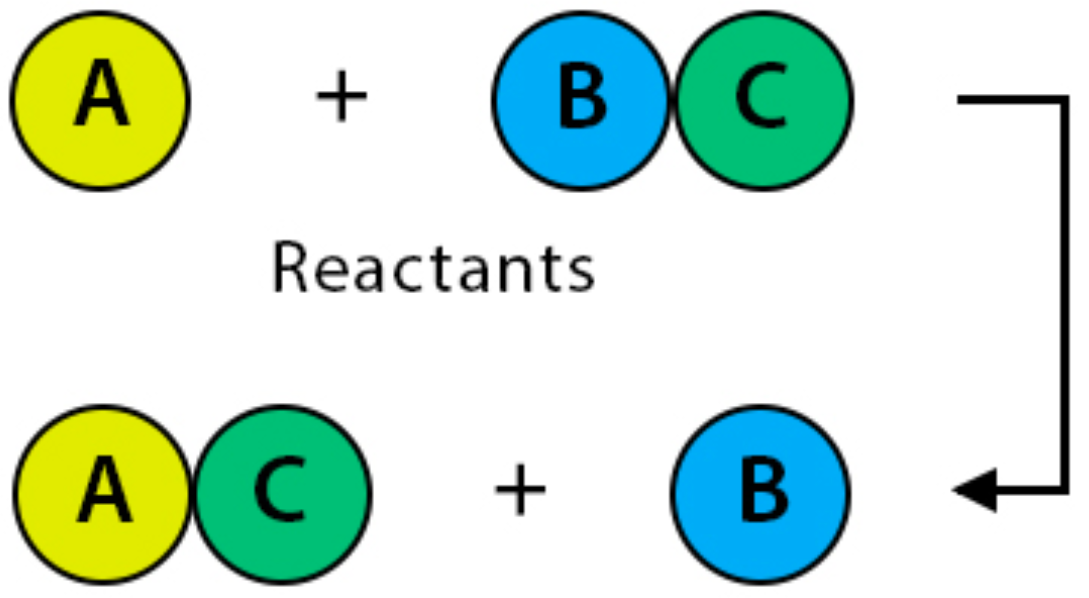
One element is replaced by another more reactive element (Example: Redox Reactions)
How do Single Displacement rxns work?
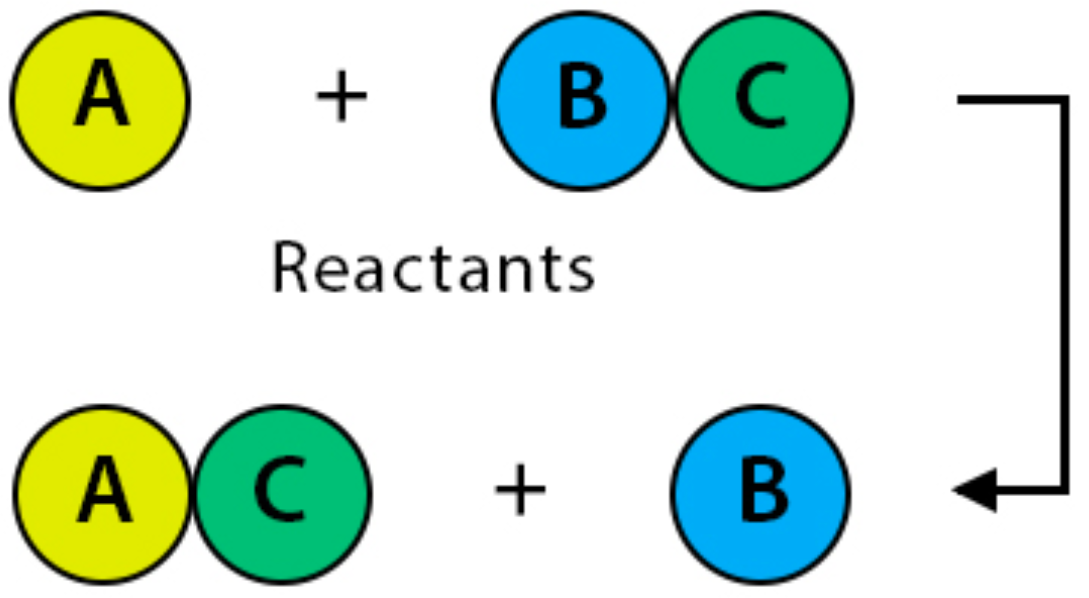
The positive or negative ions of two ionic compounds replace each other.
How do Double Displacement rxns work?
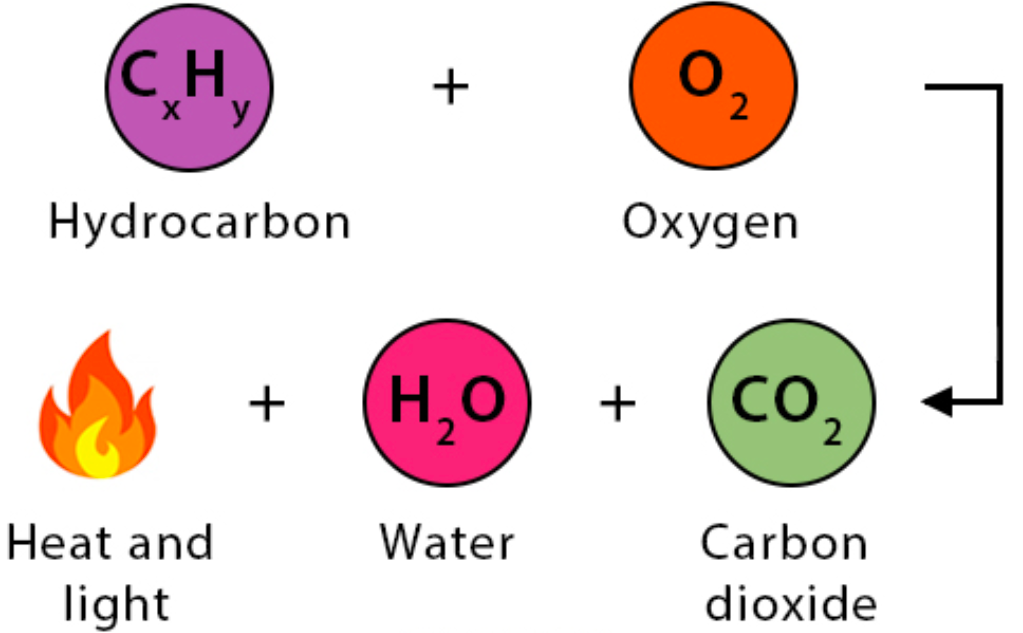
- a compound reacts with an oxidant (usually oxygen) in a highly exothermic reaction
- for hydrocarbons, the products are carbon dioxide and water.
How do Combustion reactions work?
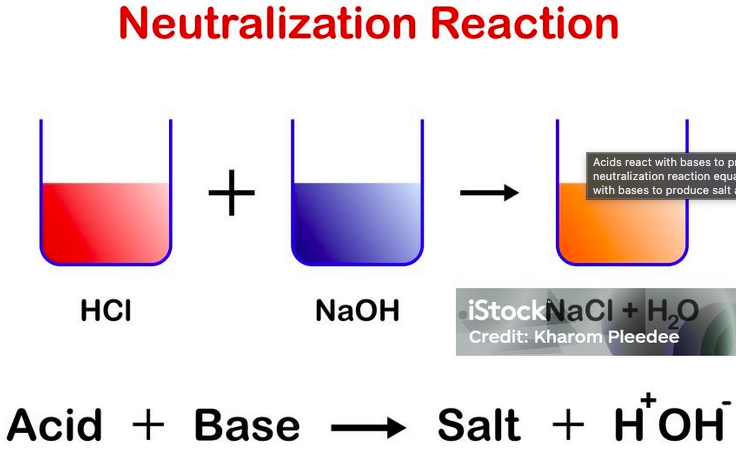
a proton is transferred from a proton donor (acid) to a proton acceptor (base)
How do Acid-Base rxns work?
2 Na (s) + Cl₂ (g)→ 2 NaCl (s)
Elemental sodium reacts with chlorine gas to produce sodium chloride.
2 Ca (s) + O₂ (g)→ 2 CaO (s)
Solid calcium reacts with oxygen gas to form calcium oxide
C₃H₈ (g) + 5O₂ (g)→ 3CO₂ (g) + 4H₂O (l)
What is the balanced equation for the combustion of propane, C₃H₈?
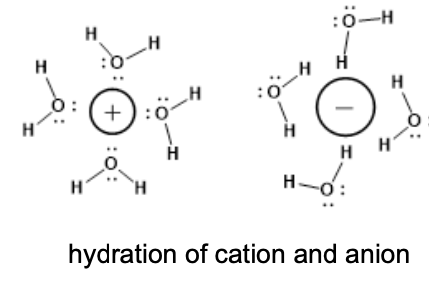
Comprised of a positive and negative ions in a repeating, regular pattern
held together by strong ionic bonds
Solid at room temps.
hydration spheres created around ions when dissolved in water
What are the components of an ionic compound?
a homogenous mixture involving a substance (solute) being dissolved in a medium (solvent)
Define Solution
Water, H₂O!
What solvent do aqueous solutions have?
Use (aq) after the molecule’s name as a subscript
How do you notate that a compound has been dissolved in water?
comprised of stable, neutral molecules in which atoms are held together by covalent bonds
their state (s, l, g) depends on the strength of the inter-molecular bonds
When dissolved in water, they become hydrated
when dissolved in water, they might create ions, but it depends on if they react with water or not
What is a Molecular Compound?
Ionic | Molecular |
metal + non-metal | 2 non-metals |
polyatomic atoms |
Ionic vs. Molecular Compounds
Ionic
Ionic or Molecular?: Sodium chloride — NaCl
Ionic
Ionic or Molecular?: Magnesium sulfate — MgSO₄
Ionic
Ionic or Molecular?: Magnesium sulfate — MgSO₄
Ionic
Cation: Potassium (K)
Anion: permanganate (MnO₄)
Ionic or Molecular?: Potassium permanganate — KMnO₄.
Molecular
Ionic or Molecular?: Carbon dioxide — CO₂.
Molecular
Ionic or Molecular?: Sulfur hexafluoride — SF₆
Following the solubility rules, a precipitate will form as a solid
How do you know if a precipitate will form when two aqueous solutions mix?
products of rxn
Solubility Rules only apply to…
alkali metals (group 1) are soluble
ammonium salts (NH₄anion) are soluble
nitrates are soluble (ex. AgNO₃⁻)
Chlorides (Cl⁻), bromides (Br⁻) and iodides (I⁻) are soluble except for the chlorides, bromides and iodides of lead (Pb²⁺), mercury (Hg+ and Hg22+) and silver (Ag+). Example: ZnCl₂ is soluble. PbCl₂ is not soluble.
Sulfates are all soluble except for the sulfates of calcium, lead, silver, mercury, barium, strontium
Carbonates (CO₃²⁻), phosphates (PO₄³⁻), and sulfides (S²⁻) are insoluble except for:
alkali salts (rule 1)
ammonium (rule 2)
Hydroxides are insoluble except:
fully soluble with alkalis (rule 1)
slightly soluble
What are the rules of solubility?
proton (H⁺) donor
give proton to the base
According to Bronsted-Lowry, what are acids?
proton acceptors
According to Bronsted-Lowry, what are bases?
proton donation rxn
when an acid donates a proton from its possession to a base, who accpts the proton (H⁺)
What is an acid-base rxn? (Bronsted-Lowry definition)
pronated
hydronium, H₃O⁺
When an acid is dissolved in water, the water becomes ________. What forms in the water?
depronated
hydroxides released, OH⁻
When an base is dissolved in water, the water becomes ________. What happens in the water?
by the amount of molecules reacting with the water
strong = almost every/every molecule reacting with water
What determines if an acid is strong?
HCl - hydrochloric acid
HBr - hydrobromic acid
HI - hydroiodic acid
HCl - perchloric acid
HCl - perbromic acid
HCl - periodic acid
H₂SO₄ - sulfuric acid
HNO₃ - hydrochloric acid
What are the strong acids?
Binary Acids
Oxo Acids
What types of acids are present when talking about common strong acids?
acids that contain H and another element, X
general formula: HₙX
the H is bonded directly to the X
HCl - hydrochloric acid
HBr - hydrobromic acid
HI - hydroiodic acid
What are Binary Acids? Which strong acids are Binary?
acids that contain H, another element, X, and an O
general formula: HₙXOa
the H is bonded directly to the O
HClO4 - perchloric acid
HBrO4 - perbromic acid
HIO4 - periodic acid
HNO3 - nitric acid
H2SO4 - sulfuric acid
What are Oxo Acids? Which strong acids are Oxo Acids?
group 1 hydroxides
ex. LiOH, NaOH, KOH, RbOH
Group 2 hydroxides are only slightly soluble or sparingly soluble in water.
ex. Mg(OH)₂, Ca(OH)₂, Sr(OH)₂, Ba(OH)₂
Hydride ions and oxide ions react with water producing hydroxide ions in solution
hydride (H⁻)
oxide ions (O²⁻)