Science - Kinematics & Forces: Test Revision
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Acceleration
Any change in velocity (speed or direction). Measured in metres per second per second. Is a vector quantity, like velocity, meaning it must have a direction.
Average Acceleration
The average change in a velocity over a period of time. Formula is (v2-v1)/(t2-t1)
Displacement
The change in position of an object. Measured in a straight line from an object’s start to end. Indicates a direction.
Distance
How far an object has travelled. Not a straight line. Length of a path from start to finish
Kinematics
The branch of physics that describes motion.
Speed
The rate of change of an object’s position
Velocity
The speed of an object in a certain direction. Must have a specific direction, e.g. 27km/h east.
Vector Quantity
A quantity that has both a size and a direction.
What do the slopes on a velocity time graph indicate (Flat, Going Up, Going Down)
Flat - Zero Acceleration
Going Up - Getting faster (positive acceleration, the steeper, the higher the rate of acceleration).
Going Down - Getting slowed or faster in negative acceleration
What do the slopes on a distance time graph indicate (Flat, Upward Slope, Upwards then starts to get flat)?
Flat - Not moving, but doesn’t drop to 0
Upward slope - Moving and covering distance (the steeper, the faster)
Upwards then starts to get flat - Started fast, now slowing down and starting to stop
What do the slopes on a speed-time graph indicate (Going up, Flat, Going down)?
Going up (travelling and moving at speed, the steeper, the faster. Not a constant speed)
Flat (at a consistent speed)
Going down (slowing down)
Convert between km/hr and m/s
Km/hr to m/s = Divide by 3.6 (1km/hr/3.6 = 0.277m/s)
M/s to km/hr = Multiply by 3.6 (1m/s x 3.6 = 3.6km/hr)
Inertia
the natural tendency of an object to maintain its velocity. Object at rest stays at rest. Moving object keeps moving in same direction and same speed.
Newton’s First Law of Motion
An object will keep moving with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by a net force.
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
(Net) Force = Mass x Acceleration
An object’s force is proportional to its mass and acceleration
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Every force has an equal and opposite reaction force of the same type.
How do cars prevent someone flying out of car
Seatbelts - prevent moving, slow down inertia change.
Airbag - Cushions force, slows down inertia change.
Crumple zones - Increase collision time, slows person down over more time
Why are opposite forces always equal even if mass is different.
Think of the Earth as having a mass of 2kg, and the moon of 1kg. The moon is attracted to both kilograms of weight. The earth on the other hand, is attracted to that 1 kilogram twice, since each kilogram is attracted to that one kilogram weight. Hence, forces are equal.
If all the forces acting on an object are balanced then the net force acting on it is zero. True or False
True
How do you know if there is a net force acting on an object
Its velocity is changing
An elevator is rising up a vertical shaft in a skyscraper. Between the 12th and 20th floors it travels at a constant speed. During this time period:
the forces acting on it are balanced so the net force is zero
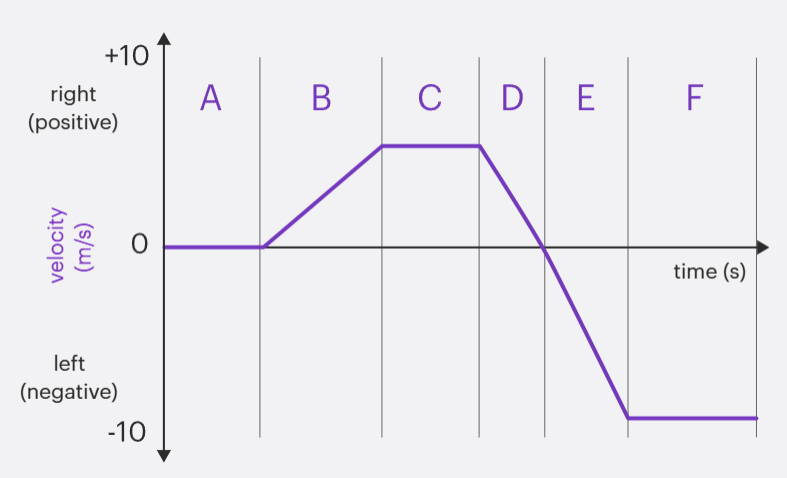
Using this graph, what happens when the line is going towards the centre? How about when it is straight?
It means you are still travelling in the direction that the line is in but not as fast. You are slowing down, but haven’t changed direction yet. You have a negative velocity when the line is pointing down, but positive if pointing up. When it is straight, you go at a constant speed, that speed may be 0 or 100.
Applied Force
a type of force exerted by a person, animal, or machine
Contact Force
a force that can only occur when two objects are touching
Non-contact force
Any force that can occur when two objects are not touching (gravity, magnetism)
Unbalanced forces
A force without an equal and opposite force acting on the same object
Balanced force
A force with an equal and opposite force acting on the same object
Friction
a force that resists and object’s motion
Air/Water Resistance
a force that resists an object’s motion through air/water
Net force
The overall force on an object
Mass
the amount of matter in an object
Tension
a force that pulls inward when a solid object is stretched
Weight
the force of gravity on an object
Force
a push or a pull. Causes an object to accelerate unless balanced by equal and opposite force.