M22
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Urinary System - Nephron
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
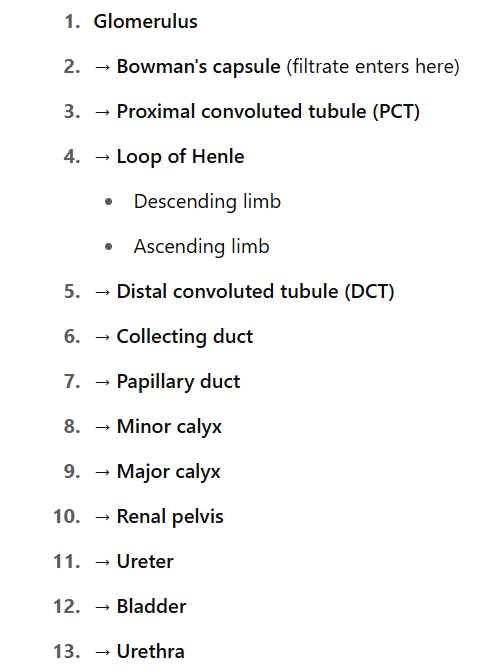
nephron
is the functional unit within each of the pyramid regions of the kidney
kidney has abt 1 million nephrons
what are parts of nephron?
renal corpuscle
renal tubule
label nephron
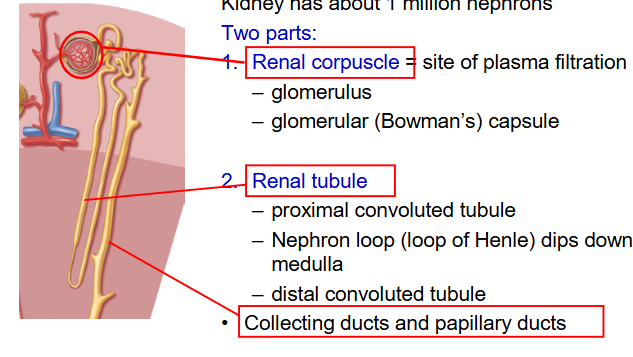
renal corpuscle
pulling plasma portion out of blood to make the filterate
called glomerular filterate bcz within renal corpuscle, the capillary beds that produce the filterate form a ball known as the glomerulus
has glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule
glomerulus
capillary bed that we are pulling the blood plasma out of
within renal corpuscle
renal tubule
proximal convoluted tubule→portion that leaves renal corpuscle
nephron loop (loop of henle)→ portion that dips down into medulla + pyramid region and come back towards cortex
distal convoluted tube→portion that reaches the cortex again
where is proximal convoluted tubule located?
in renal cortex
what do several distal convoluted tubules create?
connect tog to form collecting ducts
what collecting ducts tog form?
papillary ducts → will have final product, urine
what are the 2 types of nephron
cortical nephron (80-85%)
juxtamedullary nephron (15-20%)
cortical nephron (80-85%)
corpuscle is in outer cortex with short nephron loop (makes them diff)
loop has ascending and descending limbs
blood supply to loop via peritubular capillaries
juxtamedullary nephron (15-20%)
corpuscle near medulla in cortex (near the BASE) with long nephron loop
less abundant
loop has descending, and thin & thick ascending limbs
thin has simple squamous epithelial
thick has thicker cells
blood supply via peritubular capillaries and vasa recta
can produce dilute or concentrated urine
techincally both types of nephrons can make diluted and concentrated urine but the [] gradient is set up by long loop in juxtamedullary nephron
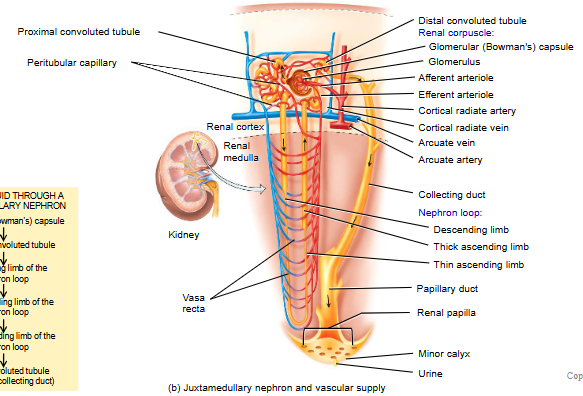
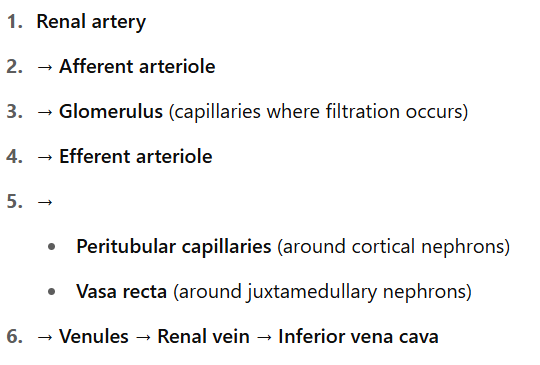
label blood supply to nephron
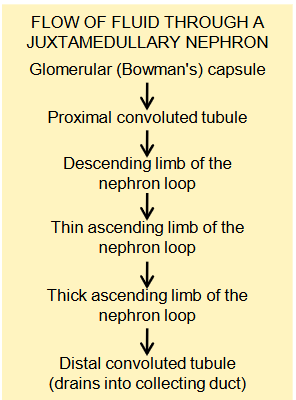
flow of fluid thru juxtamedullary nephron
goes from glomerulus to minor calyx
label histology of nephron
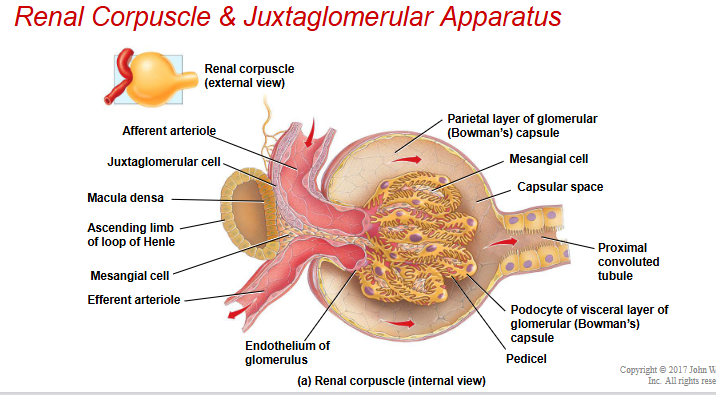
renal corpuscle
bowman’s capsule surrounds capsular space
capsular space is where filtrate accumulates
glomerular capillaries arise from afferent arteriole & form a ball
before emptying into efferent arteriole
what does efferent arteriole turn into?
peritubular capillaries
capsule portion
have parietal layer→ outer layer made of simple squamous cells
visceral layer →adhere tightly to endothelial cells that make up glomerulus
what are visceral layer cells called?
podocytes
modified simple squamous cells
have finger-like projectitons that serve as an extra barrier of filteration
pedicles
finger-like projections on podocytes
capular space
space between visceral and parietal layer
juxtaglomerular apparatus
structure where afferent arteriole makes contact with the ascending limb of nephron loop
macula densa is thickened part of ascending limb, have sensory receptors attached to them → detect water, Na+/Cl- concentrations
juxtaglomerular cells are modified smooth muscle cells in arteriole side
helps to regulate blood pressure in kidneys
what are the modified smooth muscle cells?
juxtaglomerular cells
mesangial cells
mesangial cells
located in region of afferent and efferent arterioles , also mixed in some glomerulus as well
involved in regulation
reduce surface area of glomerulus + afferent & efferent arterioles when contracted= reduces bloodflow= control how much filterate we are making
what happens when macula densa cells detect high amounts of water, Na+, Cl- []?
indicates that we are making too much filterate too quickly so it won’t be getting reabsorbed fast enough
how to stop it? sense this at lvl of tubule and send direct signal to juxtaglomerular smooth muscle cells in the afferent arteriole to contract= reduces blood flow= reduces amount of filterate we make
label filteration membrane on small portion of glomerulus
memorize 3 steps
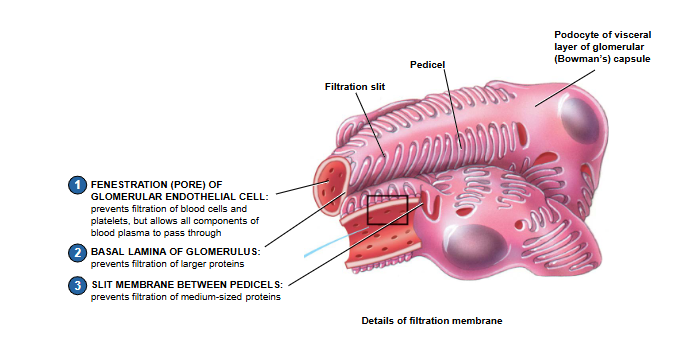
what layers make up filteration membrane?
fenestration (pore) of glomerular endothelial cell
basal lamina of glomerulus
slit membrane between pedicles
fenestration (pore) of glomerular endothelial cell
prevents filtration of blood cells and platelets, but allows all components of blood plasma to pass through
basal lamina of glomerulus
prevents filtration of larger proteins
slit membrane between pedicles
prevents filtration of medium-sized proteins
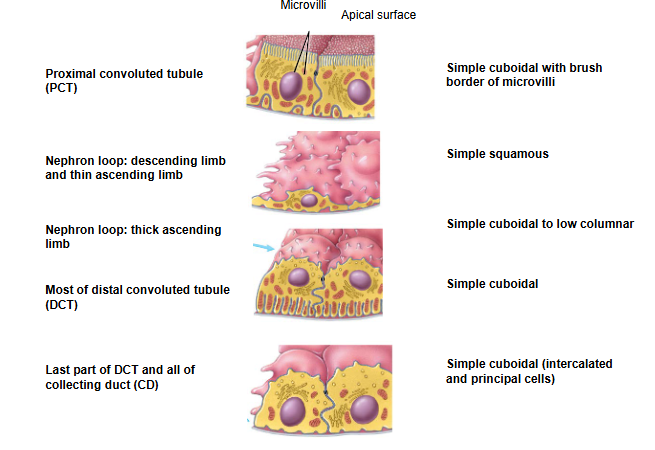
cells in proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
simple cuboidal w/ brush border of microvilli (similar to small intestine)
cells in nephron loop: descending limb and thin ascending limb
simple squamous epithelial cells
cells in nephron loop: thick ascending limb
change from simple cuboidal to low columnar cells
cells in most of of distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
simple cuboidal cells
cells in last part of DCT and all of collecting duct (CD)
simple cuboidal
also have specialized cells like intercalated and principal cells→ help w/ regulating ions []
intercalated cells
monitoring hydrogen ions and regulating pH
principal cells
under hormonal control, regulate Na+/K+ lvls in blood and renal tubule
label cells of renal tubule + collecting duct
what is blood flow in kidneys (vascular path)?
what is filterate flow in kidneys (tubular path)?