GCSE AQA Geography- Challenge of Natural Hazards
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Everything that you need for the GCSE AQA Challenge of Natural Hazards Section of the GCSE (besides case studies).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
What is a natural hazard?
A natural event that affects property and life
What are the four types of natural hazard?
Atmospheric, Tectonic, Geological and biological
What type of hazard is a tropical storm?
Atmospheric Hazard
What type of hazard is an earthquake?
Tectonic Hazard
What type of hazard is a landslide?
Geological Hazard
What type of hazard is a forest fire?
A biological hazard
What are the four hazards that affect hazard risk?
Magnitude, Location, Wealth and Quality of buildings
Give 7 reasons why people live in areas at risk at Tectonic Hazards
Naivity, farming, poverty, family, natural beauty, tourism and geothermal energy
What are the four layers of the earth?
Inner Core, outer core, mantle and crust
What are convection currents?
A movement within the Earth’s mantle caused by radioactive decay in the core.
What do convection currents cause?
Tectonic plates to move
Give the five stages of Convection Currents
The heat from the core is transferred to the mantle
Magma close the core is heated and rises
It reaches the crust and is forced sideways
Friction causes the tectonic plate to move.
Magma cools and sinks back to the core
Where are volcanoes typically found?
Along plate boundaries.
What are the collection of volcanoes found on the pacific plate margin called?
The ring of fire
Where are earthquakes typically found?
Along plate boundaries
Why might some earthquakes not follow this pattern?
Due to human activity (underground mining)
What are the two types of crust called?
Oceanic and continental crust
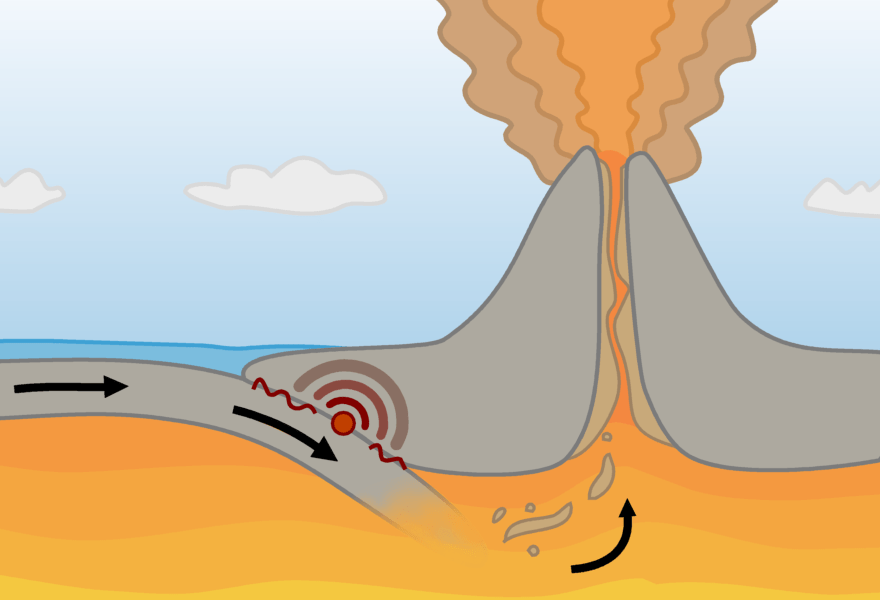
What is this plate boundary?
A destructive plate boundary
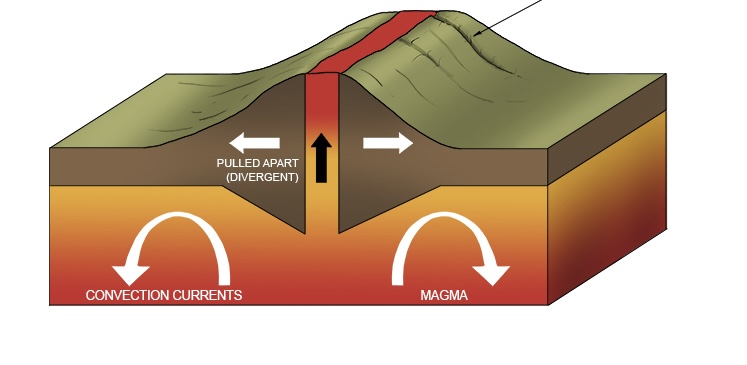
What is this plate boundary?
A constructive plate boundary
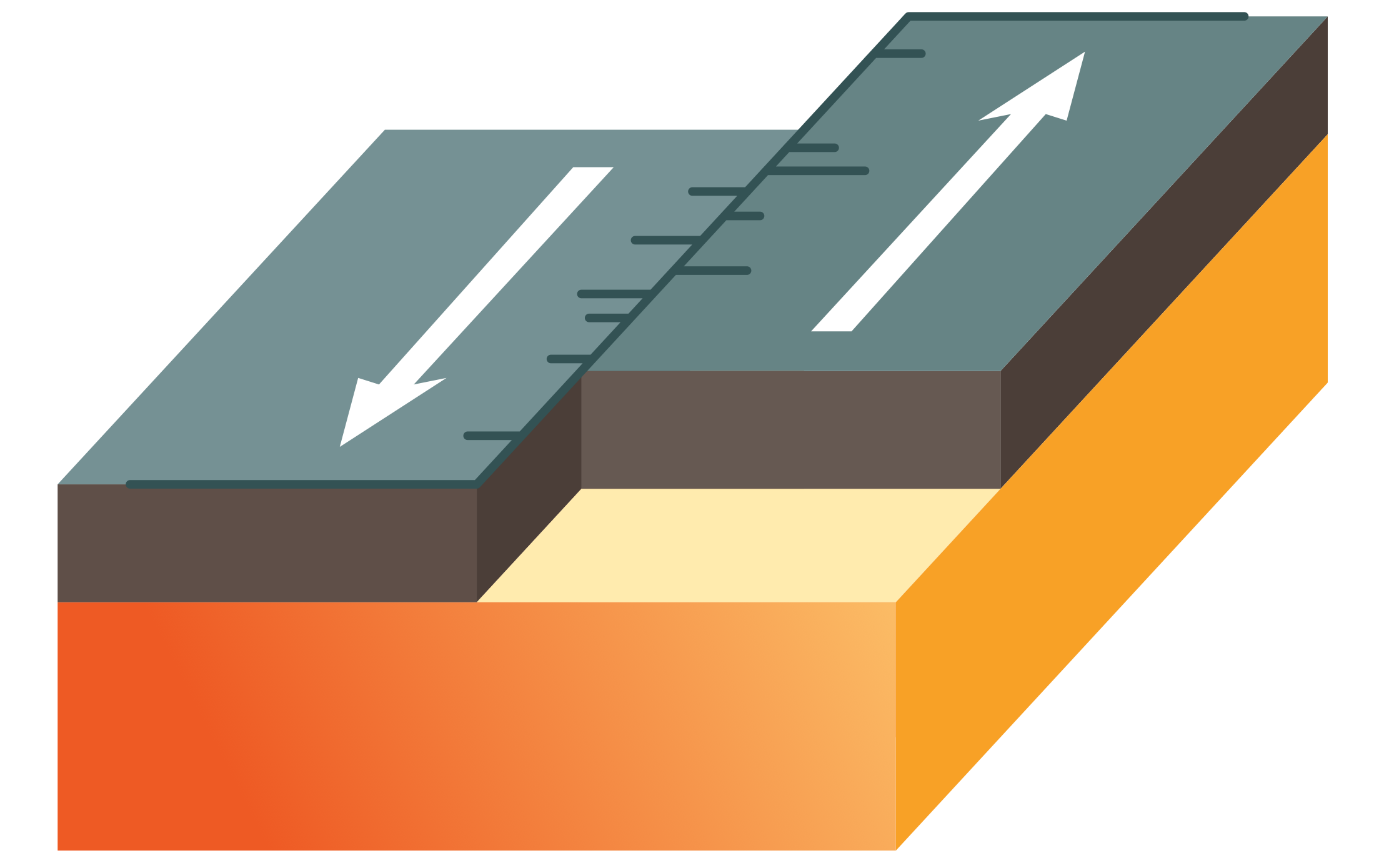
What is this plate boundary?
A conservative plate boundary
Explain the steps at a destructive plate boundary (O→←D)
The oceanic plate and the continental plate move towards one another
The Oceanic Plate subducts as it is denser
The Oceanic Plate melts to form magma
The magma escapes through weaknesses in the rock
This forms a composite volcano
What is a collision Margin?
A Plate Boundary where two continental plates collide forming fold mountains.
Describe the steps at a constructive plate boundary
Two plates move apart from one another
Magma from the mantle rises up
This causes a shield volcano
Describe the steps at a conservative plate boundary
Two plates move past each other, or are side by side at different speeds
As they move, friction occurs and plates become stuck.
Pressure builds as the plates still try to move
As the pressure is released huge amounts of energy are released through seismic waves.
This is called an earthquake
True or False: Earthquakes can occur at all plate boundaries
True
Which plate boundaries form volcanoes?
Constructive and Destructive Plate Boundaries.
What are our two case studies for Tectonic Hazards? (This may vary from school to school)
Chile and Nepal
Give two ways that volcanoes can be monitored (there are more)
Remote Sensing and Hydrology
How does Remote Sensing work? (Think volcanoes!)
Satellites detect heat and changes to the volcano shape
How does Hydrology work? (Think Volcanoes!)
Scientists measure the gases dissolved in the water to detect eruptions
True or False: Earthquakes often occur with lots of warning
False
How can volcanoes be predicted?
Through scientific monitoring
How can earthquakes be predicted?
They can’t, but we identify areas at greatest risk.
How can we prepare for volcanoes?
Use earth embankments and explosives to divert lava away from property, but otherwise, not a lot.
Give 3 ways we can prepare for earthquakes
Constructing infrastructure that is earthquake resistant, open areas for evacuation and tsunami walls
How can we plan for volcanoes?
Hazard maps and evacuation routes
How can we plan for earthquakes?
Maps to identify areas that are at most risk of damage.
What are the three E’s for planning for any Natural Hazard?
Emergency kits, Education and an evacuation Plan
What is global atmospheric circulation?
The overall circulation of the earth formed by a number of cells (circular air movements)
What is a high pressure system?
A whirling mass of sinking cool, dry air.
What type of weather does high pressure bring?
Happy weather (sunny skies and light winds)
What is a low pressure system?
A whirling mass of rising warm, moist air.
What type of weather does low pressure bring?
Lousy Weather (stormy weather and strong winds)
What are the types of cells at the GAC Model?
Hadley, Ferrel and Polar
Wind spirals ______ of a high pressure centre in a _______ rotation in the Northern Hemisphere
Out, clockwise
Wind spirals _____ a low pressure centre in a ______ rotation in the northern hemisphere
Into, anti-clockwise
‘Winds on the ground are distorted by the earth’s rotation’ What is this known as?
The Coriolis Effect
Why are surface winds important in the GAC model?
They help transfer heat and moisture from one place to another.
Where are tropical storms generally located?
Above and below the equator in between the tropics of cancer and Capricorn
What ocean has Hurricanes specifically?
The Atlantic Ocean
What ocean has Cyclones specifically?
The Indian Ocean
What ocean has Typhoons specifically?
Pacific Ocean
What is the low pressure at the equator known as?
Equatorial low
The path of a tropical storm corresponds with what?
The deflected air due to the Coriolis effect
What are the four key ingredients of a tropical storm?
A cluster of thunderstorms
Warm water of 27 degrees +
Sea depth of 60-70m
Light wind speeds
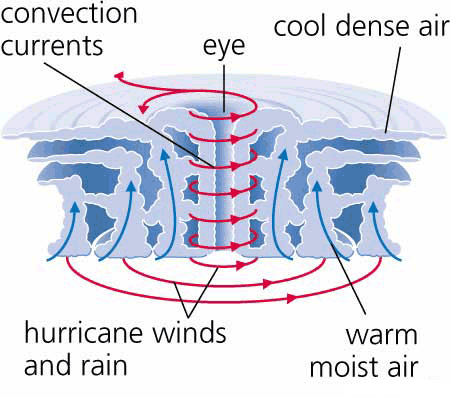
List the steps of a tropical storm forming
Once the water reaches 27 degrees, the air above the ocean is heated, and the air rises quickly, causing an area of low pressure.
This low pressure draws more warm, moist air up causing strong winds.
Large cumulonimbus clouds form as the warm rising air cools and condenses
This forms the eye wall, where there is heavy rainfall
In the eye, cold air sinks, causing calm and dry conditions.
Name the two main features of tropical storms
The eye and the eye wall.
Climate change can cause an increase in ____ _____ and an increase in the _________ of the sea.
Sea Level, Temperature
True or False: Climate change could cause tropical storms to become more frequent.
False
True or False: Climate change may increase the distribution of Tropical Storms, affecting places outside of the tropics.
True
Why might tropical storms become more intense as a result of climate change?
As warmer seas mean more energy, increasing the intensity.
What is our Case Study for Tropical Storms (This may vary school by school)
Typhoon Haiyan
Give two ways that Tropical Storms can be monitored?
Hurricane Hunters and Satellites
Give three ways that Tropical Storms can be predicted
Supercomputers, Cones and communication between countries.
How can we protect from Tropical Storms?
Building design and adaption and storm surge defences
State the 5 types of weather hazard that the UK can experience.
Thunderstorms, prolonged rainfall, drought & extreme heat, heavy snow & extreme cold and strong winds
What is our case study for extreme weather events in the UK? (This can vary from school to school)
Somerset Level Floods
What is the highest temperature recorded in the UK?
40.3 degrees Celsius
Which two storms (think 2020) were within a week apart?
Storm Dennis and Storm Ciara
Sea levels have _______ since last century
Doubled
Compared to pre-industrial times, how much has the temperature risen by in the UK?
1.2 degrees Celsius
Give 6 pieces of evidence of climate change
Shrinking glaciers, melting ice, rising sea levels, seasonal changes, more atmospheric hazards and temperature increase
Give 3 natural factors that could potentially cause climate change
The Sun Spot theory
Orbital changes
Eruption Theory
What is the sunspot theory suggesting?
That solar energy is linked to the number of sunspots present
What are sunspots?
Dark spots on the surface of the sun.
The _______ sunspots the more heat the sun gives off
More
Give a piece of evidence for the sunspot theory
There were very few sunspots between 1645-1715 when the ‘Little Ice Age’ occurred
What are the three distinct cycles relating to Orbital Change which affect the world’s climate naturally?
Eccentricity, Axial Tilt and Precession
How can violent volcanic eruptions reduce temperatures on Earth?
Volcanic ash is released into the atmosphere, blocking out the sun temporarily.
What is the name of the effect that humans have enhanced which contributes to global warming?
The Greenhouse Effect
Give three human causes of climate change
Fossil Fuels, Deforestation and Agriculture
Give three greenhouse gases
Carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide
Why is the use of fossil fuels damaging?
As burning them releases carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere.
Why is deforestation damaging?
As forests, especially the TRF store huge amounts of CO2, which when burnt or logged is released back into the atmosphere, accelerating the rate of climate change.
Why is agriculture a contributing factor to climate change?
Both the production of pesticides/fertiliser and the transportation uses fossil fuels. Forest is also cleared for use as farm land.
Give 2 Positives of climate change in the UK
Increased tourism in coastal areas and a larger variety of fruits and staples can be grown in the South of the UK
Give 2 negatives of climate change in the UK
Increase in droughts and loss of tourism in Northern Scotland due to loss of snow.
Give a ‘positive’ of climate change in the Maldives
Increased tourism due to knowledge of disappearance.
Give a negative of climate change in the Maldives
Coral reefs bleached dye to warmer seas and Tidal surges cause flooding daily.
Define mitigation
Action taken to reduce the causes
Define adaption
Resounding to the impacts by making changes to the environment or human actions.
What are the 4 ways that we can manage climate change through mitigation?
Alternative energy production, carbon capture, planting trees and international agreements
Why are renewable resources such as nuclear power, solar or wind more sustainable than fossil fuel usage?
As they do not emit large amounts of CO2
Why is planting trees a potentially effective way to reduce our impact on climate change?
As they act as carbon sinks due to their process of photosynthesis. Furthermore, they release moisture into the atmosphere which has a cooling effect.
What was the Paris Agreement of 2015?
A universal and binding global climate deal adopted by 195 countries.
Give two ways in which agriculture can adapt to climate change.
Drought resistant plants and irrigation systems.
Give two ways that we can adapt to rising sea levels.
The use of sea defences to prevent erosion and houses in vulnerable areas built on stilts to protect them.
Give two ways that we can adapt to a shortage of water supply.
Water transfer schemes and desalination plants.