Respiratory Anatomy
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
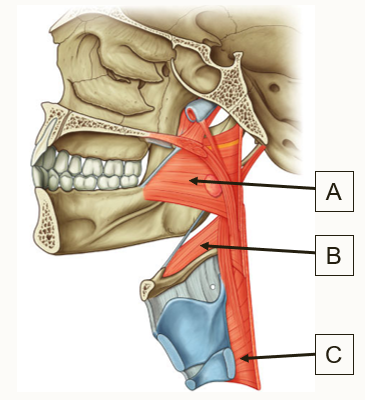
Label the muscles of the pharynx in the diagram and state their nerve supply
A: Superior constrictor
B: Middle constrictor
C: Inferior constrictor
Vagus nerve
What are some signs of loss of motor or sensory supply to the pharynx? (give two)
Diminished gag reflex
Poor swallowing reflex
Dysphagia
Aspiration pneumonia
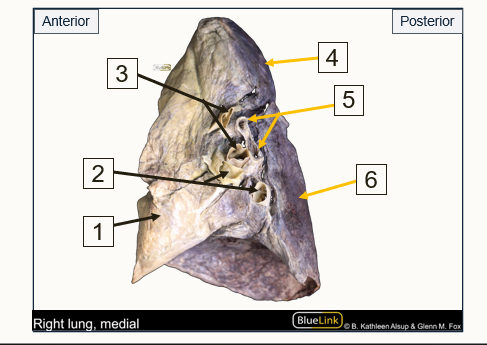
Label the structures indicated by the arrows
Middle Lobe
Pulmonary veins
Pulmonary arteries
Superior lobe
Bronchi
Inferior lobe
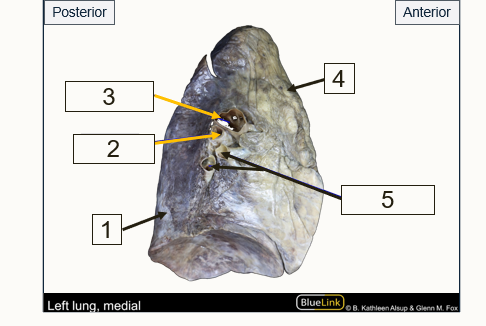
Label the structures indicated by the arrows
Inferior lobe
Bronchus
Pulmonary artery
Superior lobe
Pulmonary veins
How many bronchopulmonary segments are found in each lung?
Right: 10 Left: 9
What is the significance of the bronchopulmonary segments (3 points)
Functionally independent units.
Own tertiary/segmental bronchus, arteries and veins.
Damaged segments can be resected without affecting other segments. (localized infections)
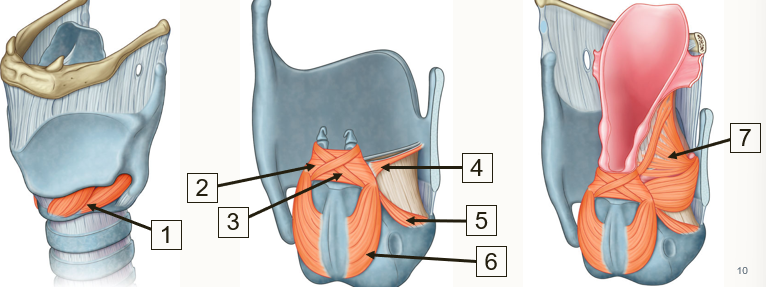
Label the laryngeal muscles in the diagrams below
Cricothyroid
Transverse arytenoids
oblique arytenoids
Vocalis
Lateral circo-arytenoids
Posterior circo-arytenoids
Thyro-arytenoids
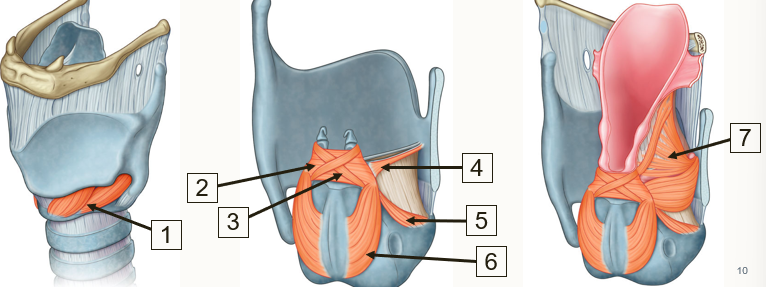
Which of these muscles would increase risk of asphyxiation if paralyzed?
Posterior cricoarytenoids
Why would a tumor near the hilum of the left lung cause a change in the characteristics of the voice?
RLN supplies most intrinsic laryngeal muscles
Branches on the left of the vagus nerve - near the hilum of the lung.
Tumor would compress the nerve.
Cause paralysis to laryngeal muscles on the left.
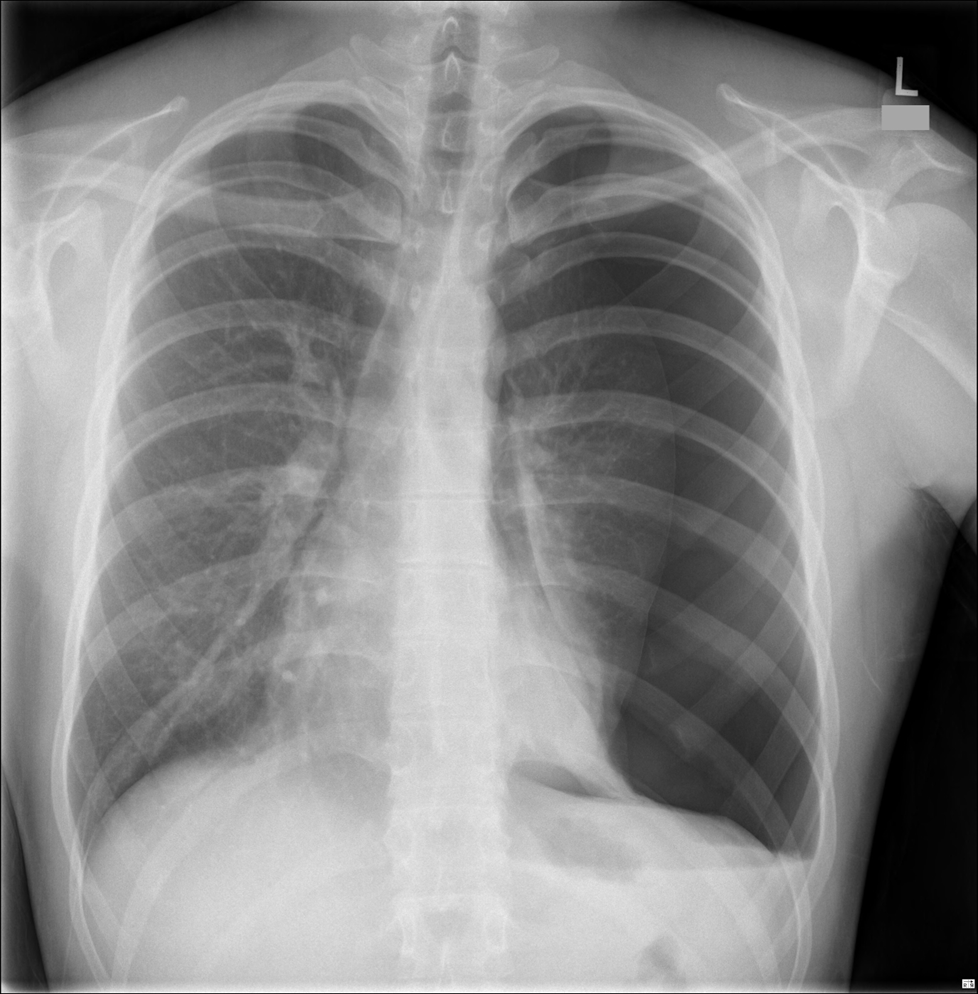
What condition does this X-ray indicate
Deviated trachea
Tension pneumothorax
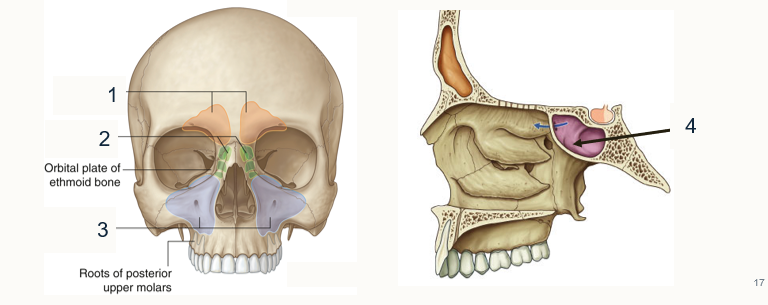
Label the paranasal sinuses
Frontal
Ethmoid
Orbital
Sphenoidal sinus
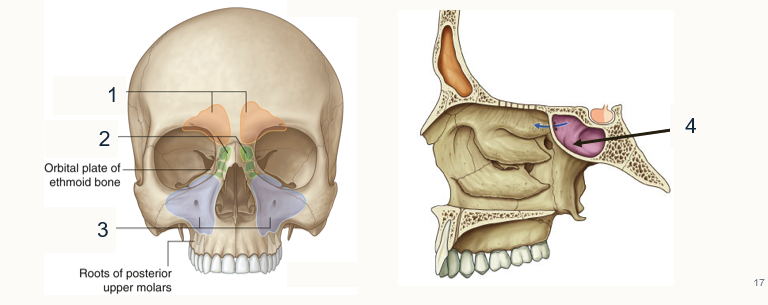
State their drainage sites
Frontal and ethmoidal → middle hiatus
Ethmoidal → Superior meatus
Sphenoidal → spheno-ethmoidal recess
Which of the paranasal sinuses is at highest risk of developing an infection?
The maxillary since it drains against gravity
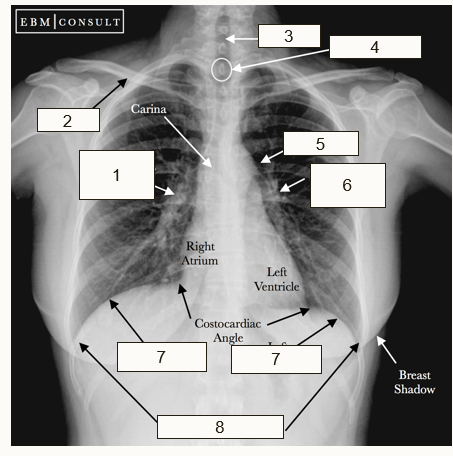
Identify the structures on the X-RAY
Right hilum and pulmonary artery
Clavicle
Trachea
Spinous process
Aortic Knob
Left Hilum and Pulmonary artery
Diaphragm
Costophrenic angle
What are the extent and components of the upper respiratory tract?
Extends from the nose and nasal passages down to the larynx.
Its components include the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx, and larynx.
What are functions of paranasal air sinuses?
Reduce skull weight
Humidify air
Add resonance to the voice
Communicate with the nasal cavity by ducts
State the sensory nerve supply of the paranasal sinuses
Maxillary → maxillary nerve
Frontal → Ophthalmic division nerve
Ethmoid + spehnoidal → Maxillary + ophthalmic
What are the boundaries of the superior thoracic aperture / thoracic inlet
Anteriorly: Superior border of the manubrium
Laterally: First ribs and their costal cartilages
Posteriorly: Superior border of the T1 vertebra
What are the openings and innervation of the diaphragm?
Caval hiatus (T8)
Esophageal hiatus (T10)
Aortic Hiatus (T12)
Innervated by the phrenic nerve
Name the intercostal muscles and their actions.
External Intercostal: Elevate ribs during forced inspiration
Internal intercostal: Depress ribs during forced expiration
Innermost intercostals: Aid in depression during forced expiration
What are the parts and nerve supply of parietal pleura?
Costal, diaphragmatic, mediastinal, cervical
Never supply from intercostal nerves and phrenic nerve
What do you mean by pleural effusion? Where and how should a chest drain be inserted to treat pleural effusion?
Pleural effusion: Collection of fluid in the pleural cavity.
Chest drain: Mid-axillary line at the 5th or 6th intercostal space.
Pneumothorax → drain points upwards
Pleural effusion → drain points downwards
What is costodiaphragmatic recess? How is it clinically important?
Potential space in the pleural cavity.
Between the costal pleura and the diaphragmatic pleura.
Where fluid tends to collect due to gravity.
Describe vocal fremitus and its implications.
Palpable vibration of the chest wall produced by speech or other vocal sounds.
Increased fremitus suggests consolidation in the underlying lung tissue.
Decreased fremitus suggests pleural effusion, pneumothorax or bronchial obstruction.