lec 8 - solute transport
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
membrane transport overview
transport of solutes can be classified by the type of energy used or the solutes pathway across the plasma membrane
pasisve transport moves solutes down a gradient - potential energy from concentration or electrochemical gradients
active transport moves solutes up a gradient - using ATP either directly or indirectly
lipophobic molecules (e.g. ions) require transmembrane proteins to cross the phospholipid bilayer
diffusion
spontaneous movement of individual molecules from a region of hgih cncentration to a region of low concentration
flux
describes the magnitude and direction of solute movement
defined as the diffusion rate per unit surface area of the membrane
proportional to concentration gradient x permeability coefficient
fluxes at equilibrium
unidirectional fluxes still occur but they are equal and opposite so cancel out and net flux at equilibrium is 0
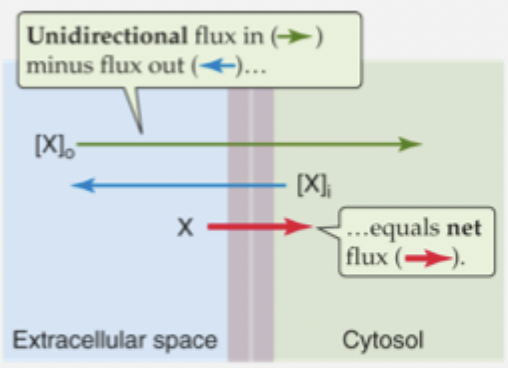
flux equation
Jx = Px ([X]i-[X]0)
linear relationship - increase in concentration gradient = increase in flux
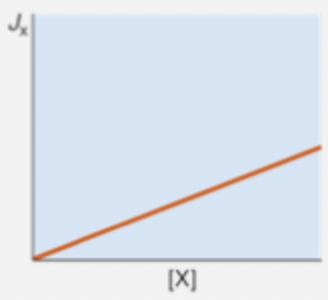
membrane permeability coefficient
represents how easily a solute crosses a membrane
Px is proportional to lipid solubility/molecular size
aquaporins
non-gated tunnel, which allow water molecules to move down as osmotic gradient
highly selective for water over ions
selectivity filter formed by conserved asparagine residues which prevents ion passage
arrange water molecules one by one through a narrow pore
ion channels
electrochemical gradient dependant
channels can. be open to ECF and ICF at the same time
ion channels are not continuously open (gated) - open wither spontaneously or in response to specific stimulus
specificity is variable and based on channel type
can be regulated by changing open probability pr the numbver of channels in the membrane
open probability
how long a channel is open for
types of important ion channels in epithelial physiology
ENaCs - sodium channels found in tight absorptive epithelium
CFTR - apical membrane channel that transports both Cl- and HCO3-
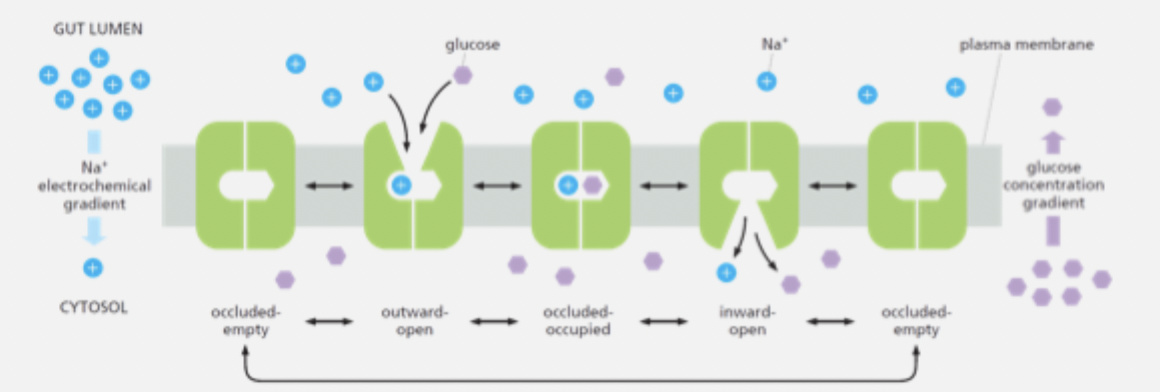
carriers (uniporters)
facilitated diffusion - transports solutes (e.g. sugars, amino acids) down a concentration gradient
binding of the solute triggers a conformational change in the carrier protein
carriers never forma. continuous connection between the intracellular and extracellular fluid
symporters (cotransporters)
secondary active transport - indirectly use energy by moving one solute (eg Na+) down its electrochemical gradient to move another solute up its electrocheical gradient
moves two or more solutes in the same direction
exchangers (antiporters)
indirectly use energy by moving one solute down its electrochrmical gradient to move another solute in the opposite direction
generally exchange cations for cations or anions for anions
essential for acid base balanc and pH refulation
primary active transporters (pumps)
use ATP hydrolysis to move ions against electrochrical gradient - undergoes a series of conformational changes
in epithelia the Na+/K+ATPase is essential for vectorial transport
maintains electrohrmical gradents to drive transport
inhibiting transporters and channels
ion channels and transporters can be blocked or inhibited by different pharmacological compounds
used in the lab to study a specific channel or transporter
also used to clinically treat different conditions - e.g. type II diabetes (SGLT2 inhibitors) or hypertension (thiazides inhibit Na+/Cl- symporters)
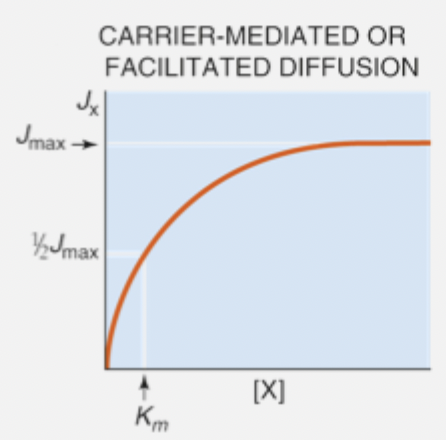
transporter saturation
transporters undergo binding, conformational change and release cycle, making them vulnerable to saturation
transport flux increases with solute concentration until it reaces a maximum rate (Jmax) when all carriers/transporters are occupied
solute competition
transporters have veraible affinities for different solutes
a transporter may move several structurally similar solutes, but those solutes compete with one another for transporter binding sites