Pregnancy and Human Development
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 28
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Fertilization
The process in sexual reproduction that involves the union of a sperm and an egg to form a diploid zygote
Oocyte Fertilization Time Window
Only viable for 24 hours (at most) after ovulation
Sperm Fertilization Window
Can survive at most 5 days in female reproductive tract
Sperm Capacitation
Because sperm are incapable of fertilizing the oocyte immediately after entering vagina, it must have its motility enhanced and have a weakened cell membrane
Rupture of cell membrane release chromosomes
Speeds up fertilization
Corona Radiata
Outer layer of the protective structures for an oocyte
Protects and nourishes the oocyte after it has been ovulated
Zona Pellucida
Inner layer of the protective structures for an oocyte
Protects secondary oocyte and is necessary for fertilization to occur
Acrosomal Reaction
At the zona pellucida, the sperms’ acrosomes release digestive enzymes to weaken the zona pellucida for fertilization to occur
Sperm bind to zona pellucida → Ca2+ levels rise in sperm
Polyspermy
Potential problem where the entry of more than one sperm cell into the oocyte
You don’t want extra chromosomes
Oocyte Membrane Blocks
Sperm-binding receptors are shed from oocyte surface
Sperm unable to bind oocyte surface and fertilize oocyte
Cortical Reaction
Oocyte releases Ca2+, which causes release of zinc
Causes whatever is left of the zona pellucida to harden
Completion of meiosis II
Male Pronucleus
As the sperm nucleus travels towards the oocyte nucleus, it swells in size to form this
Meiosis II Completion
Forms 2nd polar body and mature ovum
Isn’t done until sperm contents are inside the egg
Female Pronucleus
After meiosis II, this haploid nucleus forms, contributing to the zygote during fertilization
Monozygotic (Identical) Twins
Occurs when a single oocyte is fertilized and splits into 2 identical embryos (reason is unknown)
Usually share a placenta → can lead to competition between the two fetuses
Dizygotic (Fraternal) Twins
Occurs when 2 oocytes are ovulated and both are fertilized
Have their own placenta
Zygote
A diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes
“Single-celled embryo”
Divides mitotically at fertilization
Cleavage
Rapid divisions of the zygote
Creates multicellular organism
Blastomere Cells
Individual cells that result from the early cell divisions (cleavage) of a zygote
Two get produced from first mitotic division, which undergo their own mitotic divisions
Morula
Solid ball of cells that develops from a zygote after 72 hours after fertilization
Contains ~16 cells
Embryo
Stage of development form soon after the fertilization of the ovum to week 8 of development
No longer single-celled
Fetus
Stage of development from week 8 to birth
Infant
After birth has occurred
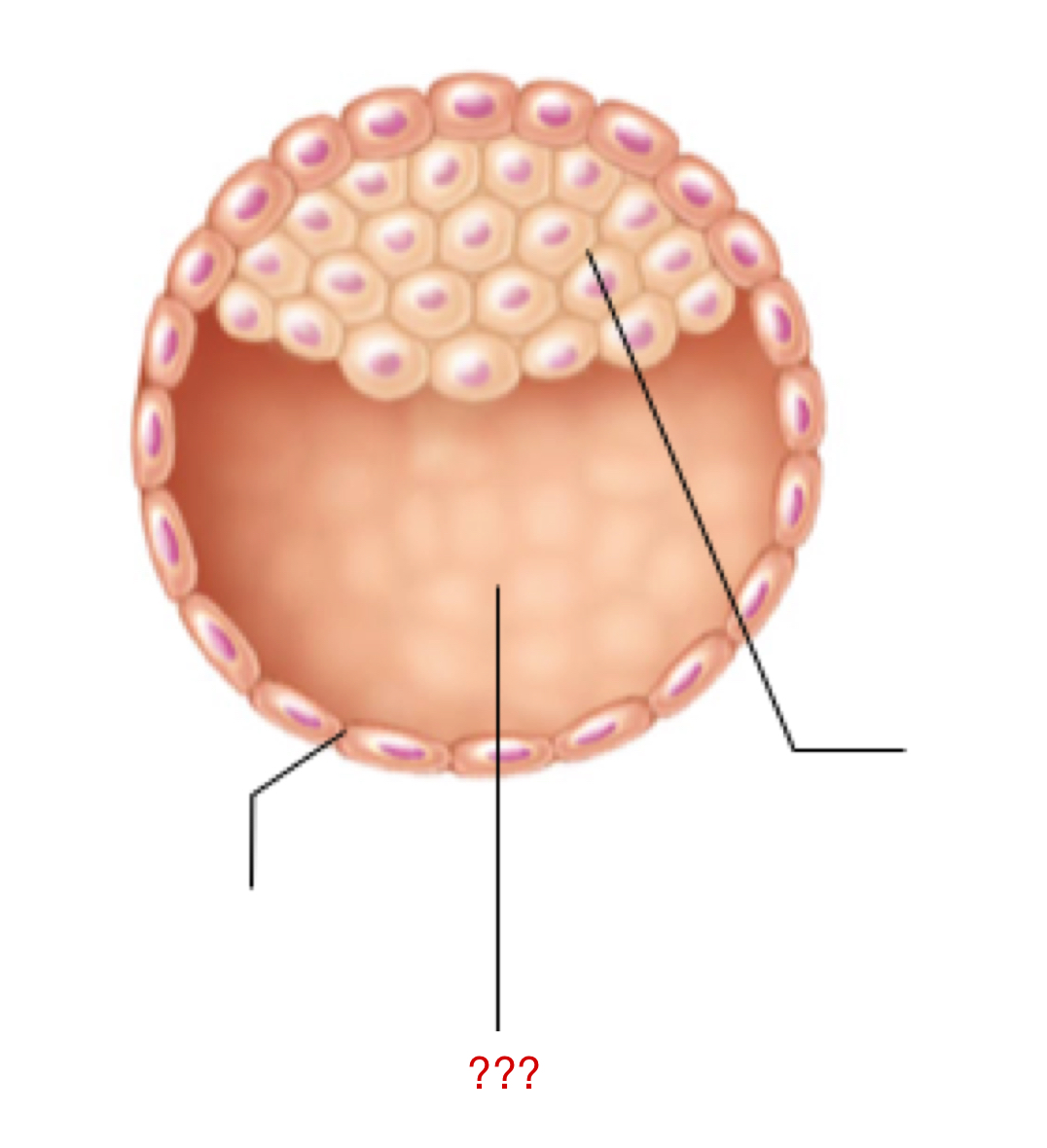
Blastocyst
Cluster of dividing cells made by a zygote
Morula cells continue to divide into this
Has two individual sets of cells that have their own form and function
Trophoblast
External layer of the blastocyst that aids in:
Embryo implantation
Chorion formation/function
Immunosuppressive effects
Ensure that the developing embryo is protected and not destroyed by the parent’s immune system
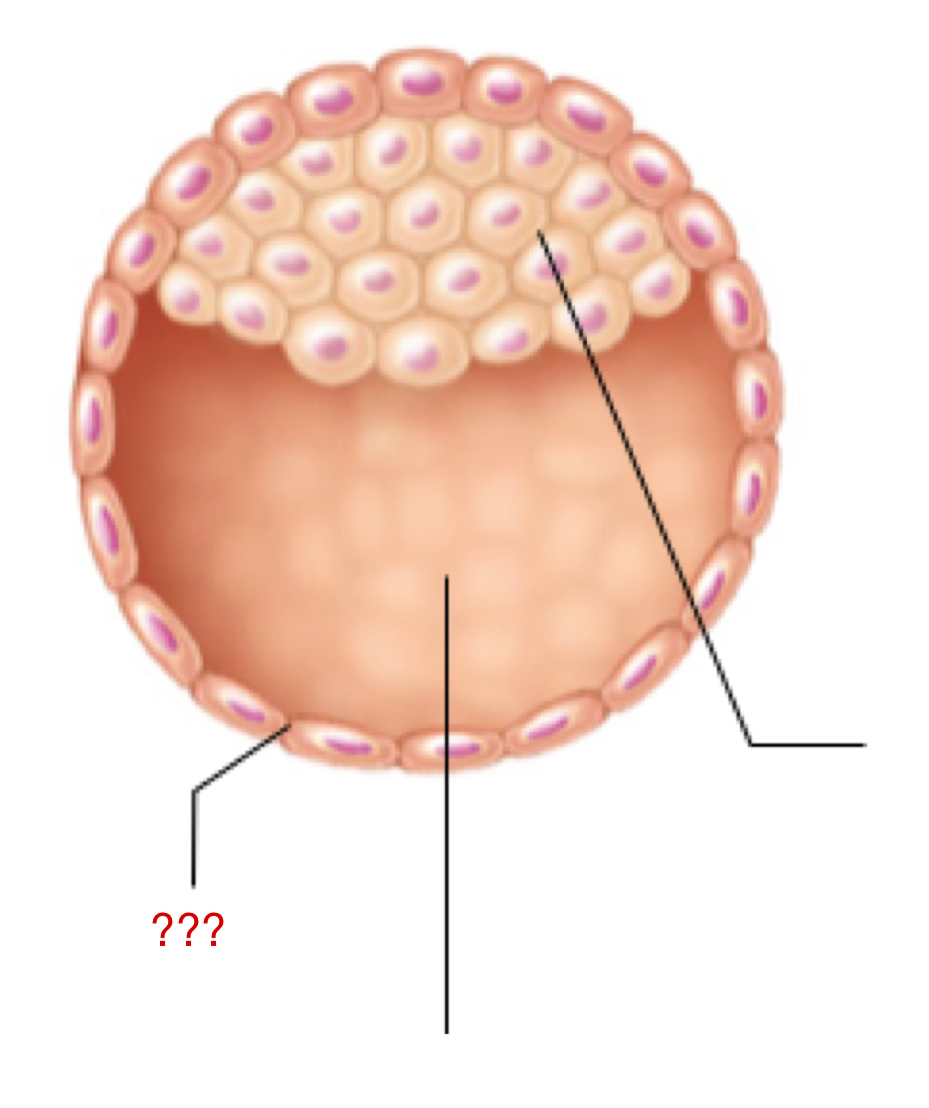
Embryoblast
Internal layer of the blastocyst that eventually forms the embryo proper and extra embryonic membranes
Inner cell mass
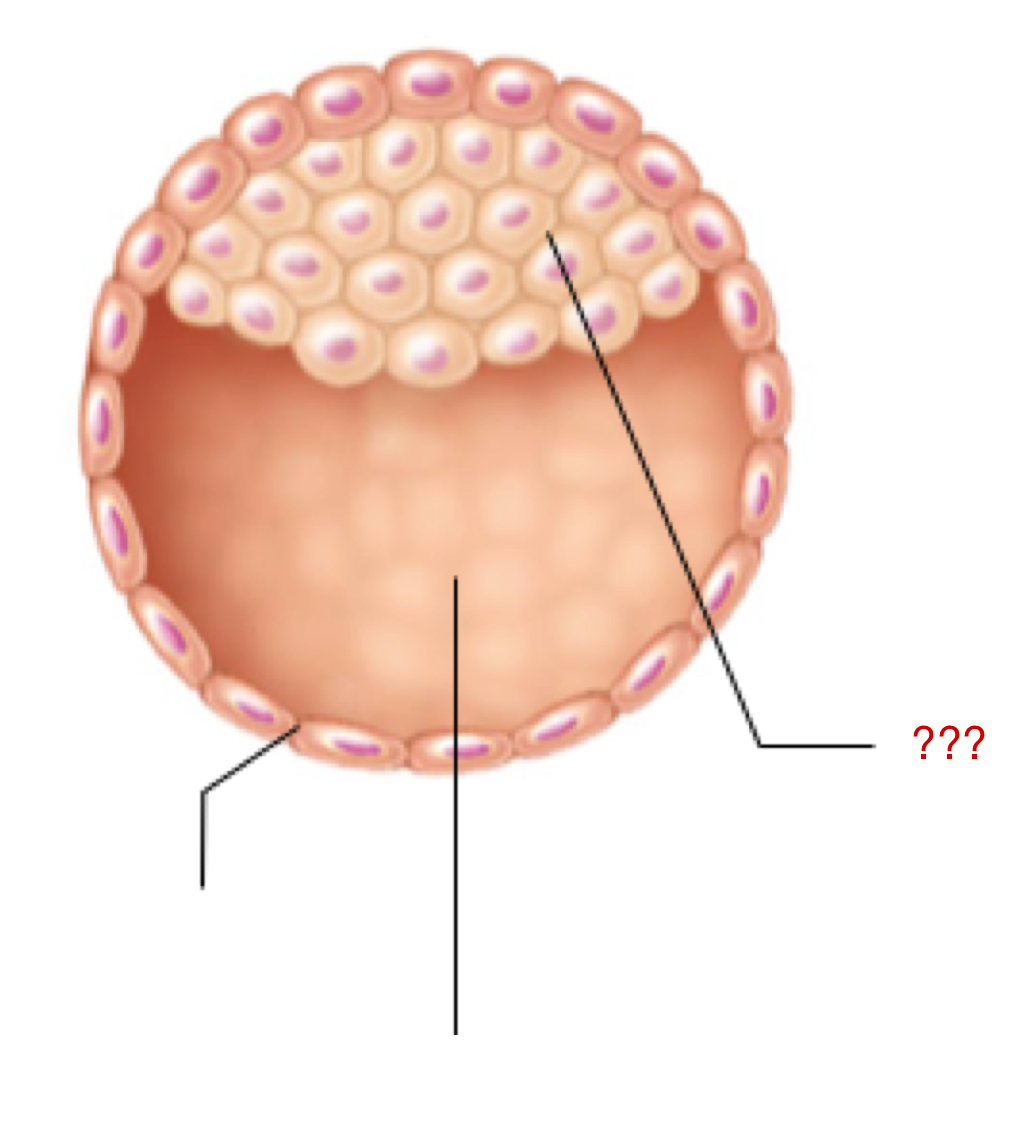
Blastocyst Cavity
Space for all of the inner cell mass to continue to proliferate/grow
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
Once implantation is complete, the embryo releases this to maintain the corpus luteum for ~12 weeks (first trimester)
Suppresses female immune system to prevent damage to the embryo
Placenta
A temporary organ originating from embryonic and maternal tissues
Major exchange organ between parent and fetus
Maintains pregnancy, exchange respiratory gases, provide nutrients to embryo/fetus, dispose of waste, etc.
Chorion
Outermost extraembryonic membrane that surrounds the embryo of a fetus
Embryo contribution to the formation of the placenta
Allows exchange of gases, nutrients, and wastes
Encloses all other extraembryonic membranes
Chorionic Villi
Finger-like projections of the outermost membrane surrounding a developing fetus → important for gas exchange and diffusion
Inside contains fetal blood, outside is bathed in maternal blood
Umbilical Vessels
The blood vessels that extend from chorionic villi form these
Serve as the life-support system for the developing fetus, connecting it to the placenta
Blood transportation
Lacunae
Blood-filled cavity or space that the functional layer of endometrium develops
Parental contribution to the placenta
Decidua Basalis
Endometrium that lies underneath the embryo becomes this, and forms the placenta with chorionic villi
Most parental contribution to the placenta
Decidua Capsularis
Formed from the surrounding endometrium of the uterine cavity face of embryo
Expands the accommodate growing fetus
Chorionic villi will degenerate as pregnancy progresses here
Extraembryonic Membranes
Membranes formed during the first few weeks of development that support and nourish developing embryo/fetus during gestation
Amnion
Layer of the extraembryonic membrane that extends AROUND the embryo
Amniotic Fluid
Fills the layer that extends around the embryo
Provides buoyancy and protection
Maintains consistent temperature
Prevents developing parts of embryo from sticking together/fusing
Allows movement of embryo/fetus
Yolk Sac
Sac-like structure of the extraembryonic membranes that spermatogonia arise from
Is a nutrient source in the early stages, but not much later on
Eventually forms digestive tube, earliest blood cells, and precursor gametes
Allantois
Extraembryonic membrane that helps form the umbilical cord alter in fetal development
Allows for gas exchange, waste disposal, and nutrient exchange
Gastrulation
Early developmental process where the blastocyst is reorganized into a 3-layered embryo
Gives rise to every single part that we have
Primitive Streak
Process of gastrulation begins with this
Groove that will eventually form the long axis of the embryo
Endoderm
Formed by cells migrating and entering the primitive streak
Inferior layer — forms the epithelial lining of GI tract
Respiratory tract forms outpocketings, in which other glands are formed
Opening of opposite ends form the mouth and the anus
Mesoderm
Cells that enter the primitive streak that do not form the endoderm, but get pushed up between upper and lower layers—“middle” layer
Forms somites for the notochord
Remaining forms kidneys and gonads, connective tissues of limbs, heart, and blood vessels, dermis of ventral body region, etc.
Notochord
Formed from the mesodermal cells immediately beneath the primitive streak
First axial support of the embryo (does NOT form the spinal chord or vertebral column)
Helps keep cells in place so embryo doesn’t develop crookedly
Ectoderm
Cells that remain at the surface form this embryo layer
Where neurulation takes place
Remaining forms the epidermis
Organogenesis
Formation of body organs and organ systems
Begins with gastrulation
Cells in 3 primary germ layers will differentiate to form organs and organ systems
Neurulation
Formation of the brain and the spinal cord
Induced by chemicals released by notochord
Neural Tube
Formed as a result from neurulation, sits over the notochord
Develops into the central nervous system, formed during the first month of pregnancy
Anterior Neural Tube
Portion of the neural tube that becomes brain
Branches form the cranial nerves
By week 8 → cerebral hemispheres evident, brain waves can be recorded
Remaining Neural Tube
Portion of neural tube that becomes the spinal cord
Somites
Mesodermal blocks that hug the notochord on either side
Sclerotome
Functional portion of semite that produce vertebrae and rib at each associated levels
Dermatome
Functional portion of somites that forms the dermis in the dorsal part of body
Myotome
Functional portion of the somite that forms skeletal muscle of the neck, body trunk, and limbs
Most of the skeletal muscle tissue comes from here
Umbilical Veins
Blood vessels that carry OXYGENATED blood TO the fetus
Umbilical Arteries
Blood vessels that carry OXYGEN-POOR blood AWAY from fetus
Supply bladder and anchors bladder to the umbilicus
Vascular Shunts
Redistributes blood to parts of body that need it most
Mostly bypasses organs not yet used by developing fetus
Ductus Venosus
Vascular shunt that bypasses the liver
Parent’s liver does all the work for the fetus
Foramen Ovale
Vascular shunt that shunts blood from right atrium to the left atrium
Causes blood to bypass lungs (fetus doesn’t use lungs)
Ductus Arteriosus
Vascular shunt that shunts blood from pulmonary trunk to aorta
Causes blood to bypass lungs (fetus doesn’t use lungs)
Round Ligament
Umbilical vein remnant becomes this of the liver
Ligamentum Venosum
Ductus venous collapses and is converted into this → doesn’t have a function, but can be used as a market for important structures during surgery
Fossa Ovalis
Indentation in the right atrium → foramen ovale closes as pulmonary circulation becomes functional
Ligamentum Arteriosum
Ductus arteriosus constricts and closes off, forming this → doesn’t have a function, but is slightly supportive for the pulmonary artery and the aorta (helps hold in place, but not much support)
Relaxin
Hormone that causes the pubic symphysis to loosen up during pregnancy
Pelvis widens (usually permanent)
~28
Average amount of pounds one might gain during pregnancy
Dependent on weight at beginning of pregnancy
If you are lighter, you will need to gain more; if you are overweight, you will only need to gain slightly
~300
Amount of extra calories one will necessarily have to consume in order to maintain healthy pregnancy
Placental Growth Hormone
Hormone that replaces GH in pregnant women
Stimulates lipolysis and glucose production for growing fetus
Breaks down more adipose tissue than GH
Human Placental Lactogen (hPL)
Hormone that stimulates the maturation of breasts for lactation, promotes fetal growth, and is glucose-sparing
Tends to make parent’s body resistant to insulin → hyperglycemia
Parent’s body cells use less glucose and is saved for the fetus
Corticotropin-releasing Hormone (CRH)
Hormone that rises only towards the end of pregnancy
Helps during birth, leads to maturation of fetal organs
Physiological Changes of the GI System
Surge in hCG, estrogen, and progesterone can result in nausea/vomiting → morning sickness
Uterus invades abdomen and presses onto other organs → heartburn, constipation, etc.
Physiological Changes of the Urinary System
Increased metabolic rate, higher blood volume, and need to dispose of extra waste form fetus → more to expel
Uterus pushes on bladder → more frequency
Physiological Changes of the Respiratory System
Respiratory rate unaffected, but taking deeper breaths
Increase in tidal volume and decrease in residual volume (need more oxygen as you are breathing for two people)
Breathing can be difficult due to the uterus pushing onto the diaphragm
Physiological Changes of the Cardiovascular System
Total blood volume increases by AT LEAST 25% → blood pressure stays the same however (hormones stimulate vasodilation)
Uterus pushes on blood vessels which can block blood flow, forming varicose veins and edema
Varicose Veins
Gnarled, enlarged veins that are very obvious underneath the skin and are very dark in color, normally irreversible
Increased Synthesis of Prostaglandins
As a result of a surge in estrogen → thins and softens mucus, making the infant easier to pass through
Increase in Oxytocin & Prostaglandin Receptors
As a result of a surge in estrogen in myometrium → stimulates uterine contractions
Addition of more Actin, Myosin, and Other Contractile Elements
As a result of a surge in estrogen → generates stronger contractions
Oxytocin
Hormone that is released by the posterior pituitary gland of parent that stimulates uterine contractions
Stretching of cervix by the fetus’ head stimulates more of this to be released
Dilation Stage
Stage of labor that occurs from onset of labor until cervix is fully widened
~10 cm in diameter
Variable in time
Expulsion
Stage of labor that occurs from full dilation to delivery
Contractions occur every 2-3 minutes and last about 1 minute each
Basically, the removal of the infant
Crowning
Occurs when the largest portion of an infant’s head distends vulva
Part of expulsion
Vertex Position
The infant should be in this position, head first (widest part of the fetus)
Dilates the cervix for the rest of the body to pass easier, can suction mucus from oral/nasal passage for breathing to occur sooner
Breech Position
Infant is in a butt-first position
If too late to detect → c-section
If early to detect → doctors will physical move around the female’s abdomen to move around the baby’s position
Placental
Stage of later that occurs ~30 minutes after the delivery of the infant
Afterbirth
Stage where the parent delivers the placenta and all of its structures
Uterine contractions compress blood vessels and tear placenta from uterine wall → if not removed, major infection will occur as perceived as “foreign” by female immune system
Glandular Alveoli
Small, sac-like structures in lobules that produce milk during lactation
Only occurs when pregnant, when not pregnant the mammary glands are not functional
Prolactin
Hormone that is released due to a rise in levels of progesterone, hPL, and estrogens for a few weeks after birth
Slows down the release of estrogen, which slows down ovulation (making the person less likely to get pregnant for safety)
Colostrum
Delay in milk production → mammary glands secretes this product
Contains less lactose than milk, very little fat, but contains much more protein, minerals, vitamin A and some antibodies
Meconium
Built up epithelial cells and other structures → the waste in the digestive system that develops during fetal development
Breast milk serves as a natural laxative that can cleanse the infants GI tract