Muscular Stimulation PT 1
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
The human body is made of over ____ skeletal muscles
650
Skeletal muscles
only voluntary muscle in the body
allows us to actively control our body + interact with the world around us
Each muscle is surrounded by
the epimysium
Epimysium function
protect muscle from damage
isolates each muscle from each other allow for each muscle to be used individually
A muscle is made several large bundles called
fascicles
Why are large blood vessels in between fascicles?
to supply the fascicles with nutrient and oxygen, and nerves to stimulate the muscles
The fascicles are surrounded by a layer called
the perimysium
Each fascicle in the muscle is made of bundles of
individual muscle fibers/myofibers
Muscle fibers/myofibers are also known as
muscle cells
Muscle fibers, or myofibers are surrounded by tissue called
the endomysium
What does the endomysium contain?
extracellular fluid + nutrients to support the muscle fiber
Within each muscle fiber are dozens of smaller protein bundles called
myofibrils
Myofibrils are made of smaller
protein filaments that perform the moving action in muscle
How are muscle cells able to grow into a big muscle?
by merging with other skeletal muscle cells
(merging results in a single skeletal muscle “cell” having multiple nuclei and other cellular structures)
Myoblasts
undeveloped muscle cells
What happens to myoblasts once muscles have formed?
they turn into satellite cells
What happens when a muscle cell is slightly damaged and needs to be replaced?
leads to the release of cytokine proteins into surrounding area
muscle satellite cells are alerted by the cytokine proteins and mature into new muscle cells
Myofibrils are surrounded by
multiple nuclei
mitochondria
sarcoplasmic reticulum
sarcolemma
sarcoplasm
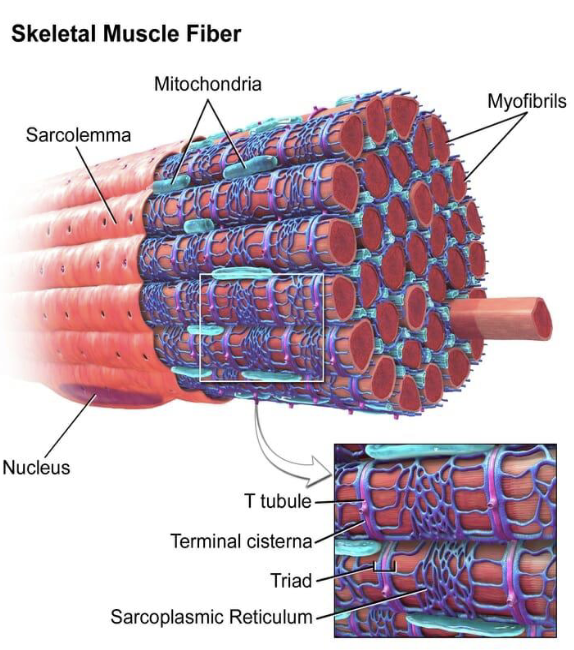
Why is there a lot of mitochondria in a muscle?
mitochondria produce ATP, so they help power the muscles
The sarcoplasmic reticulum stores…
Calcium ions
Sarcolemma
very porous to allow proteins and ions to flow quickly in and out of the cell when needed
T-Tubules
indentions in the sarcolemma that connect the sarcollema to the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Sarcoplasm
filled with lots of proteins and other nutrients needed to fuel cell
What are the repeating protein segments in myofibrils?
sarcomeres
The sarcomere is made of highly organized proteins called
myofilaments (make a strained pattern)
What are the 2 types of myofilaments?
1) Thin filaments
2) Thick filaments
How many proteins are thin filaments composed of?
three
How many proteins are thick filaments composed of?
one
Thin filament proteins (3)
Actin
Tropomyosin
Troponin
Actin
main core of the thin filament
Tropomyosin
thin protein
forms long strands around actin, helping keep its shape
Troponin
globular protein with 3 binding sites
T site
I site
C site
T site binds to
tropomyosin
I site binds to
actin
C site binds to
calcium ions
What happens when the muscle is at rest?
troponin is attached to the actin and tropomyosin with the C site opened and not bound
C site is waiting for calcium ions to bind to it
Thick filament
made of myosin proteins
A bands contain
both thick and thin filaments
I Bands contain
only thin filaments
M Band (line)
attachment point for thick filaments
Z band (disc)
ends of the sarcomere
Between the thin filaments is a protein called ____
Titin
helps prevent overstretching of sarcomere
Function of Titin in the sarcomere
hold thick filaments in place, keeping A band organized
folds and unfurled when muscle contracts and relaxes (helps muscles elasticity)
Myofibrils are anchored in the sarcolemma with proteins called
dystrophin
Dystrophin
crucial protein in muscle cells
prevents damage to muscle cells during contraction and relaxation
The heads of myosin in the thick filament are highly attracted to?
the actin in the thin filament
What is the position of troponin during the resting state of a muscle?
myosin heads are blocked by troponin, preventing the binding with actin