Judaism: Beliefs, History, and Practices for Society
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Ancient Israel
18th century BCE in Ancient Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq)
Torah
Contains stories, laws, and teachings that guide Jewish life and beliefs
The Ten Commandments
Provide guidance on ethical and moral behavior
Judaism
A monotheistic religion founded by Abraham
Abraham
The father and founder of Judaism
Moses
Freed the Israelite slaves from Egypt, received the Ten Commandments from God on Mount Sinai, and wrote the Torah
Rabbi
A spiritual leader and teacher
Babylonian Exile
Babylonian King Nebuchadnezzar II ordered the Jewish people to leave Jerusalem & live in captivity in Babylon, resulting in the destruction of their sacred temple & questioning of their status as God's 'chosen people'
Monotheism
Belief in one God (as seen in the first commandment)
Covenant
Agreement between God and Abraham telling the people to leave their homeland & go to the Holy Land
Observing the Sabbath (Shabbat)
Weekly day of rest and worship from Friday evening to Saturday evening
What group of people established a kingdom around 1030-1020 BCE?
The Israelites
What significant event happened to the Israelites in 722 BCE?
Their kingdom was conquered by the Assyrian empire.
What religion did the Israelites practice that became known as Judaism?
Judaism is the religion established by the Israelites.
What geographic region was Ancient Israel located in?
Ancient Israel was located in the Middle East.
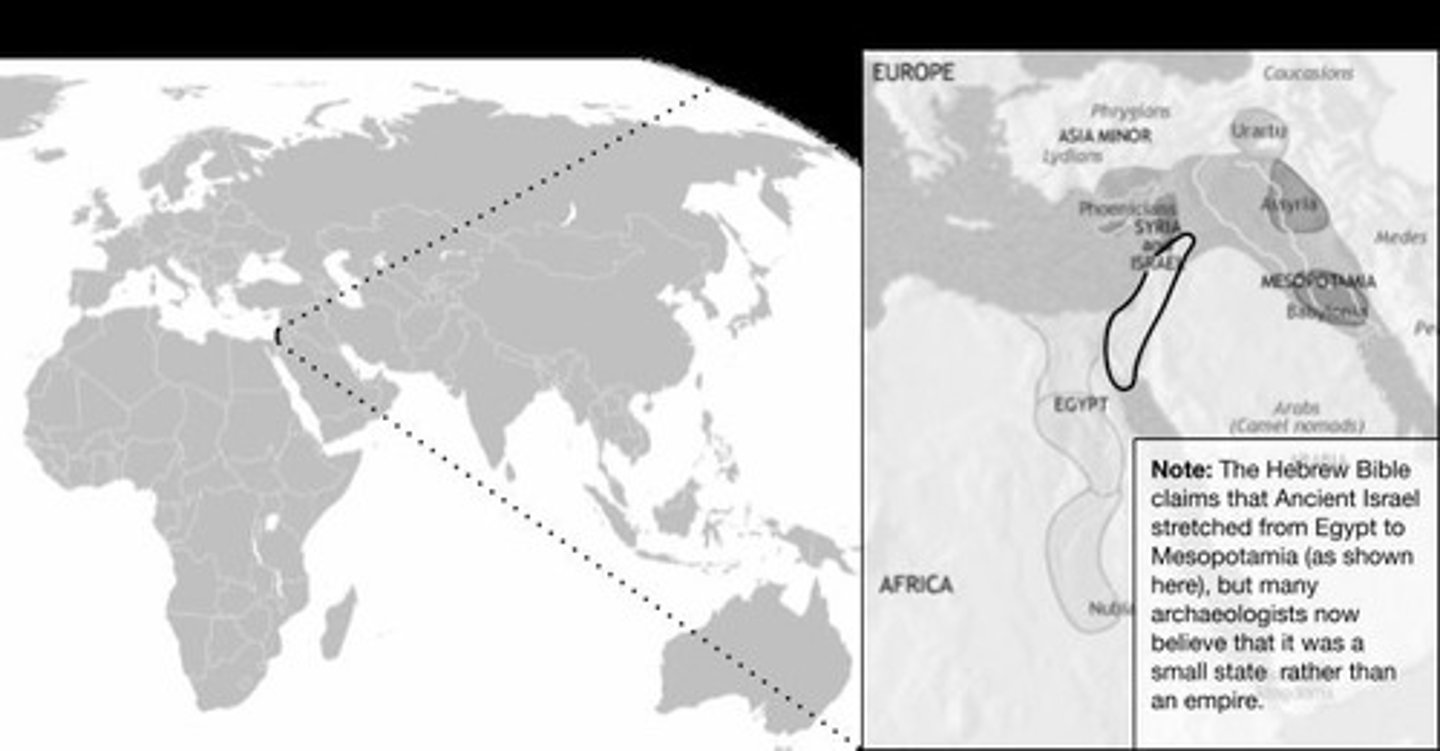
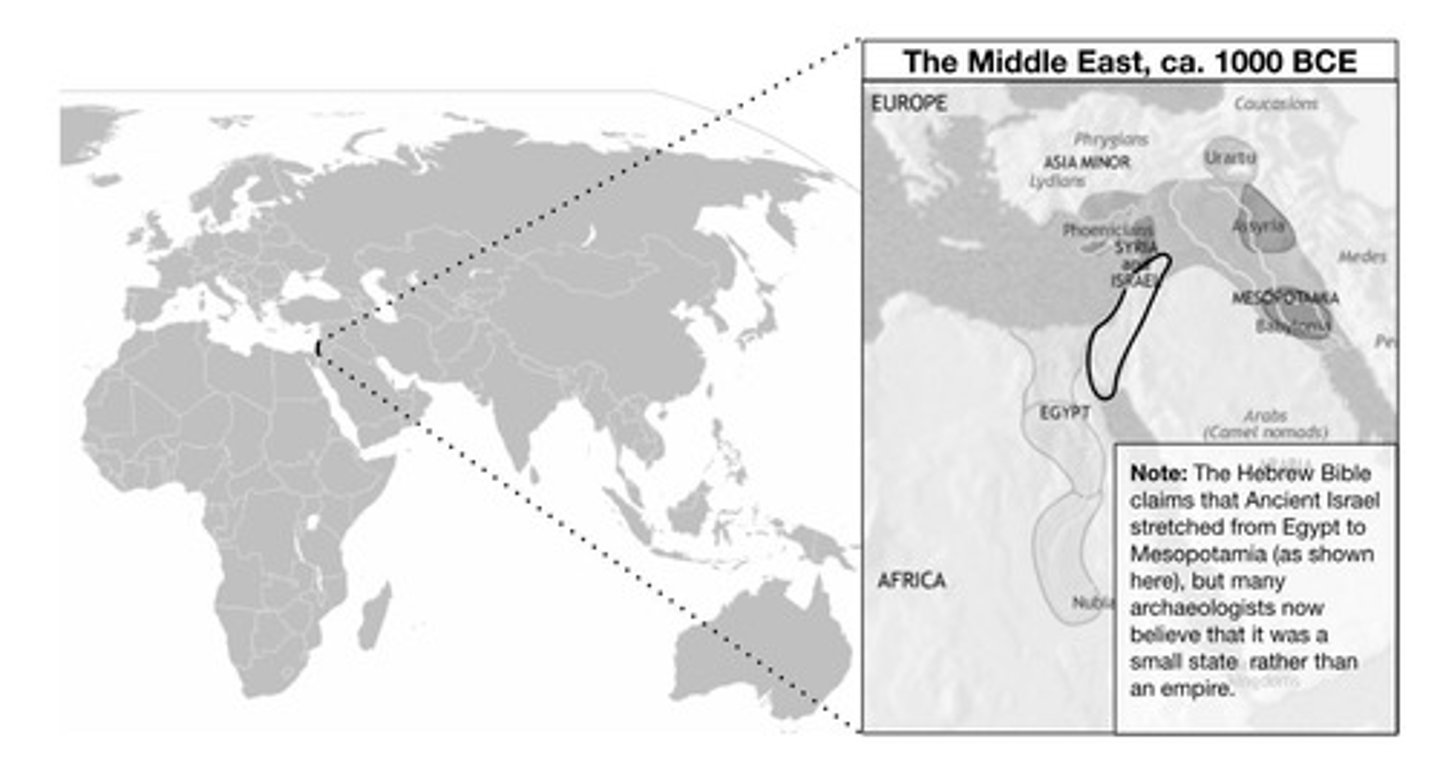
What are three geographic features that were located in Ancient Israel?
The answer may vary based on the video, but could include mountains, rivers, or deserts.
Why might the Ancient Israelites have settled in their geographic location?
They likely settled in this location due to favorable conditions for agriculture and trade, similar to other Early River Valley Civilizations.
What is the significance of the video 'Israel-Palestine for Critical Thinkers: #1 Ancient Roots'?
It provides insights into the historical context and geographic features of Ancient Israel.
What is one question you might have about the Ancient Israelites after watching the video?
Answers will vary based on individual curiosity.
What is one observation you might make about Ancient Israel from the video?
Answers will vary based on individual observations.
What is one thought you might have about who the Ancient Israelites were?
Answers will vary based on individual interpretations.
What two sources were used to create the map of Ancient Israel?
The answer will depend on the specific sources mentioned in the map note.
What different information might the sources provide about Ancient Israel?
They may provide varying details about the location, size, and significance of Ancient Israel.
What does it mean to 'Think Like a Geographer' in the context of Ancient Israel?
It involves analyzing the geographic context and its impact on the settlement and culture of the Ancient Israelites.
What was the duration of the Israelite kingdom before its conquest?
Approximately 100 years, from around 1030-1020 BCE to 722 BCE.
What is the AIM of the lesson on Judaism's historical and geographic context?
To understand the origins and significance of the Israelites and their geographic setting.
Judaism
A monotheistic religion that originated in South-west Asia, specifically in Ancient Canaan or modern-day Israel.
Monotheism
The belief in a single, all-powerful God.
The Covenant
An agreement made between God and the Jewish people, promising blessings and a nation for them.
The Ten Commandments
A set of biblical principles relating to ethics and worship, which play a fundamental role in Judaism.
Abraham
The father of Judaism, whose life story is told in the book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible.
Moses
A major figure in Judaism who freed the Israelite slaves from Egypt and received the Ten Commandments from God.

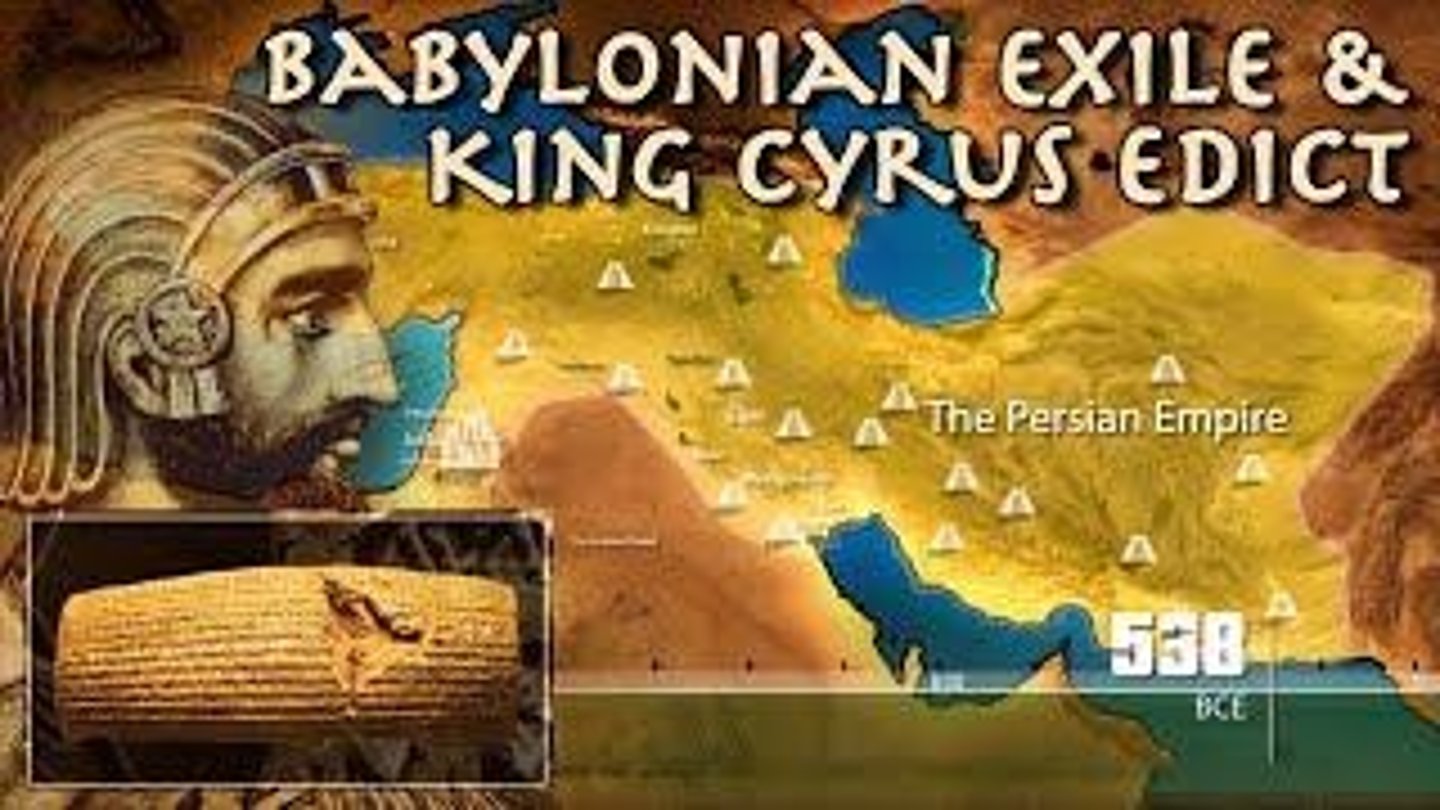
Babylonian Exile
The period from 597 to 539 BCE when Jewish people were held captive in Babylon after the conquest of the Kingdom of Judah.
Nebuchadnezzar II
The Babylonian King who ordered the upper class Jewish people to leave Jerusalem and live in captivity in Babylon.
Cyrus the Great
The Persian king who took over Babylon and allowed the Jews to return to Judah, ending the Babylonian Exile.
Scribes
People who copied religious documents and played an important role in compiling and revising historical writings and the Torah during the Babylonian Exile.
Torah
The central reference of the religious Judaic tradition, containing the laws and teachings of Judaism.

Hebrew Bible
The collection of sacred texts in Judaism, which includes the Torah and the book of Genesis.
Moral-Ethical Code of Conduct
The Ten Commandments, which guide Judeans to be honest and faithful people.
Impact of Judaism on Society
Judaism has had both positive effects, such as fostering honesty and loyalty, and negative effects, such as causing violence due to conflicts with polytheistic beliefs.
Religious Practices
Judaism includes practices such as commemorating the fall of Jerusalem with days of prayer and celebrating the Sabbath.
Fertile Crescent
The region in the Middle East where the Babylonian Empire was centered and where significant events in Jewish history took place.
Ancient Canaan
The historical region where Judaism originated, corresponding to modern-day Israel.
Polytheism
The belief in or worship of multiple gods, which was prevalent in the region where Judaism emerged.
Historical Context of Judaism
Judaism emerged in a time of conflict and change, particularly during the Babylonian Exile, which shaped its development as a religion.
Religious Documents
Texts that were copied and preserved by scribes, contributing to the formation of the Torah.
Days of Prayer
Special days commemorated by Jewish people during the Babylonian Exile to mourn the fall of Jerusalem.
Sabbath
A day of rest set aside for religious reasons, celebrated by Jewish people.
Chosen People
The belief that the Jewish people are selected by God for a special purpose.
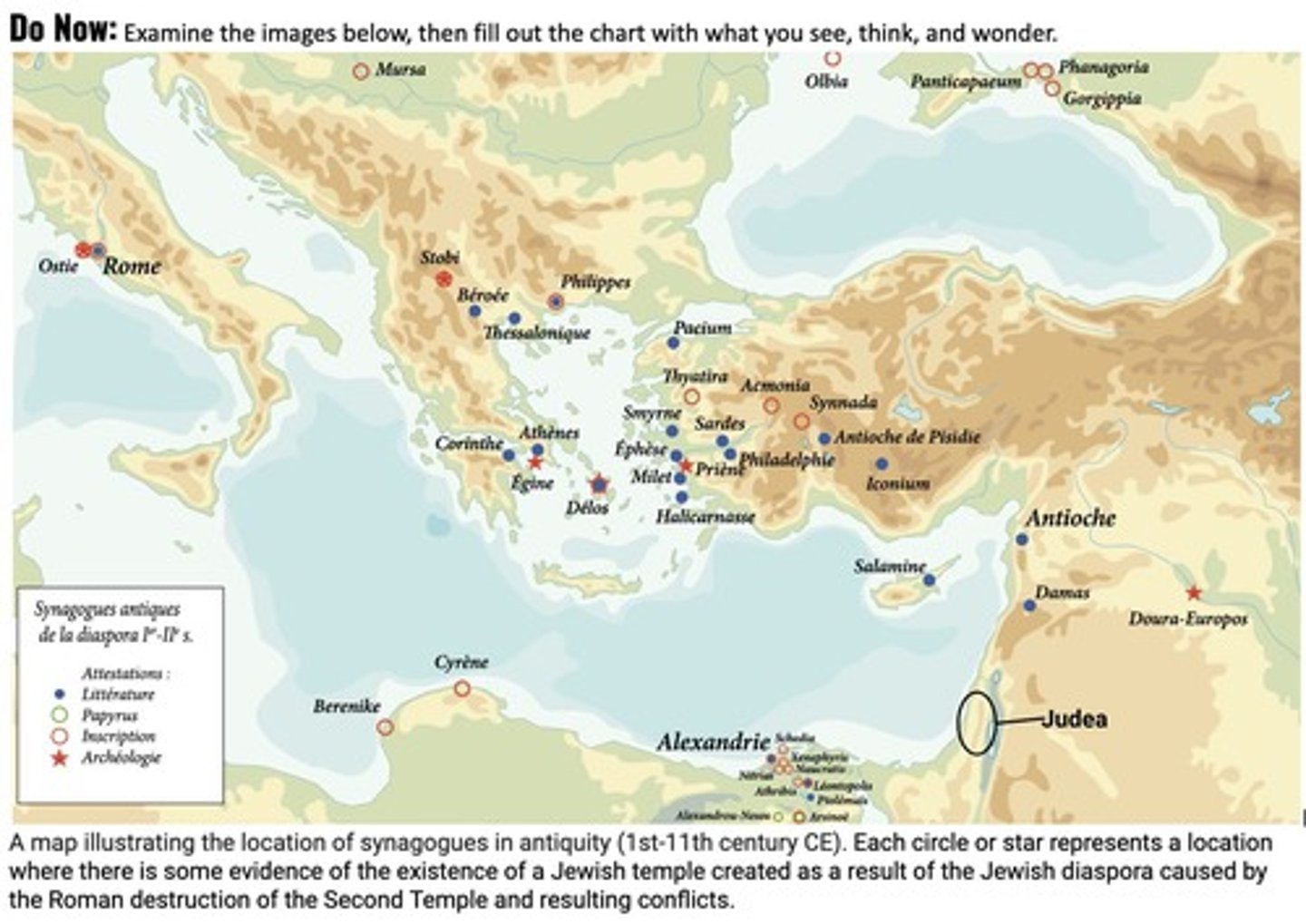
Diaspora
The term diaspora (in Ancient Greek, διασπορά - 'a scattering or sowing of seeds') refers to any people or ethnic group forced to leave its traditional homeland, and the spreading out of those people that results from it.
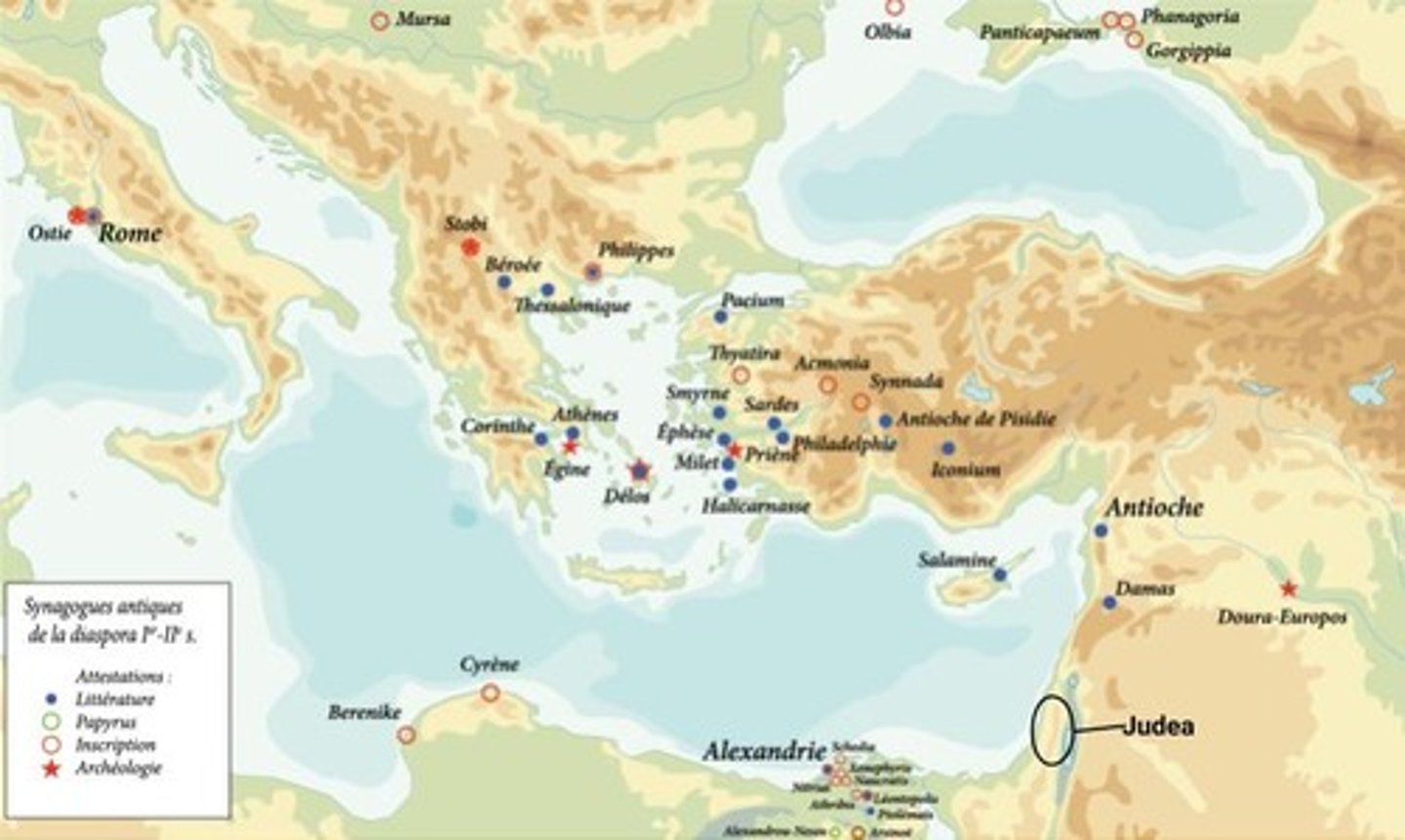
Jewish Diaspora
The Jewish diaspora began with the Babylonian Exile, where some captives returned to Judea while others settled elsewhere, dispersing around the Mediterranean Sea.
Babylonian Exile
The Babylonian Exile refers to the period when Jewish captives were forced to live in Babylon, leading to the beginnings of the Jewish diaspora.
Major centers of Jewish culture
Major centers of Jewish diasporan culture emerged in such places as Alexandria, Asia Minor, and Babylonia.
Roman expulsion
A second major expulsion and diaspora of the Jewish people from Judea took place between 66 CE and 136 CE due to Roman military actions and tensions.
Second Temple
The Second Temple was destroyed by the Roman military during the Jewish-Roman conflict, significantly impacting Jewish religious life.
Jewish communities in Palestine
In the sixth century, there were 43 Jewish communities in Palestine, scattered along the coast, in the Negev, east of the Jordan, and in villages in the Galilee region.
Roman provinces
Jewish communities expelled from Judea were sent, or decided to go, to various Roman provinces in the Middle East, Europe, and North Africa.
66 CE
In 66 CE, the Roman Empire had been in control of Judea for some time, leading to tensions and ultimately the destruction of Jerusalem.
Cyrus the Great
Cyrus the Great was the Persian King who allowed some Jewish captives to return to Judea after the Babylonian Exile.
Judean rebellion
The Judean rebellion against the Romans was sparked by disrespectful Roman administrators and disagreements over taxes.
Mediterranean world
The Mediterranean world refers to the regions surrounding the Mediterranean Sea where Jewish people sought new homes during the diaspora.
Tensions between Judeans and Romans
Tensions between the Judeans and Romans intensified with riots and wars, culminating in the destruction of Jerusalem.
Jewish religious practice
The rights of the Jewish people to practice their religion were mostly respected by the Roman Empire before the Judean rebellion.
Galilee region
The Galilee region is one of the areas in Palestine where Jewish communities were located during the sixth century.
Jordan River valley
The Jordan River valley is another area in Palestine that had Jewish communities during the sixth century.
Negev
The Negev is a region in Palestine where Jewish communities were established during the sixth century.
Alexandria
Alexandria was one of the major centers of Jewish diasporan culture.
Asia Minor
Asia Minor was another significant location for Jewish diasporan culture.
Destruction of Jerusalem
The destruction of Jerusalem by the Roman military was a pivotal event that led to the Jewish diaspora.
Roman military
The Roman military played a crucial role in the expulsion of Jewish people from Judea during the conflicts.
Monotheism
Judaism was the first monotheistic religion that continued to exist and impact world history.
Polytheism
The belief in many gods, as practiced by civilizations such as the Ancient Egyptians and Sumerians.
Covenant
An agreement believed by Jewish people to have been made by God with several figures mentioned in the Torah, particularly with Abraham.
The Ten Commandments
The clearest code of conduct in Judaism, inscribed by God on two stone tablets and given to Moses.
Yahweh
The name used by Jewish people to refer to the singular God they worship.
God
The term used by Christians to refer to the singular deity they worship.
Allah
The term used by Muslims to refer to the singular God they worship.
The Torah
The central reference of the religious Judaic tradition, containing the laws and teachings of Judaism.

Genesis
The first book of the Torah, which includes the creation narrative and the covenants made with Abraham.
The LORD
A title used in the Bible to refer to God, particularly in the context of the covenants with Abraham.
Sabbath
A day of religious observance and abstinence from work, which is to be kept holy according to the Ten Commandments.
Ethical/Moral Codes
Guidelines that describe how one should live their life based on the beliefs of their religion.
Stone Tablets
The physical medium on which the Ten Commandments were inscribed by God.
Moses
The prophet who received the Ten Commandments from God and shared them with the Israelites.

Adultery
The act of cheating on one's spouse, prohibited by the Ten Commandments.
Stealing
The act of taking someone else's property without permission, prohibited by the Ten Commandments.
Killing
The act of causing the death of another person, prohibited by the Ten Commandments.
Honoring Parents
The commandment that instructs individuals to respect and care for their father and mother.
Graven Images
Idols or images made for worship, which are prohibited by the Ten Commandments.
Work on Sabbath
The prohibition against performing any work on the Sabbath day.
Thou shalt not steal.
A commandment prohibiting theft.
Thou shalt not bear false witness [lie] against thy neighbour.
A commandment prohibiting lying about others.
Thou shalt not covet [want] thy neighbour's house, wife, manservant, maidservant, ox, *** [donkey], nor any thing that is thy neighbour's.
A commandment prohibiting the desire for others' possessions.
Abraham
Father of Judaism; his life story is told in the book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible.

Covenant with Abraham
God promised to bless Abraham with descendants 'like the sands of the sea' and a nation for him and the Israelites.
Torah
The central reference of the religious Judaic tradition, believed by many Jewish people to have been written by Moses.
Babylonian Exile (Captivity)
The period from 597 to 539 BCE when Jewish people were conquered by the Babylonian Empire and forced to live in captivity.
Nebuchadnezzar II
The Babylonian King who ordered the upper class Jewish people to leave Jerusalem.
Impact of Babylonian Exile
The exile led to increased religiosity among Jews, the importance of the scribes, and the compilation of historical writings and religious teachings.
Days of prayer
Days commemorating the fall of Jerusalem, observed by Jewish people during the Babylonian Exile.