MT 116: LEC 5 - QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Clinical Chemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What does Quality Assurance ensure in the lab?
Accuracy, reliability, and timeliness of test results.
In which stage do most lab errors occur?
Pre-analytical stage (≈70%).
Who is mainly involved in the analytical stage?
The Medical Technologist and the analyzer.
What is checked in post-analytical QA?
Results, reporting, interpretation, and communication with physicians.
What does "Pre–A–Post" stand for?
Patient → Analyzer → Physician.
What are the 4 main components of the Quality Management Framework?
Quality Planning, Quality Assessment, Quality Improvement, Quality Control.
Which part of QMF creates SOPs and personnel policies?
Quality Planning.
Which QMF step monitors lab performance and verifies quality of results?
Quality Assessment.
Which QMF step eliminates causes of problems?
Quality Improvement.
Which QMF step is limited to the analytical process only?
Quality Control.
What is the difference between a standard and a control?
Standard = calibrates assay; Control = checks performance after calibration.
How many times should controls be run for QC validation?
20 times over 30 days.
What chart is used to monitor QC results?
Levey-Jennings chart.
According to CLIA, how often should QC be performed with Level 1 & 2 controls?
Once a day.
If a lab has only Level 1 control, how often should QC be done?
Twice a day.
How many days minimum are needed for QC evaluation?
20 days (Levey-Jennings chart).
What does internal QC monitor?
Daily accuracy and precision.
What does external QC monitor?
Long-term accuracy (via proficiency testing).
Which organization handles NEQAS in the Philippines?
Lung Center of the Philippines.
What does NEQAS do to assess clinical chemistry labs?
Sends unknown specimens for testing and comparison.
What does PCQACL stand for?
Philippine Council for Quality Assurance in Clinical Laboratory.
What does accuracy mean in internal QC?
Ability to obtain the established or “true” value.
What does precision mean in internal QC?
Ability to obtain the same value on repeat measurements.
Accuracy is related to what concept?
Correctness of a result.
Precision is related to what concept?
Reproducibility/consistency of results.
What’s the ideal lab result characteristic?
Both accurate and precise.
What does sensitivity measure?
The % of diseased individuals correctly identified by the test (true positives).
What does specificity measure?
The % of healthy individuals correctly identified as disease-free (true negatives).
Which test parameter is better for ruling out disease?
Sensitivity (SnNout).
Which test parameter is better for ruling in disease?
Specificity (SpPin).
What does Positive Predictive Value (PPV) mean?
% of people with positive test results who actually have the disease.
What does Negative Predictive Value (NPV) mean?
% of people with negative test results who are truly disease-free.
Which factor affects predictive values but not sensitivity/specificity?
Disease prevalence.
Which is NOT a requirement for a QC material?
Independence from assay method.
What type of curve is used in a Levey-Jennings chart?
Normal/Gaussian distribution curve.
What are the warning limits in a Levey-Jennings chart?
±2 standard deviations (SD).
What should be done if results fall between 2s and 3s?
Repeat the analysis (possible error).
What are the rejection limits in a Levey-Jennings chart?
±3 standard deviations (SD).
What should be done if results fall beyond ±3s?
Stop testing, hold patient results, and investigate the system.
What is the main purpose of Westgard multi-rules?
To decide whether to accept or reject a QC run.
Which Westgard rule is a warning rule, not a rejection?
1-2s.
What type of error does 1-3s indicate?
Random error.
What type of error does 2-2s indicate?
Systematic error.
Which rule means 10 consecutive results on one side of the mean?
10x → Systematic error.
What does a skewed Gaussian distribution in a control chart suggest?
Data problems (e.g., small sample size, flawed sampling).
What completes a lab QC program aside from internal QC?
External QC (e.g., proficiency testing, inspections).
What parameter checks Random Error?
SD & CV.
What parameter checks Systematic Error?
Mean (𝑋̅).
Give 2 examples of Random Error causes.
Pipetting error, voltage fluctuation.
Give 2 examples of Systematic Error causes.
Improper calibration, deteriorated reagents.
First step if control value falls outside acceptable range?
Don’t release patient test results.
Where do you record unresolved QC problems?
Out-of-Control Logbook.
What must be done once the QC problem is resolved?
Rerun patient specimens and re-evaluate past results.
What does a trend in QC mean?
A gradual change in the mean in one direction.
What does a trend indicate?
Gradual loss of reliability in the test system.
Give 2 common causes of a trend.
Reagent deterioration, calibrator deterioration.
How is trend different from shift?
Trend = gradual drift, Shift = sudden change.
What does a shift in QC mean?
An abrupt change in the mean that becomes continuous.
How do QC values appear in a shift?
All on one side of the mean (above or below).
Main cause of a shift?
Improper calibration.
Difference between trend and shift?
Trend = gradual change; Shift = sudden change.
What are the 2 key factors in error detection?
Probability of error detection and probability of false rejection.
What does “probability of error detection” mean?
Ability of QC to catch errors beyond normal instrument imprecision.
What does “probability of false rejection” mean?
Chance of QC showing an alarm when no error exists.
What are the Five W’s in error investigation?
What, Where, When, Who, Why.
What does dispersion in QC mean?
Control values are widely scattered in an unexplained pattern.
What does dispersion usually indicate?
Increased imprecision in the test system.
How is dispersion different from trend and shift?
Trend = gradual drift, Shift = sudden jump, Dispersion = random scatter.
What does the mean represent?
The average of all data points, related to accuracy.
Formula for mean?
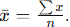
What is the median?
The middle value when data is arranged in order.
How is median calculated for an even number of values?
Average of the two middle values.
What is the mode?
The most frequently occurring value.
Which measure is least affected by outliers?
Median.
Formula for variance?
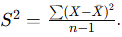
What does SD measure in lab QC?
The precision (random error).
What does a large SD indicate?
Poor precision, more random error.
Confidence interval values for ±1, ±2, ±3 SD?
68.2%, 95.5%, 99.7%.
Formula for CV?
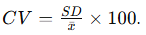
Acceptable CV limit for repeated lab tests?
Less than 5%.
What is a delta check used for?
Comparing current and previous patient results for consistency.
What is a Youden Plot used for?
Detecting within- and between-laboratory variability.
Who pioneered Six Sigma and when?
Motorola, 1980s.
What does 6𝛿 compliance mean?
Only 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
Difference between Six Sigma and Lean?
Six Sigma = removes variation/errors; Lean = removes waste.
What does DMAIC stand for?
Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control.
What is TEa in lab QC?
Total Allowable Error = maximum acceptable error limit.
Formula for Sigma Metric?
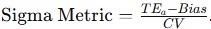
What does DPMO stand for?
Defects Per Million Opportunities.
Acceptable defects in Six Sigma per million?
3.4.
Which Six Sigma belt level oversees implementation at an executive level?
Champion.