4.1.8 - exchange rates
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
define exchange rate
the price of one currency in terms of another
international currencies are….
…products that can be bought and sold on the foreign exchange market (forex)
who chooses the exchange rate system used
the central bank
what are the three exchange rate systems
floating exchange rate
fixed exchange rate
managed exchange rate
define floating exchange rate
demand and supply determines the rate at which one currency exchanges for another
how does a floating exchange rate go up or down
excess demand for the currency = currency WORTH MORE (appreciation)
and vice versa
define a fixed exchange rate
central bank fixes the exchange rate in relation to another currency (eg. USD)
parity peg (fixing) = same (1 to 1 rate to another currency)
not always at parity (can be 1 to something else rate to another currency)
how does fixed exchange rate go up or down
central bank decides to peg and increase currency strength = revaluation
opposite = devaluation
managed exchange rate definition
free market determines currency value, but central banks can also intervene to keep the value within a desired range
two types of managed exchange rate
managed/‘dirty’ float —> ER flows freely but gov intervenes
semi-fixed rates/crawling peg system —> ER allowed to float between an upper and lower limit
crawling peg system diagram
.
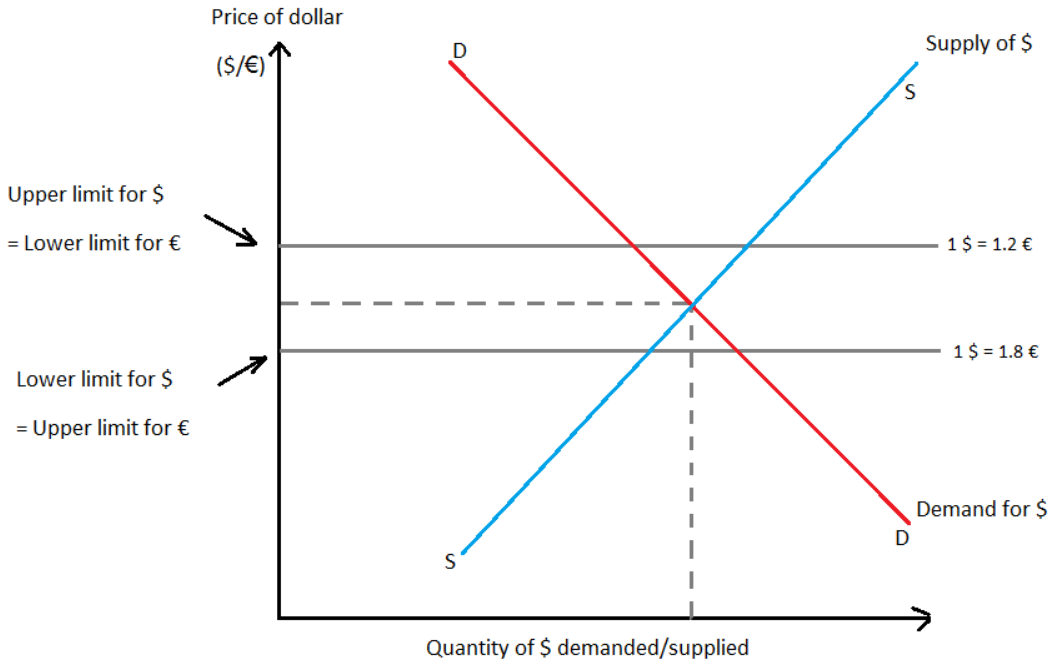
how do managed exchange rates go up or down
currency fluctuates above the range = central bank sells its own currency in forex markets = increased supply = decreased value
currency fluctuates below the range = central bank buys its own currency in forex markets (using foreign reserves) = reduced supply = increased value
this is called EXCHANGE EQUALISATION
can also use interest rates to intervene (hot money flows)
can also use currency controls to regulate how much people can send into/out of the country
factors influencing floating exchange rates
relative interest rates —> affects hot money flows
relative inflation rates —> ↑inflation = ↑export price = ↓demand for pound = ↓pound value
net investment —> ↑FDI = ↑pound demand = ↑pound value
the current account —> trade surplus = appreciate
speculation —> ppl buying currency to sell for profit - only if they expect it to appreciate
QE —> foreign owned gov bonds bought back = foreigners exchange their pounds = ↑supply of pounds = depreciates
consequences of competitive devaluation/depreciation
exports cheaper = higher revenues (if price elastic)
retaliation devaluation = potentially not much change
imports expensive = higher costs of production
impacts of changes in exchange rates to ME objectives, + standards of living
current account - SPICED
unemployment - depreciation = less unemployment bc more exports (and vice versa)
inflation - depreciation = AD shift right = demand pull inflation. appreciation = imports expensive = cost push inflation
economic growth - depreciation = AD shift right = ↑growth
SoL - depreciation = imports expensive = ↓SoL.
also = ↓unemployment bc ↑exports = ↑wages = ↑SoL
FDI - depreciation = ↑FDI (money invested is worth more when investing in a country with a weaker currency)