CHAPTER 11: FIELD SYMMETRY AND FLATNESS
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
The purpose of this spot check is to ensure that the symmetry and flatness of the radiation beam are
within the limits established at the baseline testing
Significant deviations in beam flatness and symmetry may result in
unacceptably high or low dose regions in the irradiated tissues.
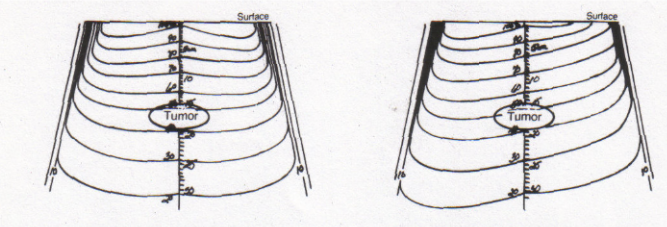
term. flatness
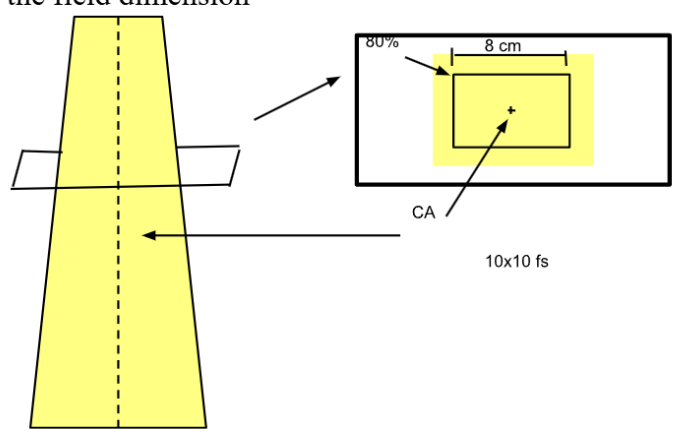
def. the maximum difference of dose on the central axis (CA) over 80% of the field dimension
term. Symmetry
def. the difference in dose between any 2 symmetrical points within the inner 80% of the field size
T/F: If the field is flat, it also is symmetrical.
True
T/F: If the field is symmetrical, the field is flat.
False.
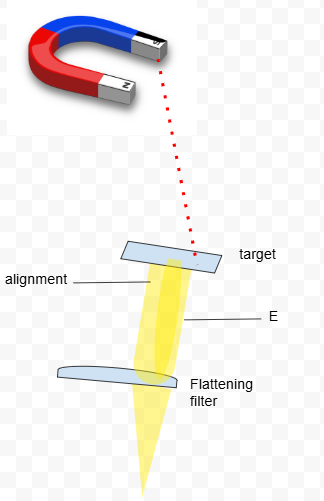
Sources of Malfunction
Flatness and symmetry may be affected by
mechanical and electronic parameters.
Small changes in:
Beam alignment
Beam energy
Bending magnet function
target position
Flattening filter selection and position
FYI: Beam without flattening filter is a comb-shaped/ forward-peaked beam
Frequency: FIELD SYMMETRY AND FLATNESS
Varies by institution
May range from weekly to monthly
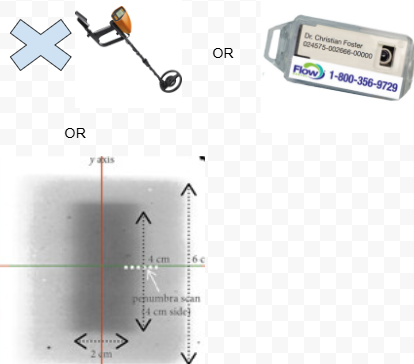
Materials
multiple detector device which can use:
ion chambers or,
diodes
Advantageous because the desired info can be acquired very quickly.
OR: Film exposure or TLD’s work in principle, but their accuracy is affected by the need for remote processing.
(FYI: multiple detector devices contain multiple detectors (such as ion chambers or diodes) arranged in an array. These devices can simultaneously measure radiation dose at different points in the beam)
Action Guidelines
The field must be flat and symmetrical to within:
+/- 2% across 80% of the field dimension
Technique of the spot check using film
Materials
redi-pak film
Masking tape
Densitometer
Pencil/paper/calculator
Technique of the spot check using film
Steps

Why take densitometer readings at 4 cm from CR? Why not 4.5 cm or at the field edge? Why exactly 4 cm?
By definition field flatness and symmetry is only the inner 80% (i.e. 8x8 within that 10x10)
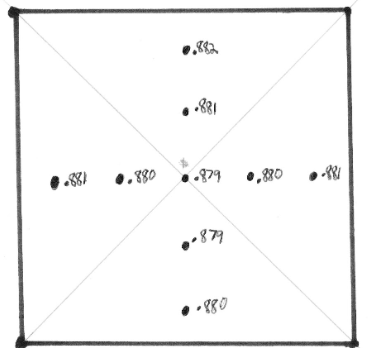
establish baseline
establish low and high tolerance #s
Compare all 9 readings. Is the beam flat?