marine & coastal processes (#5)
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
🍂
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
coastal zone
this is the interface between land and water;
this is continually changing because of the dynamic interaction between the oceans and the land
tides, currents, and waves
3 factors that bring energy to the coast
coastal processes
activities or events happening in the marine environment
ex. waves, tides, sea level change, crustal movement, and storm surge
atmospheric pressure, temperature, movement of the Earth, moon
some environmental factors which drive coastal processes
tides
COASTAL PROCESSES:
refers to the gravitational pull between the Earth and the moon;
because the moon is closer to the Earth than the Sun, it has a larger effect and causes the Earth to bulge toward the moon
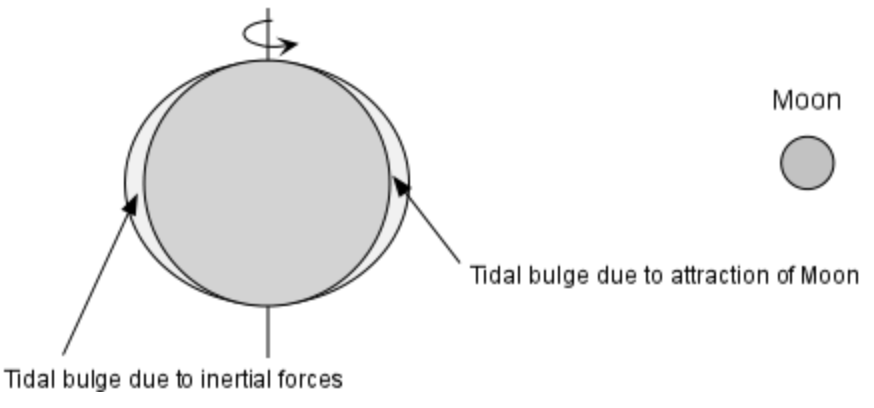
2 high tides and 2 low tides
usually, how many high tides and low tides each day?
ocean currents
COASTAL PROCESSES:
when the surface of the oceans move in response to winds blowing over the surface;
oceanic circulation is 3-dimensional
surface ocean currents
COASTAL PROCESSES:
these tend to flow in patterns similar to the winds as discussed previously, and are reinforced by the Coriolis Effect;
unlike winds, these are diverted when they encounter a continental land mass
clockwise, counterclockwise
UNDER OCEAN CURRENTS:
Because of the Coriolis effect, ocean current circulation is ________ in the northern hemisphere and ________ in the southern hemisphere.
vertically
UNDER OCEAN CURRENTS:
Seawater also circulates ________ as a result of changes in density controlled by changing salinity and temperature.
ocean waves
COASTAL PROCESSES:
these are caused by the movement of the air masses in the coastal environment;
water travels in loops in these
coastal erosion / erosion by waves
COASTAL PROCESSES:
waves can only erode if the water along a coastline is shallower than 1/2 times the wavelength;
when the wave breaks as it approaches the shoreline, vigorous _____ is possible due to the sudden release of energy as the wave flings itself onto the shore
rigorous erosion
UNDER COASTAL EROSION:
______ erosion of sea floor takes place in the surf zone
transportation of sediment by waves & currents
COASTAL PROCESSES:
sediment that is created by the abrasive action of the waves or sediment brought to the shoreline by streams is then picked up by the waves and transported;
where beach material is transported in the sea and along the coast;
mainly done by longshore drift
finer grained sediments
UNDER TRANSPORTATION OF SEDIMENT:
these sediments are carried offshore to be deposited on the continental shelf or in offshore bars
coarser grained sediment
UNDER COASTAL TRANSPORTATION:
these can be transported by longshore currents and beach drift
coastlines
these represent a balance between wave energy and sediment supply
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
If wave energy and sediment supply are constant, then a steady state is reached. If any one of these factors change, then shoreline will adjust.
longshore drift
UNDER COASTAL TRANSPORTATION:
when waves move in the direction of the prevailing wind at an angle to the beach
still-water deposition
COASTAL PROCESSES:
the laying down of sediment carried by wind, flowing water, the sea or ice;
sediment can be transported as pebbles, sand and mud, or as salts dissolved in water.
rocky coasts
TYPES OF COASTS:
coastlines that have experienced recent tectonic uplift as a result of either active tectonic processes;
this may occur anywhere where wave action has not had time to lower the coastline to sea level

beaches
TYPES OF COASTS:
wave washed sediment along a coast;
these occur where sand is deposited along the shoreline
barrier islands
TYPES OF COASTS:
long narrow ridge of sand just offshore running parallel to the coast;
most of these were built during after the last glaciation as a result of sea level rise
ex. some along the east and Gulf coasts of the US
beach drift and longshore drift
UNDER BARRIER ISLANDS:
barrier islands are constantly changing & grow parallel to the coast by _____ drift and ______ drift;
these are eroded by storm surges that often cut them into smaller islands.
lagoon
UNDER BARRIER ISLANDS:
narrow channel of water separating the island and coast
reefs
TYPES OF COASTS:
these consist of colonies of organisms like corals;
these only form in shallow tropical seas as the mentioned organisms can only live in warm waters & need sunlight to survive;
these protect the coastline from waves
fringing reefs
2 TYPES OF REEFS:
these form along coastlines close to the sea shore
barrier reefs
2 TYPES OF REEFS:
these form offshore, separated from the land by a lagoon
atoll
TYPES OF COASTS:
a circular island forms as reefs trap sediment;
this surrounds a body of water called a lagoon
atoll
TYPES OF COASTS:
these develop with underwater volcanoes, called seamounts;
first, the volcano erupts, piling up lava on the seafloor. as the volcano continues to erupt, the seamount's elevation grows higher, eventually breaking the surface of the water.
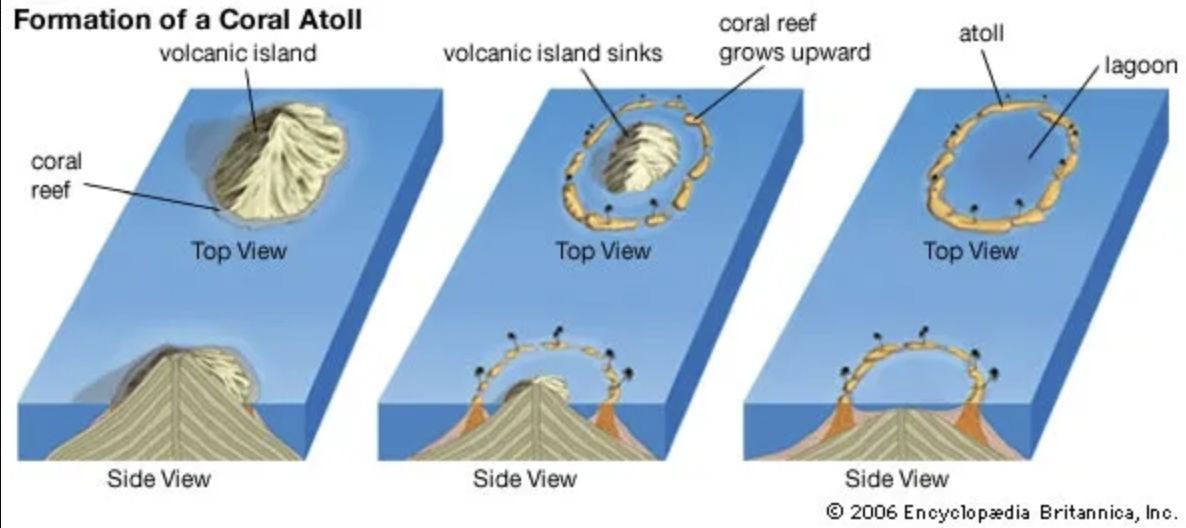
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
In the deeper oceans reefs can build up on the margins of volcanic islands, but only do so after the volcanoes have become extinct. After the volcanism ceases, the volcanic island begins to erode and also begins to subside. As the island subsides, the reefs continue to grow upward. Eventually, the original volcanic island subsides and is eroded below sea level.
After this, an atoll forms.
estuaries
TYPES OF COASTS:
these are coastal river valleys flooded by sea water;
characterized by mixing of fresh & salt water

tidal flats
TYPES OF COASTS:
these are zones along the coast that are flooded during hight tides and form in the intertidal zones lacking strong waves;
they’re common behind barrier islands or in estuaries

sediment starvation
COASTAL HAZARDS:
when rivers do not bring enough sediment to be deposited on the beach
biological activities
COASTAL PROCESSES:
marine _____ includes energy-fixing microorganisms in transferring to and sustaining all of the other organisms in the marine system
TIDES BASED ON FREQUENCY:
when any region experiences only 1 high tide & 1 low tide on a lunar day cycle
semi-diurnal tide
TIDES BASED ON FREQUENCY:
2 high tides & 2 low tides occur on a lunar day;
the height of peaks & the depth of troughs for both high & low tides are the same
TIDES BASED ON FREQUENCY:
2 high tides & 2 low tides occur;
height of both high tides & depth of both low tides are not the same
TIDES BASED ON FREQUENCY:
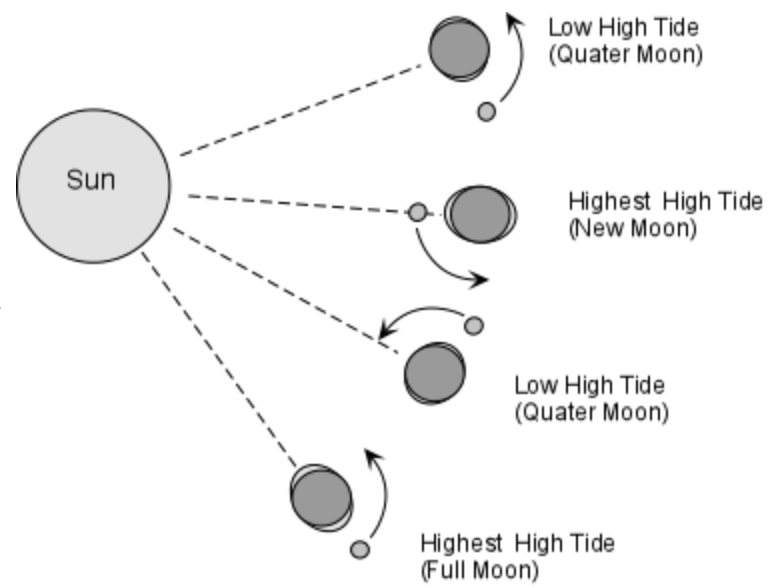
sun and moon align & pull the ocean's surface in the same direction;
happens 2x in a lunar month during a full or new moon
TIDES BASED ON FREQUENCY:
sun & moon are at a perfect angle to one another;
happens 7 days after spring tide & during the first and last quarters of the moon;
resulting oceanic bulge & gravitational attraction of the sun cancel each other out