lecture exam 5 (ch 27 male repro)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
y
male chromosome
lacking y
female chromosome
primary sex organs
produce gametes
testes or ovaries
male secondary sex organs
system of cuts, glands; penis delivers sperm cells
female secondary sex organs
uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina receive sperm, provide place for union of gametes, harbor developing fetus, give birth nourish offspring
secondary sex organs
organs other than gonads that are necessary for reproduction
secondary sex characteristics
features that distinguish the sexes and influence mate attraction
both sexes secondary sex characteristics
pubic and axillary hair and their associated scent glands, and the pitch of the voice
male secondary sex characteristics
facial hair, coarse and visible hair on the torso and limbs, relatively muscular physique
female secondary sex characteristics
distribution of body fat, breast enlargement, and relatively hairless appearance of the skin
23 chromosomes
22 pairs of autosomes
1 pair of sex chromosomes
sex chromosomes
can either be x or y
all eggs have x
males produce half y half x
SRY gene
in y chromosome
sex determining region of y chromosome
testosterone
testes begin to secrete at 8 to 9 weeks
females develop due to an absence of this
at same time, mullerian-inhibiting factor is also developing
mullerian-inhibiting factor
in xy fetus, secreted by testes
causes atrophy of a certain duct associated with female development
females develop due to absence of testosterone
descent of male gonads
initially develop high, then migrate to pelvic cavity
beings at week 6, stimulated by testosterone
male external genitalia
scrotum
penis
occupy the perinium
scrotum
pouch of skin, muscle, and fibrous connective tissue containing the testes
internal median septum of scrotum
divides scrotum into R/L compartments
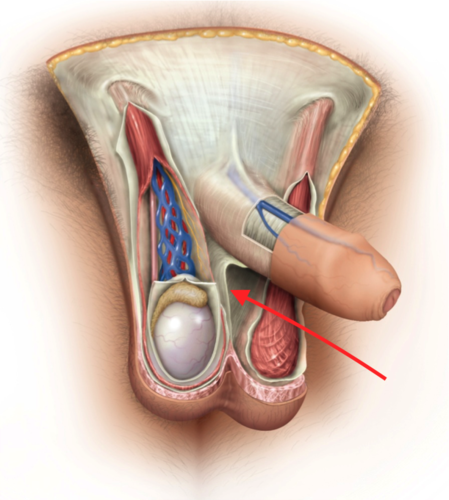
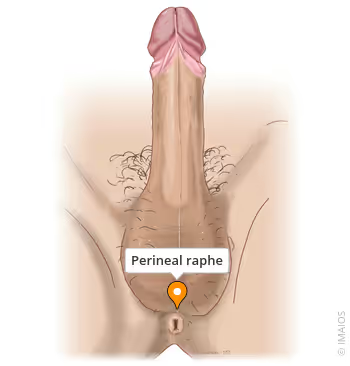
perineal raphe
superficial median seam that overlies median septum
extends anteriorly along ventral side of penis and posteriorly to anus
spermatic cord
bundle of fibrous connective tissue containing the ductus deferens (sperm duct), blood and lymphatic vessels, and
must be held at 35 degrees C
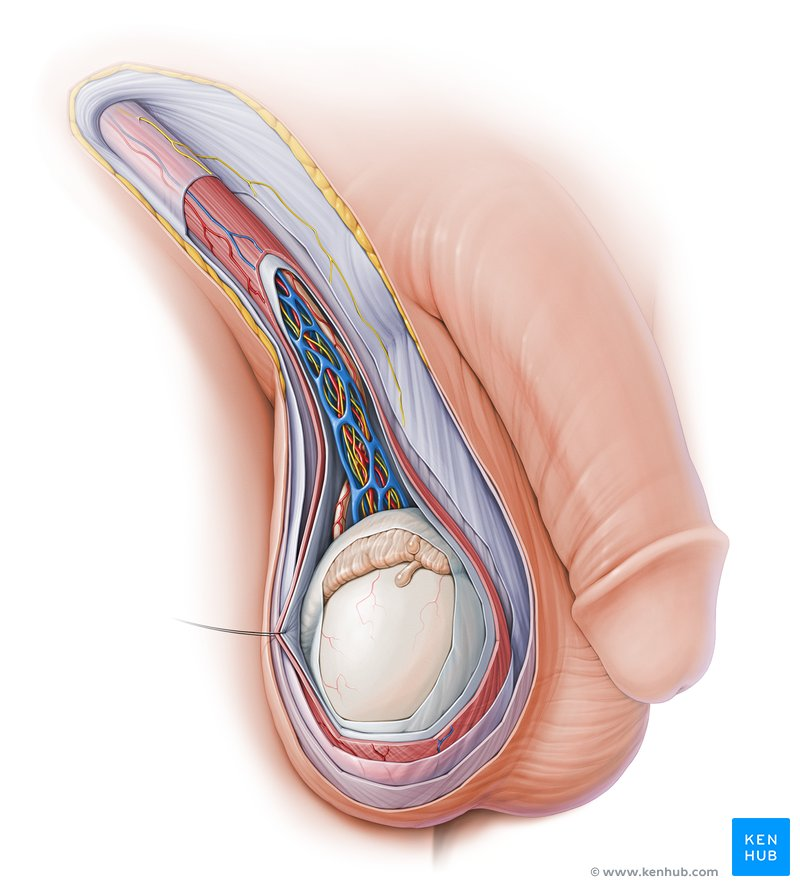
temperature regulation of the testes
cremaster
dartos fascia
pampiniform plexus
cremaster
strips of the internal abdominal oblique muscle that enmesh the spermatic cord
in environmental cold temps, contracts and draws testes upward toward body; in warm temps, relaxes suspending testes further from body
dartos fascia
subcutaneous layer containing dartos msucles
smooth muscle contracts when cold, wrinkling the scrotum, holding testes snugly against warm body; acts to reduce
pampiniform plexus
extensive network of veins from testes that surround testicular artery and spermatic cord
functions as countercurrent heat exchanger to maintain optimum temp for sperm
removes heat from arterial blood, so when it reaches testis its cooler
the testes
combined endocrine and exocrine glands that produce sex hormones and sperm
tunica albugenia
seminiferous tubules
testes histology
germ cells
nurse cells
blood-testis barrier
interstitial endocrine cells (leyDIG)
germ cells
in process of becoming sperm
nurse cells
protect germ cells and promote their development
tight junctions form BLOOD-TESTIS BARRIER
blood-testis barrier
functions to separate sperm from immune system, preventing antibodies and other large molecules in the blood from getting to germ cells
interstitial endocrine cells
lie between seminiferous tubules and produce testosterone
four sperm ducts
efferent ductules
duct of epididymus
ductus (vas) deferens
ejaculatory duct
efferent ductules
about 12 small ciliated ducts collecting sperm from rete testes
duct of epididymis
site of sperm maturation and storage
contains a single coiled duct, adhering to posterior of testes
sperm mature as they travel through
sperm remain fertile 40-60 days; if they are not ejaculated, they disintegrate and are reabsorbed
ductus (vas) deferens
muscular tube passing from scrotum through inguinal canal to posterior surface of bladder
duct widens behind bladder into ampulla
duct ends by uniting w seminal vesicle
cut in vasectomy
ejaculatory duct
formed from ductus deferens and seminal vesicle; passes through the prostate to empty into prostatic urethra
three sets of accessory gland
seminal vesicles
prostate
bulbourethral glands
seminal vesicles
posterior to bladder, empties into ejaculatory duct
secretions form 65-75% of semen
prostate
surrounds urethra and ejaculatory duct just inferior to bladder
thin milky secretion forms 25-30% of semen
bulbourethral glands
near a dilated bulb at inner end of penis
during sexual arousal, produce pre-ejaculate that lubricates head of penis for intercourse
protects sperm by neutralizing acidity of urine in urethra
adolesence
period from onset of gonadotropin secretion and reproductive development to when a person attains full adult height
puberty
first few years of adolescence, until the first menstrual period in girls or the first ejaculation of viable sperm in boys
testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
growth of sex organs and generalized body growth
erythropoiesis, increased basal metabolic rate, and increase in appetite
pubic hair, axillary hair, and facial hair develop in response to DHT; associated scent and sebaceous glands develop
stimulates sperm production and libido
lutenizing hormone
stimulates interstitial endocrine cells in testes to product testosterone
follicle stimulating hormone
stimulates nurse cells of seminiferous tubules to secrete ABP that binds/concentrates testosterone keeping testosterone in seminiferous tubule and epididymis; in this way testosterone stimulates spermatogenesis in presence of ABP
negative feedback of sperm production
nurse cells secrete inhibin to suppress FSH
too-high testosterone negatively feeds back to hypothalamus to reduce GnRH secretion
old man sexual function
testosterone secretion declines with age
decline in leydig cells
whether andropause occurs is still being debated
age-related drop in testosterone and inhibin that triggers a rise in FSH and LH that could be responsible
spermatogenesis
process of sperm production in seminiferous tubules; involves three principle events
division and remodeling of large germ cells into small mobile sperm with flagella
reduction of chromosome number (1/2)
shuffling of genes so each chromosome contains new gene combination
ensures genetic variation
mitosis
body cells doubles its dna and then divides to produce identical daughter cells
division of single-cell fertilized egg, growth of embryo, postnatal growth, and tissue repair
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
meiosis
produces four gametes (haploid cells), each with only HALF the dna of diploid body cells
male and female gametes
spermatogenesis
steps to spermatogenesis
spermatogonia divide by mitosis
primary spermatocytes → blood-testes barrier
(1)-spermatocytes goes thru meiosis I
(2)-spermatocytes goes thru meiosis II, dividing into two spermaTIDS
each spermatid undergoes spermiogenesis, into single spermatozoan
spermatozoan head
nucleus - houses genetic material
acrosome - forms thin cap over apical half; consists of lysosome to penetrate egg
basal body - where tail attaches; assists in fertilization
spermatozoan tail
middle piece - contains large mitochondria that produce ATP for motility
principal piece and end piece - axoneme, which is motor apparatus for movement of sperm tail