Motivation Theories
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
motivation
when workers do something because they want to not just because they have to
scientific management theory of motivation (taylor)
managers and business owners only want obedience
main reason why people work is money, what workers want from employers most is higher wages
encourages rest breaks
what does scientific management use
differentiated piece rate/differentiated compensation to motivate workers
limitations of scientific management theory of motivation
rather authoritarian, may be less suitable in modern businesses
subsequent theorists feel money is not the only motivation & there is no scientific way to manage people
ignores qualitative factors that affect level of motivation
hierarchy of needs (maslow)
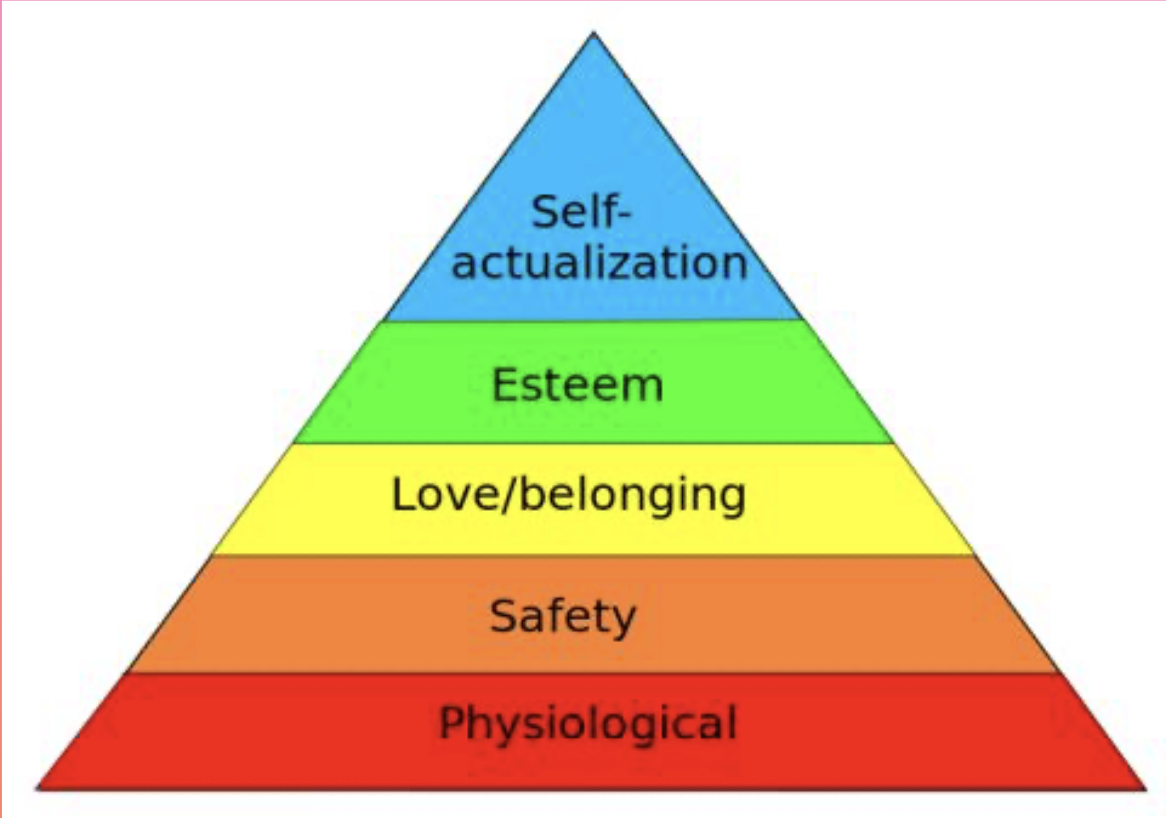
suggests one level of needs must be met for next level to be addressed
lower order needs
physiological, safety, and social needs. must be met to prevent dissatisfaction or unhappiness.
higher order needs.
esteem and self-actualization needs. help provide genuine sense of contentedness.
criticisms of marlow’s theory
people are not necessarily motivated in the same way
levels of needs do not apply to everyone in all contexts
two-factor theory (herzberg)
argues it is essential to first remove factors (hygiene factors) that cause dissatisfaction to create motivation (motivators)
what are hygiene factors, give 2 examples
lower level needs
wages
working conditions/working environment
job security
supervision
relationship with colleagues
relationship with management
what are motivators, give 2 examples
factors that define job context
advancement
purpose
challenging work
decision making
responsibility
opportunities to improve