1.AMINES N AMIDES
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
if a hydrogen from ammonia is replaced with an akyl group/aromatic group
you get an amine
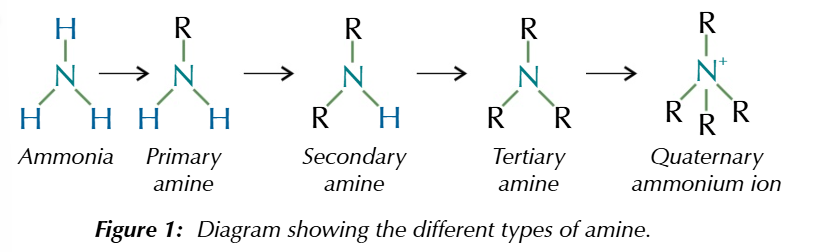
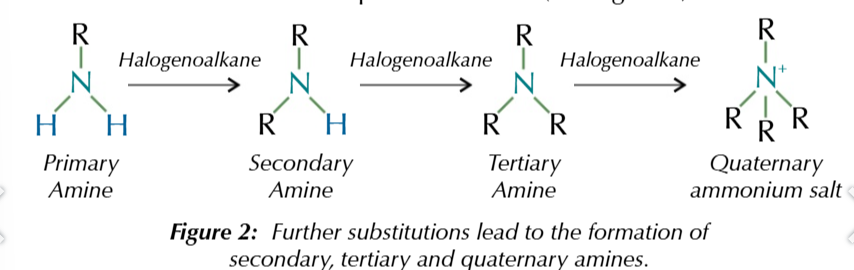
i hydrogen replaced
primary amine
2 hydrogen replaced
secondary amine
3 hydrogen replaced
tertiary amine
4th organic group added
quaternary ammonium ion
quaternary ammonium ions are positively charged
attracted to negative ions to form quaternary ammonium salt complexes
ammonium salt example
tetramethylammonium chloride
small amines smell slightly fishy
large amines smell very fishy
amine suffix
-amine/-amine ion

surfactants
compounds partially soluble/ insoluble in water
some quaternary ammonium compounds can be used as cationic sufactants
positively charged surfactants
cationic ammonium compound surfactants have at least 1 long hydrocarbon chain
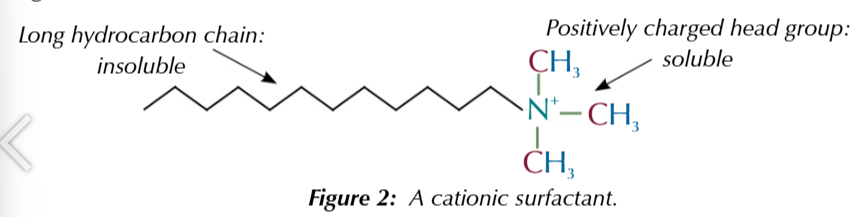
long hydrocarbon chain is insoluble in water
and binds to non polar substances like grease
positively charged head group is soluble
in water
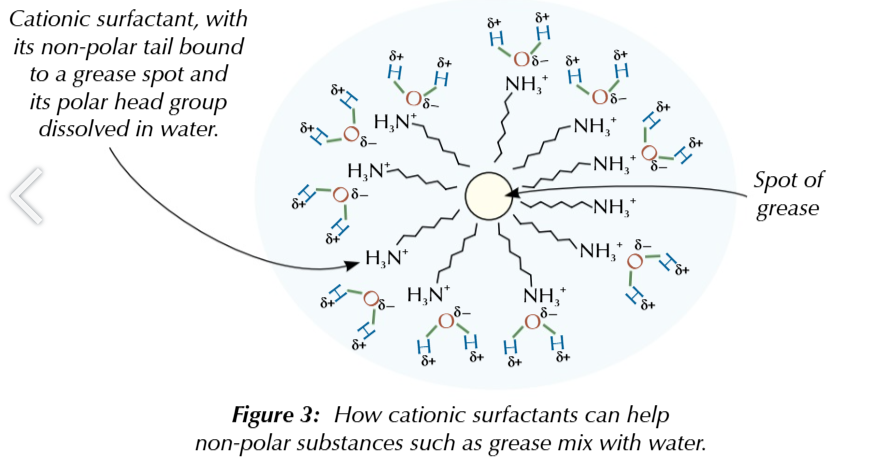
cationic surfactants are good detergents
the non polar part binds to grease and the polar part dissolves in water allowing spots of grease to mix with water and be washed away
cationic surfactants are used in things like
fabric conditioners and hair products
when hair/ fabrics get wet they pick up negative charges on their surface
positively charged parts of the cationic surfactant is attracted to these negatively charged surfaces to form a coating over the surface
the coating prevents the build up of static electricity
this is important to keep the fabric smooth in fabric conditioners and hair flat in hair products
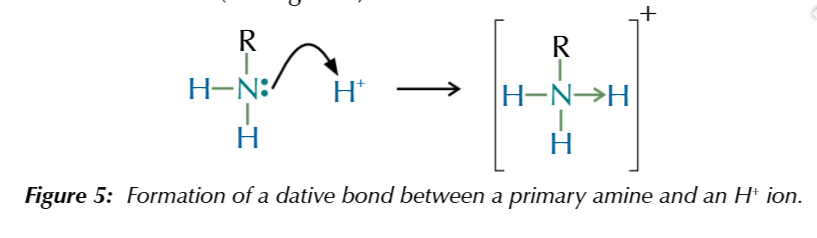
amines act as weak bases
because they accept protons due to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom that forms a coordinate bond
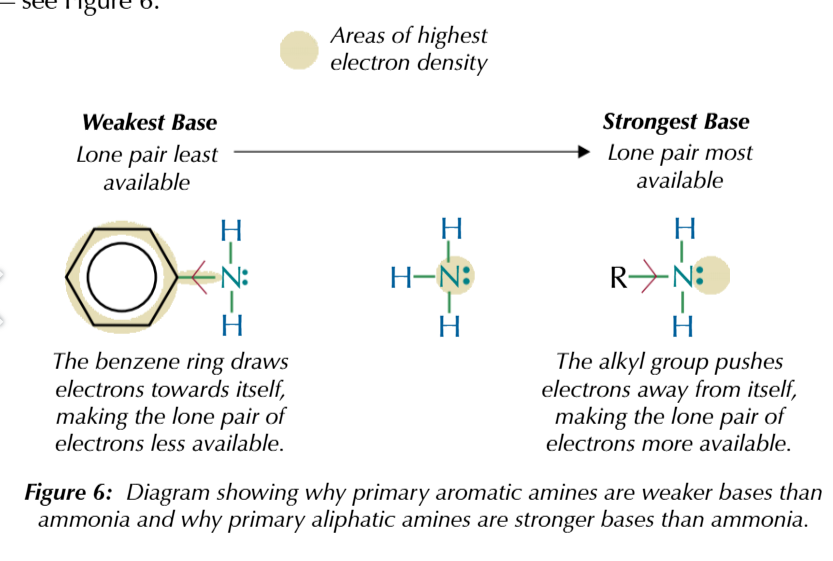
the avaliability of the lone pair electrons on nutrogen
affects its strength as a base
the more avaliable the lone pair
the stronger the base
a lone pair of electrons will be more available
if its electron density is higher
primary aromatic amine are WEAK bases
because benzene ring draws electrons towards itself and the nitrogen lone pair gets partially delocalised onto the ring
electron density on nitrogen decreases
making the lone pair less avaliable
alaphatic amines
amines w akyl groups
primary alaphatic amines are strong bases
because the akyl group poushes electrons onto attached groups
electron density on nitrogen atom increases
making lone pair more available
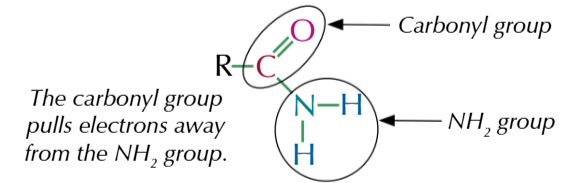
amides are a derivative of carboxylic acids
-CONH2
naming
-amide suffix
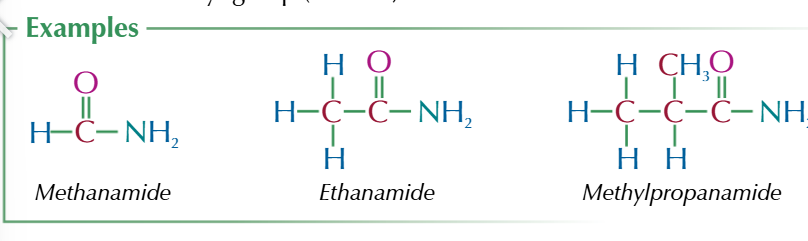
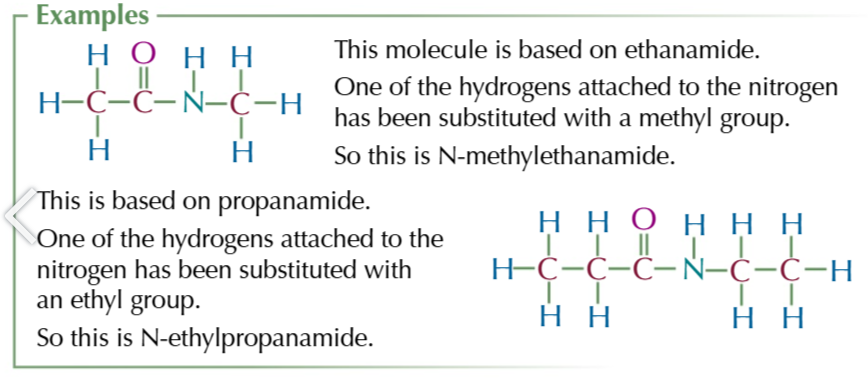
n substituted amides
amides where 1 hydrogen has been substituted for an akyl group
n substituted naming
N-Methyl/ethly/propyl
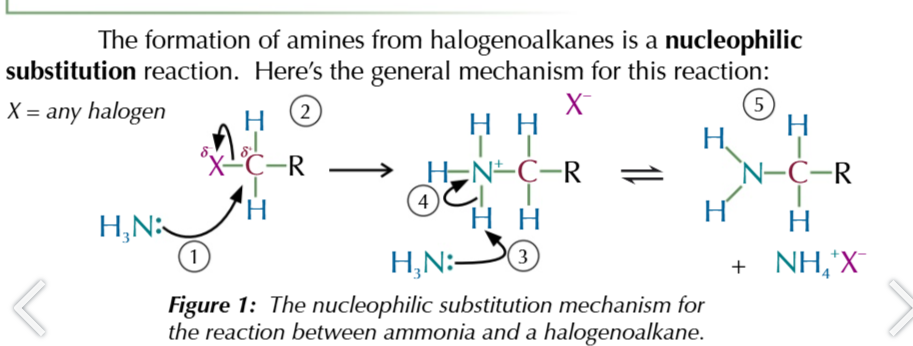
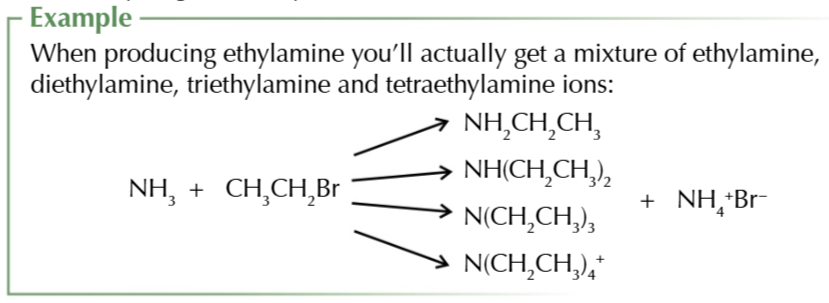
heating halogenoalkanes w excess ethanolic ammonia forms
aliphatic amines
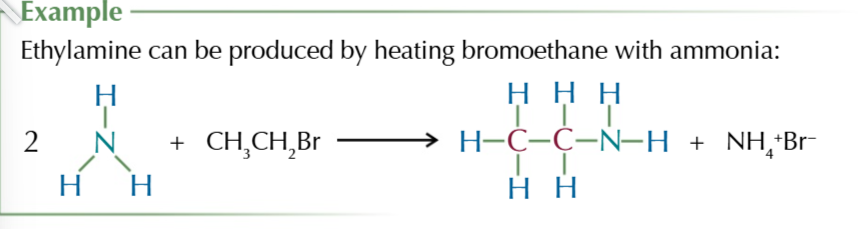
this process can produce a mixture of primary secondary and tertiary amines and quaternary ammonium salts as more than 1 hydrogen can be substituted
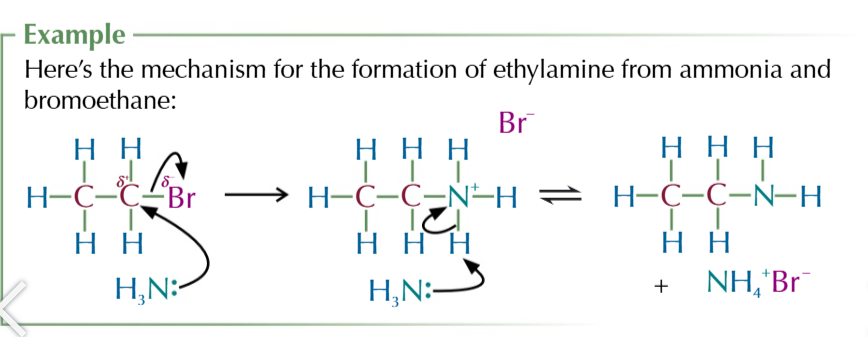
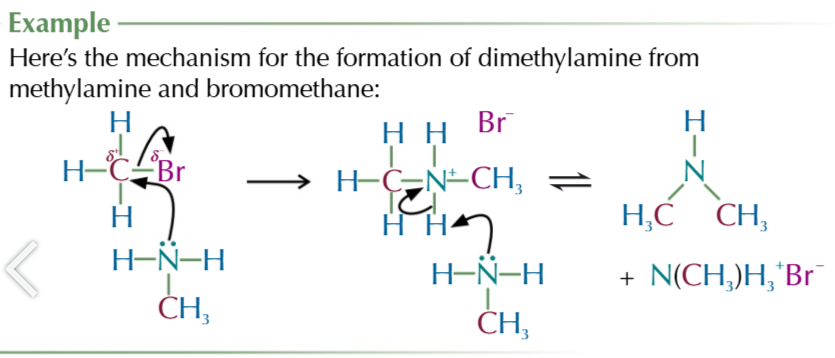
halogenoalkane nuceophilic substitution to produce amines
NH3 attacks ð+ carbon attacked to halogen
carbon donates electons to halogen from its broken bond as it forms a new one with ammonia
forms an akylammonium salt + negatively charged halide ion
second ammonia molecule donates its lone pair of electrons to a hydrogen attached to first ammonia
this hydrogen breaks from the akyl ammonium salt and joins ammonia to form NH4+ ion
products are a primary amine, NH4+Halide complex
the amine product still has a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen
so it can still act as a nuceophile meaning further substitutions will take place till a quaternary ammonium salt is formed
nitrile reduction ujsing LiAlH4 in dry ether and dilute acid forms
amines

LiAlH4 is tooe xpensive for industrial use
the industry uses a metal catalyst: platinum/nickel at high temperature n pressure in a process called catalytic hydrogenation

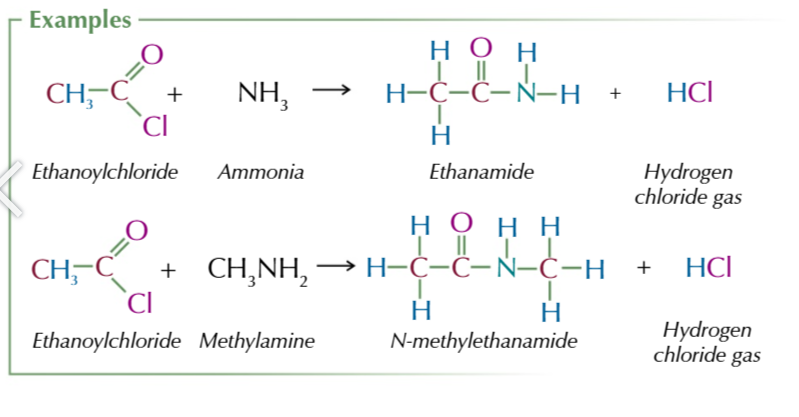
acyl chlorides react w ammonia to form primary amides: nuceophilic addition elimination
and acy chlorides react with AMINES o form n substituted amides: nuceophilic addition-elimination
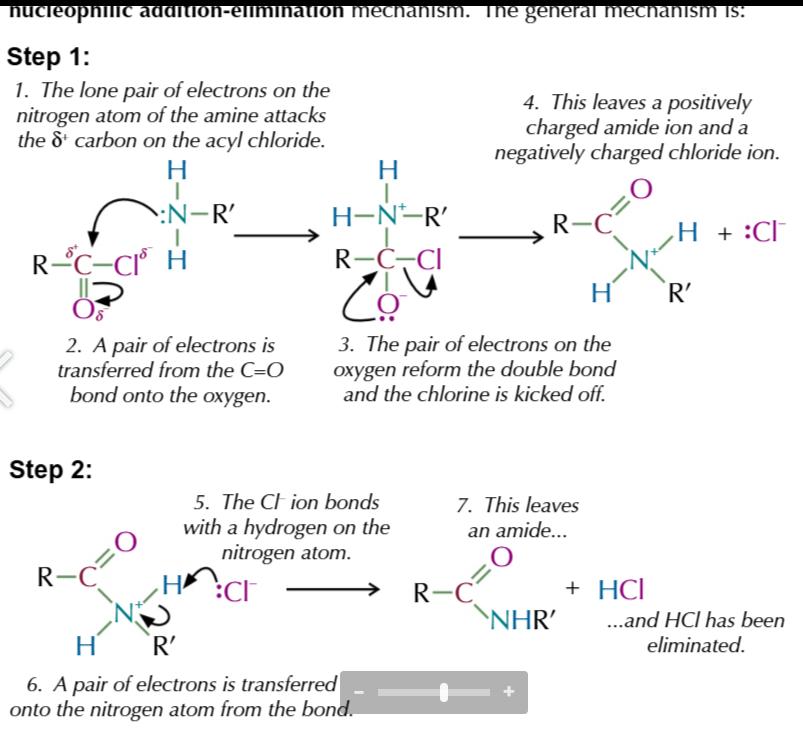
nuceophilic addition elimination mechanism step 1
lone pair of electrons on nitrogen attacks ð+ carbon on acyl chloride
pair of electrons transfer to Oxygen from C=O
pair of electrons on oxygen return to reform double bond and chlorine is kicked off w electrons from C-Cl transfered to it making it negative
leaving positively charged amide ion and negatively charged chloride ion
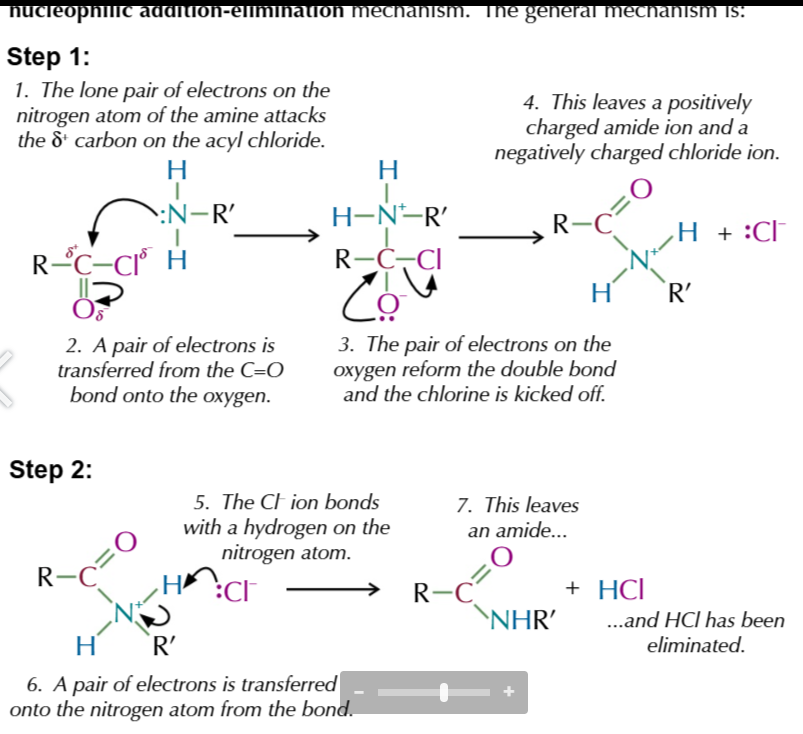
nucleophilic addition elemination reaction part 2
Cl- bonds w hydrogen from nutrogen aotm
pair of electrons transfered onto nitrogen atom from the bond
this names amide and HCl
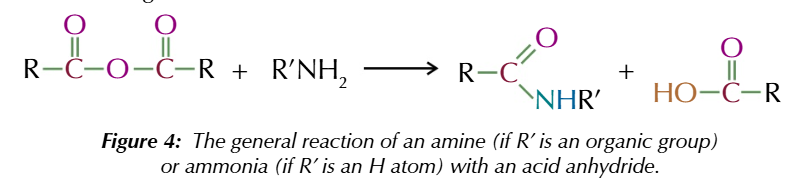
acid anhydrides also react w primary amines/ ammonia to form
amides and carboxylic acid
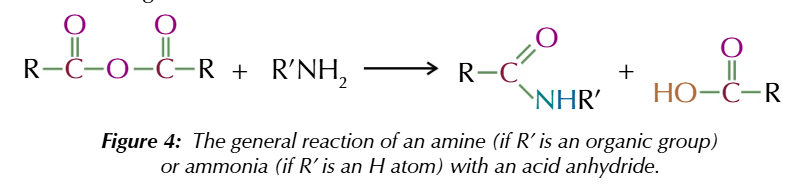
acid anhydrides + primary amines forms
n substituted amides
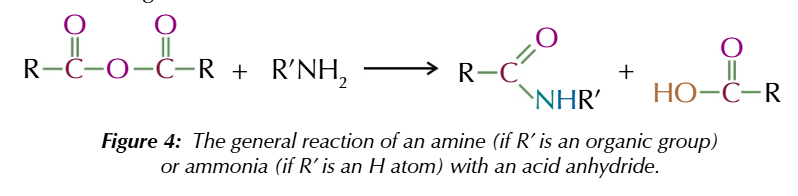
acid anhydride + ammonia forms
primary amide
reducing nitro compounds like nitrobenzene forms
aromatic amines
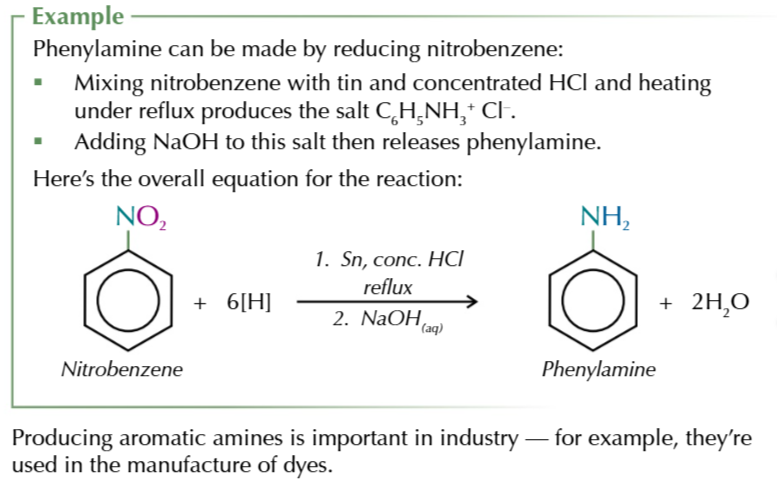
methodology
nitrobenze + tin + conc HCl is reated under reflux to form salt
salt is turned into an aromatic amine, using sodium hydroxide solution