diseases of the orbit
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What makes up the medial wall of the orbit?
1. maxilla
2. lacrimal
3. ethmoid
4. sphenoid
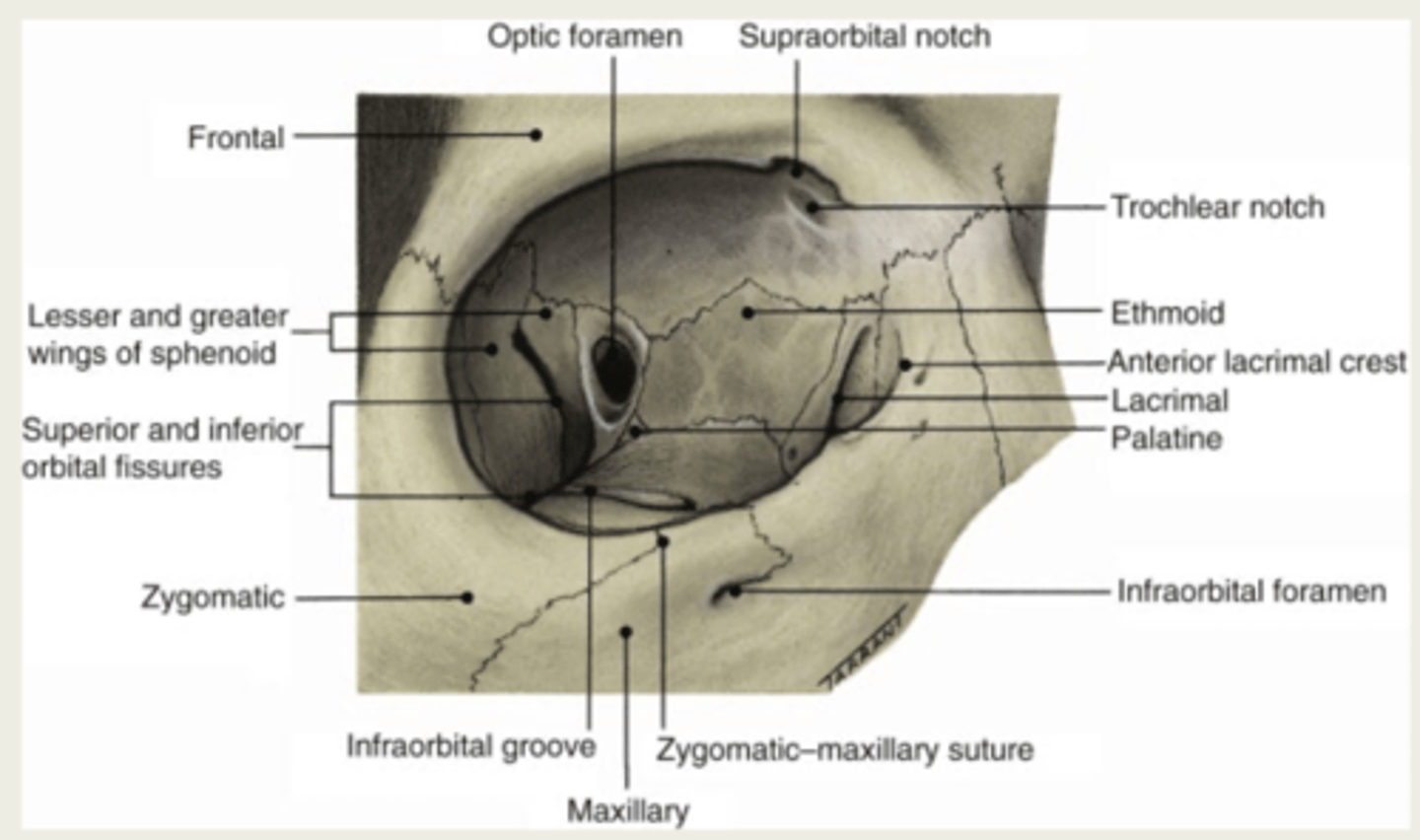
What makes up the floor of the orbit?
1. maxillary
2. palatine
3. zygomatic
What makes up the roof of the orbit?
1. frontal bone
2. lesser wing of the sphenoid bone
What makes up the temporal wall of the orbit?
1. zygomatic
2. greater wing of sphenoid
What is orbital myositis?
inflammation of the EOMs
Who gets orbital myositis? what age?
females in their 30s
What are the symptoms of orbital myositis?
1. pain with eye movement
2. diplopia
What is the presentation of orbital myositis?
1. lid edema and ptosis
2. proptosis
3. chemosis
4. injection over affected muscle
5. restricted motility
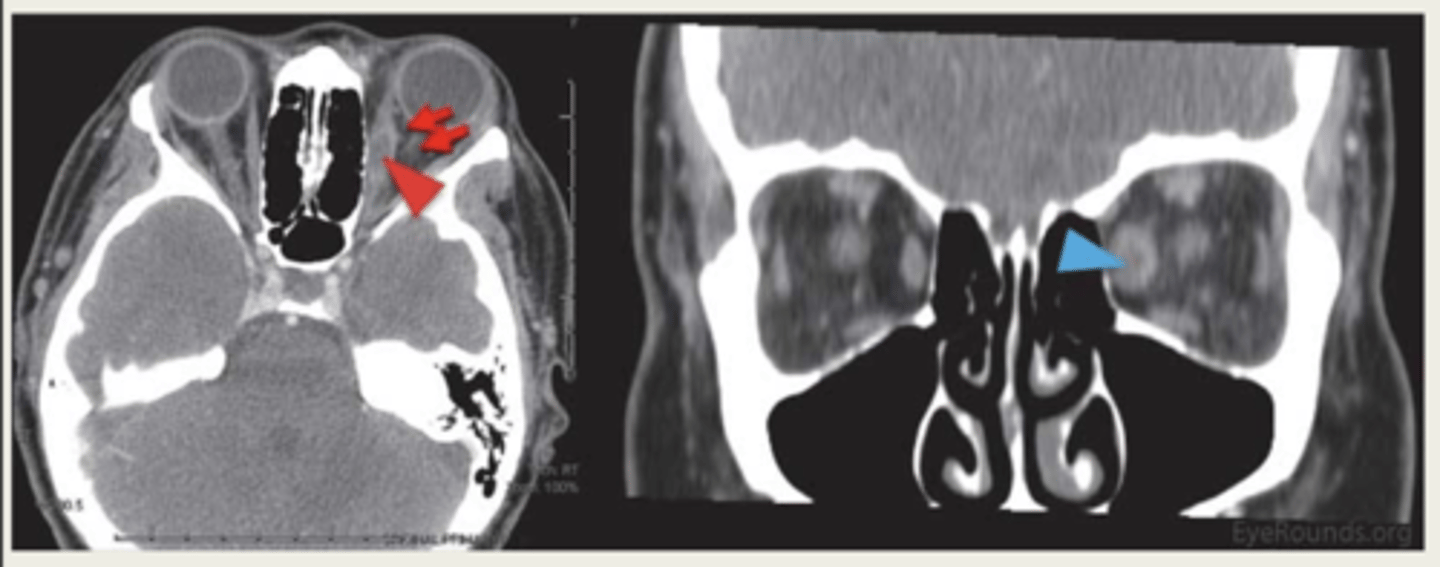
What is the work up for orbital myositis?
MRI or CT scan
What is the treatment for orbital myositis?
1. oral NSAIDs (mild)
2. oral steroids (severe)
What causes an orbital fracture?
blunt trauma
What are the types of orbital fractures?
1. orbital floor (48%)
2. medial wall
force is displaced inferior and transmits energy from impact
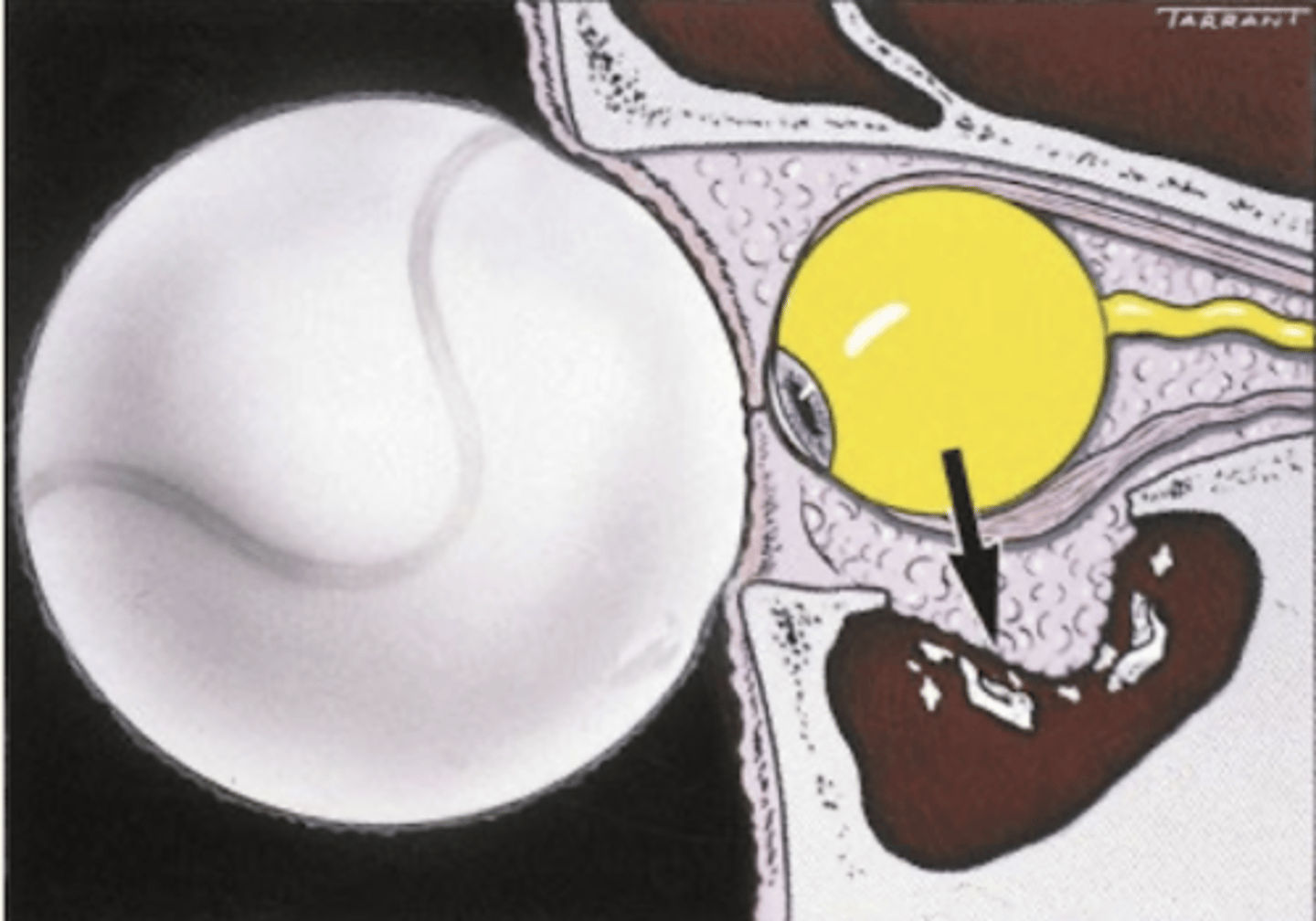
What is the presentation of an orbital floor fracture?
1. lid bruising and edema
2. subcutaneous crepitus (crackling)
3. anesthesia of infraorbital nerve
4. limited IR & IO motility
5. bone step-off
6. proptosis
7. enophthalmos (if severe) - posterior displacement
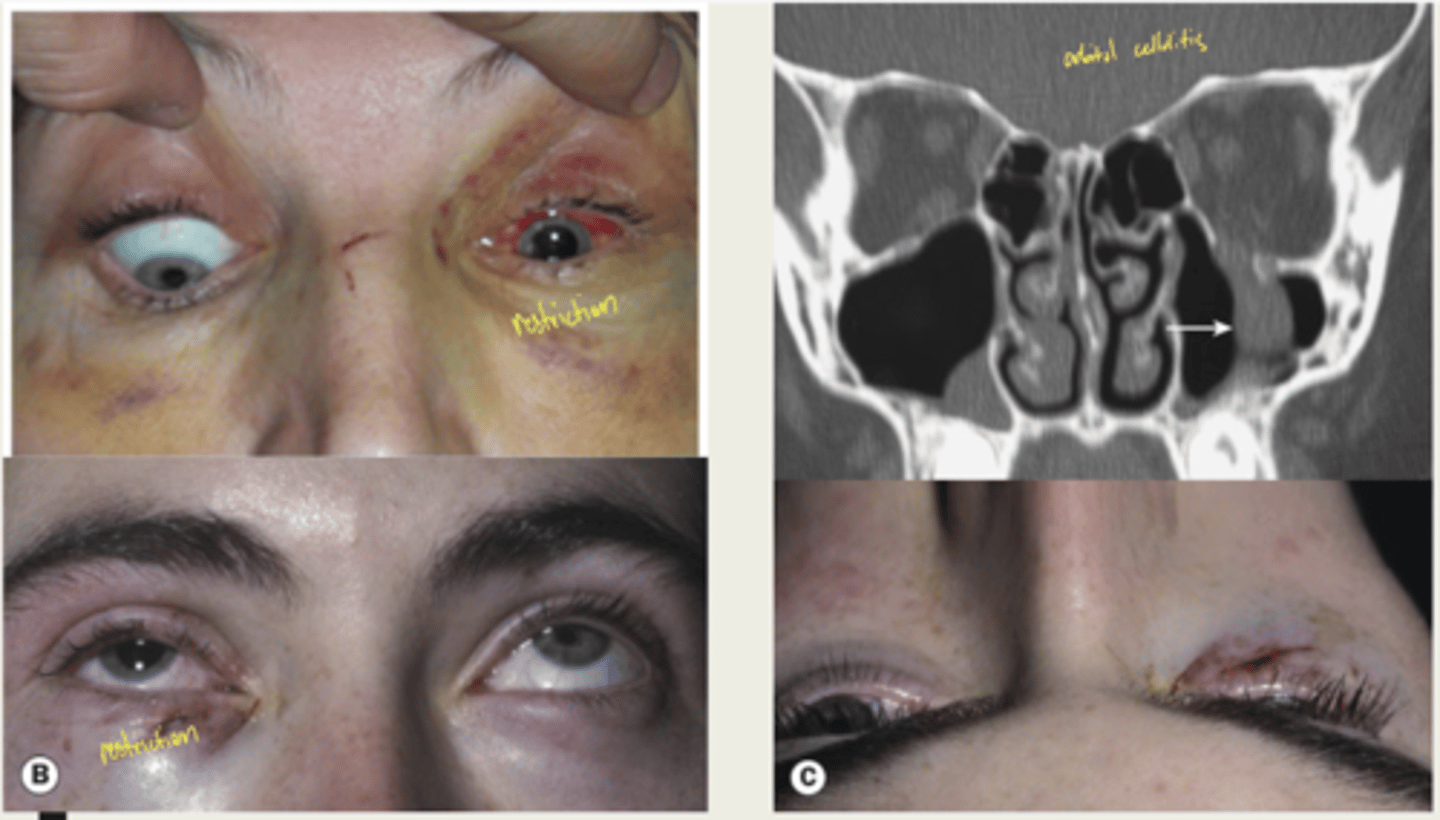
What is the presentation of orbital medial wall fractures?
1. periorbital bruising
2. subcutaneous crepitus (crackling)
3. medial rectus entrapment, limited adduction
4. CSF rhinorrhea
What is the workup for an orbital fracture?
CT scan
What is the treatment for an orbital fracture?
1. nasal decongestants - no blowing nose (orbital cellulitis)
2. systemic abx
3. systemic steroids (severe edema)
4. surgical repair
What is an intraorbital foreign body?
foreign body inside orbit but outside globe
What causes an intraorbital foreign body?
high velocity injury
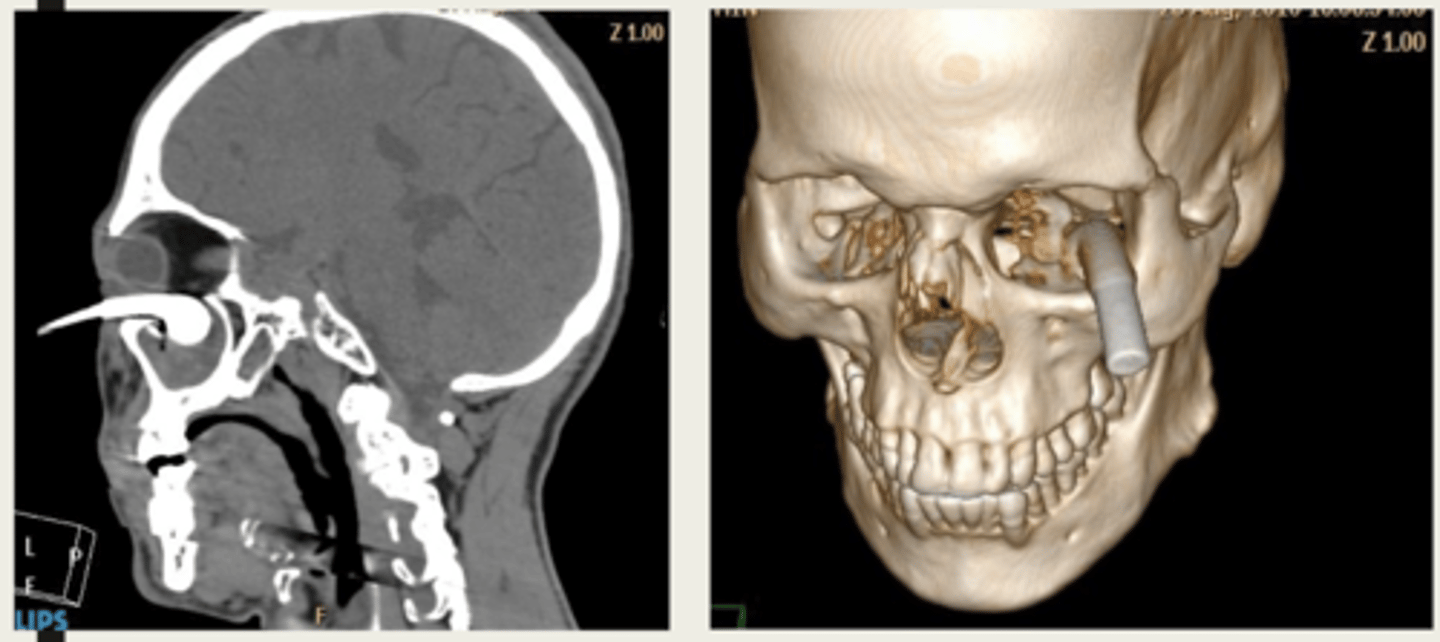
What is the presentation of intraorbital foreign body?
orbital mass:
1. proptosis if mass is large
2. ptosis if mass is superior
3. restricted EOM movement if mass is near EOM
What is the workup for infraorbital foreign body?
CT scan or MRI (no metal)
What is the treatment for an intraorbital foreign body?
observe if small and deep
1. tetanus prophylaxis
2. oral abx
3. surgery
What is an intraocular foreign body?
foreign body in globe
What causes an intraocular foreign body?
metal from metal tasks
What is the presentation of a scleral entry intraocular foreign body?
depends on entry and foreign body:
1. scleral - may lead to deep anterior chamber
2. corneal - corneal edema & a positive Seidel sign
3. iris - transillumination defect & heterochromia
What is the presentation of a corneal entry intraocular foreign body?
corneal edema @ entry site
+ or - Seidel sign
What is the presentation of iris entry intraocular foreign body?
transillumination
heterochromia
peaked pupil (peaked toward entry site)
What is the presentation of EOM entry intraocular foreign body?
restriction
What is the presentation of an anterior chamber entry (corneal) intraocular foreign body?
focal corneal edema over foreign body
What is the presentation of a lens entry intraocular foreign body?
focal lens opacities
What is the presentation of a retinal entry intraocular foreign body?
FB rests on retina
What are the complications seen with an intraocular foreign body?
1. endophthalmitis
2. vitreous heme
3. retinal detachment
4. corneal scar
5. cataract
6. glaucoma
7. sympathetic ophthalmitis
8. siderosis bulbi
9. chalicosis
What is siderosis bulbi caused by?
retained foreign body containing iron
the pigmentary, degenerative process of the eye following chronic retention of an iron-containing intraocular foreign body (IOFB)

What is the presentation of siderosis bulbi?
the pigmentary, degenerative process of the eye following chronic retention of an iron-containing intraocular foreign body (IOFB)
iris heterochromia
mydriasis
cataract
glaucoma
retinal pigment changes

What is a complication of siderosis bulbi ??
irreversible blindness
What is chalcosis due to?
retained foreign body containing copper
What is the presentation of chalcosis?
1. chronic endophthalmitis
2. sunflower cataract
3. blue-green deposits on descemets
4. copper particles in anterior chamber
5. reversible retinal toxicity
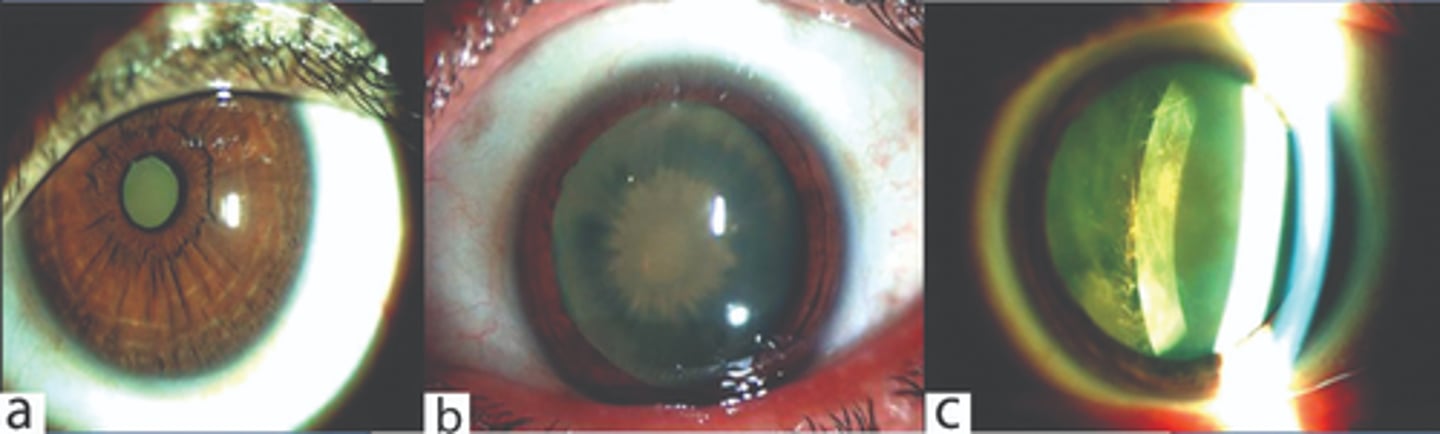
What is the workup for an intraocular foreign body?
CT or MRI (no MRI if metallic!)
What is the treatment for intraocular foreign body?
1. FB removed within 24 hours
2. systemic abx
3. surgical removal
What is phthisis bulbi?
shrinkage and disorganization of the eye, resulting in loss of function
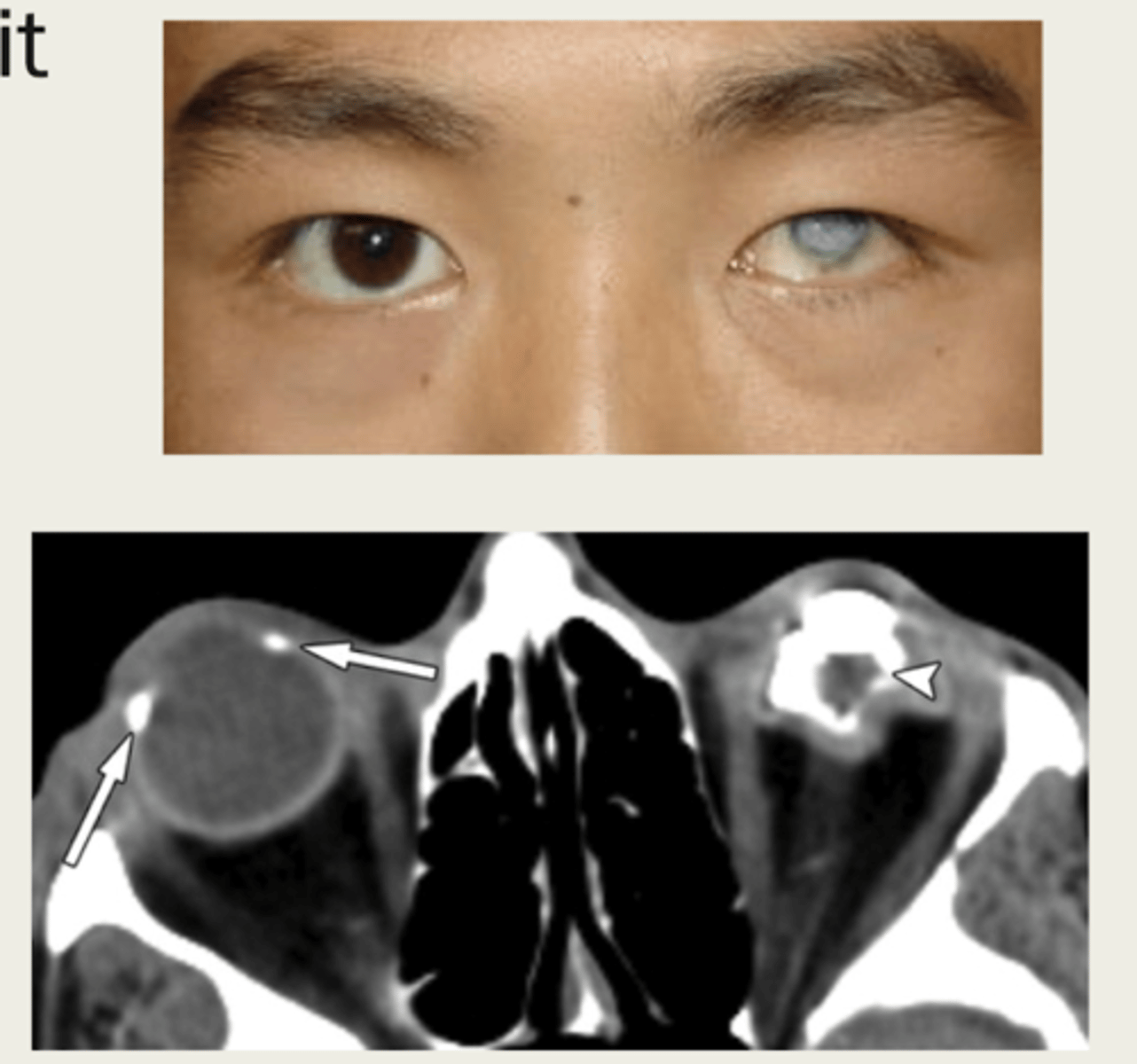
What causes phthisis bulbi?
1. trauma
2. infection
3. malignancy
4. retinal detachment
5. vascular lesion
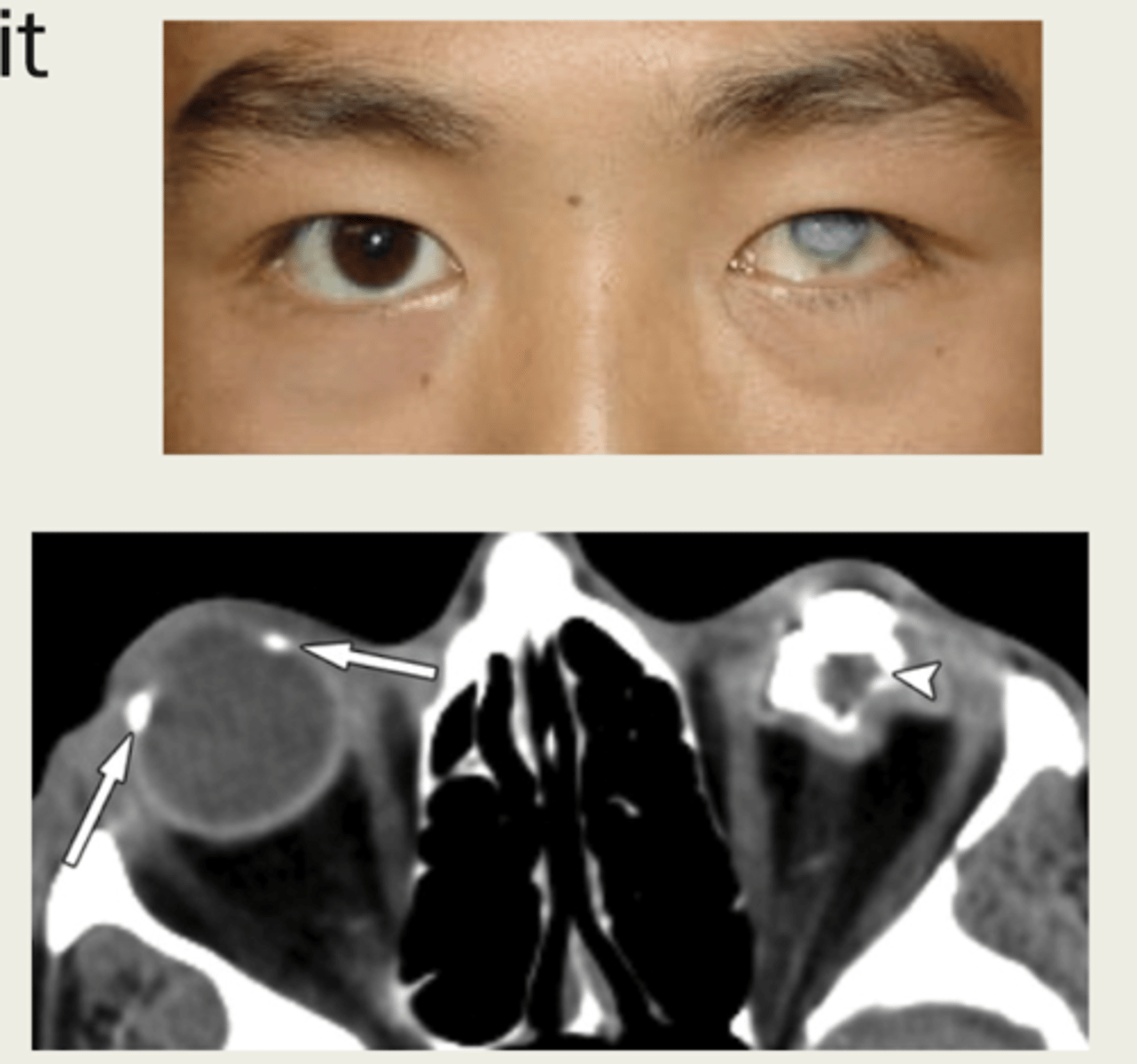
What is the presentation of phthisis bulbi?
1. square shaped eye
2. thick & opaque cornea that you cannot see through
3. iris neovascularization
4. scleral thickening
5. cataract
6. retina detachment

What is the treatment for phthisis bulbi?
1. prosthetic
2. pain management