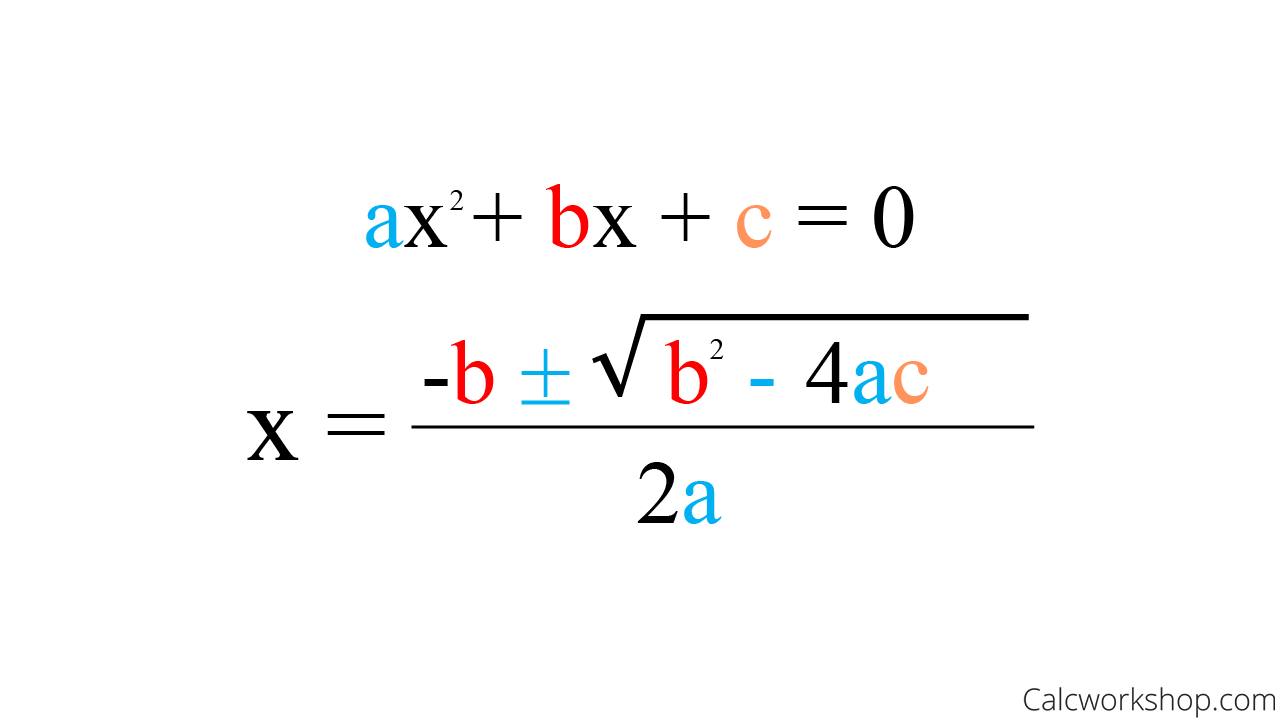Chem 1312, Exam 1
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Molarity
mol solute / L solution
Molality
(moles of solute) / (kg of solvent)
Mole Fraction
(# moles solute) / (Total # of moles)
Mass Percent
(Mass of solute) / (Mass of solution) x100
Henry’s Law
C = kP
where C: concentration of the dissolved gas
P: partial pressure of the gaseous solute
Raoult’s Law (vapor pressure)
Psolution = Xsolvent . P*vapor pressure of pure solvent
if they ask for 2 just add the results together
Boiling Point Elevation
changeT = Kbmsolute
Freezing Point Depression
changeT = Kfmsolute
Osmotic Pressure
piosmotic p = MRT
R: 0.08206
T in kelvin
i
(moles of particles in solution) / (moles of solute dissolved)
rate
(over the same temperature)
[A]t2 - [A]t1 / t2 - t1 = k[A]n
Order of reaction
n + m + l ….
Arrehenius Equation for 1
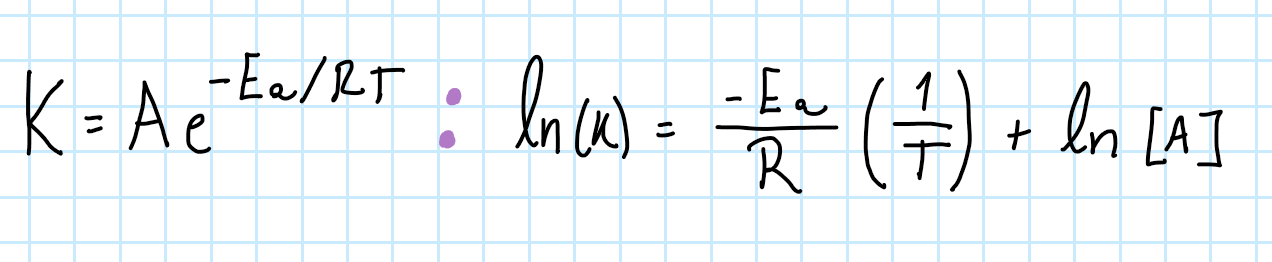
Arrehenius Equation for 2
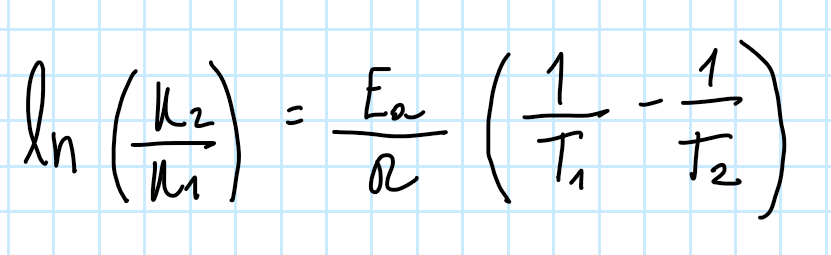
0 order Rate Law
Rate = k
[A] = -kt + [A]0
T1/2 = [A]0 / 2k
units: M/S
![<p>Rate = k</p><p>[A] = -kt + [A]<sub>0</sub></p><p>T<sub>1/2 </sub>= [A]<sub>0</sub> / 2k</p><p>units: M/S</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2281f2b1-6ca3-44a9-aac4-68fa00e03366.png)
1st Order Rate Law
rate = k[A]1
ln[A] = -kT + ln[A]0
T1/2 = 0.693 / k
units: s-1
![<p>rate = k[A]<sup>1</sup></p><p>ln[A] = -kT + ln[A]<sub>0</sub></p><p>T<sub>1/2</sub> = 0.693 / k</p><p>units: s<sup>-1</sup></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3fc7e5f2-e1df-48df-a144-bc1c8a4a7692.png)
2nd Order rate law
rate = k[A]2
1/[A] = kt + 1/[A]0
T1/2 = 1/k[A]0
units: M-1S-1
![<p>rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup></p><p>1/[A] = kt + 1/[A]<sub>0</sub></p><p>T<sub>1/2 </sub>= 1/k[A]<sub>0</sub></p><p>units: M<sup>-1</sup>S<sup>-1</sup></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/520baf2b-5cc0-4a71-be57-84b0e11d8435.png)
K
Equilibium Constant
on a reaction
jA + kB >< lC +mD
the law mass action = picture
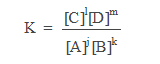
reverse Kc
1/Kc
Kc when there is a coefficient (n) multiplying the equation
Kcn
pressure and concentraiton equation
P = CRT
C: concentration (M)
Equilibrium of Partial Pressure in a gas
Kp
(same as Kc but with partial pressures)
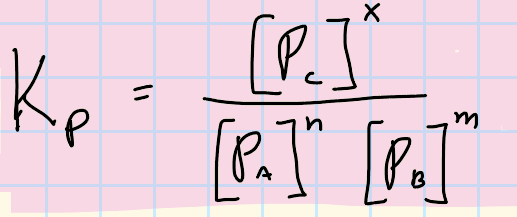
Kc in terms of Kp
K = Kp(RT)-changen
change in n = product coefficients - reactant coefficients
Q = K
Equilibrium
Q > K
shift to the left
consuming products and creating reactants
Q < K
shift to the right
consuming reactants and creating products
I.C.E shift to the right
-x of the reactants
I.C.E shift to the left
-x to the products
Quadratic Formula
x = (-b ± √(b²-4ac)) / (2a)