9 - Microbial Growth (OpenStax - Microbiology)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
1. Which of the following methods would be used to measure the concentration of bacterial contamination in processed peanut butter?
A. turbidity measurement
B. total plate count
C. dry weight measurement
D. direct counting of bacteria on a calibrated slide under the microscope
B. total plate count
2. In which phase would you expect to observe the most endospores in a Bacillus cell culture?
A. death phase
B. lag phase
C. log phase
D. log, lag, and death phases would all have roughly the same number of endospores.
A. death phase
3. During which phase would penicillin, an antibiotic that inhibits cell-wall synthesis, be most effective?
A. death phase
B. lag phase
C. log phase
D. stationary phase
C. log phase
4. Which of the following is the best definition of generation time in a bacterium?
A. the length of time it takes to reach the log phase
B. the length of time it takes for a population of cells to double
C. the time it takes to reach stationary phase
D. the length of time of the exponential phase
B. the length of time it takes for a population of cells to double
5. What is the function of the Z ring in binary fission?
A. It controls the replication of DNA.
B. It forms a contractile ring at the septum.
C. It separates the newly synthesized DNA molecules.
D. It mediates the addition of new peptidoglycan subunits.
B. It forms a contractile ring at the septum.
6. If a culture starts with 50 cells, how many cells will be present after five generations with no cell death?
A. 200
B. 400
C. 1600
D. 3200
C. 1600
7. Filamentous cyanobacteria often divide by which of the following?
A. budding
B. mitosis
C. fragmentation
D. formation of endospores
C. fragmentation
8. Which is a reason for antimicrobial resistance being higher in a biofilm than in free-floating bacterial cells?
A. The EPS allows faster diffusion of chemicals in the biofilm.
B. Cells are more metabolically active at the base of a biofilm.
C. Cells are metabolically inactive at the base of a biofilm.
D. The structure of a biofilm favors the survival of antibiotic resistant cells.
C. Cells are metabolically inactive at the base of a biofilm.
9. Quorum sensing is used by bacterial cells to determine which of the following?
A. the size of the population
B. the availability of nutrients
C. the speed of water flow
D. the density of the population
D. the density of the population
10. Which of the following statements about autoinducers is incorrect?
A. They bind directly to DNA to activate transcription.
B. They can activate the cell that secreted them.
C. N-acylated homoserine lactones are autoinducers in gram-negative cells.
D. Autoinducers may stimulate the production of virulence factors.
A. They bind directly to DNA to activate transcription.
11. An inoculated thioglycolate medium culture tube shows dense growth at the surface and turbidity throughout the rest of the tube. What is your conclusion?
A. The organisms die in the presence of oxygen
B. The organisms are facultative anaerobes.
C. The organisms should be grown in an anaerobic chamber.
D. The organisms are obligate aerobes.
B. The organisms are facultative anaerobes.
12. An inoculated thioglycolate medium culture tube is clear throughout the tube except for dense growth at the bottom of the tube. What is your conclusion?
A. The organisms are obligate anaerobes.
B. The organisms are facultative anaerobes.
C. The organisms are aerotolerant.
D. The organisms are obligate aerobes.
A. The organisms are obligate anaerobes.
13. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common pathogen that infects the airways of patients with cystic fibrosis. It does not grow in the absence of oxygen. The bacterium is probably which of the following?
A. an aerotolerant anaerobe
B. an obligate aerobe
C. an obligate anaerobe
D. a facultative anaerobe
B. an obligate aerobe
14. Streptococcus mutans is a major cause of cavities. It resides in the gum pockets, does not have catalase activity, and can be grown outside of an anaerobic chamber. The bacterium is probably which of the following?
A. a facultative anaerobe
B. an obligate aerobe
C. an obligate anaerobe
D. an aerotolerant anaerobe
D. an aerotolerant anaerobe
15. Why do the instructions for the growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae recommend a CO2-enriched atmosphere?
A. It uses CO2 as a final electron acceptor in respiration.
B. It is an obligate anaerobe.
C. It is a capnophile.
D. It fixes CO2 through photosynthesis.
C. It is a capnophile.
16. Bacteria that grow in mine drainage at pH 1-2 are probably which of the following?
A. alkaliphiles
B. acidophiles
C. neutrophiles
D. obligate anaerobes
B. acidophiles
17. Bacteria isolated from Lake Natron, where the water pH is close to 10, are which of the following?
A. alkaliphiles
B. facultative anaerobes
C. neutrophiles
D. obligate anaerobes
A. alkaliphiles
18. In which environment are you most likely to encounter an acidophile?
A. human blood at pH 7.2
B. a hot vent at pH 1.5
C. human intestine at pH 8.5
D. milk at pH 6.5
B. a hot vent at pH 1.5
19. A soup container was forgotten in the refrigerator and shows contamination. The contaminants are probably which of the following?
A. thermophiles
B. acidophiles
C. mesophiles
D. psychrotrophs
D. psychrotrophs
20. Bacteria isolated from a hot tub at 39 °C are probably which of the following?
A. thermophiles
B. psychrotrophs
C. mesophiles
D. hyperthermophiles
C. mesophiles
21. In which environment are you most likely to encounter a hyperthermophile?
A. hot tub
B. warm ocean water in Florida
C. hydrothermal vent at the bottom of the ocean
D. human body
C. hydrothermal vent at the bottom of the ocean
22. Which of the following environments would harbor psychrophiles?
A. mountain lake with a water temperature of 12 °C
B. contaminated plates left in a 35 °C incubator
C. yogurt cultured at room temperature
D. salt pond in the desert with a daytime temperature of 34 °C
A. mountain lake with a water temperature of 12 °C
23. Which of the following is the reason jams and dried meats often do not require refrigeration to prevent spoilage?
A. low pH
B. toxic alkaline chemicals
C. naturally occurring antibiotics
D. low water activity
D. low water activity
24. Bacteria living in salt marshes are most likely which of the following?
A. acidophiles
B. barophiles
C. halotolerant
D. thermophiles
C. halotolerant
25. EMB agar is a medium used in the identification and isolation of pathogenic bacteria. It contains digested meat proteins as a source of organic nutrients. Two indicator dyes, eosin and methylene blue, inhibit the growth of gram-positive bacteria and distinguish between lactose fermenting and nonlactose fermenting organisms. Lactose fermenters form metallic green or deep purple colonies, whereas the nonlactose fermenters form completely colorless colonies. EMB agar is an example of which of the following?
A. a selective medium only
B. a differential medium only
C. a selective medium and a chemically defined medium
D. a selective medium, a differential medium, and a complex medium
D. a selective medium, a differential medium, and a complex medium
26. Haemophilus influenzae must be grown on chocolate agar, which is blood agar treated with heat to release growth factors in the medium. H. influenzae is described as ________.
A. an acidophile
B. a thermophile
C. an obligate anaerobe
D. fastidious
D. fastidious
27. Match the definition with the name of the growth phase in the growth curve.
___Number of dying cells is higher than the number of cells dividing
___Number of new cells equal to number of dying cells
___New enzymes to use available nutrients are induced
___Binary fission is occurring at maximum rate
A. Lag phase
B. Log phase
C. Stationary phase
D. Death phase
27. D, C, A, B
28. Four tubes are illustrated with cultures grown in a medium that slows oxygen diffusion. Match the culture tube with the correct type of bacteria from the following list: facultative anaerobe, obligate anaerobe, microaerophile, aerotolerant anaerobe, obligate aerobe.
28. (a) obligate anaerobe, (b) obligate aerobe, (c) microaerophile, (d) facultative anaerobe
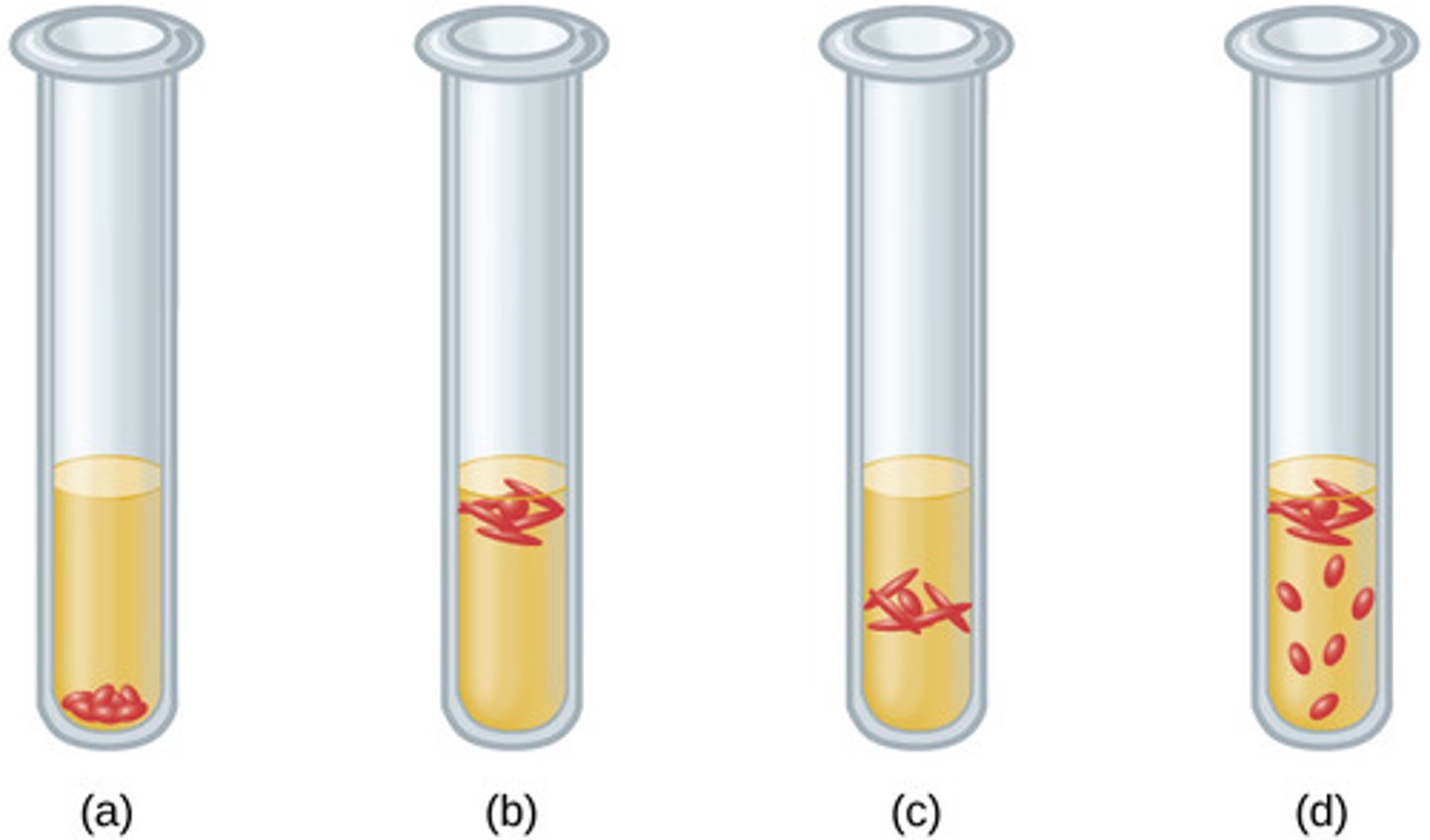
29. Match the type of bacterium with its environment. Each choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Put the appropriate letter beside the environment.
___psychotroph
___mesophile
___thermophile
___hyperthermophile
___psychrophile
A. food spoiling in refrigerator
B. hydrothermal vent
C. deep ocean waters
D. human pathogen
E. garden compost
29. A, D, E, B, C
30. Direct count of total cells can be performed using a ________ or a ________.
hemocytometer, Petroff-Hausser counting chamber
31. The ________ method allows direct count of total cells growing on solid medium.
plate count
32. A statistical estimate of the number of live cells in a liquid is usually done by ________.
most probable number
33. For this indirect method of estimating the growth of a culture, you measure ________ using a spectrophotometer.
turbidity
34. Active growth of a culture may be estimated indirectly by measuring the following products of cell metabolism: ________ or ________.
ATP, acid from fermentation
35. A bacterium that thrives in a soda lake where the average pH is 10.5 can be classified as a(n) ________.
alkaliphile
36. Lactobacillus acidophilus grows best at pH 4.5. It is considered a(n) ________.
acidophile
37. A bacterium that thrives in the Great Salt Lake but not in fresh water is probably a ________.
halophile
38. Bacteria isolated from the bottom of the ocean need high atmospheric pressures to survive. They are ________.
barophiles
39. Staphylococcus aureus can be grown on multipurpose growth medium or on mannitol salt agar that contains 7.5% NaCl. The bacterium is ________.
halotolerant
40. Blood agar contains many unspecified nutrients, supports the growth of a large number of bacteria, and allows differentiation of bacteria according to hemolysis (breakdown of blood). The medium is ________ and ________.
complex, differential
41. Rogosa agar contains yeast extract. The pH is adjusted to 5.2 and discourages the growth of many microorganisms; however, all the colonies look similar. The medium is ________ and ________.
complex, selective