Intrscellular accumulation and Pathological Calcification/ Causes of cell injury
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lect 2 pt 2/3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Intracellular Accumulations
The buildup of various substances inside cells that cant immediately be used or eliminated
Can be temp or permanent
Mechanisms of intracellular accumulations
Excessive production of endogenous substance
Impaired removal of endogenous substances
Abnormal disposition of exogenous substances
Excessive production of endogenous substance
Substances that originate from within the body
Ex: Steatosis
Steatosis
Abnormal intracellular accumulation of triglycerides (fat) in the cytoplasm of the hepatocytes (cells in the liver)
Result of excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption
Condition is reversible after stoppage of consumption
Signat ring
Impaired removal of endogenous substances
Can occur in people with genetic or acquired disorders that disrupt metabolism
Ex : Von Gierke disease
Von Gierk Disease
Large amounts of glycogen accumulate in the liver and kidneys, reduction in blood glucose levels resulting in weakness and stunted growth '
Diagnosed between 3-6 months
Most common form of glycogen storage disorders
Abnormal disposition of exogenous substances
Can occur in people who are exposed to heavily polluted environments
Ex: Coal workers Pneumoconiosis
Coal workers Pneumoconiosis
Macrophages lining the alveoli engulf coal dust and release cytokines that stimulate inflammation of the surrounding tissues
Include distortion of the lung architecture (scarring) and airflow obstruction
Lungs look black instead of pink- "Black lung disease”
Pathologic Calcification
Refers to the deposition of calcium salts, along with smaller amounts of iron, mag, and other minerals, in tissues other than where they are normally found (bones/teeth)
Alt name: Heterotypic calcification
Forms of Pathologic Calcification:
Dystrophic
Metastatic
Dystrophic Calcification
Abnormal deposition of calcium salts in injured, dying, or dead tissue despite normal blood levels of calcium
Seen in damaged heart valves or arterial walls
Appear macroscopically as fine, white clumps and feels gritty
Metastatic Calcification
Abnormal deposition of calcium salts in normal tissue following elevated blood levels of calcium (Hypercalcemia)
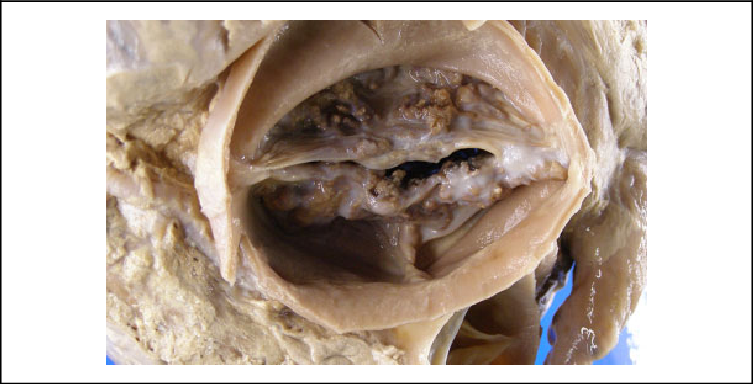
What calcification is this?
Dystrophic
Causes of hypercalcemia:
Destruction of bone tissue due to tumors of the bone marrow or following prolonged immobilization
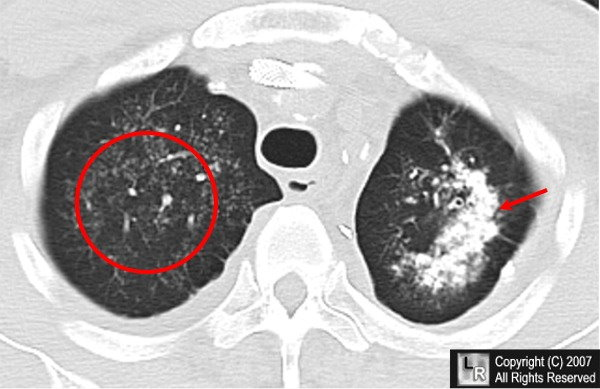
What calcification is this?
Metastatic
Cell Injury: Exposure of physical agents
Mechanical trauma can tear soft tissue, fract bones and injure blood vessels
Extreme heat can damage cell mem and other structures, accelerate cell metabolism, etc
Extreme cold can induce vasoconstriction, which deprives tissues of oxygen
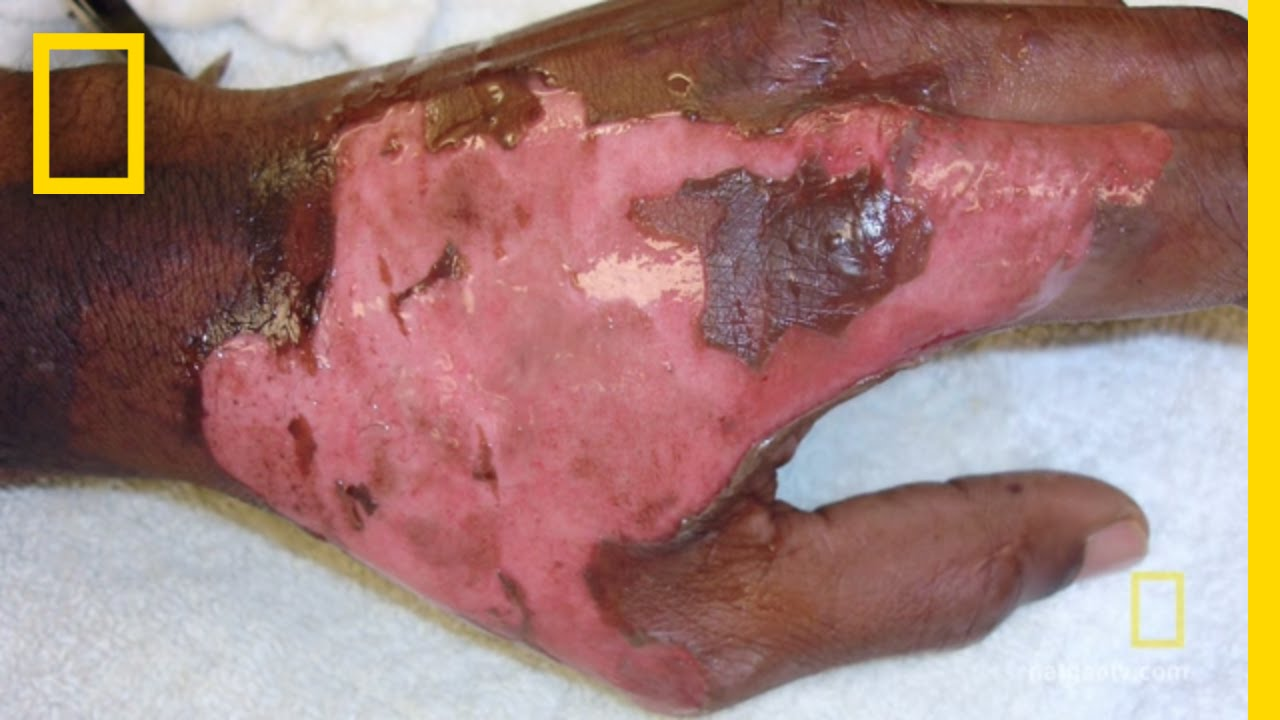
What example of cell injury is this?
Exposure of physical agents
Electrical burn
Cell Injury: Exposure to radiation
Ionizing radiation incudes high energy waves (gamma rays, X rays)
Can kill cells immediately or interrupt cell division by interfering with DNA synthesis)
Non-ionizing radiation includes low energy waves (visible light, microwaves)
Can cause sunburn, increase the risk of skin cancer depending on exposure and melanin in the skin
Rarely has a big effect
Cell Injury: Exposure to chemicals
Strong acids/bases can injure cell and other structures
Led exposure can interfere with brain development in children
Mercury exposure can result in neurotoxicity, manifesting as slurred speech, tremors and paralysis
Cell Injury: Exposure to biologic agents
Viruses, bacteria, fungi
Can replicate inside humans and continue their damaging effect until adequately treated
Viruses can enter cell and damage DNA
Bacteria release toxins that can interfere with cellular ATP production
Fungi can cause an immune response, resulting in hypersensitivity (allergic) reactions
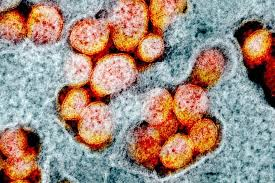
What example of cell injury is this?
Exposure to biologic agents
Cell Injury: Nutritional Imbalances
Both nutritional excesses and deficiencies predisposed cells to injury
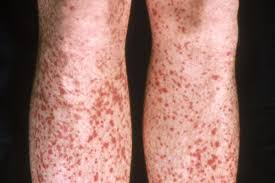
What is this?
Petechiae
(Puh-tee-key-uh)
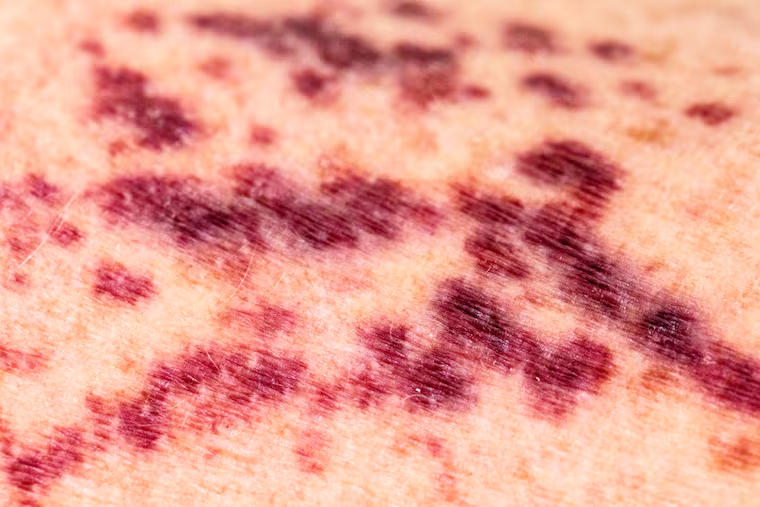
What is this?
Purpura
(pur-pry-uh)