Biology - B4 Using food and controlling growth
0.0(0)Studied by 2 people
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
OCR GCSE (excluding microscopy)
Last updated 6:58 PM on 3/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
Respiration
the process of transferring energy from breaking down glucose. It happens continuously in every cell in every living organism. (Glucose is typically used but other substances such as carbohydrates, lipids and proteins can be used instead)
2
New cards
ATP
energy from respiration cannot be directly used so it is turned into this which stores energy that is used for essential processes like making and breaking molecules, active transport and contracting muscles.
3
New cards
Cellular respiration
A process which includes several different chemical reactions that are controlled by enzymes so are effected by temperature and pH and is exothermic
4
New cards
Aerobic respiration
This happens when there is plenty of oxygen and is the most efficient way of producing ATP - 32 molecules per molecule of glucose. Takes place in the mitochondria of Eukaryotic cells and the cytoplasm of prokaryotic

5
New cards

Respiration rate (practical)
6
New cards
Anaerobic respiration
This occurs when there is very little oxygen in the cytoplasm of animal and plant cells. It produces 2 molecules of ATP. In animals it happens in muscle cells and root hair cells in plants. Animals turn glucose to lactic acid and plants, glucose to ethanol and CO2
7
New cards
Interphase
This is the process before the beginning of mitosis where the DNA is copied and makes an x shaped chromosome (to identical arms)
8
New cards
Prophase
The first phase of mitosis. The DNA increase in size and becomes more visible.
9
New cards
Metaphase
The second phase of mitosis. The chromosomes and their copies move to the centre of the cell.
10
New cards
Anaphase
The third phase of mitosis. chromosomes and their copies are pulled to opposite sides of the cell.
11
New cards
Telophase
The final phase of mitosis. Membrane begins to reform around the chromosomes at each end of the cell
12
New cards
Cytokinesis
The phase following mitosis where the cell splits into two daughter cells.
13
New cards
Estimate the number of cells
Number of cells = 2^n where ‘n’ is the number of divisions
14
New cards
Cancer
This can be caused by uncontrolled cell divisions
15
New cards
Sexual reproduction
This is where two sets of genetic information is used to create offspring
16
New cards
gamete
These contain half the amount of chromosomes and are used in sexual reproduction
17
New cards
diploid cell
a cell that contains two sets of chromosomes
18
New cards
haploid cell
a cell that contains one set of chromosomes
19
New cards
Zygote
A fertilized egg
20
New cards
Fertilisation
When a male gamete fertilizes a female gamete. This creates a full set of chromosomes.
21
New cards
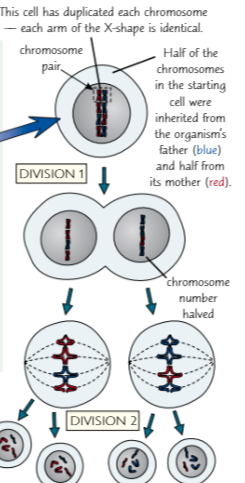
Meiosis
This is a process where the cell divides twice to create 4 daughter, haploid cells. The information splits then so does the cells
22
New cards
Stem cells
These are unspecialized cells that are all the same. They can differentiate to any type of cell. Embryonic ones can specialize into anything but adult ones are only found in the bone marrow and can only differentiate into certain types of cells
23
New cards
Meristems
These are plant stem cells that are found in the roots and shoots and can specialize into anything for as long as the plants live
24
New cards
Adult stem cells
These can be used in medicine by being transferred to a patient to replace cells that are damaged in some way. However these could cause tumors as they divide quickly or illness if the transplanted cells host a disease.
25
New cards
Embryonic stem cells
These can be transplanted into patients however its ethically debated because as the embryos are destroyed in the process.
26
New cards
Auxins
These are plant hormones that promote growth in shoots but inhibit it in shoots
27
New cards
Phototropism
Shoots are positively phototrophic which means auxins are produced faster in the shade causing the plants to grow towards the light. Roots are negatively phototrophic which means auxins are produced faster where there is light which causes the roots to grow away from the light
28
New cards
Gravitropism
Shoots are negatively gravitropic because gravity causes and imbalance of auxins in the tip which causes the lower part of the plant to grow faster and therefore growing upwards. Roots are positively gravitropic which means the auxins are more condensed on the higher part of the plant which means the plant grows downwards.
29
New cards
investigating phototropism
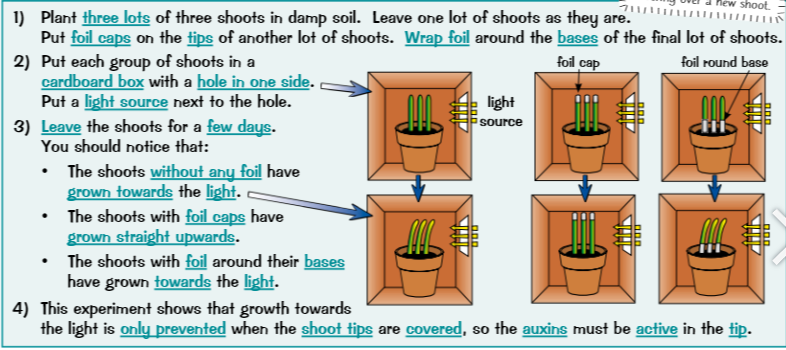
30
New cards
Gibberellins
These are plant hormones that allow plants to germinate and flower. Farmers can use them to allow plants to flower early
31
New cards
Ethene
This is produced by decaying leaves and causes the shedding of leaves and ripening of fruit. This allows farmers to collect their fruit while its unripe and then pump ethne into the vehicle transporting them, causing them to ripen before the supermarket.