Lecture 21 - Fetal Radiation Effects & Cataractogenesis
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 335 - Radiobiology. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is embryogenesis
Embryogenesis is the process by which the embryo forms and develops from fertilization to the formation of critical structures and organ systems
what part of development does embryogenesis cover?
the first 8 weeks
what is the term for the embryo after 9 weeks
fetus
what is a fetus
a prenatal human between the embryonic state and it’s birth
implies that the embryo has developed to to a stage of being recognizable as a human, with the development of major organs and body systems.
3 radiation effects on embryo/fetus
lethal effects
malformations
growth disturbances/retardation
what do radiation effects to embryo/fetus depend on?
dose
dose rate
stage of gestation when irradiated
when are lethal effects (prenatal/neonatal deaths) most common
in the early stages of pregnancy: before or immediatly after implantation
after implantation, do you need more or less dose to cause lethality
more
when are embryo malformations most common
during organogenesis, between weeks 3 and 8 of gestation
when are growth disturbances/retardation most common
can happen at all stages, but particulary later in pregnancy
what is the average human gestation period?
40 weeks / 280 days
what animals do humans have a similar gestation period to?
cattle and bison
what two animals have the longest gestation period
elephants (22 months)
deep sea octopus (4.5 years)
gestation period of mice
19-21 days
gestation period of rats
20-22 days
what is pre-implantation
fertilization w/o attachment to uterus wall
what radiation effect is most common in mice during pre-implantation period after 2 Gy
prenatal death
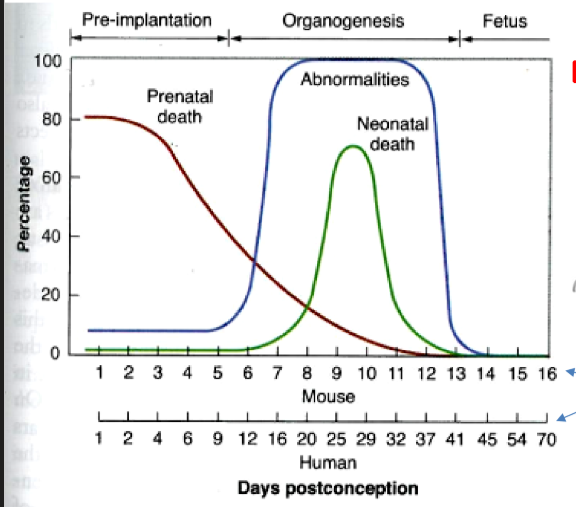
what is organogenesis
period of major organ formation (after implantation)
what two radiation effects are most common in mice during organogenesis period after 2 Gy
abnormalities (most common)
neonatal death
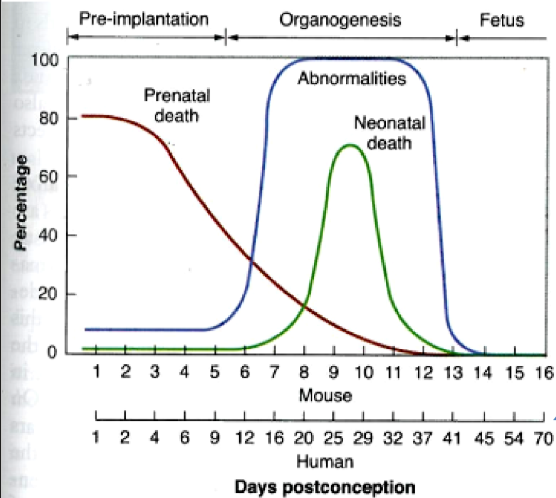
do genetic malformations occur in rats during the pre-implantation stage?
no
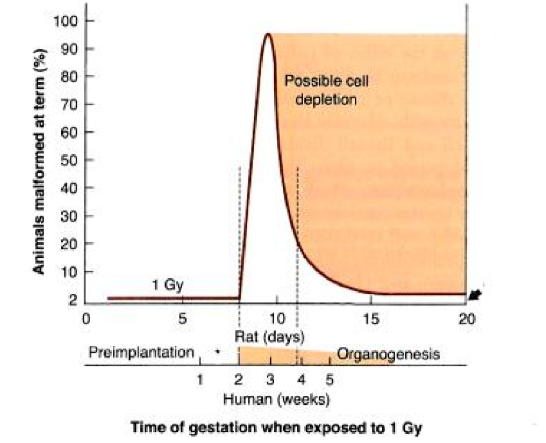
what two reasons explain why we dont see malformations in rats when irradiated in pre-implantation period
embryo does not make it to term
embryo survives as it recovers during organogenesis
in both mice and rats, what is the most radiosensitive period of pregnancy
pre-implantation
does growth retardation and abnormalities occur in radiated pre-implantation
no
either death or survival without malformations.
when will a mouse/rat survive irradiation in the pre-implantation period
if the radiation only damages a few cells as cell division will make up for it
if too many cells affected = death
what is the threshold dose to cause embryonic death in pre-implantation period
100 mGy
what dose causes 100% incidence of congenital anomalies in mice and rats in the organogenesis period
mice = 1 Gy
rats = 2 Gy
what congential anomalies occur in organogenesis period
growth retardation
what is the least radiosensitive period in mouse/rat gestation?
fetal period
high doses needed for effects
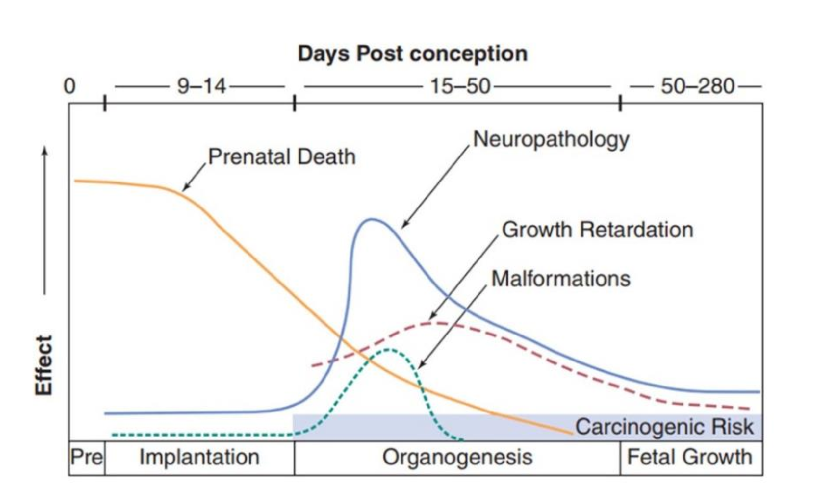
where did we get the data for radiation effects on embryo/fetus in humans?
from atomic bomb survivors
if the bomb went off and the embryo was <4 weeks old, would babies come to term?
no
prenatal death would occur
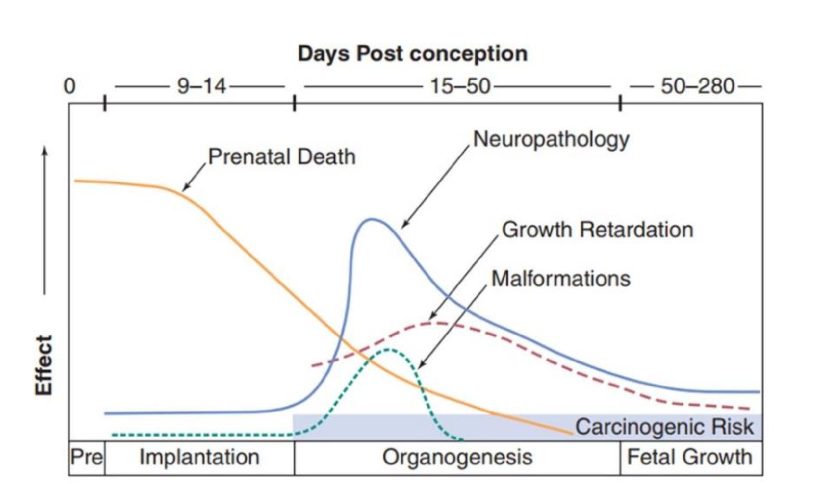
Did birth defects occur in embryos <15 weeks when bomb went off?
no
all or nothing effect
three most common effects to embryos who survived till birth
growth retardation
mental retardation
microcephaly
all later effects
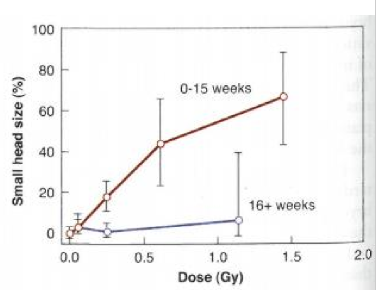
what gestational stage does microcephaly occur
seen in gestational weeks less than 16 weeks
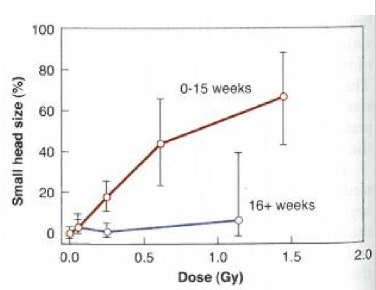
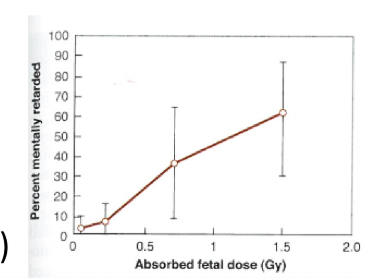
what gestational stage does mental retardation occur
between 8-15 weeks
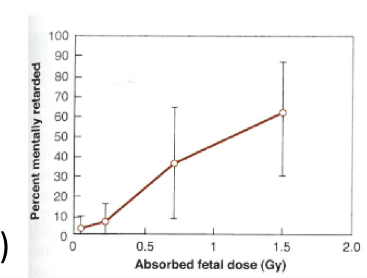
what doses were required for mental retardation and severe mental retardation
normal = 0.1 Gy
severe = 0.3 Gy
list three other defects associated with radiation to human fetus
childhood cancer
cataracts
spina bifida
stochastic effects require damage to a_____ cell
a single cell
deterministic (threshold) effects require damage to ____
multiple cells
severity increases with dose
generally, at what dose do consequences to human embryos and fetuses occur
0.1 Gy

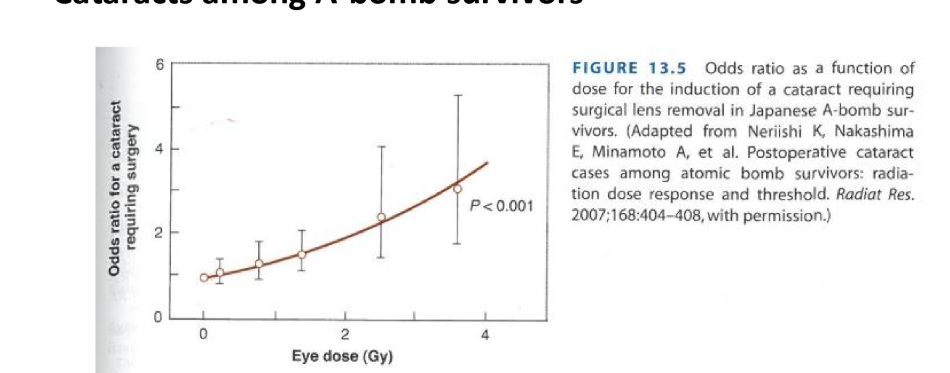
What are cataracts
a clouding of the lens of the eye that decreases visions
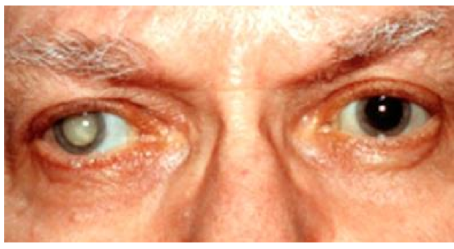
symptoms of cataracts
faded colors, blurry vision, halos around light, trouble seeing in bright or dark environments
what causes radiation induced cataracts
irradiation to transparent lens fibres causes clouding
why are cataracts deterministic effects?
the more radiation = more fibres damaged = more clouding
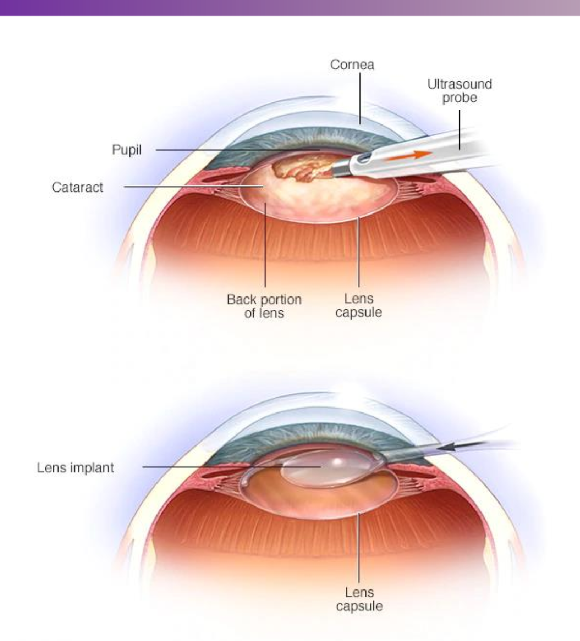
describe the surgery to remove cataracts
ultrasound probe breaks lens and removes it, then a fake lens is put in
when do cataracts normally form
in old age
irradiation speeds up the formation of them
what type of radiation is strong at inducing cataracts
neutrons
where do cataracts most commonly form
the posterior portion of the eye
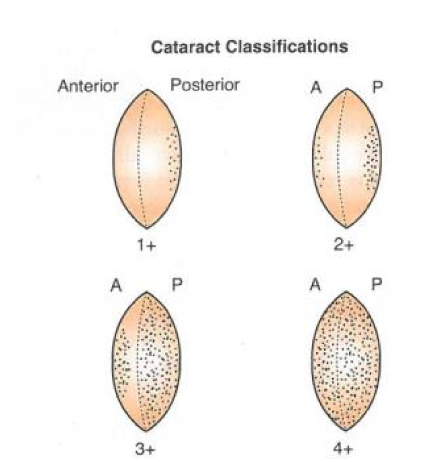
if a person receives a dose of 2.5-6.5 Gy, how long will it take for cataracts to form
8 years
if a person receives a dose of 6.5-11.5 Gy, how long will it take for cataracts to form
4 years
how is the opasity of cataracts measure
with a scheimpflug imaging system
how does a scheimpflug imaging system diagnose cataracts
system captures high-resolution, cross-sectional images of the anterior segment of the eye by using an angled camera and slit-beam illumination to assess lens opacity and diagnose cataracts objectively.
what is the threshold dose for getting cataracts?
2 Gy
threshold deterministic effect