Summative: Cell unit
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Everything that you will need to study is on our topics page for Unit 3. You have completed a few charts for HW and for classwork that you can also use as a study guide. If you would like to create another one and email it to me so I can review it. You can share it with me and I will give you some feedback. Remember: making your study guides are not only helpful to study but also help you review the material and evaluate what are the topics you need to spend more time on.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
cells
forms the part of an organism and carries out all of its functions; the basic unit of structure and function in living things; means “small rooms”; made of water, molecules, and other substances
the cell theory
a common theory explaining how cells and living organisms interact
what the cell theory states
All living things are composed of cells
Cells are the basic units of the structure and function in living things
All cells are produced from other cells
nucleus
a large oval structure; acts as a cell’s control center, directing all of the cell’s activities; the largest of many tiny cell structures; functions in a similar way as the brain
ribosome
small grain-shaped organelles that produce proteins (which are important substances in cells); some dot some parts of the ER, while others float in the cytoplasm; newly made proteins and other substances leave the ER and move to another organelle; made in nucleolus
organelle
tiny cell structures that carry out specific functions within a cell
cytoplasm
a thick, clear, gel-like fluid; fills the region between the cell membrane and the nucleus; its fluid moves constantly within a cell, carrying along the nucleus and other organelles that have specific jobs
organ system
a group of organs that work together to perform a major function
organ
made of different kinds of tissues that function together (such as your brain)
ex: the brain also has blood vessels that carry the blood that supplied oxygen to your brain cells; your brain is part of your nervous system, which directs body activities and processes
tissue
a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function
ex: your brain is made mostly of nerve tissue, which consists of nerve cells that relay information to other parts of your body
unicellular
single-celled organisms
multicellular
means “made of many cells”, cells often look different from one another and they perform different cells
eukaryote
a type of cell that has a nucleus
prokaryote
a type of cell without a nucleus
cell wall
a rigid layer that surrounds the cells; made mostly of a strong material called cellulose; only found in plant cells
function - protects and supports cell
mitochondria
rod-shaped structures that float in the cytoplasm; nicknamed the “powerhouse” of a cell
function - converts energy stored in food to energy that the cell can use to live and function
chloroplast
green structures inside of cytoplasm; makes leaves green because leaf cells contain many; only found in plant cells
function - captures energy from sunlight and changes it to a form of energy cells can use in making food
microscope
an instrument that makes small objects look larger; allows people to look at very small objects; invented around 1590
cell membrane
found in all cells; everything that the cell needs (such as food particles, water, and oxygen) enters through this organelle
function - controls which substances pass into and out of a cell; prevents harmful materials from entering the cell
carbohydrates
energy-rich organic compounds made of the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; found on cell membranes; provides energy, fuels our brains, supports muscle functions
ex: sugar and starch (potatoes, rice, bread, pasta)
DNA
the generic material that carries information about an organism and is passed from parent to offspring; directs a cells’ functions; mostly found in a cell’s nucleus
nucleic acids
very long organic molecules consisting of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorus; carries and stores genetic information; contains instructions for building our bodies; creates chemical code that cells can read
ex: red meat, shellfish, mushrooms, and peas
enzymes
a group of proteins that speeds up chemical reactions in living things
proteins
large organic molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur; forms part of a cell’s membrane; makes up parts if the organelles within a cell; builds and repairs functions; production of enzymes; transports molecules
ex: meat, dairy products, fish, nuts, and beans
Golgi apparatus
looks like flattened sacs and tubes; can be thought of as a cell’s warehouse; receives proteins and other newly formed materials from the ER, packages them, and distributes them to other parts of the cell or to the outside of the cell
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
an organelle with a network of membranes that produces many substances, looks like a maze of passageways, helps the attached ribosomes make proteins
vacuole
a water-filled sac floating in the cytoplasm; usually one or more of this large organelle in a plant cell; stores water, food, or other materials needed by the cell; can also store waste products until the wastes are removed; found in both plant and animal cells but has a bigger role in plant cells
lipids
compounds that are mostly of carbon, hydrogen, and some oxygen; cell membrane consists of mostly this organelle; concentrated source of energy, protects our organs, plays a role in cell structure; speeds up chemical reactions with enzymes
ex: fats, oils, waxes (whole milk, ice cream, and fried food)
double helix
the shape of a DNA molecule; forms from many small molecules connected together; the pattern and sequence in which these molecules connect make a kind of chemical code that the cell can “read”
lysosome
sac-like organelles which contain substances that break down large food particles into smaller ones; also breaks down old cell parts and releases the substances so they can be used again; called a cell’s “recyling center”; only found in animal cells
Robert Hooke
named cells after “small rooms” while observing a thin piece of cork
Antony van Leewenhoek
observed one-celled moving organisms called “animalcules”
Matthias Schleiden
concluded that all plants are made of cells
Theodor Schwann
concluded that all animals are made of cells
Rudolph Virchow
proposed that “all living cells come from other living cells”
cells vs organisms
both are living; have similar necessities such as food, water, and living space, both get rid of wastes and excess water; cells can be unicellular or multicellular but all organisms are multicellular
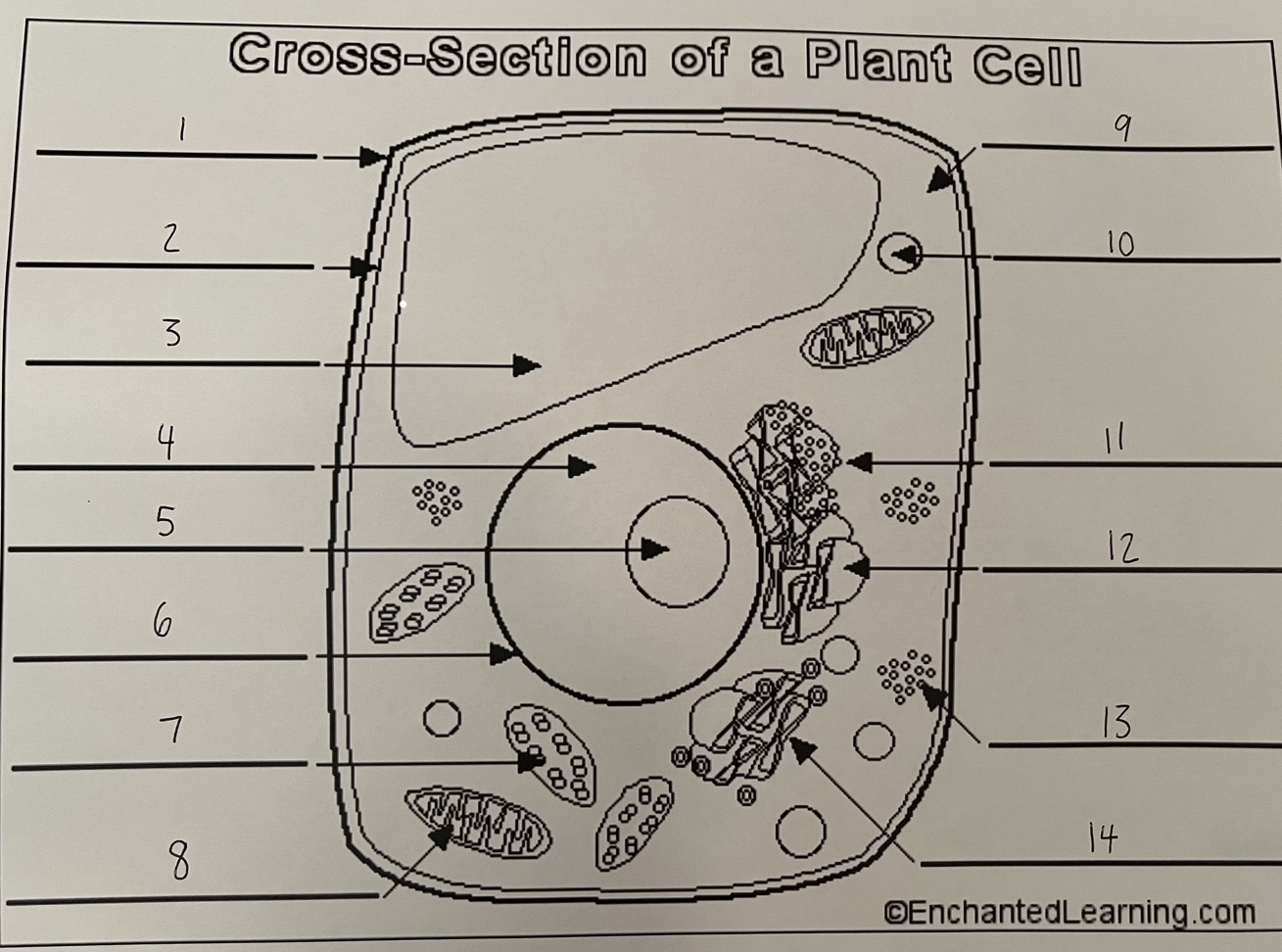
1
cell wall (plant)
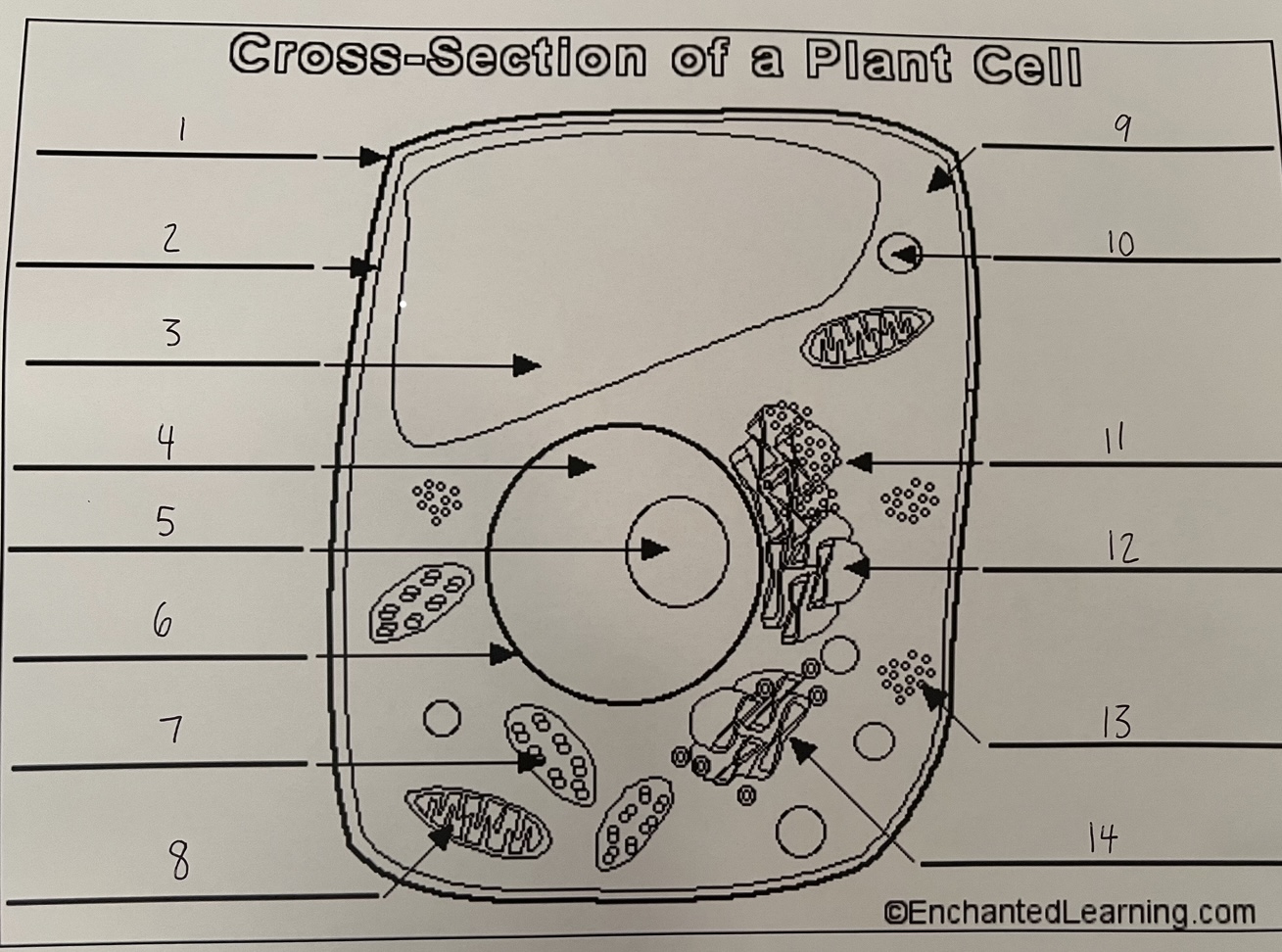
2
cell membrane (plant)
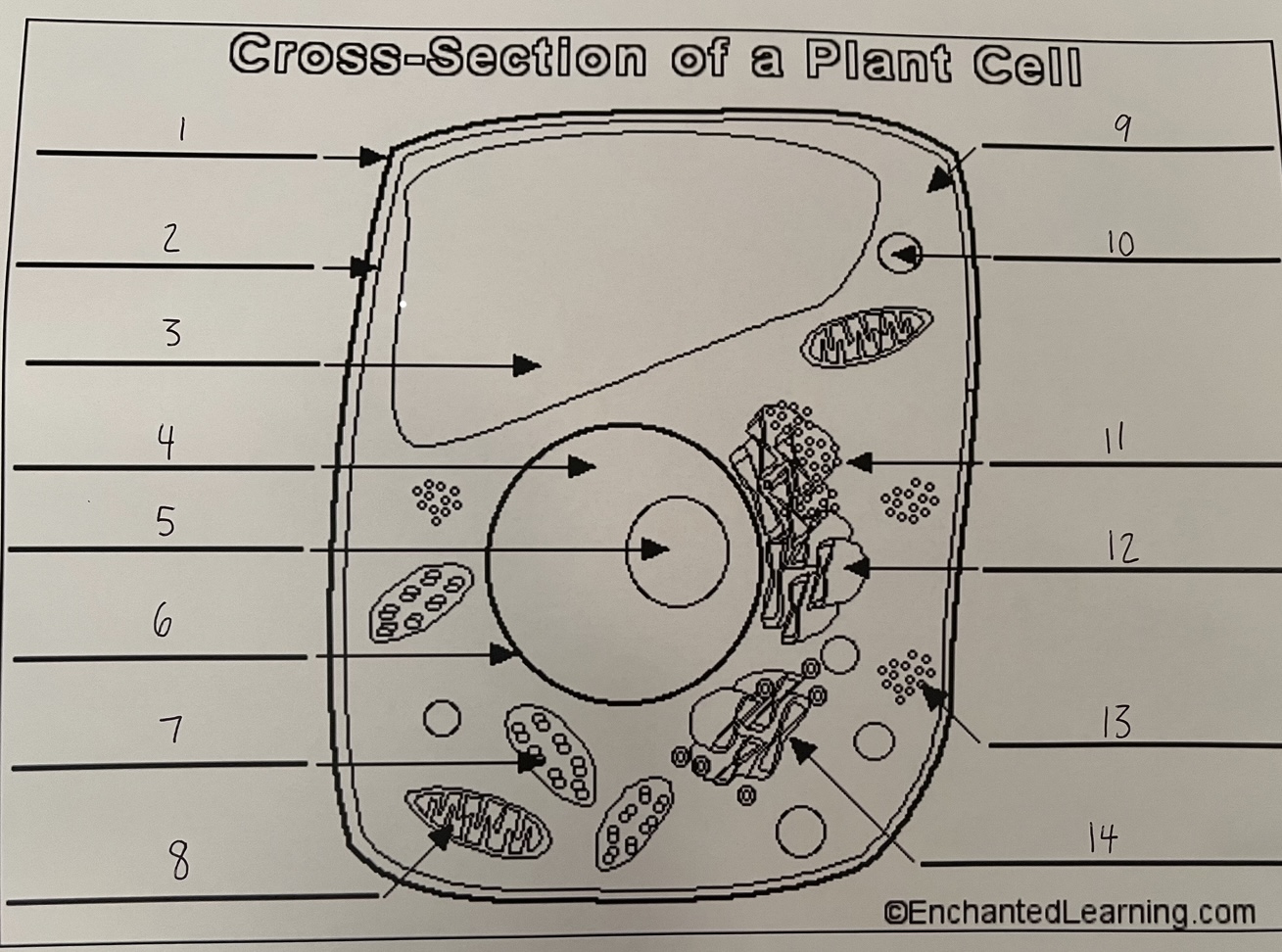
3
vacuole (plant)
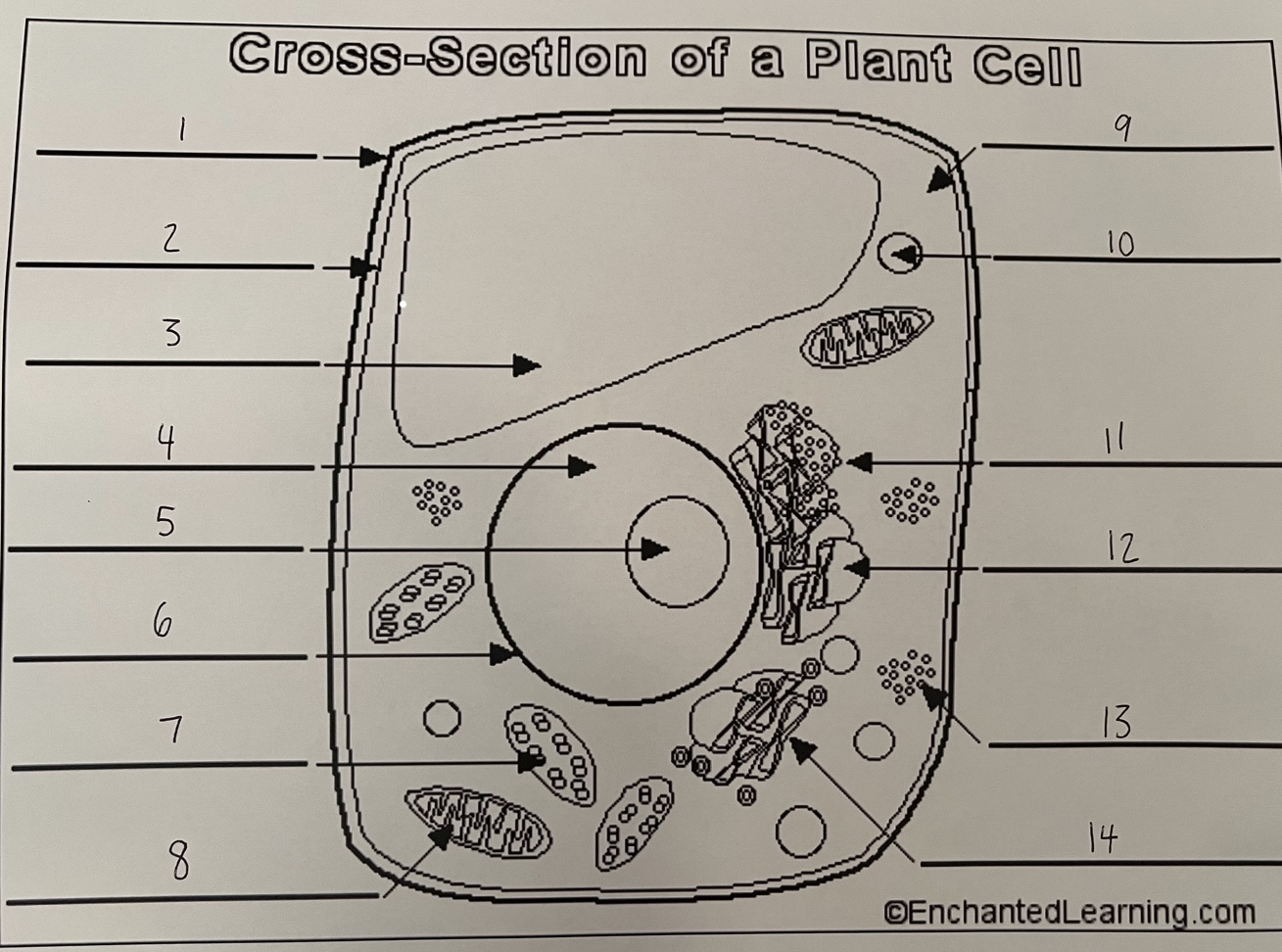
4
nucleus (plant)
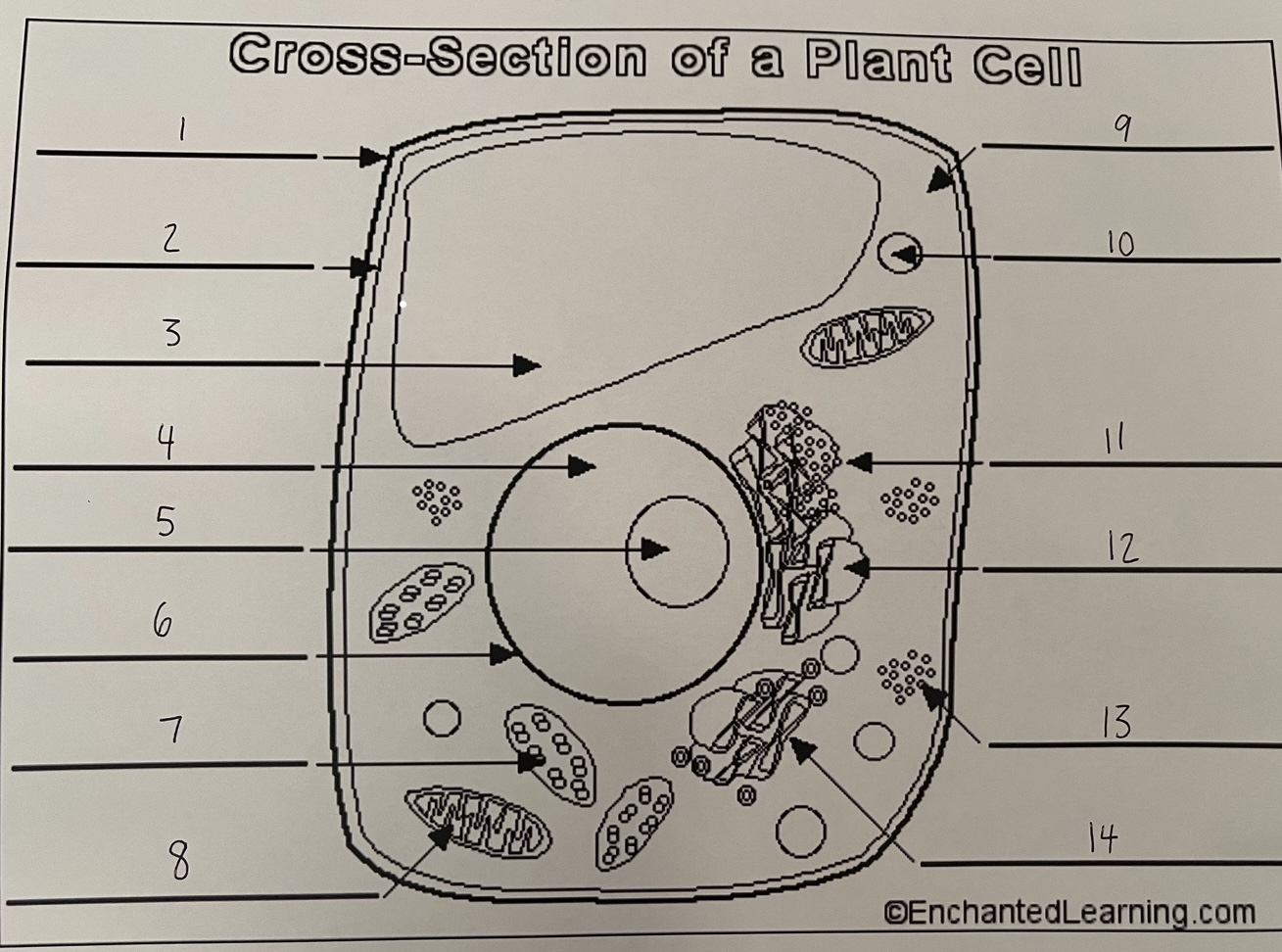
5
nucleolus (plant)
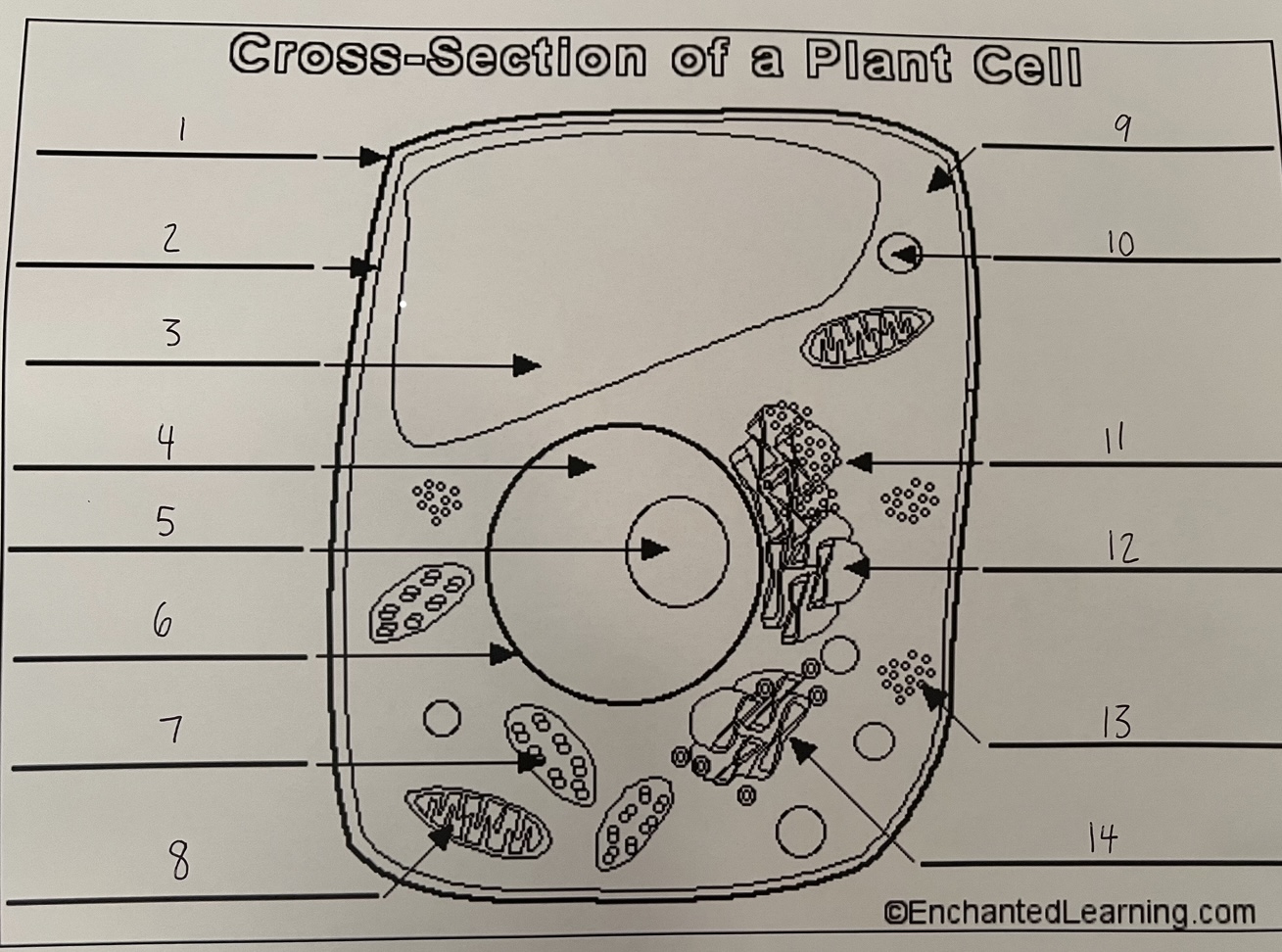
6
nuclear membrane (plant)
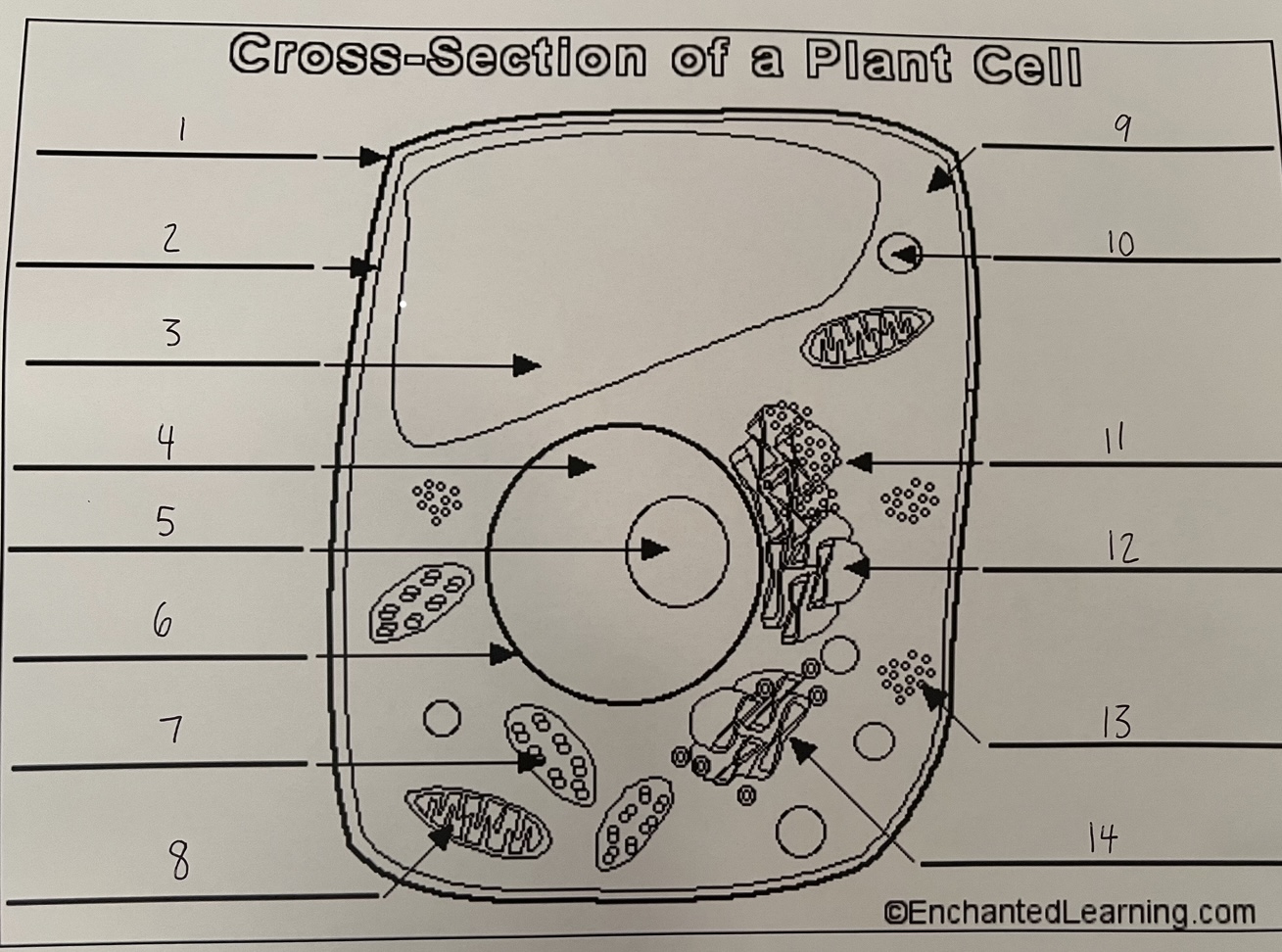
7
chloroplast (plant)
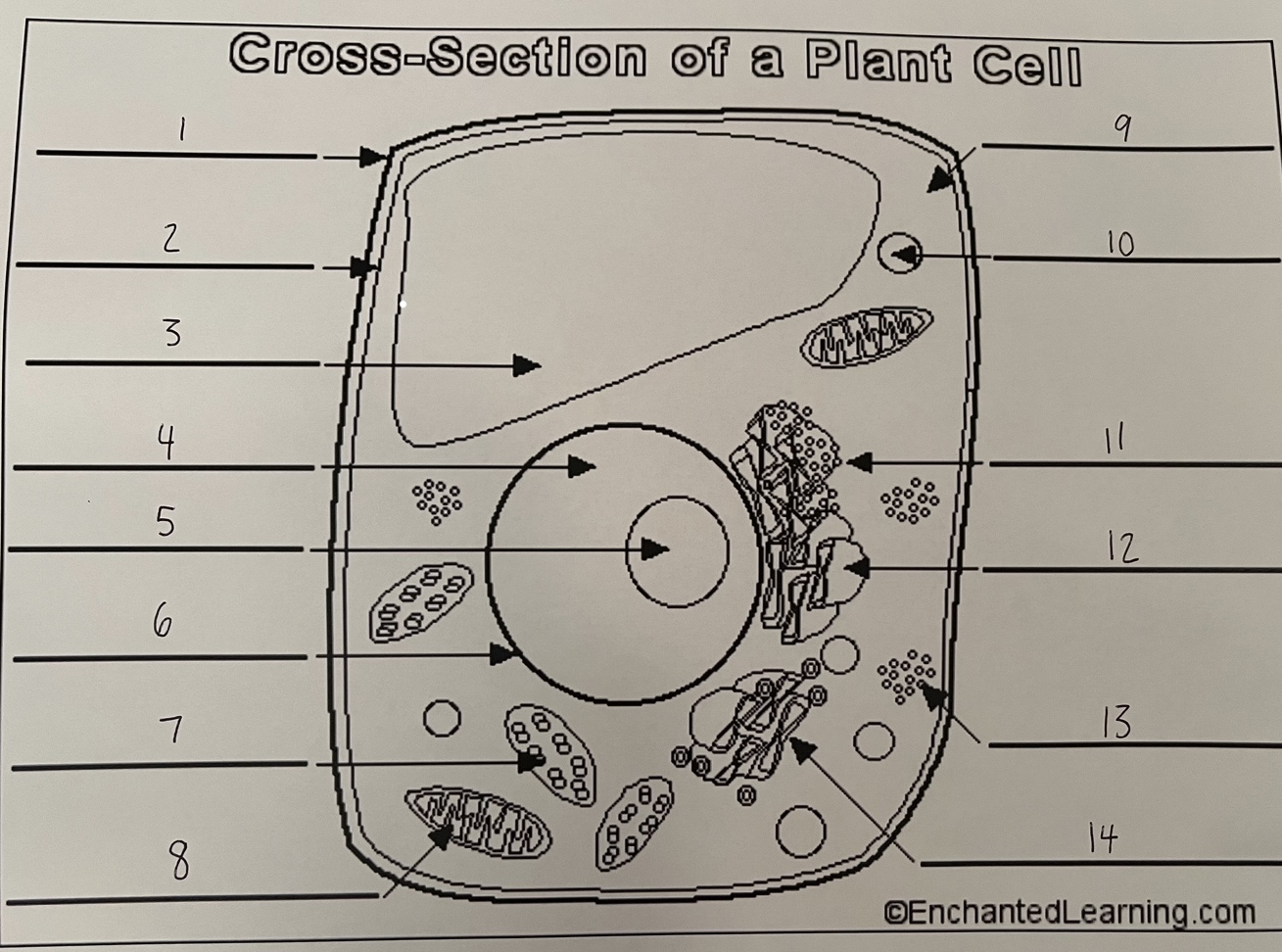
8
mitochondrion (plant)
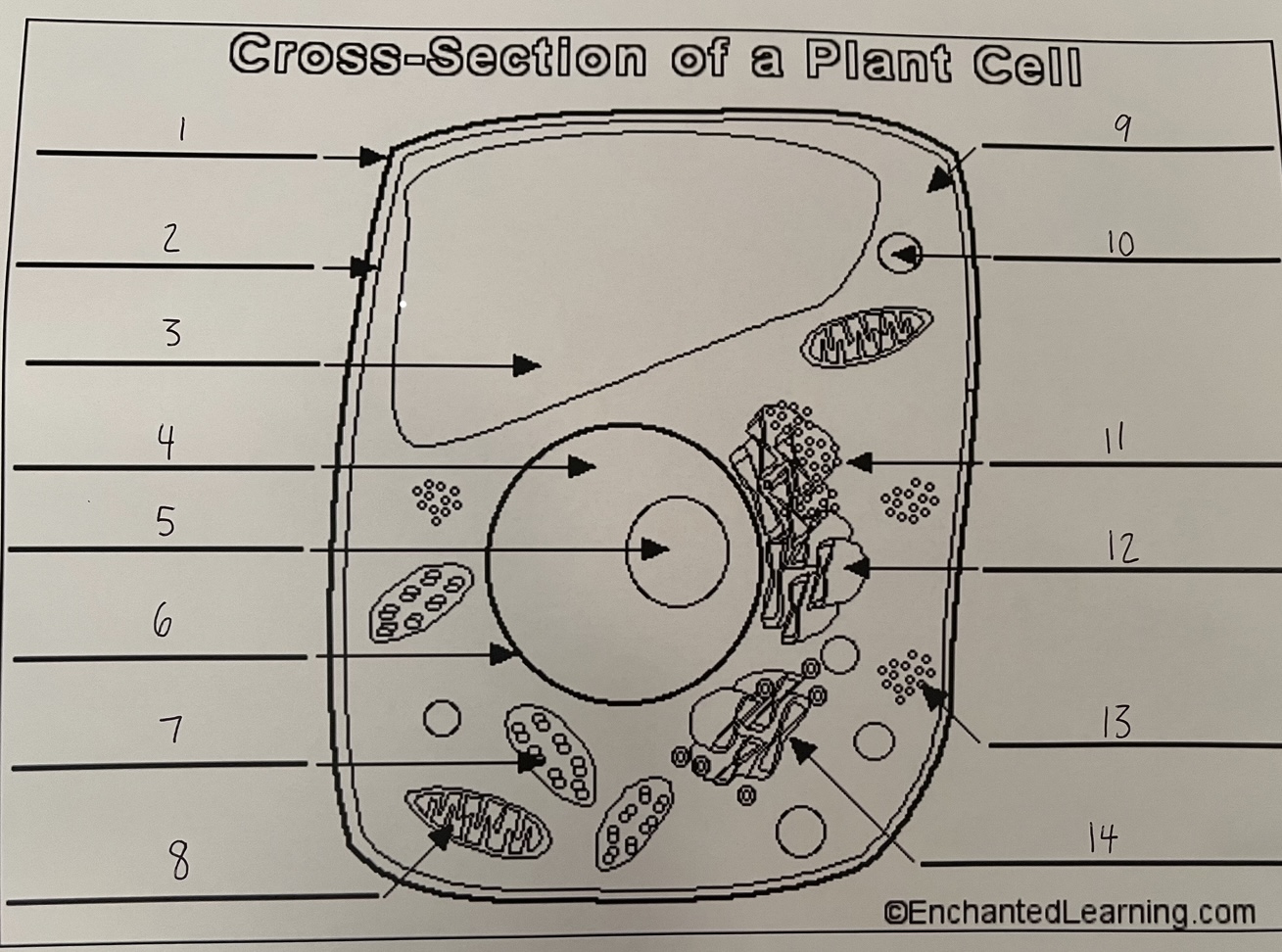
9
cytoplasm (plant)
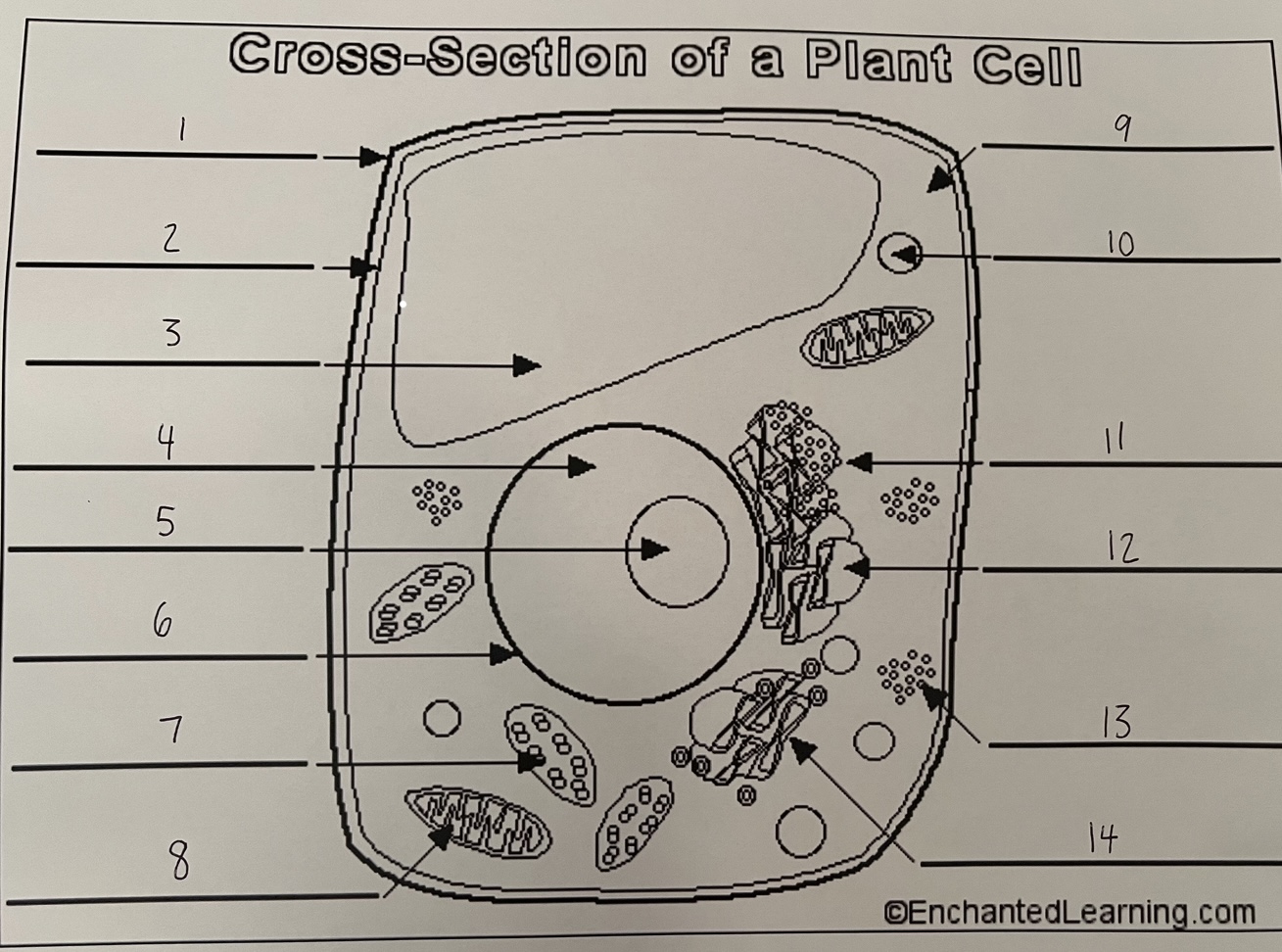
10
lysosome (plant)
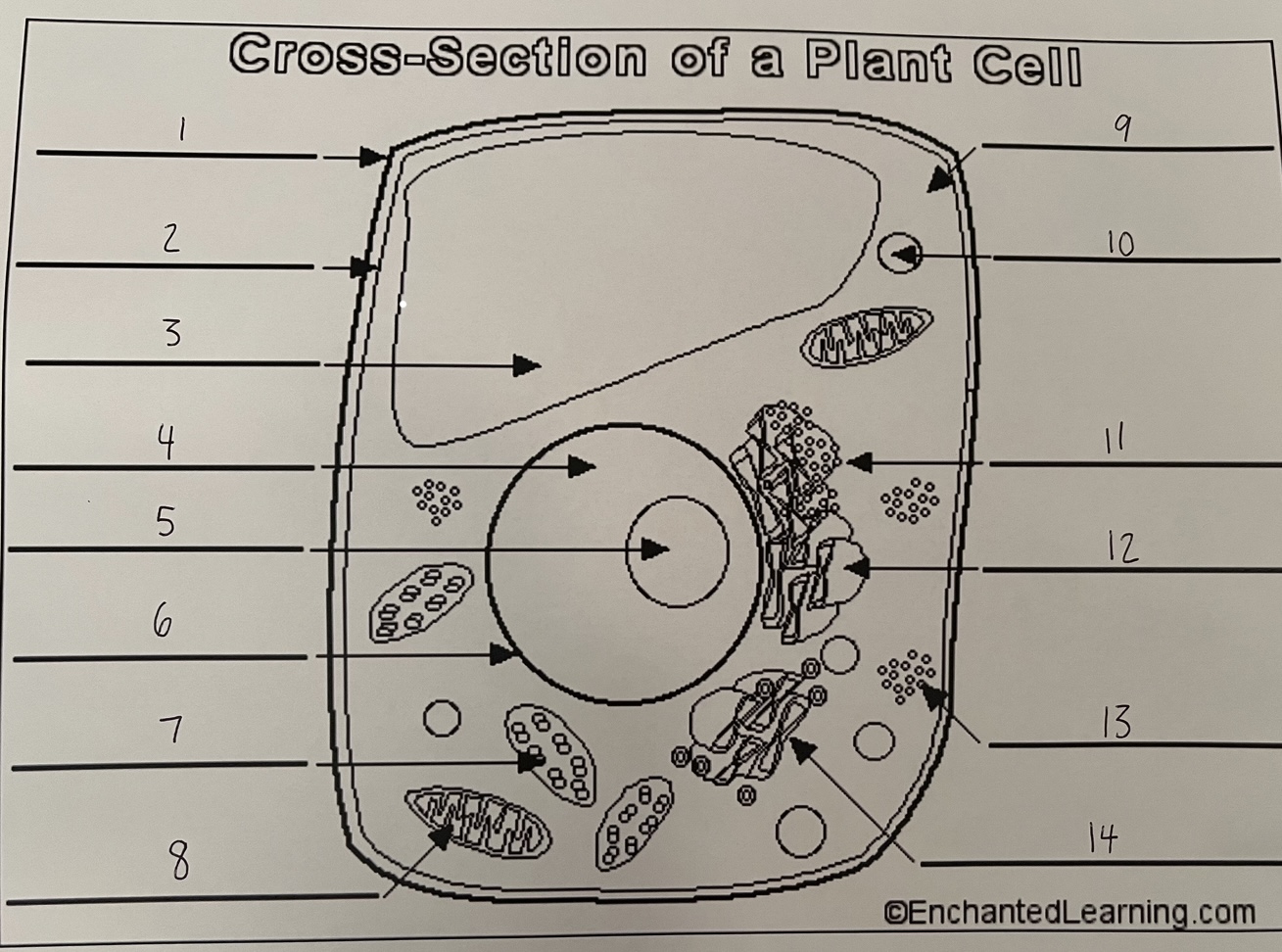
11
rough ER (plant)
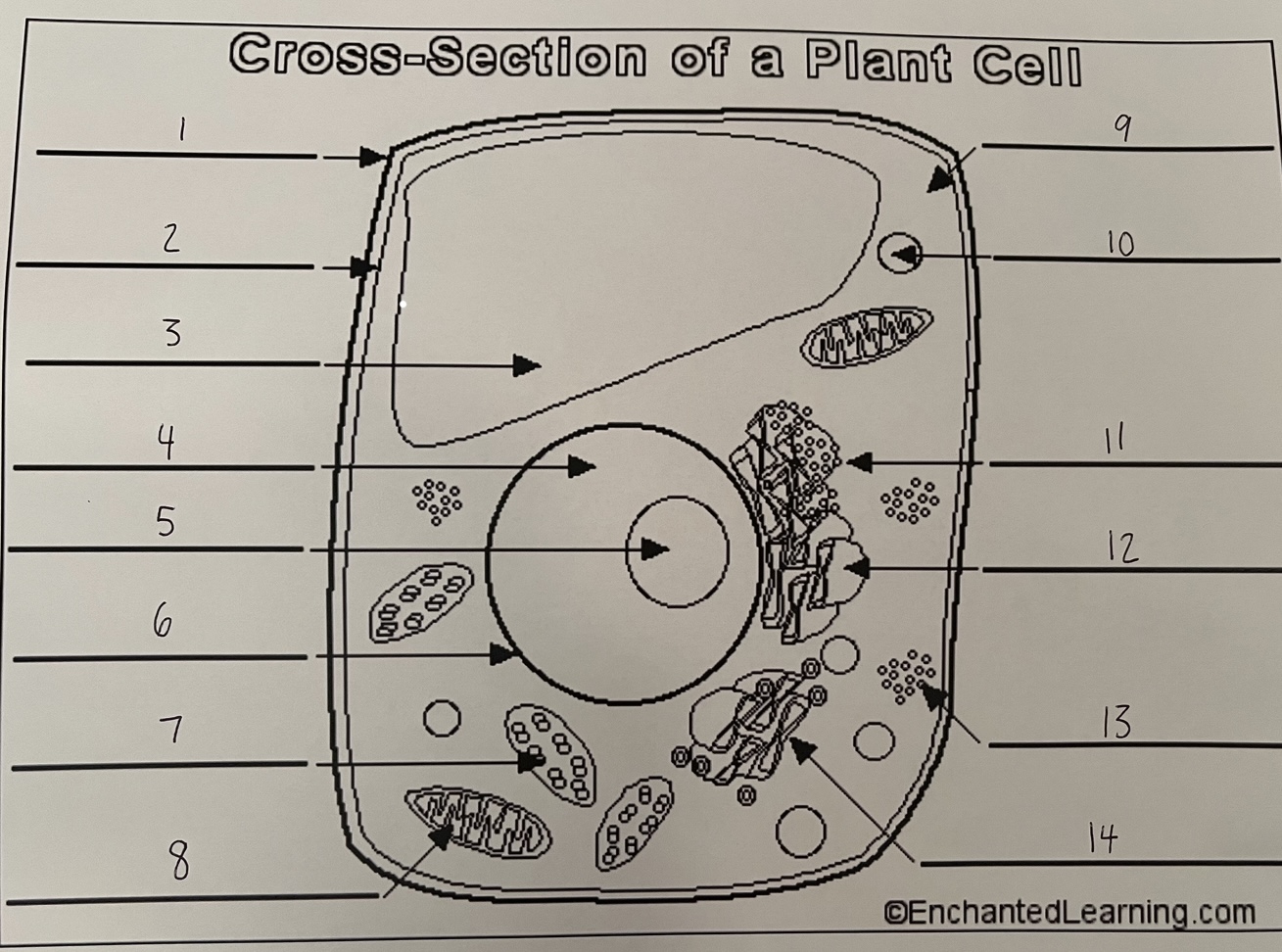
12
smooth ER (plant)
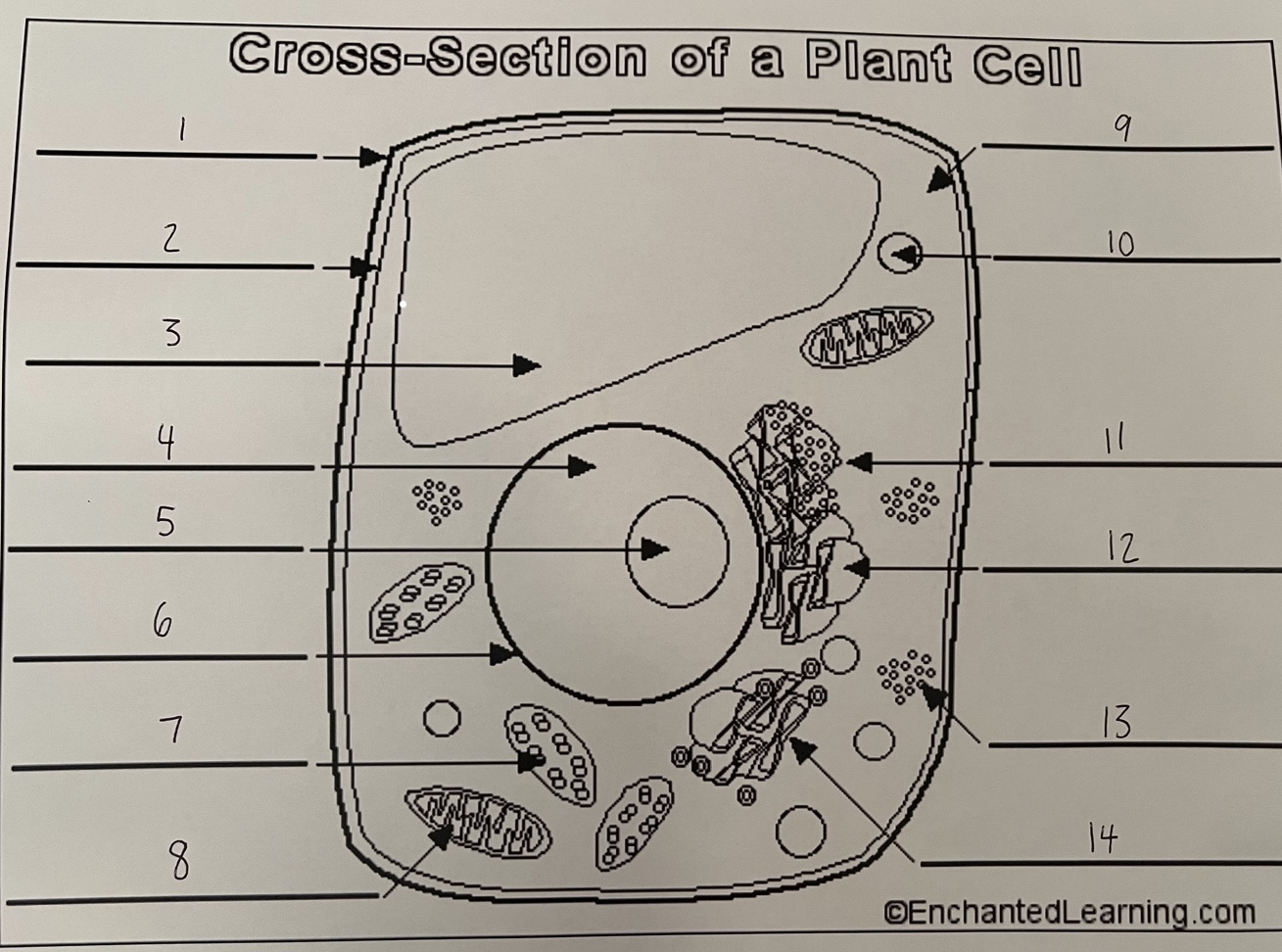
13
ribosomes (plant)
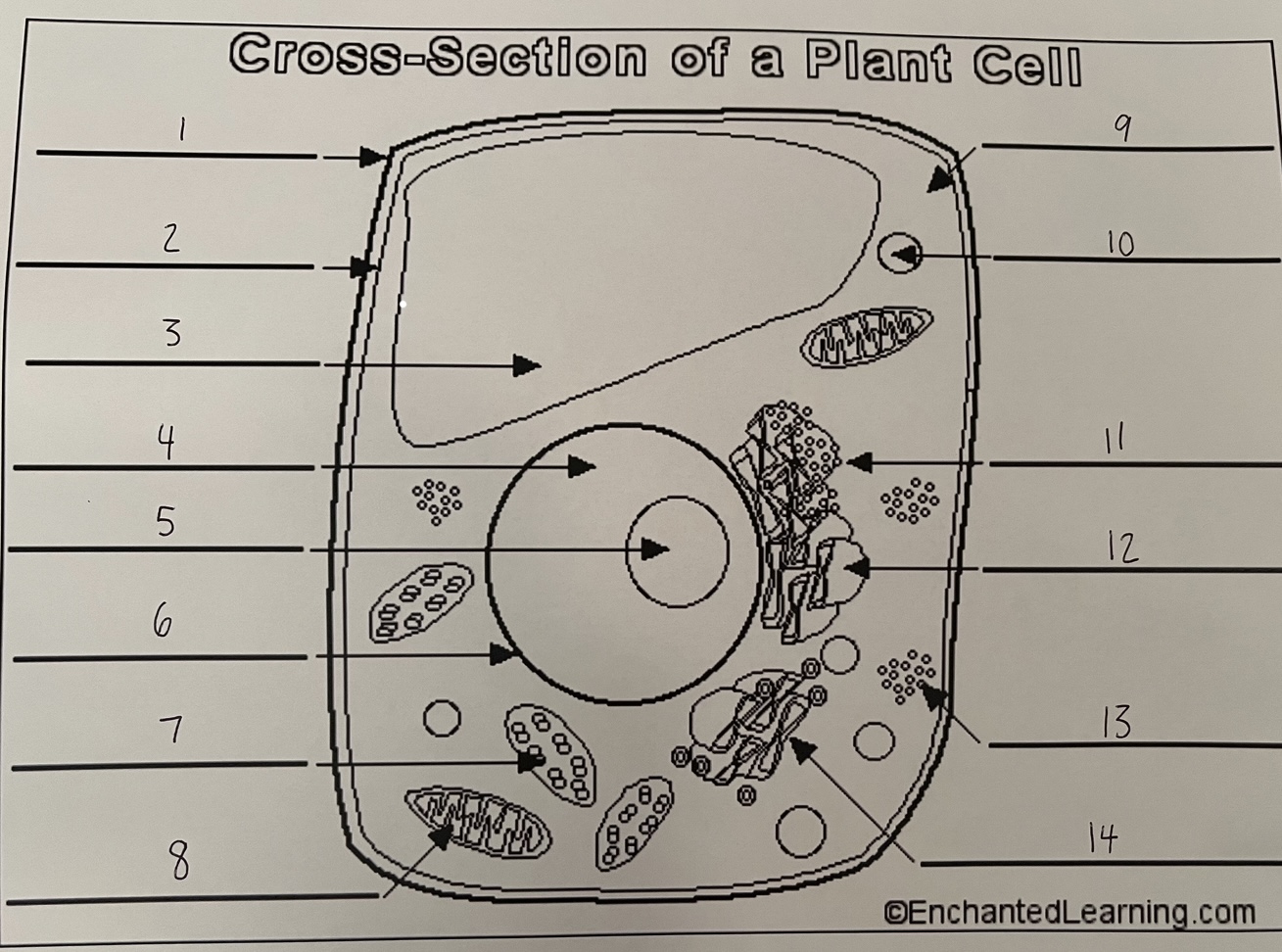
14
Golgi apparatus (plant)
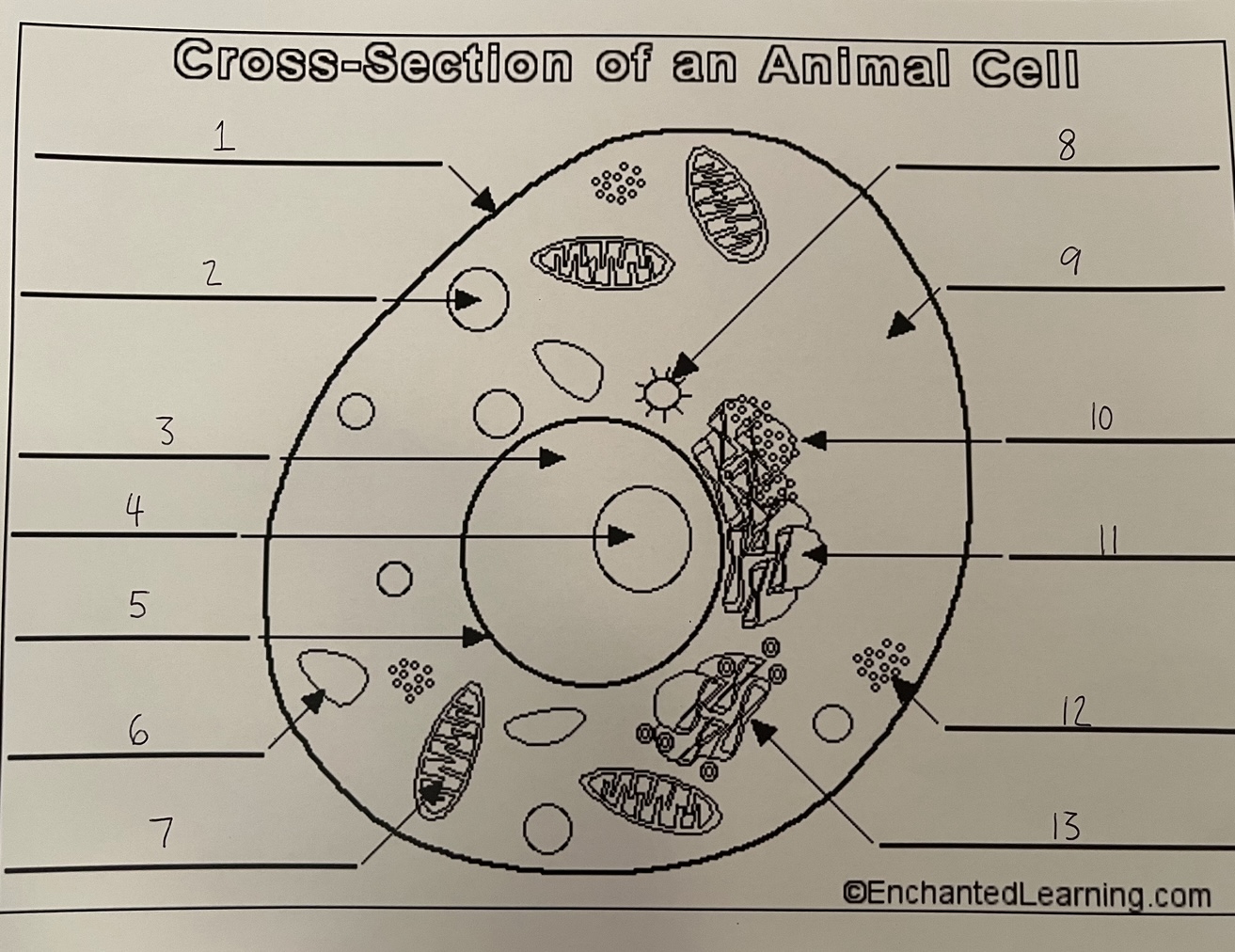
1
cell membrane (animal)
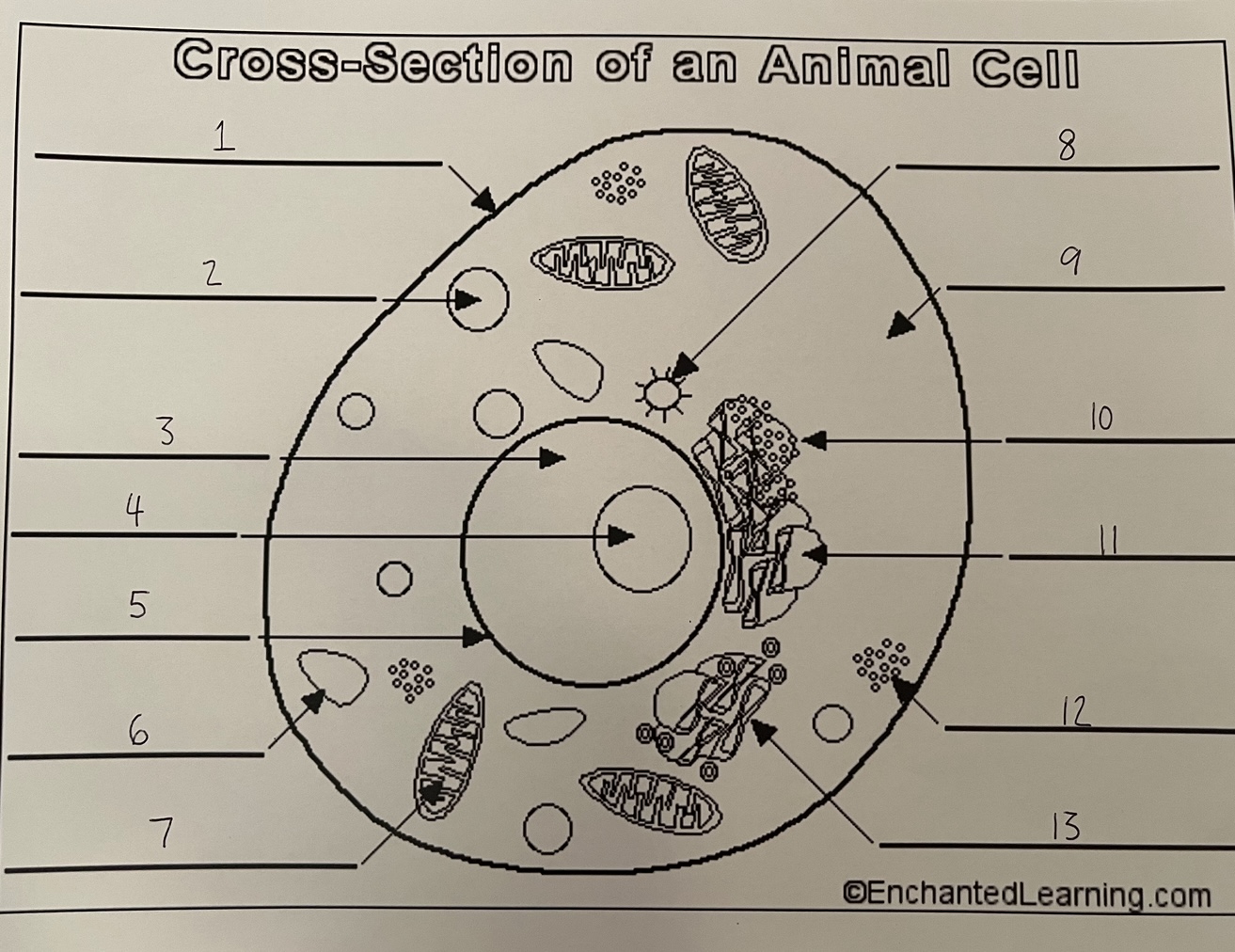
2
lysosome (animal)
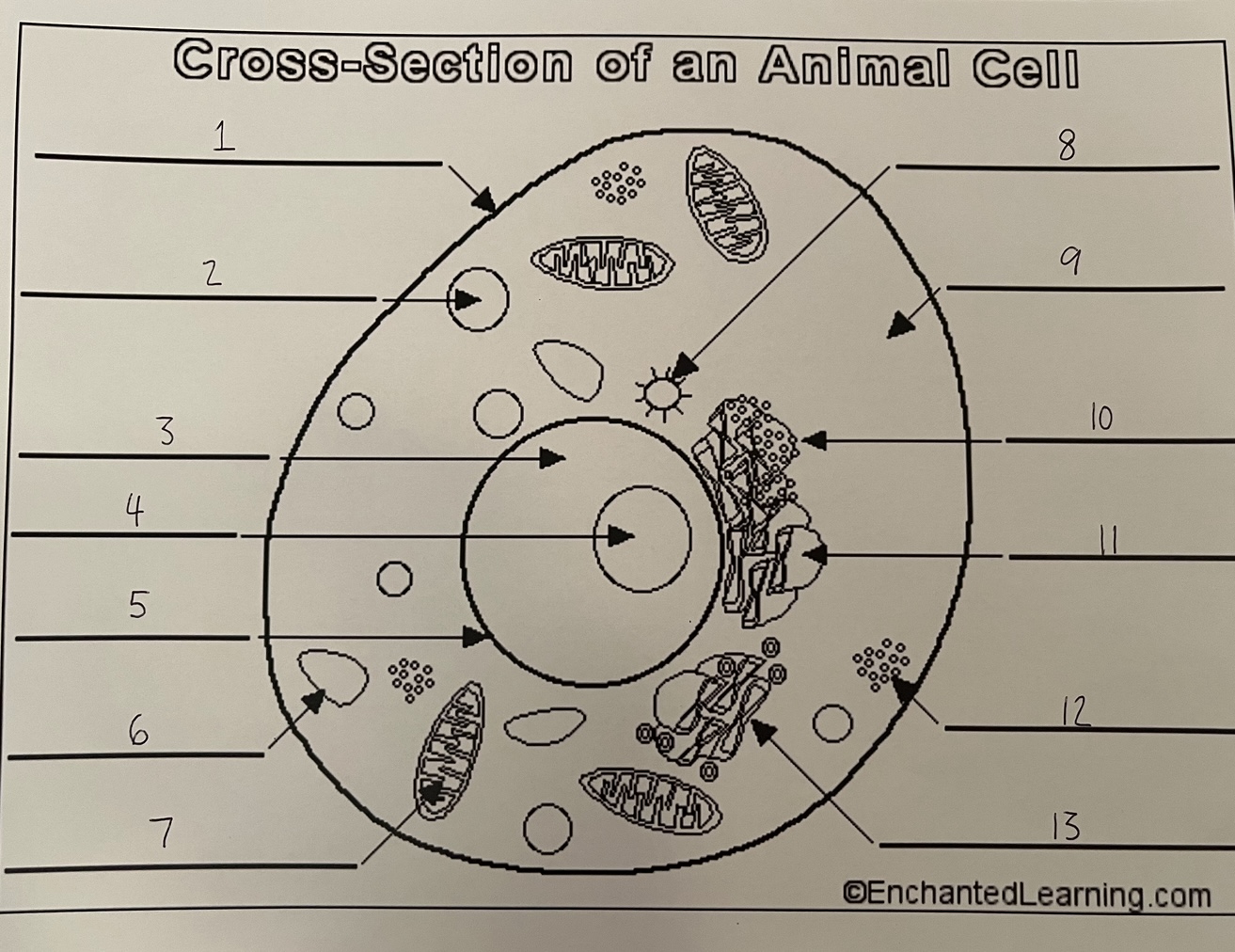
3
nucleus (animal)
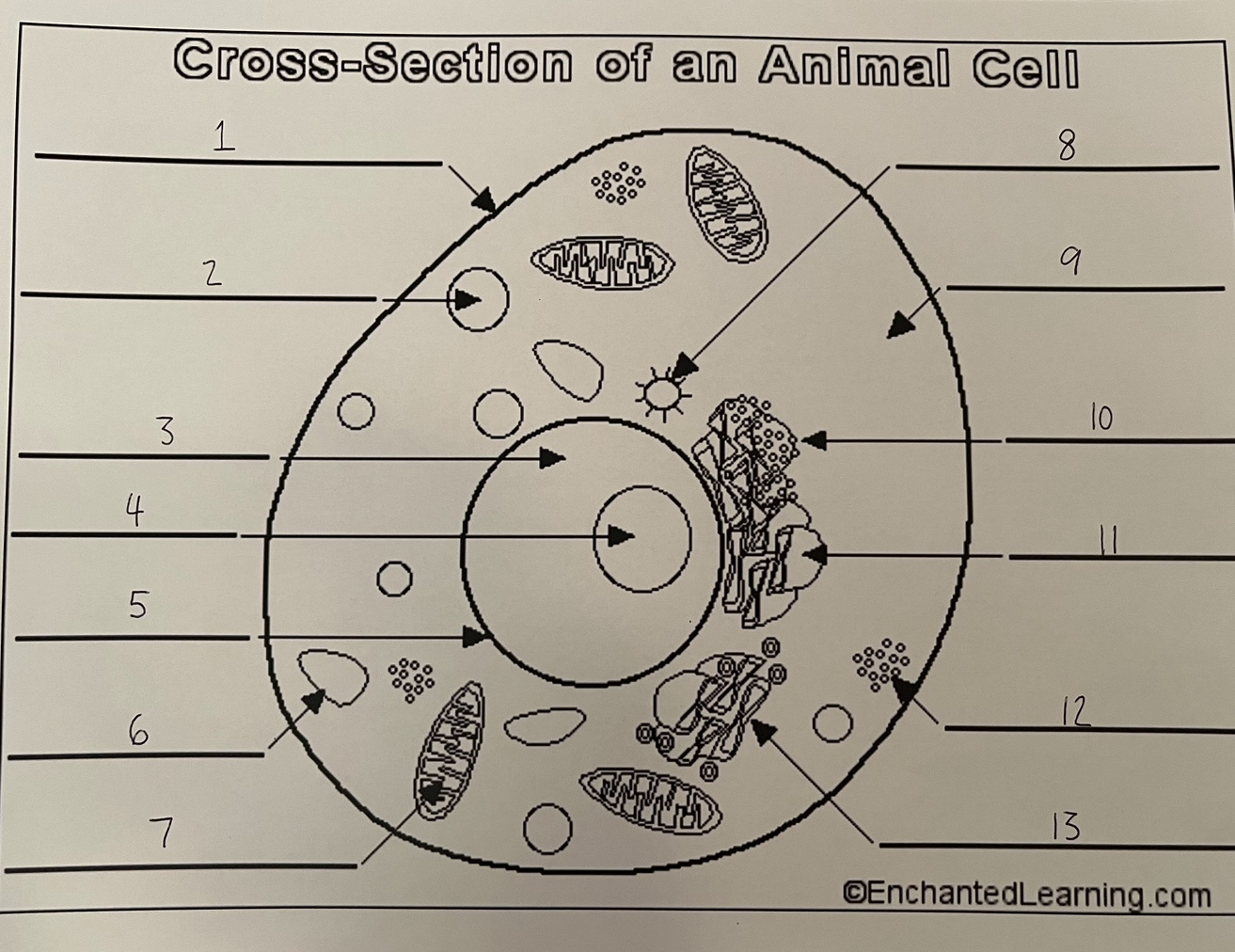
4
nucleolus (animal)
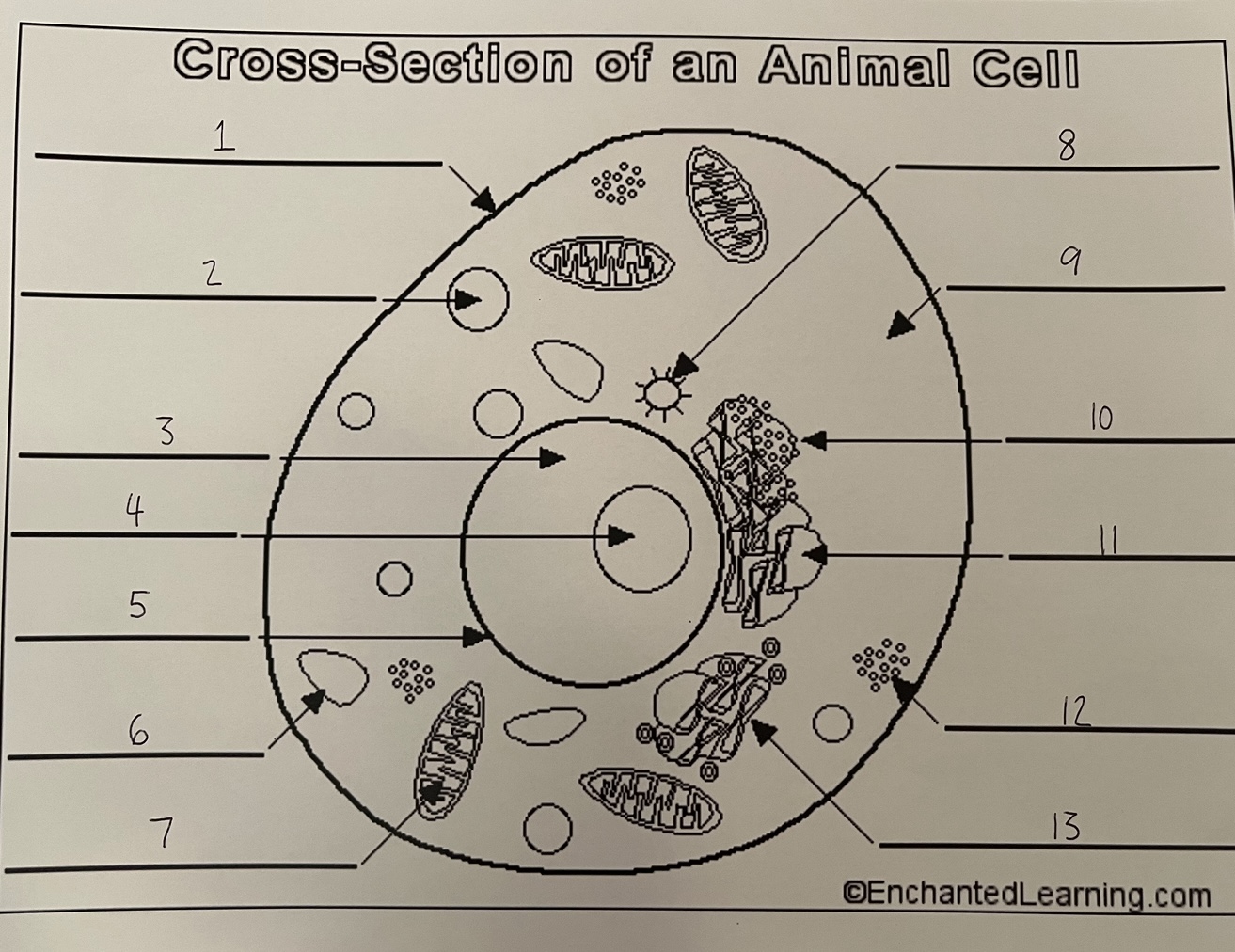
5
nuclear membrane (animal)
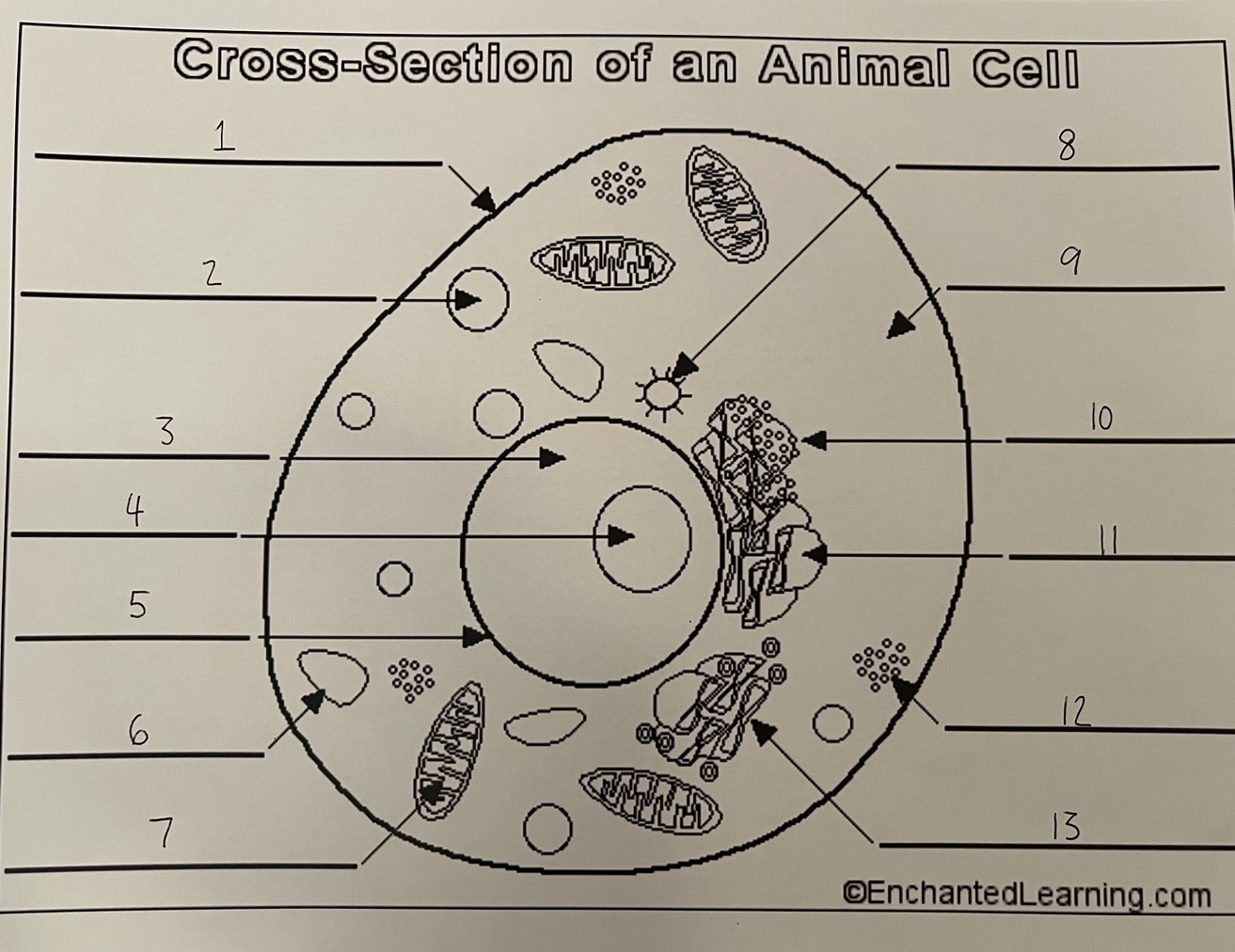
6
vacuole (animal)
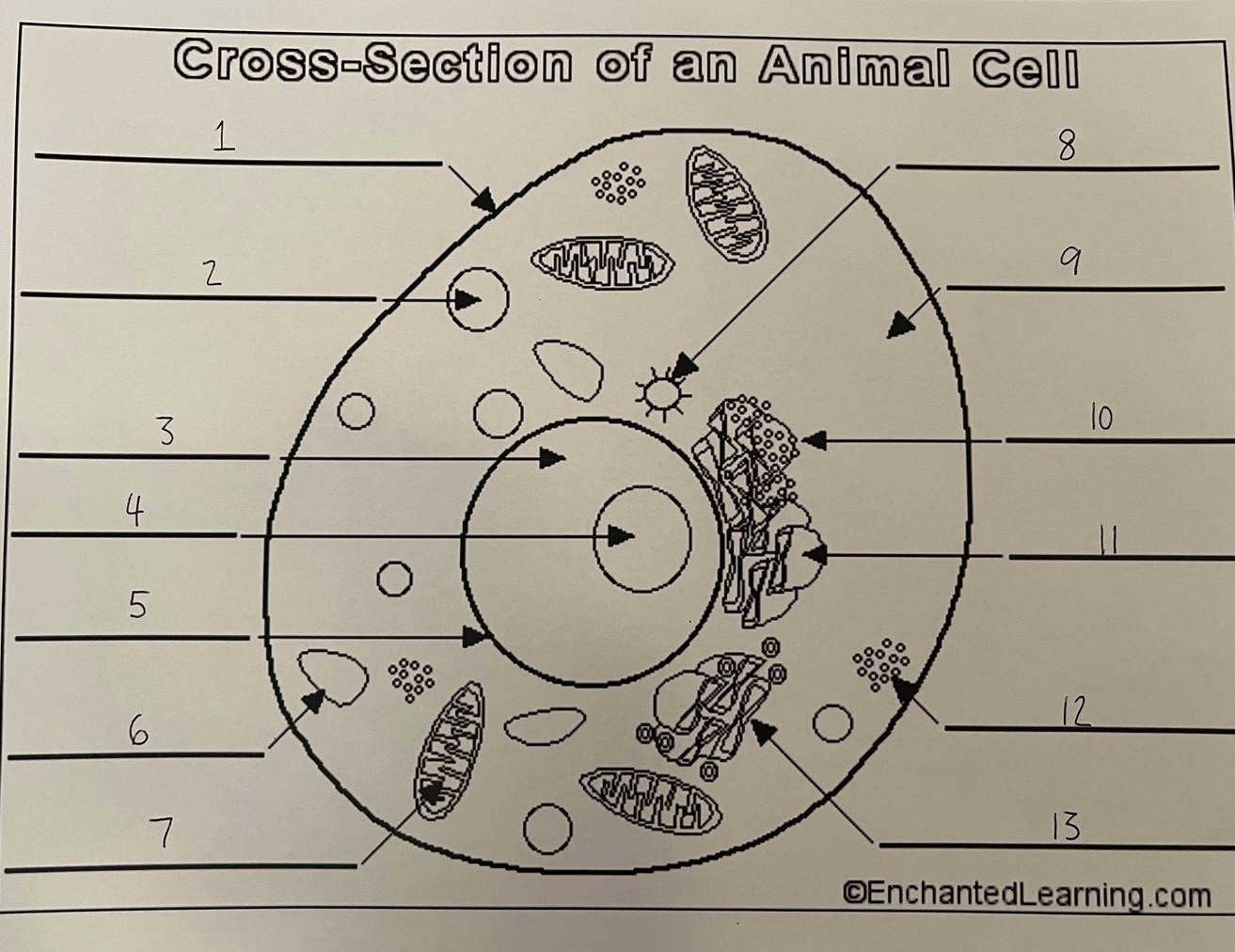
7
mitochondrion (animal)
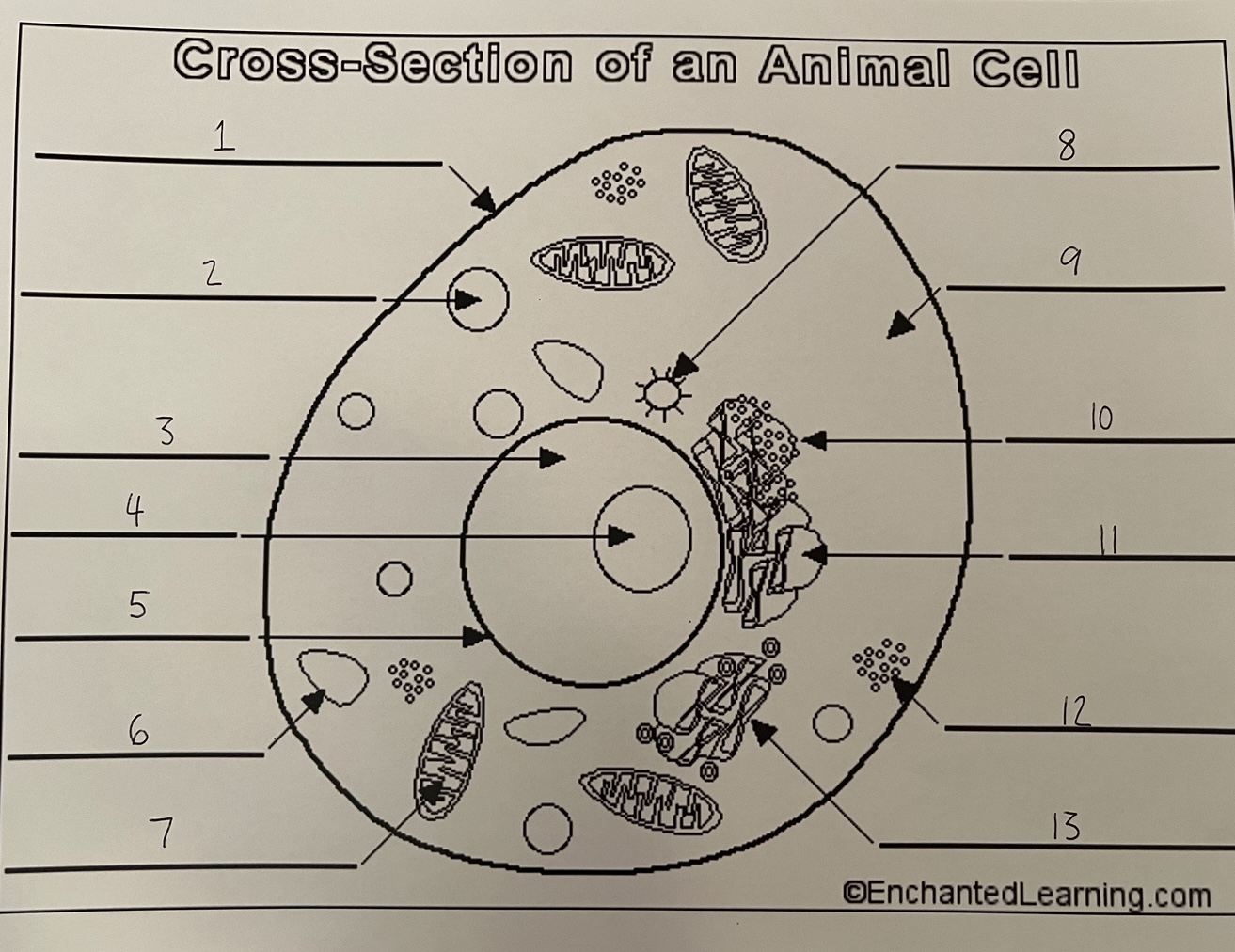
8
centrosome (animal)
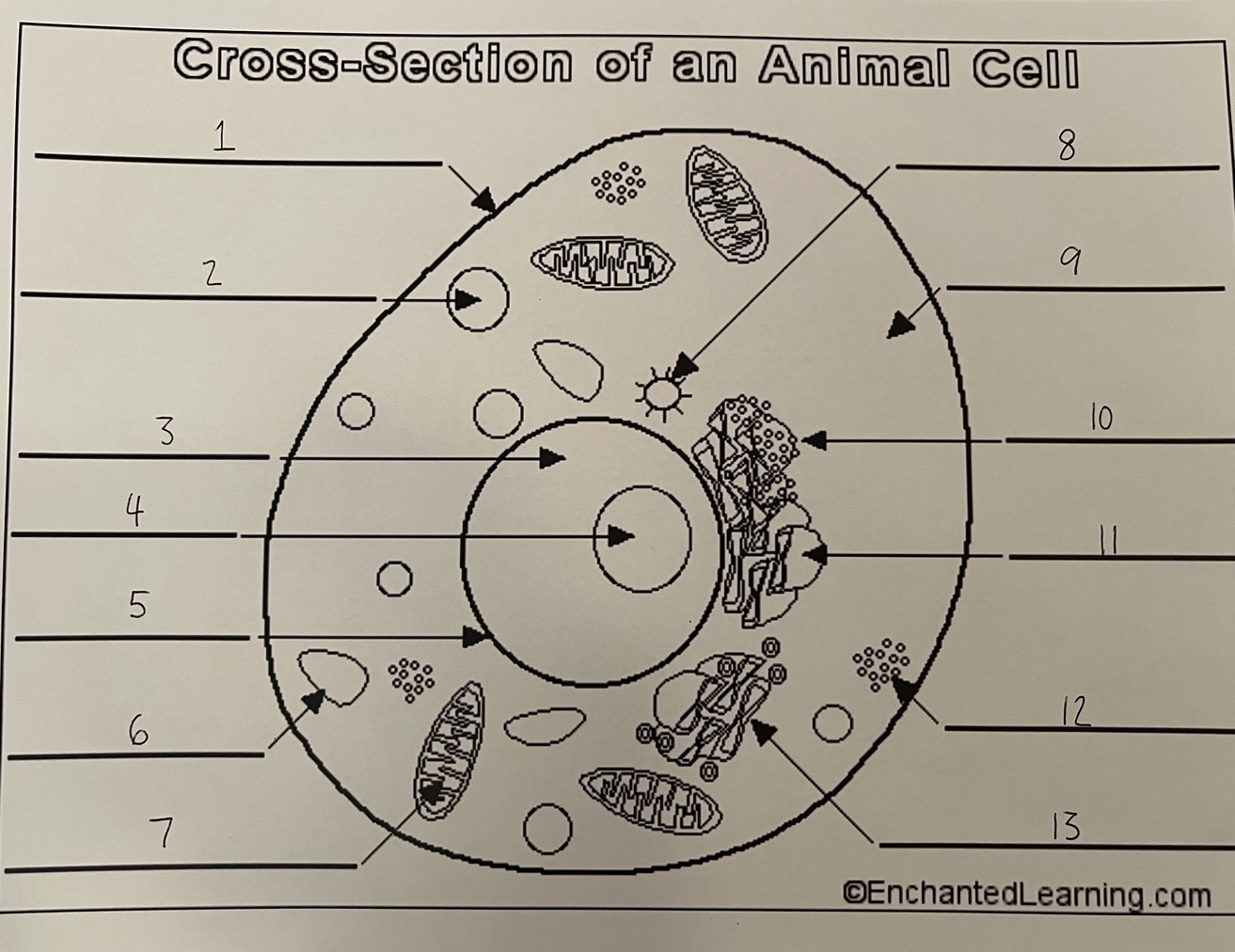
9
cytoplasm (animal)
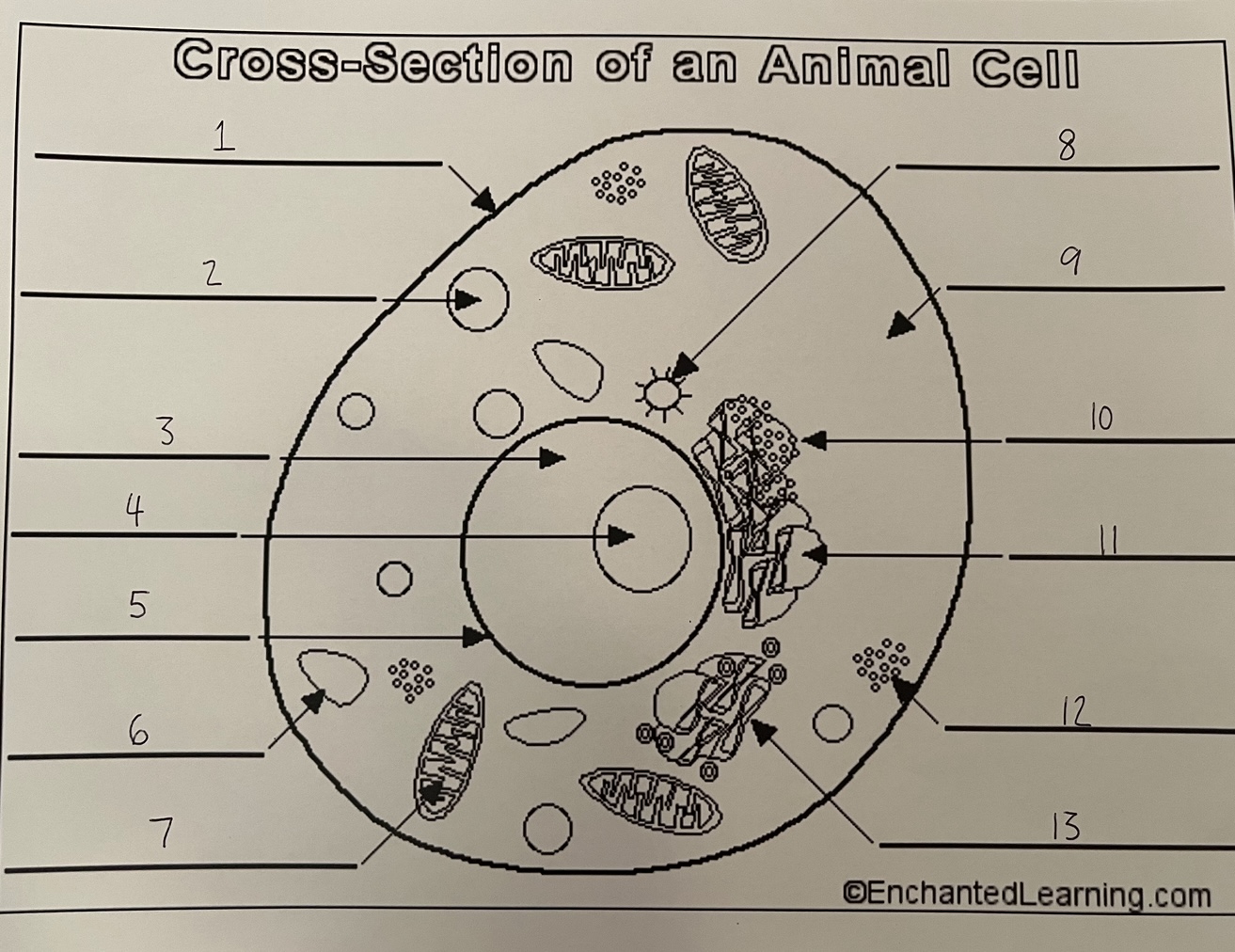
10
rough ER (animal)
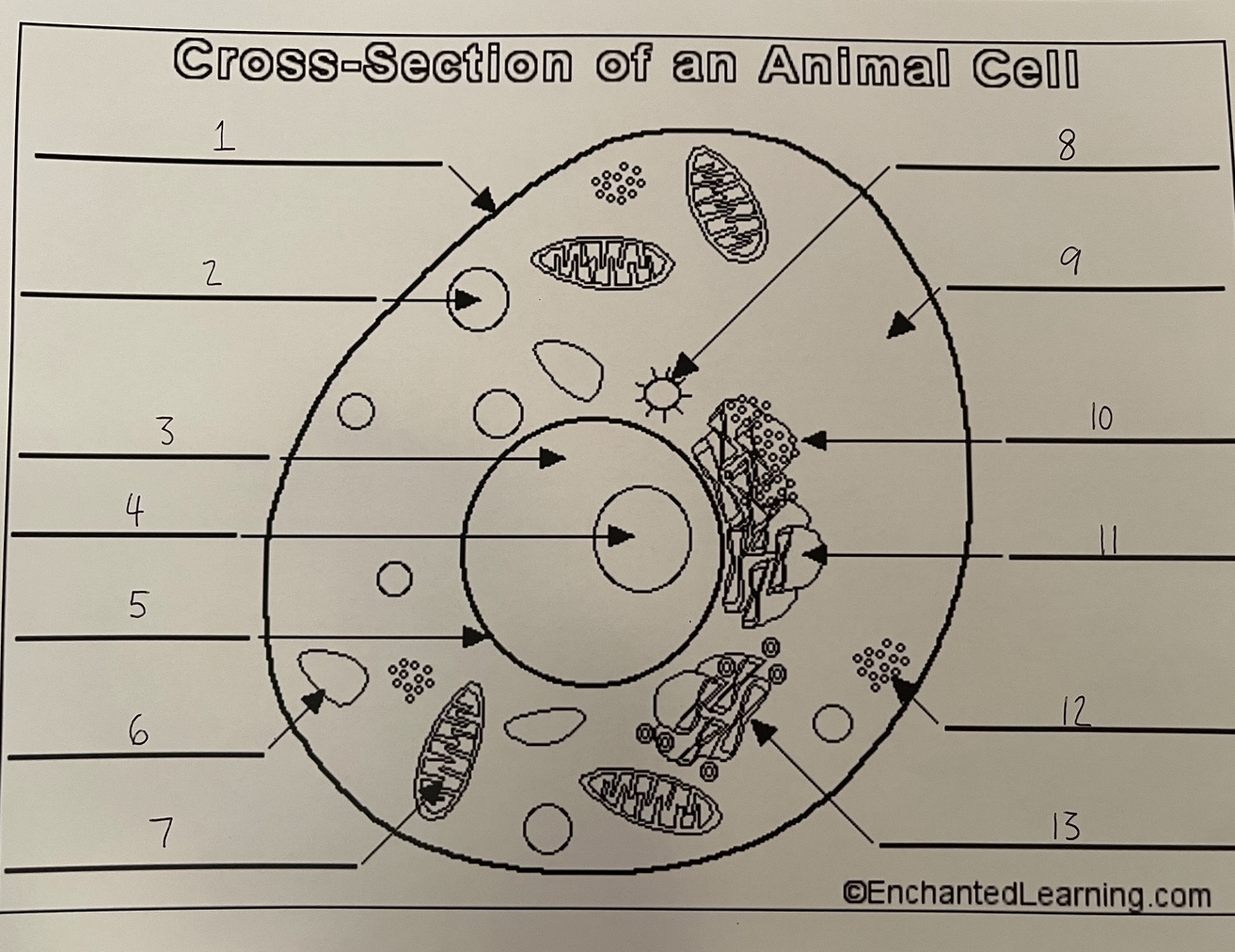
11
smooth ER (animal)
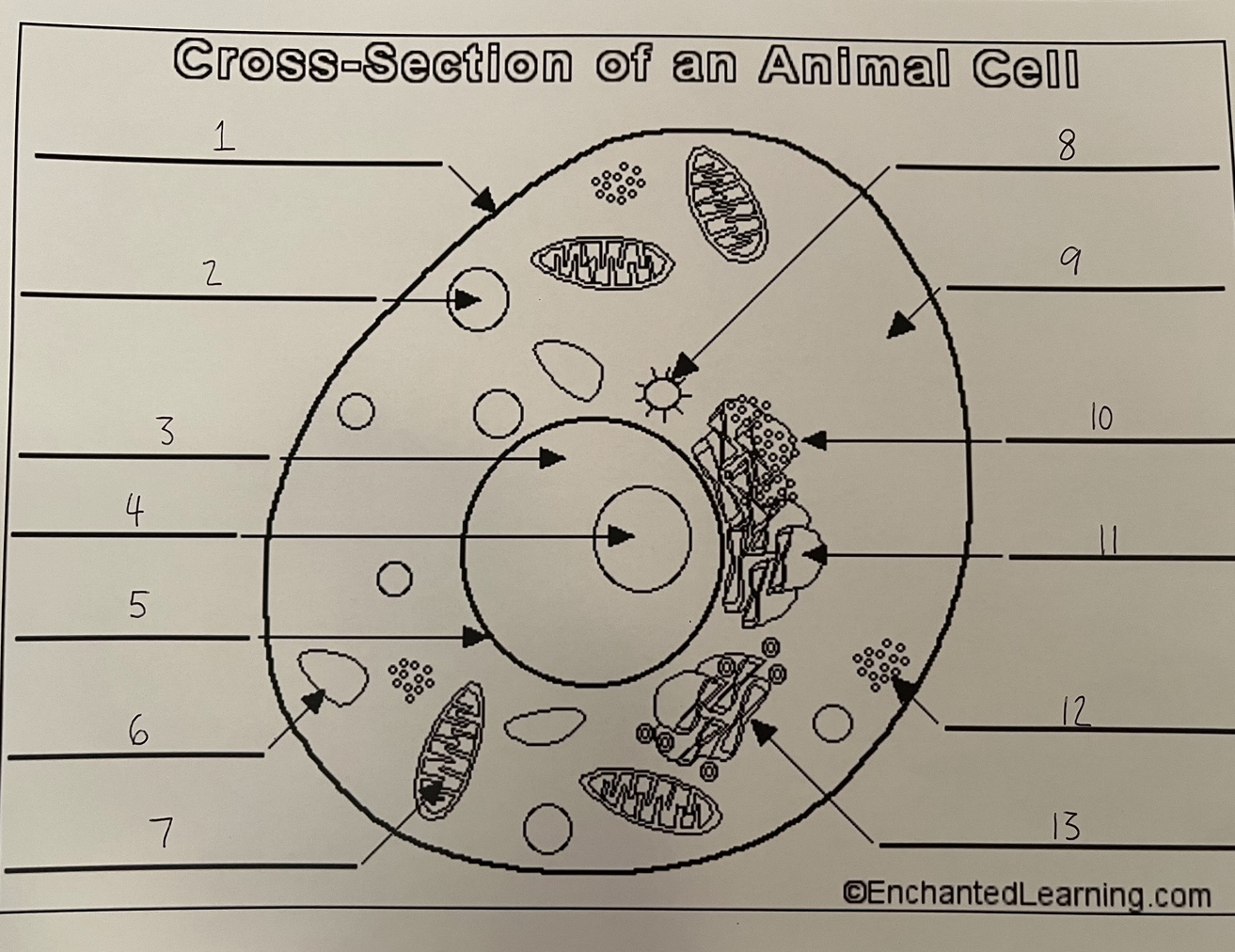
12
ribosomes (animal)
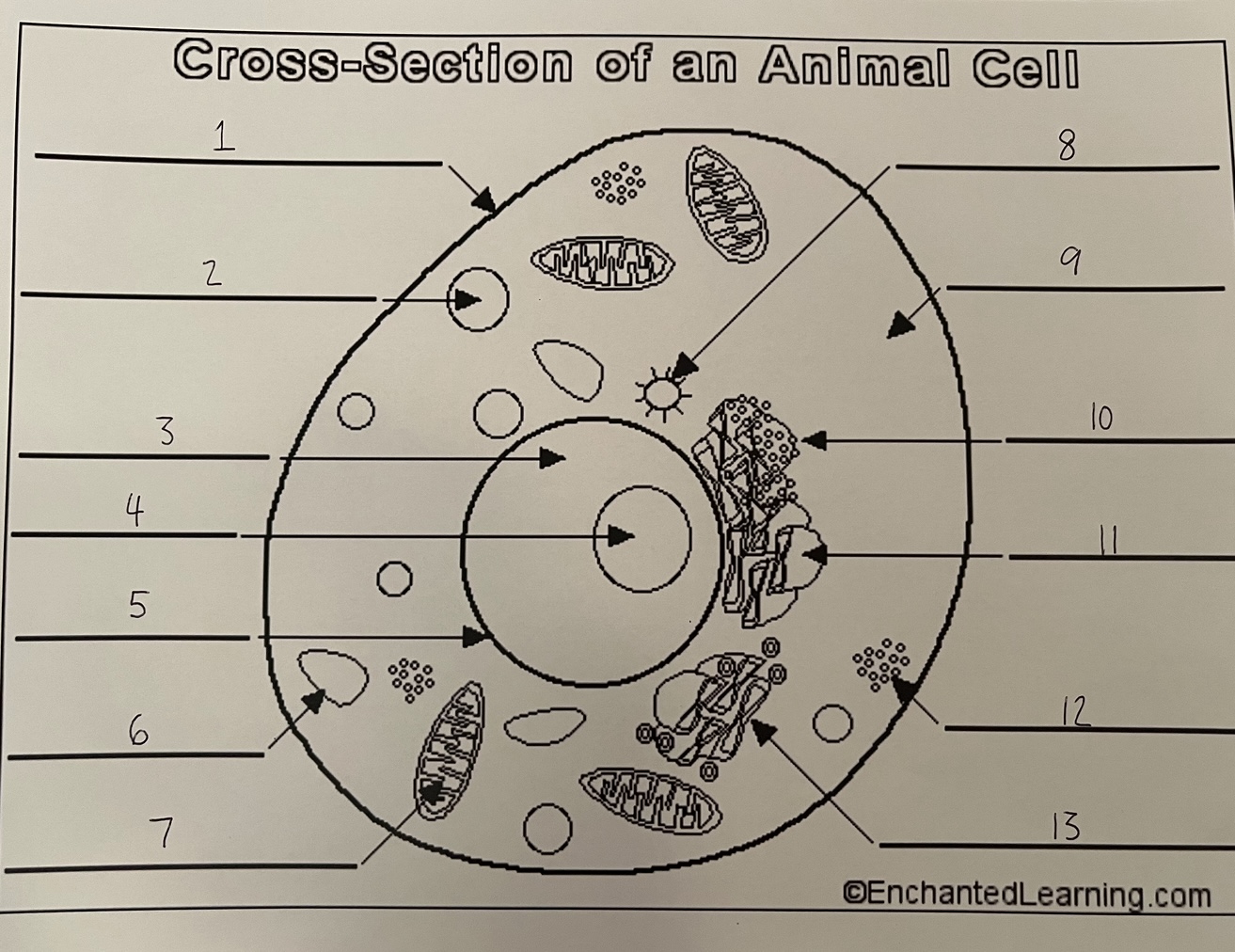
13
Golgi apparatus (animal)
water
regulates body temperature; flushes out wastes and toxins from our system
ex: mineral water, lakes, oceans, and rivers
lysosomes vs vacuoles
lysosomes break down food while vacuoles store food/wastes and get rid of it
diffusion
the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration; one form of passive transport; the concentration of oxygen is higher outside of the cell; oxygen moves easily into the cell
osmosis
the diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane; a form of passive transport; can have important effects on cells and entire organisms; can cause water to move out of the cells more quickly than it moves in; causes cytoplasm to shrink and cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall
passive transport
the movement of dissolved materials across a cell membrane without using the cell’s energy
active transport
the movement of materials across a cell membrane using cellular energy; proteins within the cell membrane play a key role in this; substances that are carried into and out of cells by this process include calcium, potassium, and sodium; using the cell’s energy, transport proteins “pick up” specific methods and carry them across the membrane
facilitated diffusion
when proteins in the cell membrane form channels through which the sugars can pass; uses no cell energy and is another form of passive transport; means “to make easier”
compounds
formed when two or more elements combine chemically; cells rely on these such as water, nucleic acids, etc
ex: proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates
elements
any substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances
ex: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
selectively permeable
allows certain substances to pass through membrane while turning away others; filters certain substances
magnification
the condition of things appearing larger than they are; changes how you can see objects and reveals details; occurs when light passes through the lens into your eye
compound microscope
magnifies the image using two lenses at once; one is fixed in the eyepiece and the other is chosen in the revolving nosepiece
resolution
the degree to which two separate structures that are close together can be distinguished; the better it is, the more detail is shown
resolution vs magnification
resolution allows you see to see more details (clarity and quality) while magnification is the act of zooming in
total magnification
can be found by multiplying the magnification of the two lens together
organization of body
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
specialized cells
perform specific functions that benefit the entire organism; share a "division of labor."
osmosis vs diffusion
osmosis is the movement of water molecules which diffusion is the movement of other gases and solids
absorbs nutrients, balances cell, helps passage of vital molecules,