Biochemistry Final Exam
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
What amino acids are Nonpolar?
GIVPALM
Glycine, Isoleucine, Valine, Proline, Alanine, Leucine, Methionine
What amino acids are Aromatic?
FYM
Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan
What amino acids are Polar, Uncharged?
STCNQ
Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Asparagine, Glutamine
What amino acids are Negative?
ED
Glutamic Acid, Aspartic Acid
What amino acids are Hydrophobic?
FLAVI
Phenylalanine, Leucine, Alanine, Valine, Isoleucine
What amino acids are Hydrophilic?
REKHN
Arginine, Glutamic Acid, Lysine, Histidine, Asparagine
What amino acids are Positive?
KRH
Lysine, Arginine, Histidine
What nucleic acids are purines?
Adenine and Guanine
“as pure as gold” - 2 rings
What nucleic acids are pyrimidines?
Cytosine, Uracil, Thymine
“cut” - 1 ring
Difference between DNA and RNA
DNA (B Form) - deoxyribose
RNA (A Form) - ribose
Peptide Bonds
C=ONH; strongest bond; cleaved by peptidase
Secondary Structure
Alpha-helix, right handed. Beta-sheets are parallel and antiparallel (antiparallel is stronger since the hydrogen bonding is head on)
Tertiary Stucture
Disulfide bonds stabilize cystine and forms a bond
N terminus
Considered positive therefore negative amino acids are located here
C terminus
Considered negative therefore positive amino acids are located here
Glycine and Proline
Glycine is the only amino acid that is not chiral (has two Hydrogens)
Proline is the only amino acids that is an imino acid (not amino)
Molten Globule
Hydrophobic effect stabilizes the initial intermediate. Hydrophobic collapse determines stability
KD
Dissociation constant, inverse to KA (association constant)
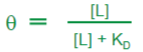
Lower the KD the tighter the binding
Myoglobin
Binds to oxygen in low KD (stays bound) storage molecule
Hemoglobin
High and low KD (in lung low = picks up oxygen); R and T state. Binds to 4 O2 molecules max
Tense
HIS HC3 is protonated (pulls ion out of plate and O2 cannot bind). The ion binds to O2 and HIS HC3 (thermodynamically more stable)
Relaxed
HIS HC3 is deprotonated (less stable thermodynamically). 2,3-bPG stabilizes T state (donut hole of hemoglobin)
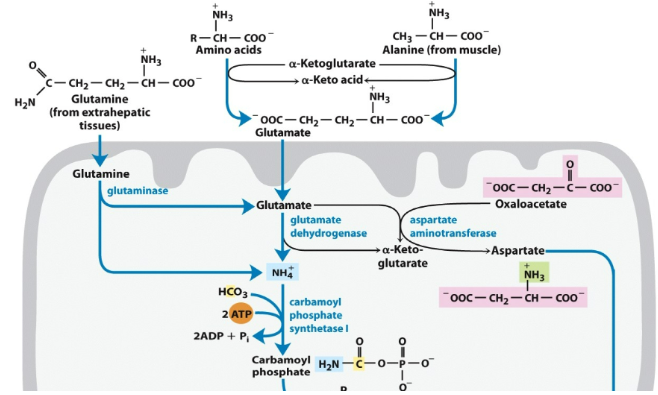
What is a nontoxic way to transport ammonia to the liver?
GLN (glutamine)
Urea Cycle: Step 1
Ornithine + carbomyl phosphate → citrulline + Pi
Catalyzed by ornithine transcarbamolyase
Citrulline exported to cytosol
Urea Cycle: Step 2
Citrulline + aspartate → arginosuccinate
Catalyzed by arginosuccinate synthetase. 2 more phosphate bonds cleaved (to adenylate to activate the citrulline). 1 more amino group enters
Activation of citrulline. AMP excellent leaving group as aspartate is added. Incorporates second amino acid
Urea Cycle: Step 3 and 4
Arginase catalyzes hydrolysis of arginine
Arginine + H2O → ornithine + urea
Arginosuccinase catalyzes:
Arginosuccinate → fumarate + arginine
Glycerophospholipids
Will be asked how many times B-oxidation takes place
For example: 8C = 3 steps → 4 AcCoA
Know the general names of the pathway (ex: thiolase, dehydrogenase, etc)
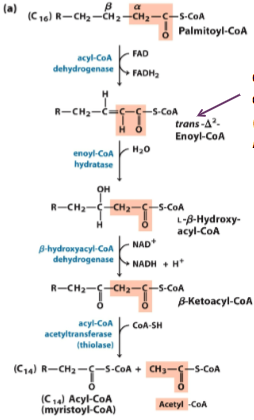
What is the starting material for B-oxidation?
Malonyl CoA (not Acetyl CoA)
What do hydratases work on?
Trans Delta 2 bonds
Metabolic catabolism and anabolism
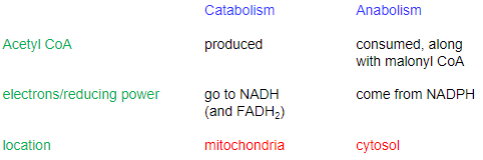
What units are utilized in fatty acid synthesis?
Acetyl and Malonyl Coa
What is the active group of the acyl carrier protein?
Thiol group (SH)
Fatty Acid Synthesis
Step 1: Condensation
KS catalyzes condensation of 2C and 3C units
Acetate added to malonate
Release of CO2 drives reaction forward (2C + 3C - 1C = 4C)
Fatty Acid Synthesis
Step 2: Reduction
Catalyzed by KR (ꞵ-ketoacyl-ACP reductase)
Electron donor is NADPH
Fatty Acid Synthesis
Step 3: Dehydration
Catalyzed by DH (ꞵ-hydroxy acyl-ACP dehydratase)
Fatty Acid Synthesis
Step 4: Second Reduction
Catalyzes by ER (enoyl-ACP reductase)
NADPH is the electron donor
Product is an acyl group that is 2C long than the substrate primer linked to ACP
Know the aspects of a Reaction Coordinate Diagram
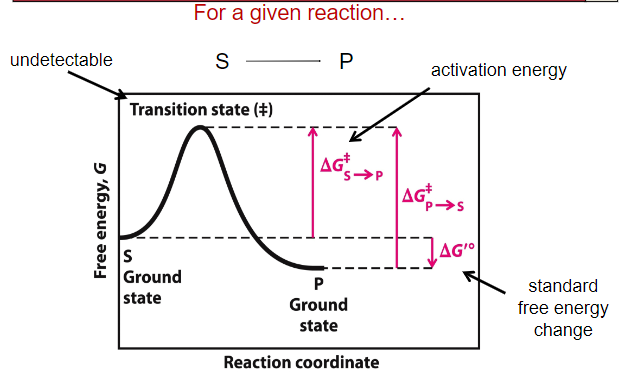
What does ΔG‡ mean?
How fast a reaction will occur
What does ΔG’o mean?
How likely a reaction will occur
Do enzyme impact ΔG’o?
No
Lower the Km
The higher the affinity for enzyme to substrate
Graph and Equation for Enzyme Kinematics
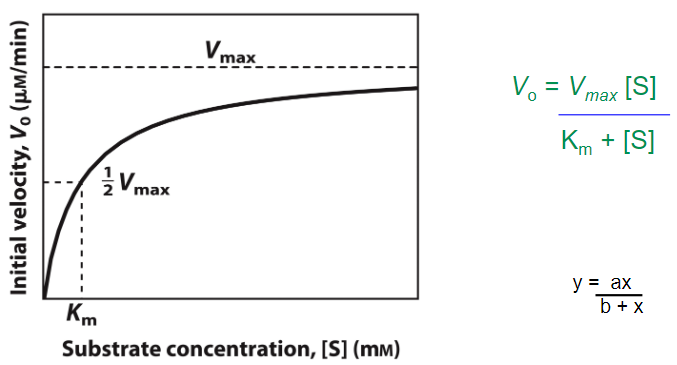
What state is enzyme kinematics always looked under?
Steady State (Rate of formation = Rate of breakdown)
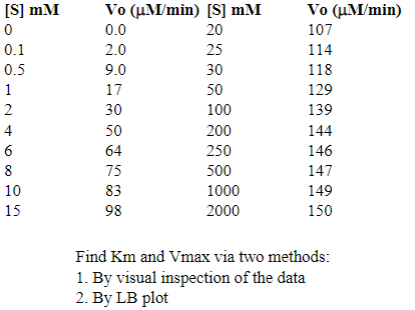
Solve for Vmax given data
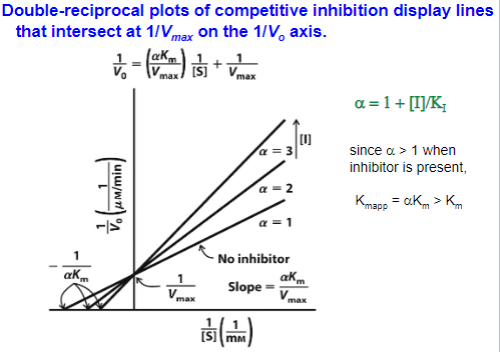
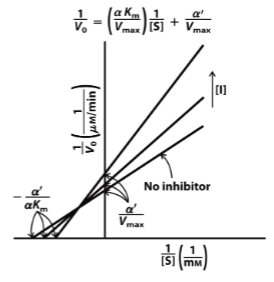
Competitive Inhibition
Binds to enzyme
Calculate for Vmax and Km
Uncompetitive Inhibition
Binds to enzyme substrate complex
Identify values in graph (Km and Vmax are altered)
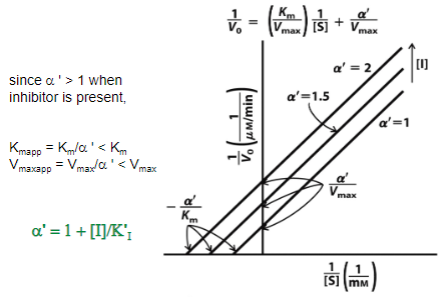
Mixed Inhibition
Km and Vmax are altered
HIV Protease
Water directly attacks the peptide bond and releases the peptide
Enolase
Utilizes Mg2+ ions to stabilize the transition state
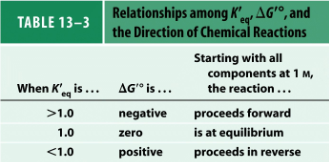
What is Keq?
[Products] / [Reactants]
Know the equation
ΔG = -RTln (K’eq)
How are unfavorable reactions able to proceed?
Via product removal, coupling, or tagging with a good leaving group
What is the movement of electrons?
From lower affinity to higher affinity
Know what an oxidizing and reducing agent is?
OIL RIG
Know what an aldose and ketose is
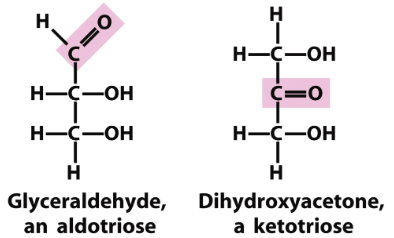
What is the difference between a D and L isomer?
D (OH is on the right) and L (OH is on the left)
What form of amino acids do we use?
L amino acids
What form of sugars do we use?
D sugars
What is the difference between 𝛂 and 𝛃 anomers?
𝛂 (below the plane) 𝛃 (above the plane)
What are the two phases of glycolysis?
Prep Phase - making intermediates to drive reaction
Payoff Phase - regenerate NADH)
6C sugar to 2 3C sugars
What are the 3 bypass steps?
1, 3 (point of no return), 10
Glucokinase
(Hexokinase IV) has a very low affinity for glucose (found in liver) which is where we store our glucose
What are the energy yielding steps of Glycolysis?
6, 7, and 10
What are the PDH cofactors?
E1 (TPP), E2 (lipoamide), E3 (FAD)
What is the result of the PDH complex?
Removal of CO2 (decarboxylation) and formation of Acetyl-CoA
What is the result of the Citric Acid Cycle?
1 turn = 1 GTP, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 2 CO2
(amphibolic cycle - intermediates can come and leave at various points)
What does high levels of Acetyl CoA do?
It will turn off the PDH complex but activate pyruvate carboxylase (reciprocally regulated)
Malate-Aspartate Shuttle
NADH → NADH2
Glycerol-3-Phosphate Shuttle
NADH → FADH2
Brings electrons to electron transport chain
Electron Transport Chain
Movement of e- from complex I to ubiquinol is a favorable reaction. Ubiquinol donates e- to complex III (half cycle due to cytochrome) e- get dropped off to Complex IV
Electron Transport Chain Complex II
Electron donor is succinate, converted to fumarate
FADH pushes 6 protons (1.5 ATP)
Electron Transport Chain Complex IV
Loose (ADP bound), Tight (ATP bound), Open (nothing)
Glycogenesis
Making of glycogen molecules (highly fed state)
Glucose-6-phosphate → glucose-1-phosphate (via phosphoglucomutase)
What is the starting product for Glycogenesis?
UDP glucose (allows for the synthesis of glycogen)
What does glycogen synthase catalyze the formation of?
𝛂 1→4 linkages (branching enzymes make 1→6 linkages)
How do we get amino acids?
From dietary amino acids, or non-dietary protein breakdown
What occurs in the Liver?
Glutamate acting as a nitrogen sink (transamination reaction) donate amino group to alpha-keto acid to mane an amino acid (glutamate in the liver is the carrier of the amino group)
Transdeamination
Removing of amino group in the cytosol (done by enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase)
What occurs in the extrahepatic tissue?
carry 2 molecules of ammonia
L-glutamate → L-glutamine
What occurs in the muscle?
It can take an alternative pathway (glucose-alanine cycle). Amino acids are broken down and put onto glutamate. Donate NH4 and get converted to alanine
Urea Cycle
Think about what is the input (glutamate or glutamine), how much ATP is being input (1 ATP in step 1) (put in 3 ATP) (get 2.5 molecules ATP out)
Glycerophospholipids
Glycerol + 2 fatty acids + alcohol + PO4
Sphingolipids
Sphingosine + fatty acid + PO4 + Choline
Sterols
Rings (function as hormones in our body)
What are the signaling molecules in our body?
PIP2 (Phosphoenol phosphate)
They are usually going to be something with a phosphate attached to it
Membrane Fluidity
Saturated fatty acid (melting point is high)
Unsaturated fatty acid (low melting point)
Trans fatty acid (extremely low)
What are occurring at the same time?
B-oxidation and gluconeogenesis
Fate of Glycerol
1 net molecule of ATP
Carnitine
Transport of fatty acids from cytosol to mitochondria
Acyl carnitine is what is being transferred across the membrane
4 steps of B-oxidation
Oxidation, hydration, oxidation, cleavage
1st step the e- acceptor is FAH, 2nd step the e- acceptor is NAD
Breakdown of a 16C molecule
Acyl-CoA → Acetyl-CoA and C14 molecule
We then run 7 cycle of B-oxidation
16C molecule yield 106 molecules of ATP
Monounsaturated Fatty Acid
Cis-delta-3 → Trans-delta-2 (via an isomerase)
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid
1st enzyme is reductase and 2nd is an isomerase allowing B-oxidation to proceed
How can CoA pools be regenerated?
The formation of ketone bodies