VTNE chp1
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
animal anatomy and physiology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Anatomy
the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts
physiology
the science of how the body functions
what are the two types a cell can be
prokaryote or eukaryote
what type of cell are all bacteria?
prokaryotes
prokaryote
a cell that lacks a true membrane-bound nucleus and organelles
eukaryote
a cell that has a membrane-bound nucleus and contains many different membrane-bound organelles
what cells are all multicellular organisms composed of
eukaryotic cells
what are the three major parts of eukaryotic cells
membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus
purpose of the cell membrane (plasma membrane)
separates the cell from its external environment
solute
a substance that can be dissolved
solvent
a substance that does the dissolving
solution
when the solute has dissolved and is no longer
what are some types of passive processes?
diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, filtration
passive process
no energy is expended by the cell
diffusion
movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration
facilitated diffusion
diffusion with the aid of carrier proteins
osmosis
Movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration (high solvent) to a region of high solute concentration (low solvent)
osmotic pressure
the amount of pressure necessary to stop the flow of water across the membrane
filtration
Substances are forced through a membrane by hydrostatic pressure; small solutes will pass through; larger molecules will not
what type of passive process does glucose use to enter cells?
facilitated diffusion
what passive process is important in kidney function?
filtration
active process
energy is expended by the cell
what are the types of active processes?
endocytosis, exocytosis, active transport
endocytosis
materials are taken into the cell
what are the three types of endocytosis?
phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor mediated
phagocytosis
(“cell eating”): cell membrane extends around solid particles
pinocytosis (bulk-phase)
(“cell drinking”): cell membrane extends around fluid droplets
receptor mediated
Specialized membrane receptors bind to substances entering the cell
what type of endocytosis do enzymes, insulin, hormones, iron and cholesterol use to enter the cell?
receptor mediated
exocytosis
materials are expelled by a cell
what is the purpose of exocytosis?
waste products are excreted and useful products are secreted into the extracellular space
what active process is used by hormones, neurotransmitters, and mucus to be released from cells?
exocytosis
active transport
Movement of molecules from a low concentration to a high concentration with the aid of carrier proteins
active transport and facilitated diffusion are
opposites of each other
what is a form of active transport?
Sodium-potassium pump is an active transport pump within cell membranes; most ions and amino acids move into cells by this method
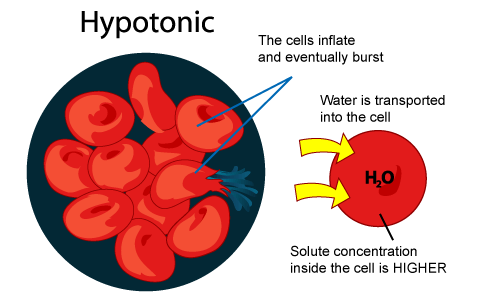
hypotonic
extracellular fluid is less concentrated than the intracellular fluid
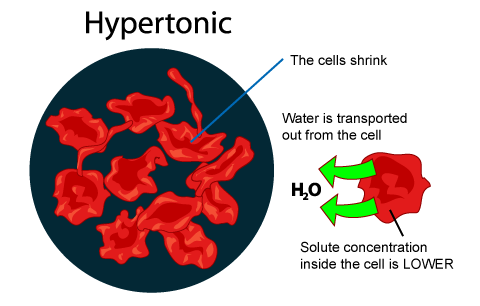
hypertonic
extracellular fluid is more concentrated than the intracellular fluid
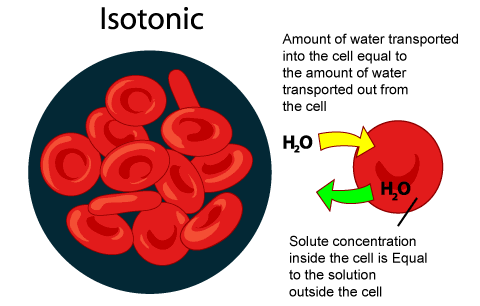
isotonic
concentrations of the extracellular and intracellular fluids are equal
Red blood cells placed in a hypotonic solution will gain water through osmosis and __
burst (hemolysis)
Red blood cells placed in a hypertonic solution will lose water through osmosis and __
crenate (shrivel)
Red blood cells placed in an isotonic solution will __
remain unchanged because osmotic pressures are equal
tissue
groups of similar cells with related functions
what are the four primary types of tissue?
epithelial, connective, nervous, muscle
epithelial tissue
covers body surface, lines body cavities, and forms the active part of glands
what are the functions of epithelial tissue?
protection, secretion, excretion, filtration, absorption of nutrients, and receipt of sensory information
epithelial tissue can form which two types of tissue
simple (one cell layer) or stratified (more than one cell layer) tissue
what are the 6 subtypes of epithelial tissue?
squamous epithelium (simple or stratified)
cuboidal epithelium (simple or stratified)
columnar epithelium (simple columnar epithelial tissue, simple columnar epithelial tissue with cilia, stratified columnar epithelial tissue)
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
transitional epithelium
glandular epithelium (endocrine and exocrine)
what three elements are connective tissue composed of?
cells, fibers, and matrix (ground substance)
what are the functions of connective tissue?
Has a variety of functions depending on tissue type
(connects and supports, protects, insulates, transports fluids, and stores energy)
what are the three fiber types that are in connective tissues?
collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers
collagen fibers
white, long, straight, very strong, composed of collagen
elastic fibers
yellow, long, thin, branching, stretchable fibers composed of elastin
suffix for immature and active cells
-blast
suffix for mature cells
-cyte
suffix for cells that break substances down
-clast
what two categories are connective tissue divided into?
proper and specialized (each has their own subtypes)
what are the three types of muscle tissue?
skeletal (striated), smooth, and cardiac
skeletal (striated) muscle tissue has ___ control
voluntary
skeletal (striated) muscle tissue
attach to and move bones
smooth muscle tissue has __ control
involuntary
smooth muscle tissue
found in walls of hollow organs (digestive tract, blood vessels, etc.)
cardiac muscle tissue has __ control
involuntary
cardiac muscle tissue is found only in the __
heart (myocardium)
what is the main purpose of nervous tissue?
Specialized for conducting electrical impulses
what are the main locations of nervous tissue?
brain, spinal cord, and nerves
what are the two major cell types in nervous tissue?
neurons and neuroglial (glial)
which out of neurons and neuroglial cells conducts impulses?
neurons
membranes
are made up of more than one tissue, which is usually a type of epithelial tissue attached to a type of connective tissue
what are the three types of membranes?
mucous membranes (mucosae)
serous membranes (serosa)
cutaneous membranes (integument or skin)
mucous membranes (muscosae)
membranes that line hollow organs and connect to the exterior
function of mucous membranes
they are adapted to absorb and secrete; normally secrete mucus, which lubricates both the respiratory and digestive pathways
why is the color of mucous membranes important?
the color is used to evaluate many conditions in animals
serous membranes (serosa)
membranes that line body cavities but do not connect to the exterior
what is the function of serous membranes (serosa)?
they secrete a thin, watery fluid (serous fluid) which reduces friction between parietal (inner wall of the body cavity) and visceral (surrounds organ) surfaces
the serous membranes make up the parietal and visceral surfaces
how are serous membranes named?
according to their location and organ
parietal peritoneum
serosa that lines the abdominal cavity
visceral peritoneum
serosa that lines abdominal organs like the stomach, intestines, and liver
parietal pericardium
serosa that lines the cavity where the heart sits
visceral pericardium
serosa that lines the heart itself (aka epicardium)
parietal pleura
serosa that lines the inside of the chest cavity including the ribs and diaphragm
visceral pleura
serosa layer directly covering the lungs
Cutaneous membranes (integument or skin)
it is exposed to the environment, it provides durability, protection, and waterproofing
cranial
toward the head
rostral
toward the nose (used to describe structures on the head)
caudal
toward the tail
dorsal
toward the backbone
ventral
away from the backbone (toward the belly)
medial
closest to the median plane
lateral
farthest from the medial plane
proximal
the point closest to the backbone; used especially in reference to limbs
distal
the point farthest from the backbone; used especially in reference to limbs
anterior
toward the head; used especially in reference to limbs
posterior
toward the tail; used especially in reference to limbs
palmar
bottom of the front foot
plantar
bottom of the rear foot
superficial
toward the outer surface of the animal
deep
away from the outer surface of the animal
osteology
study of bones
what are the two skeletal divisions?
axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton
axial skeleton
bones found on the midline or attached to it (excludes the limbs)
For example: ribs, skull, vertebral column, and sternum