HumanA&P 8: Axial Skeleton
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
3 Major Regions & Number of Bones in Axial Skeleton
Skull
Vertebral Column
Thoracic Cage
80 Bones
Articulation Bone Marking
Where 2 bones meet
Knee joint
Head Bone Marking
Prominent round surface
Head of femur
Facet Bone Marking
Flat surface
Vertebrae
Condyle Bone Marking
Rounded surface
Occipital Condyles
Projection Bone Markings
Raised markings
Spinous process of vertebrae
Protuberance Bone Marking
Protruding
Chin
Process Bone Marking
Prominence feature
Transverse process of vertebrae
Spine Bone Marking
Sharp process
Ischial spine
Tubercle Bone Marking
Small, rounded process
Tubercle of humerus
Tuberosity Bone Marking
Rough surface
Deltoid tuberosity
Line Bone Marking
Slight, elongated line
Temporal lines of the parietal bones
Crest Bone Marking
Ridge
Iliac crest
Hole Bone Marking
Holes & depressions
Foramen
Fossa Bone Marking
Elongated basin
Mandibular fossa
Fovea Bone Marking
Small pit
Fovea capitis on the head of femur
Sulcus Bone Marking
Groove
Sigmoid sulcus of temporal bone
Canal Bone Marking
Passage in bone
Auditory canal
Fissure Bone Marking
Slit through bone
Auricular fissure
Foramen Bone Marking
Hole through bone
Foramen magnum in the occipital bones
Meatus Bone Marking
Opening into canal
External auditory meatus
Sinus
Air filled space in bone
Nasal sinus
2 Sets of Skull Bones
Cranial Bones
Facial Bones
Cranial Bone Functions
Enclose brain in cavity
Provides attachment sites for muscles
Facial Bone Functions
Framework of face
Cavities for organs
Openings for air/food
Secure teeth
Anchor muscles
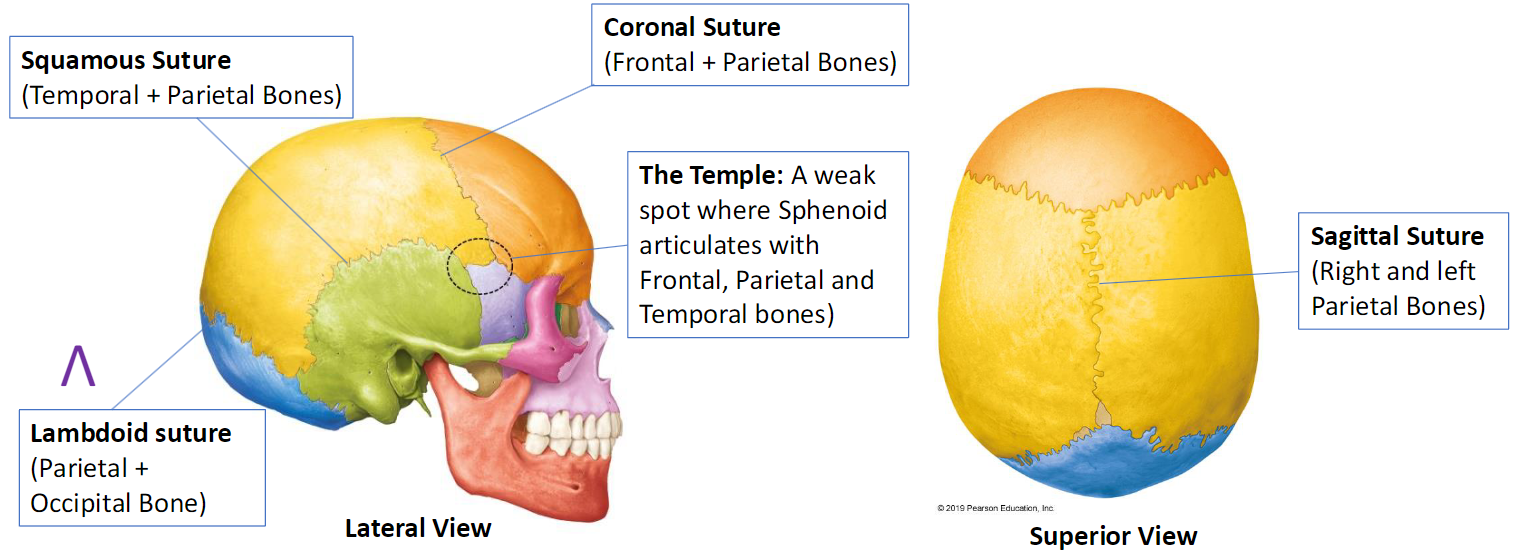
Sutures
Immoveable joint between cranial bones
Cranial Vault
Forms superior aspect of cranial cavity
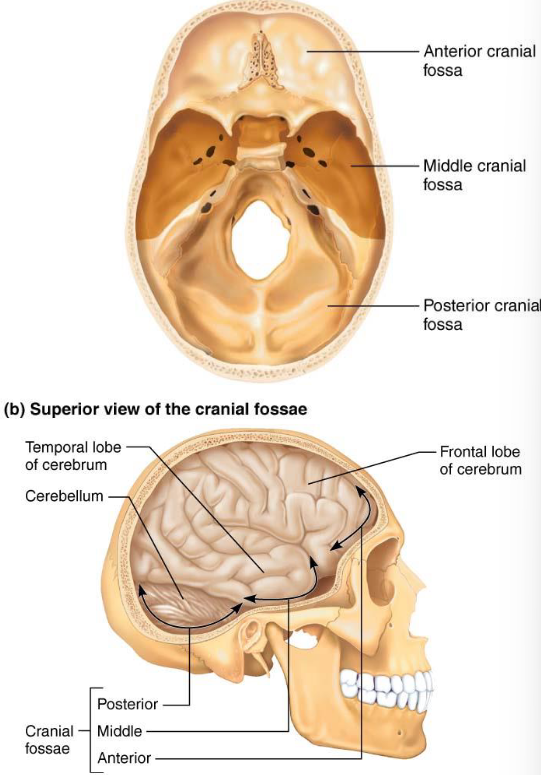
Cranial Base
Forms inferior aspect of skull
Divided into anterior, middle & posterior fossae
Brain sits within fossae
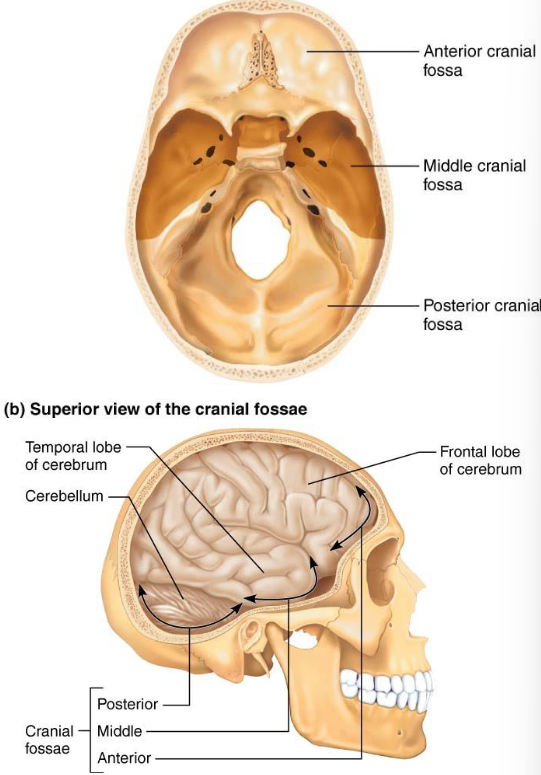
Other Cranial Cavities
85 named openings
Middle/external ears
Nasal
Orbits
8 Cranial Bones
Frontal Bone
Parietal Bones (2)
Occipital Bone
Temporal Bones (2)
Sphenoid Bone
Ethmoid Bone
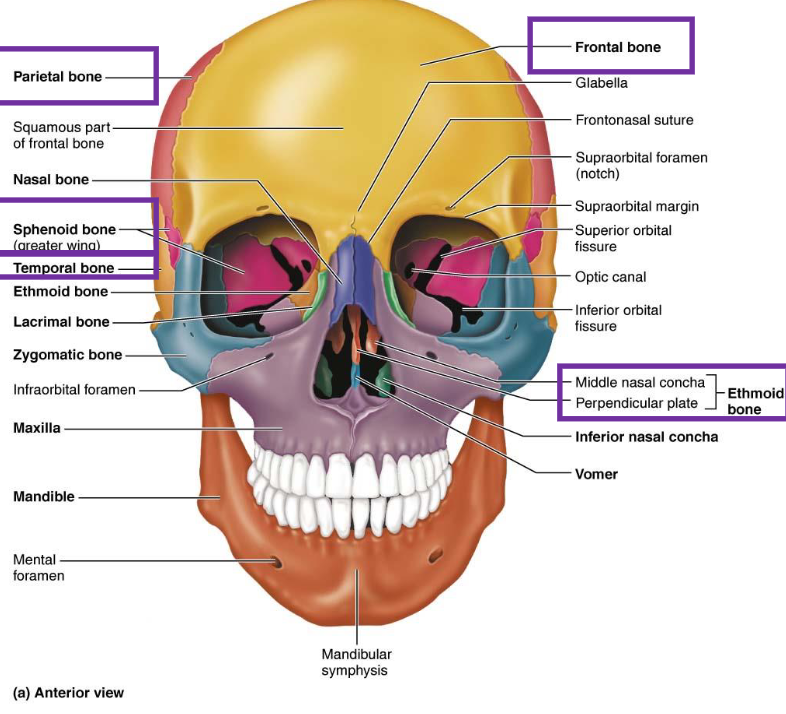
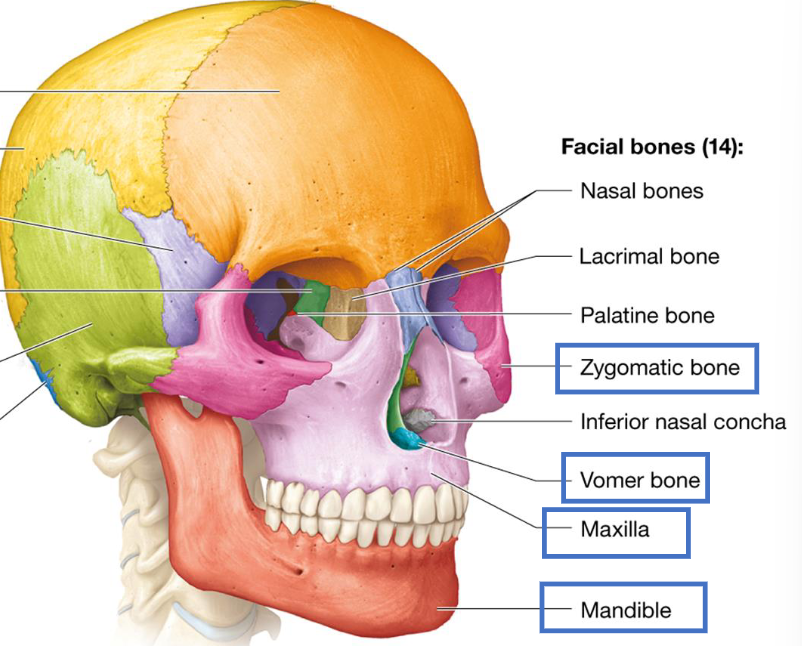
14 Facial Bones
Mandible
Maxillary Bones (2)
Zygomatic Bones (2)
Nasal Bones (2)
Lacrimal Bones (2)
Palatine Bones (2)
Vomer Bone
Inferior Nasal Conchae (2)
Cranial Bone Sutures
Foramen Magnum
Large hole that spinal cord passes through to enter vertebral cavity
4 Cavities of the Skull
Cranial
Orbit
Nasal
Oral
Cranial Cavity
Surrounds brain
Formed by 8 cranial bones
Orbit Cavity
Houses eyeball, nerves, blood vessels & muscles
7 Bones
Nasal Cavity
First part of respiratory tract
Formed by several bones with mucous membranes
Oral Cavity
First part of GI tract
Houses:
teeth
tongue
other structures
Roof is hard palate
Anterior & lateral walls formed by maxillae & mandible
Floor/posterior are soft tissues
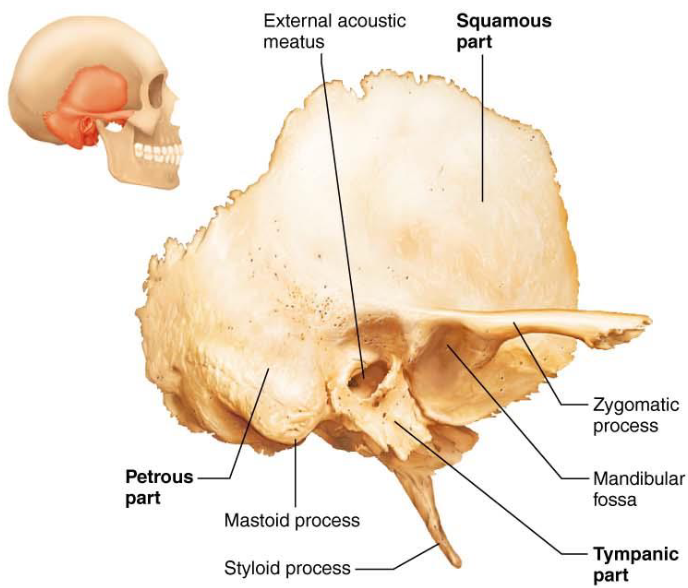
Temporal Bone
Squamous part
Petrous Part
Tympanic Part
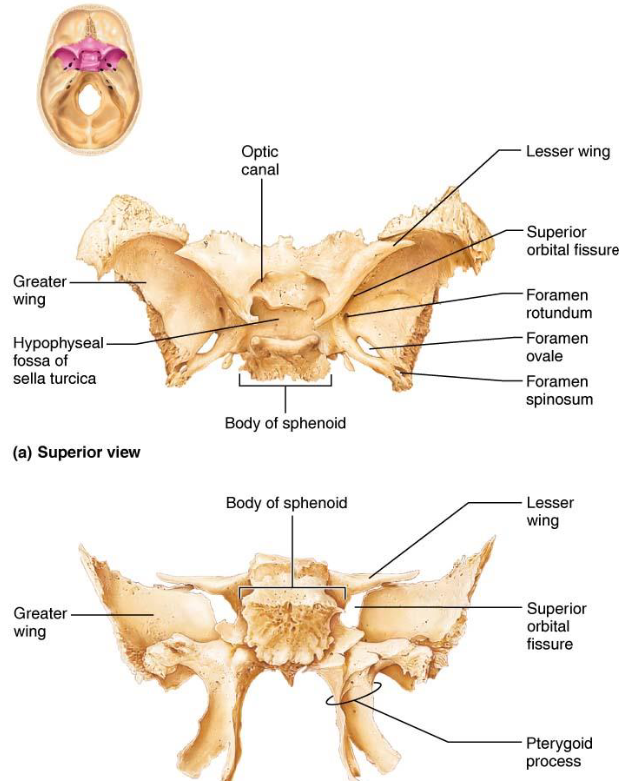
Sphenoid Bone
Hypohyseal fossa of sella turcica
Saddle like
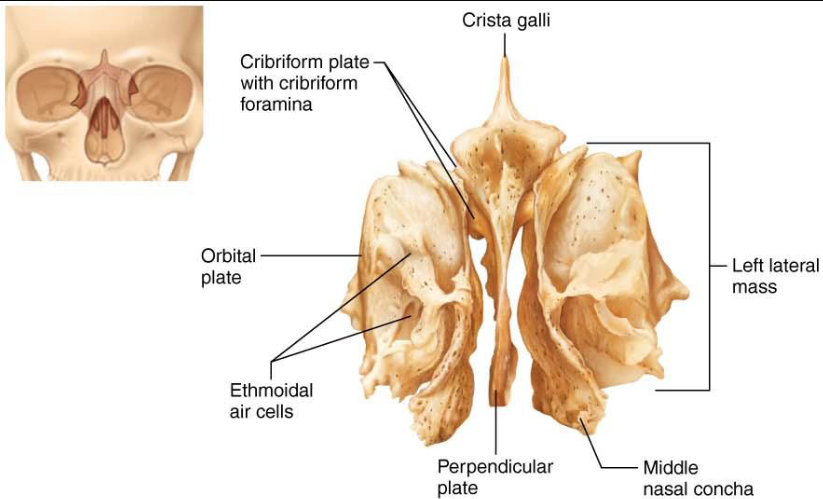
Ethmoid Bone
Deepest skull bone
Cribriform Plates: superior part
Crista Galli: Triangular process, dura mater
Perpendicular Plate: superior part of nasal septum
superior & middle nasal conchae
Orbital Plates: contribute to medial orbits
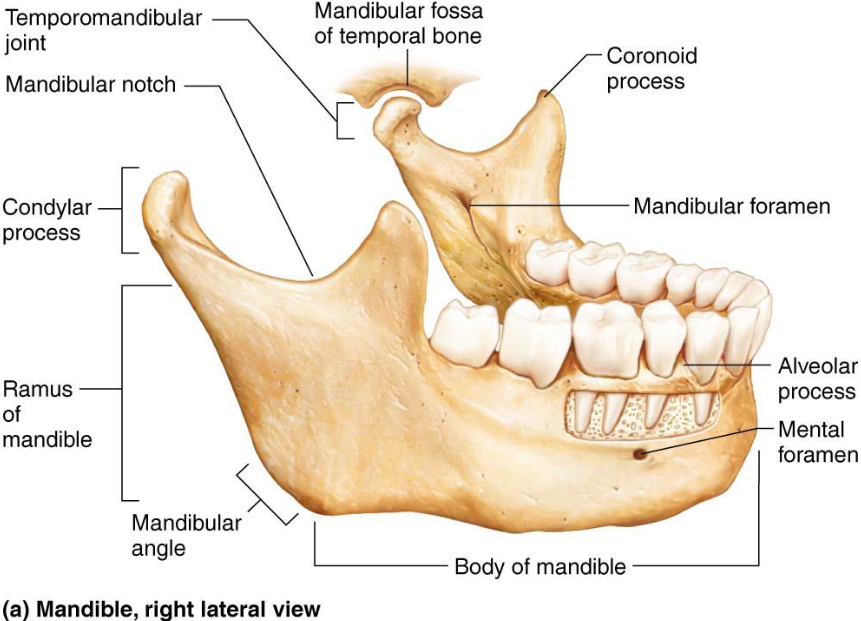
Mandible
Largest, strongest facial bone
Made up of body and 2 rami
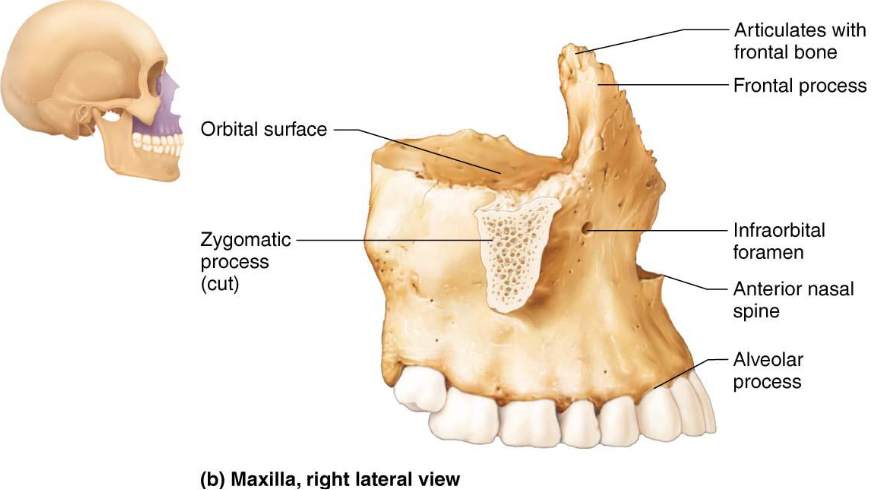
Maxillary Bones
Medially fused to form upper jaw & central facial skeleton
Palatine Bones
L shaped bones made from 2 bony plates
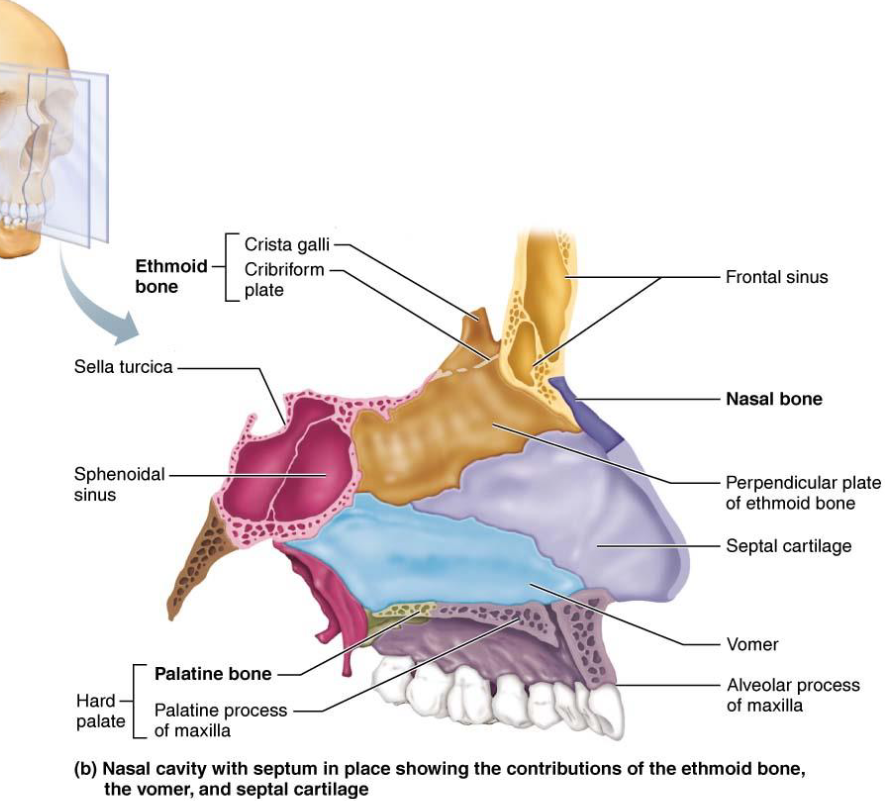
Vomer
Plow shaped bone
Forms part of nasal septum
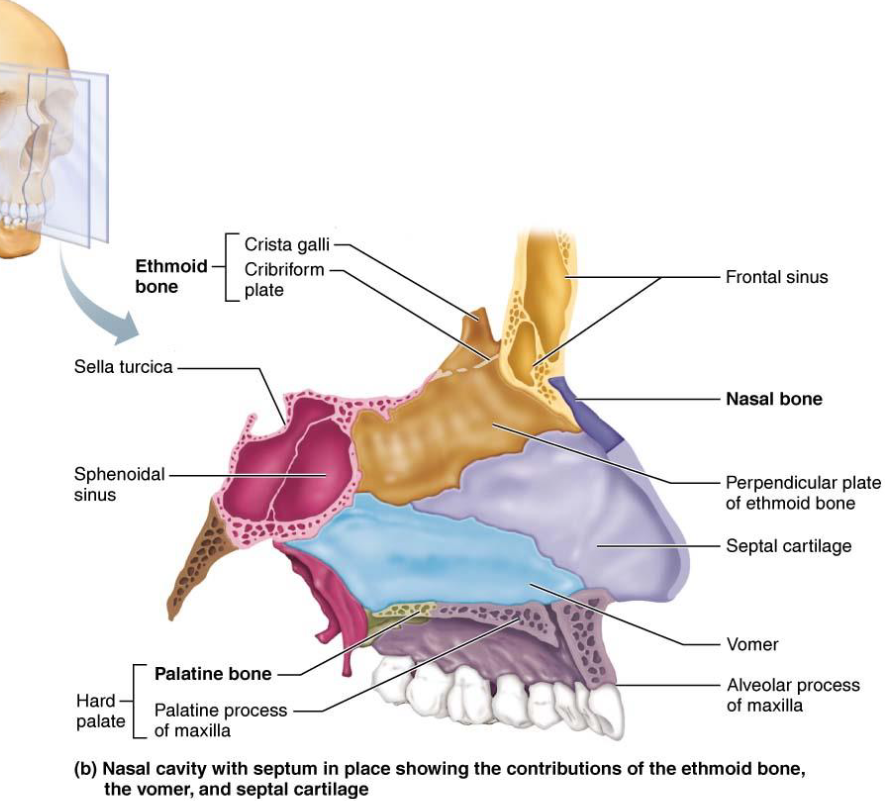
Inferior Nasal Conchae
Paired bones that form part of nasal cavity
Largest of 3 pairs of conchae
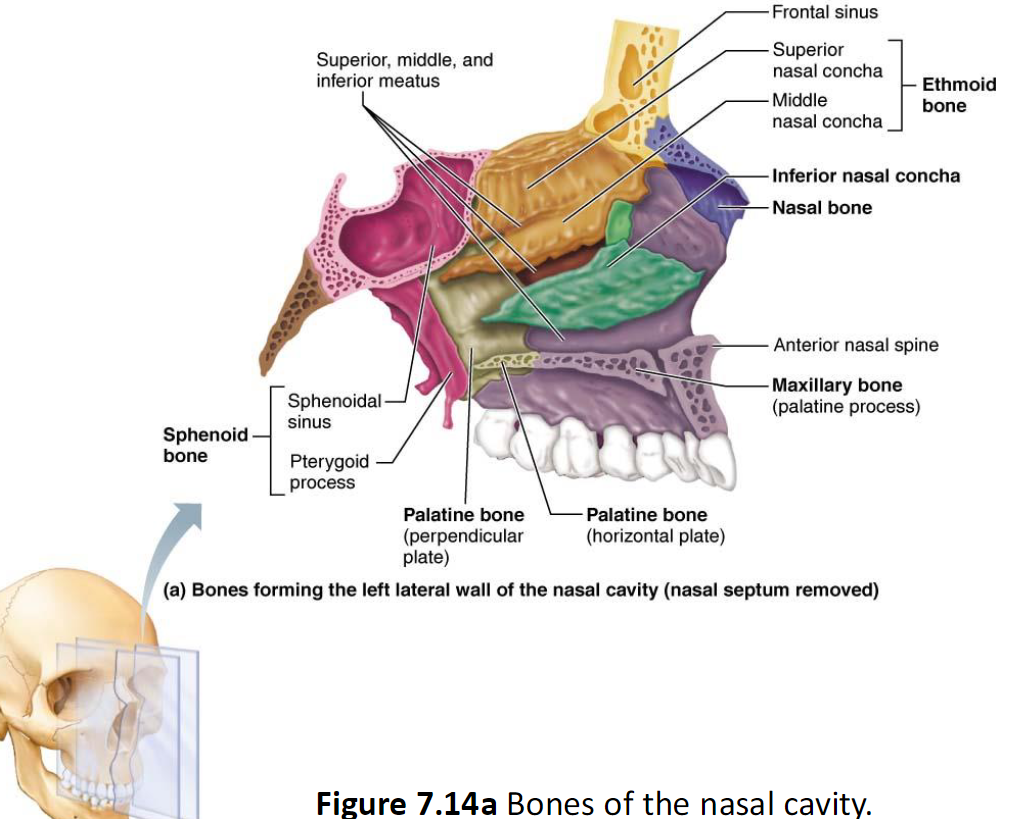
Hyoid Bone
Anterior neck
Only bone that does not articulate directly to another bone
Movable base for tongue
Attachment site for muscles
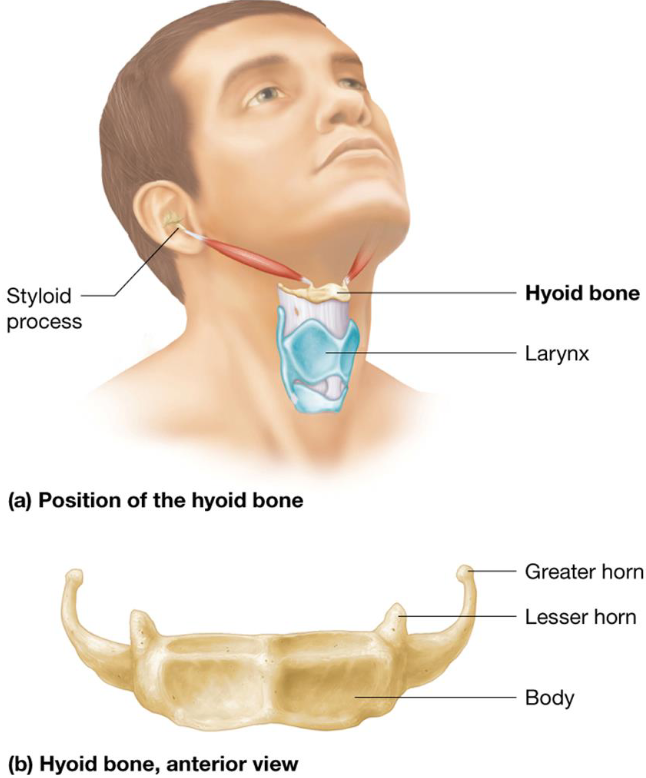
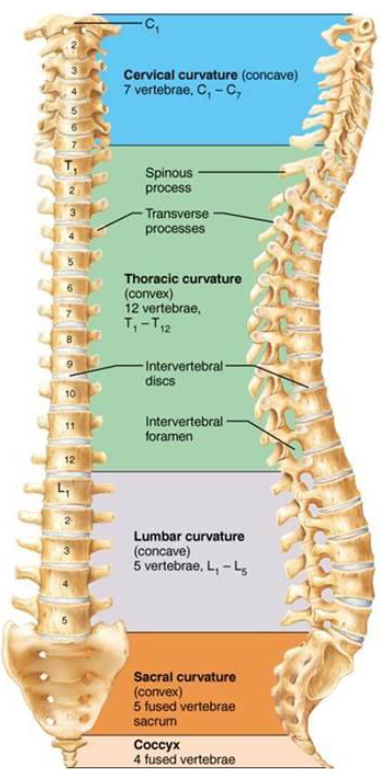
Vertebral Column General Characteristics
26 vertebrae
~28” long
5 regions
4 curves
5 Major Vertebral Regions
Cervical: 7 vertebrae
Thoracic: 12 vertebrae
Lumbar: 5
Sacrum: 1 bone made of several fused bones, at the hip
Coccyx: Fused bones the form terminus of column
4 Main Vertebral Curves
Cervical: Concave posteriorly
Lumbar: Concave posteriorly
Thoracic: Convex posteriorly
Sacral: Convex posteriorly
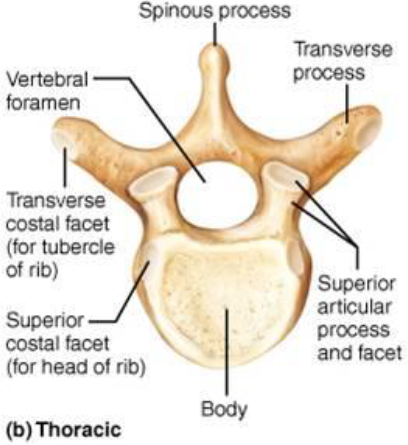
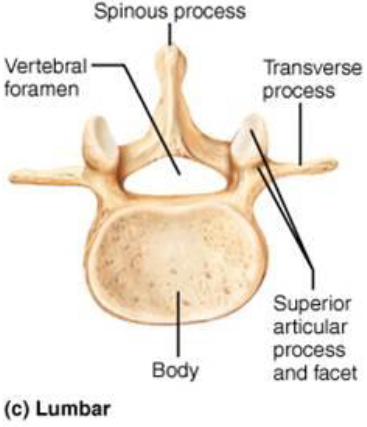
Vertebrae General Structure
Body: anterior region
Vertebral Arch:
2 Pedicles
2 Laminae
Vertebral Foramen: enclosure formed by body & arch
Vertebral Canal: series of foramina
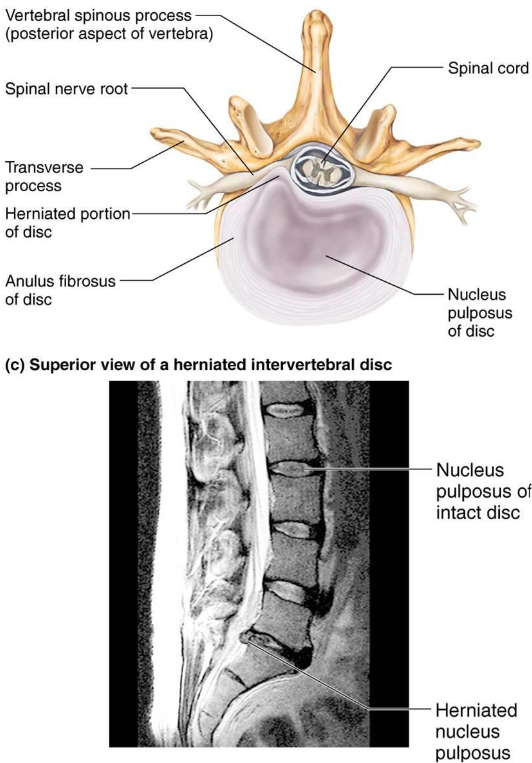
Intervertebral Foramina: lateral openings between vertebrae
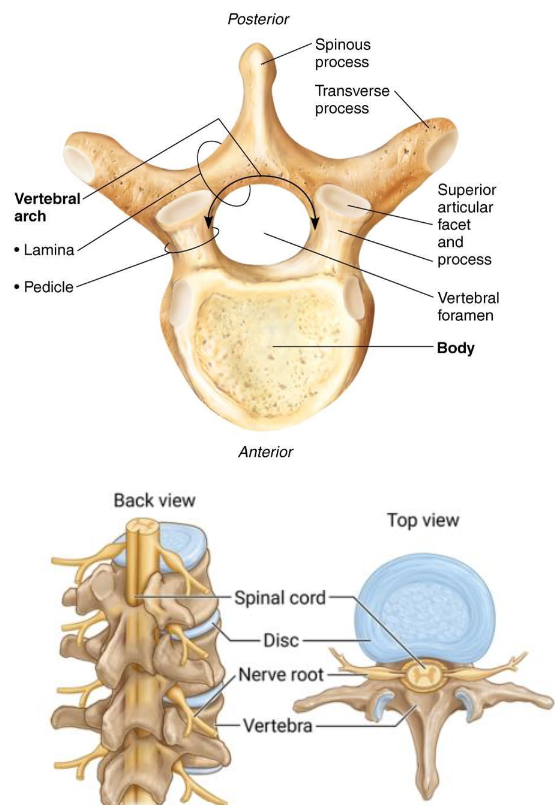
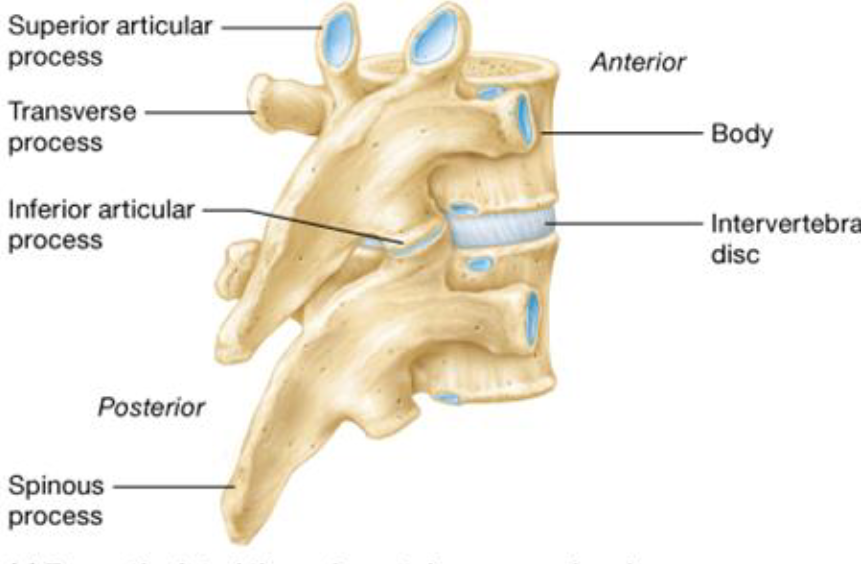
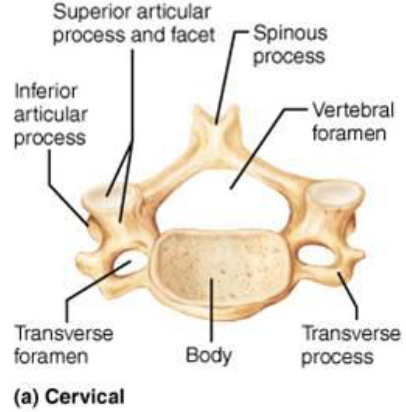
7 Vertebral Processes
Spinous Processes: posteriorly
Transverse Processes: laterally
Superior Articular Process: superiorly
Inferior Articular Process: Inferiorly
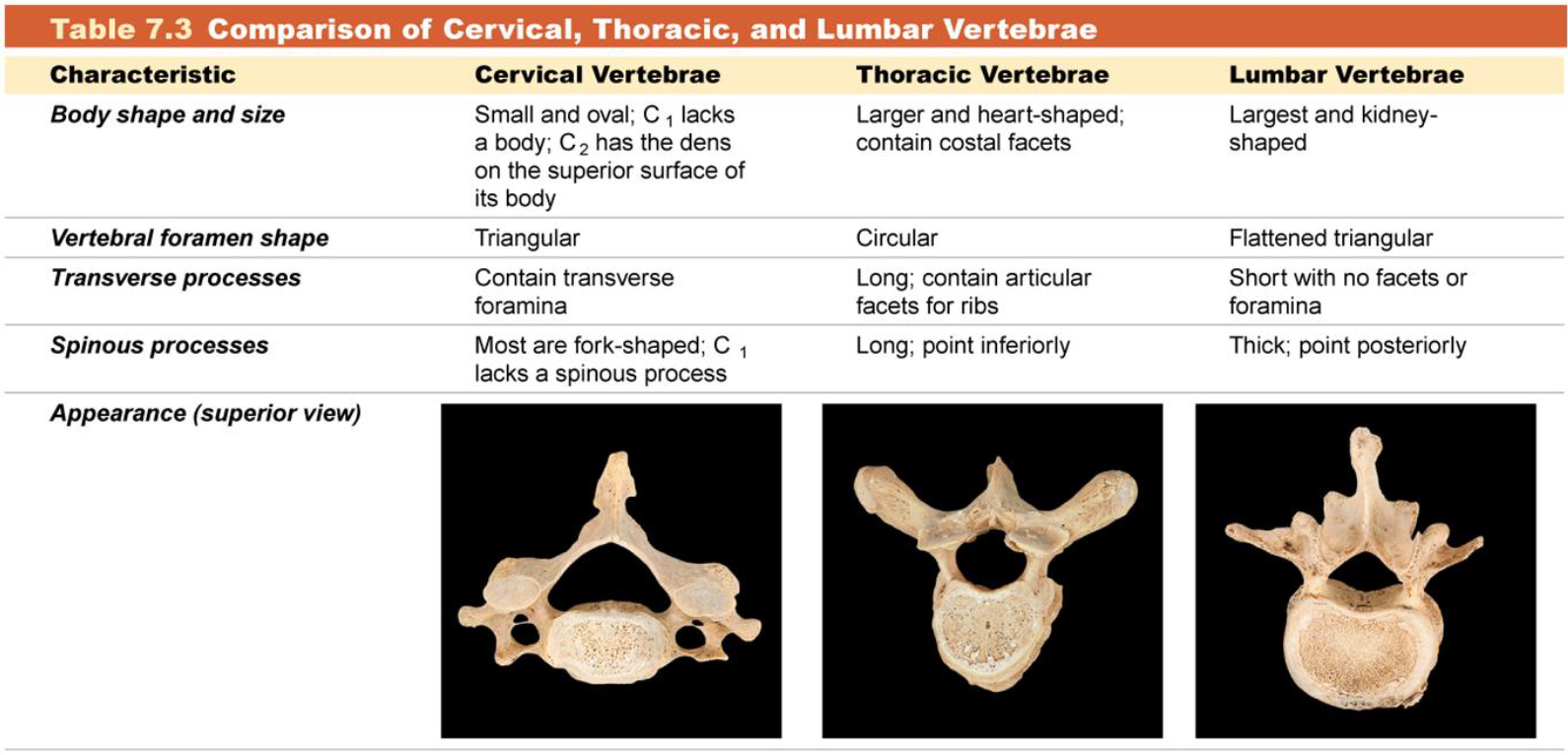
Cervical Vertebrae
Concave
C1 - C7
Thoracic Vertebrae
Convex
T1 -T12
Lumbar Vertebrae
Concave
L1 - L5
Vertebrae Comparison
Vertebral Ligaments
Support vertebral column
Anterior & posterior longitudinal
continuous bands from neck to sacrum
Supraspinous Ligament
interconnects spinous processes of thoracic & lumbar vertebrae
nuchal ligament at neck
Ligamentum Flavum
connects adjacent vertebrae
provides support during forward bending
Intervertebral Discs
Cushion-like pad between vertebrae
Shock absorbers
2 Parts:
Nucleus Pulposus: Inner gelatinous nucleus
Anulus Fibrosis: outer collar of collagen & fibrocartilage
Sacrum
Triangular bone shapes posterior wall of pelvis
5 Fused vertebrae
Superior articular process articulates with L5
Auricular Surfaces articulate with coccyx & hip forming sacroiliac joints
Anterior Sacral Foramina: lateral ends of ridges
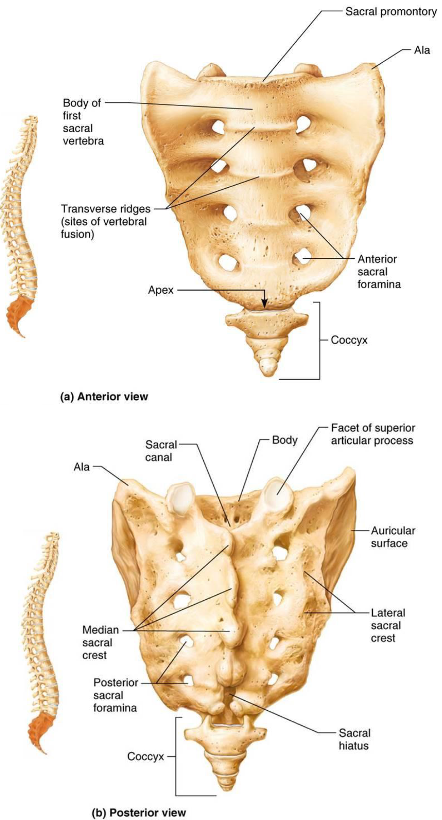
Coccyx
Tailbone formed of 3-5 fused vertebrae
Articulates with sacrum
Thoracic Cage
Composed of:
Vertebrae
Sternum & costal cartilages
Ribs
Functions:
Protection
Supports shoulders
Attachment sites for muscles
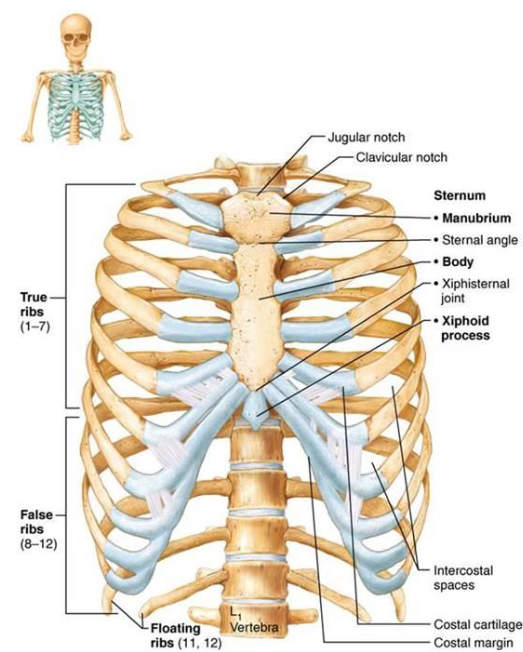
Sternum
3 Fused bones
Manubrium: superior with clavicular notches
Body: midportion
Xiphoid Process: inferior site of muscle attachment
not ossified till 40
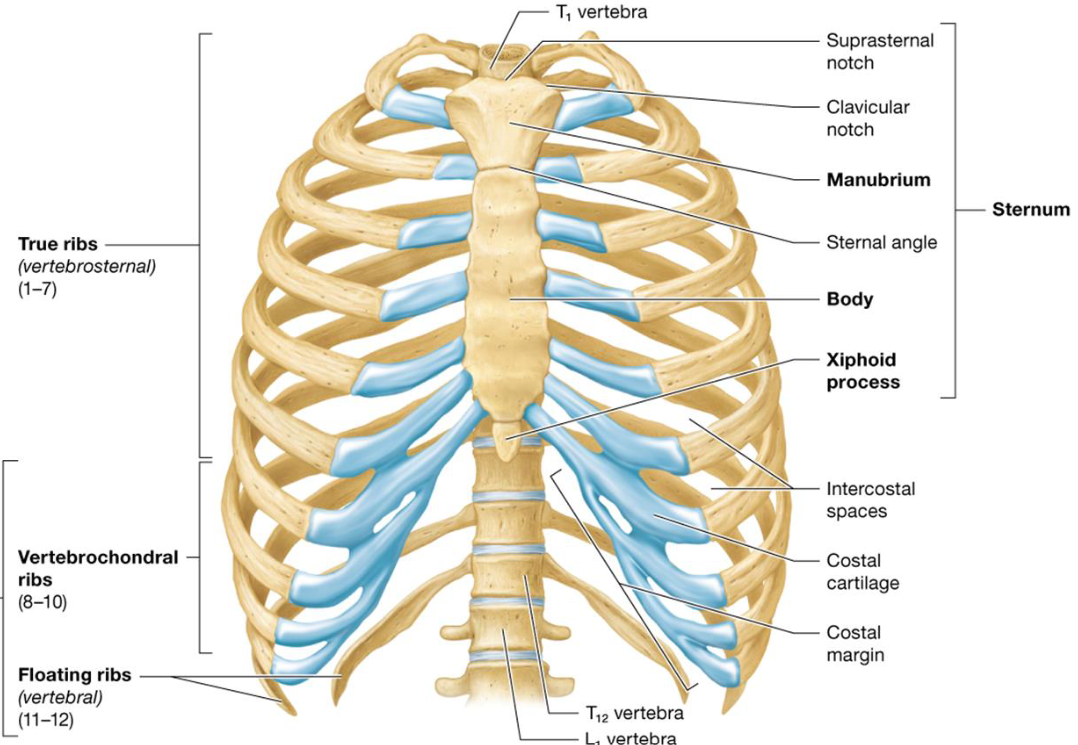
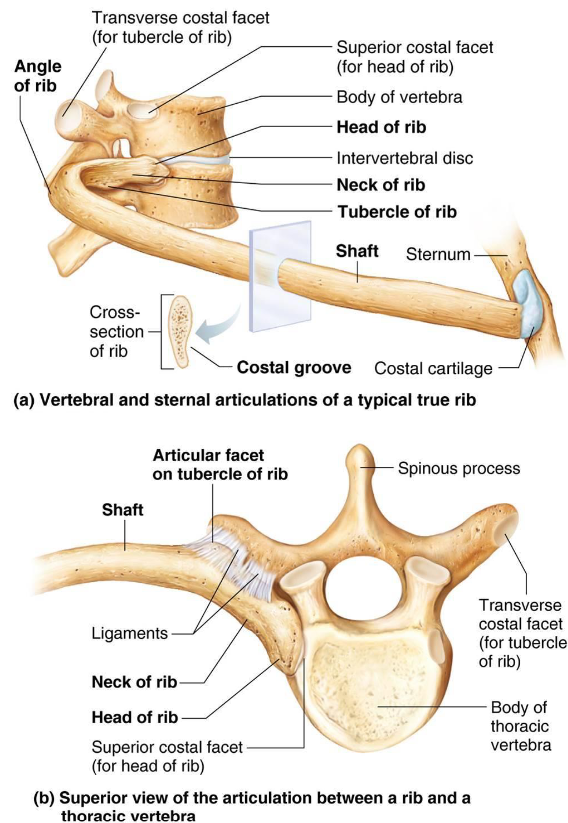
Ribs
Main parts:
Shaft: flat bone, most of rib
Head: articulates with facets on 2 adjacent vertebrae
Neck: constricted portion beyond head
Tubercle: knoblike structure later to neck