Chapter 16 Please Save Me
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
What is fiscal policy?
Changes in federal government purchases, transfer payments, and taxes that are intended to achieve macroeconomic policy objectives.
Economists typically use the term fiscal policy to refer only to the actions of the __________.
federal government.
Economists use the term fiscal policy to refer to changes in taxing and spending policies
only by the federal government.
There is an important distinction between __________ and __________.
automatic stabilizers and discretionary fiscal policy.
Government spending and taxes that automatically increase or decrease with the flow of the business cycle _____.
Automatic stabilizers
What are automatic stabilizers?
Government spending and taxes that automatically increase or decrease with the flow of the business cycle.
With discretionary fiscal policy, the government takes actions to change spending or taxes.
Think of it like this - discretionary fiscal policy entails the government specifically going out of their way to change spending or taxes.
NOT automatic!
If the government cuts taxes in order to increase aggregate demand, the action is called
a discretionary fiscal policy
Changes in taxes and spending that happen without actions by the government are called
automatic stabilizers
Government expenditures include ___________—such as Social Security payments by the federal government or pension payments to retired police officers by local governments—that does not involve purchases.
purchases plus government spending
Purchases plus government spending are included in what?
Government expenditures
Economists often measure government spending relative to the size of the economy by calculating government spending as a
percentage of GDP.
Federal government purchases as a percentage of GDP have actually been slowly _____ over the period since the end of the Korean War in the early 1950s.
declining
The _________ between 1992 and 2000 was partly the result of the end of the Cold War between the Soviet Union and the United States, which allowed for a substantial reduction in defense spending.
decline in expenditures
In addition to purchases, the three other categories of federal government expenditures that are most important in a typical year are_____.
interest on the national debt, grants to state and local governments, and transfer payments.
_____ represents payments to holders of the bonds the federal government has issued to borrow money.
Interest on the national debt
Grants to state and local governments are _____.
payments made by the federal government to support government activity at the state and local levels.
The largest and fastest-growing category of federal expenditures is __________. Some of these programs, such as Social Security and unemployment insurance, began in the 1930s.
transfer payments
As the U.S. population ages and medical costs continue to increase, federal government spending on the Social Security and Medicare programs will continue to_____ causing transfer payments to consume an increasing share of federal expenditures
rise
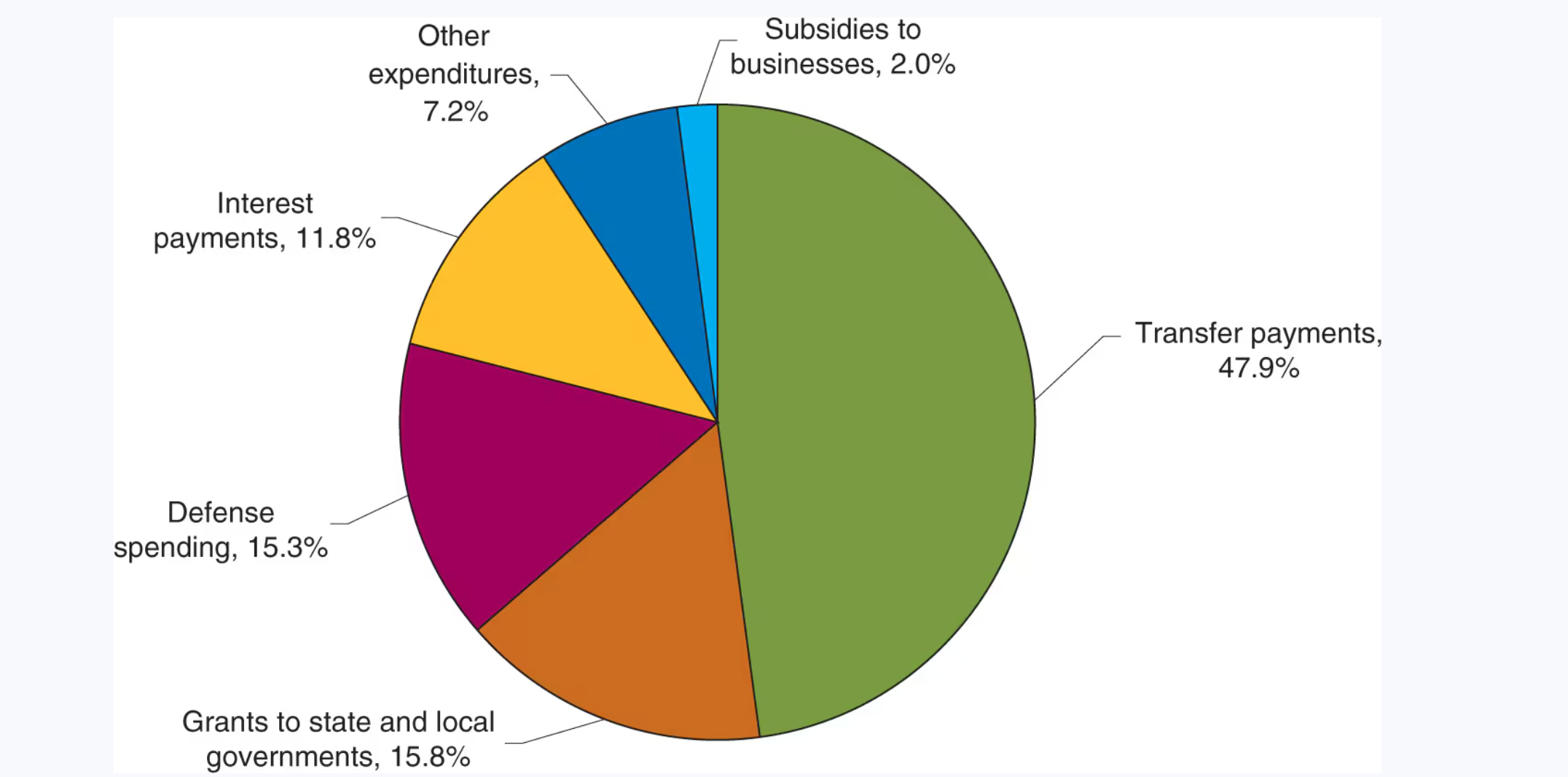
Federal government expenditures 2022
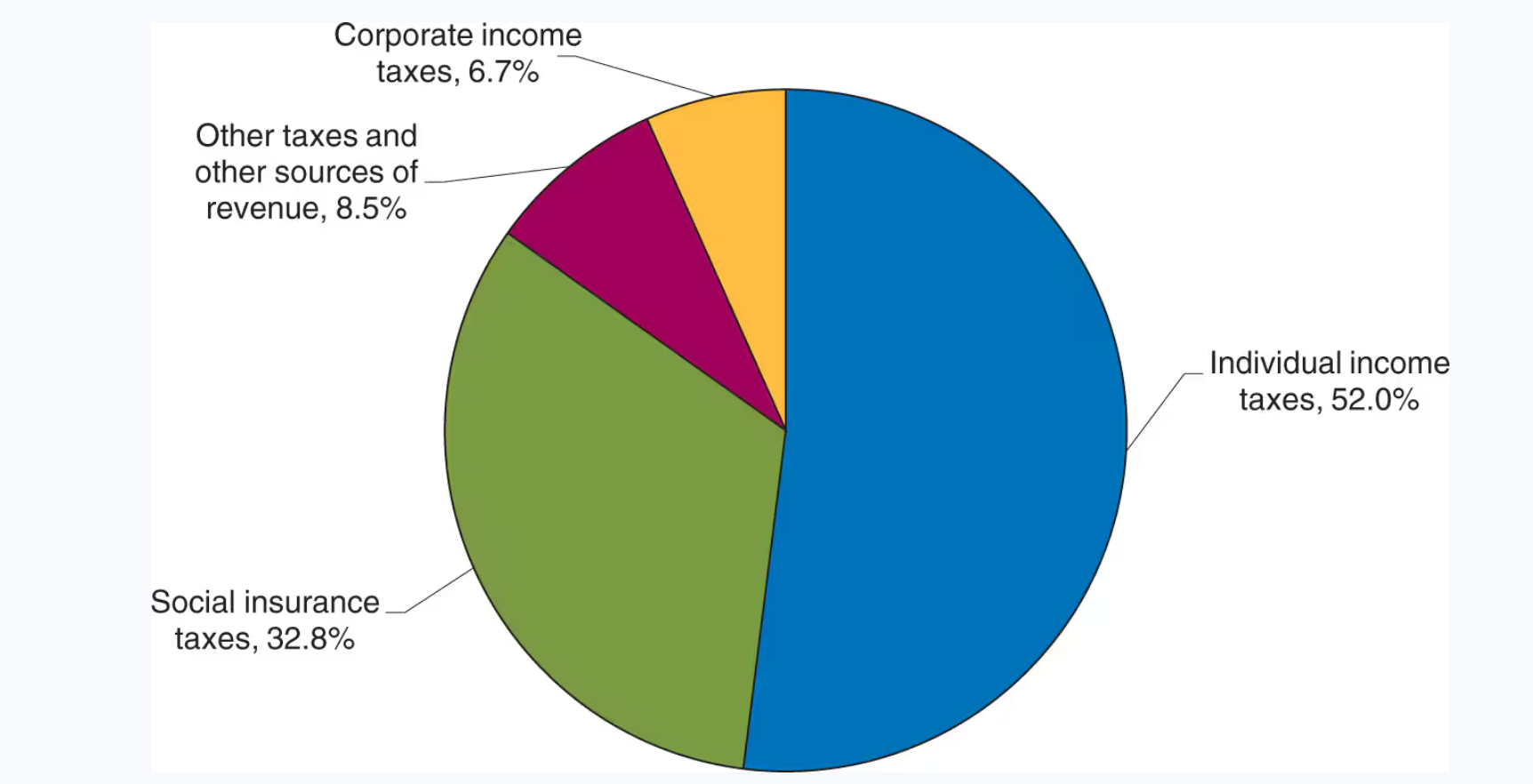
Federal government revenue
What are the three largest federal transfer programs in the U.S.?
Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid.
When was Social Security established, and by whom?
In 1935 by Congress and President Franklin Roosevelt.
Q: What impact have Social Security and Medicare had on older Americans?
A: They have significantly reduced poverty among older Americans.
Q: Who was the first Social Security beneficiary, and how much did she pay versus collect?
A: Ida May Fuller; she paid $24.75 and collected $22,888.92 in benefits.
Q: What was the worker-to-retiree ratio in 1940?
A: Over 150 workers for every retiree.
Q: How did the Social Security system originally work?
A: It was a "pay-as-you-go" system where current workers’ taxes paid for current retirees.
Q: What funding challenges does Congress face with these programs?
A: Difficulty in securing sustainable funding for Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid in the future.
Q: What is the purpose of the Medicare program?
A: To provide health care coverage to people age 65 and older.
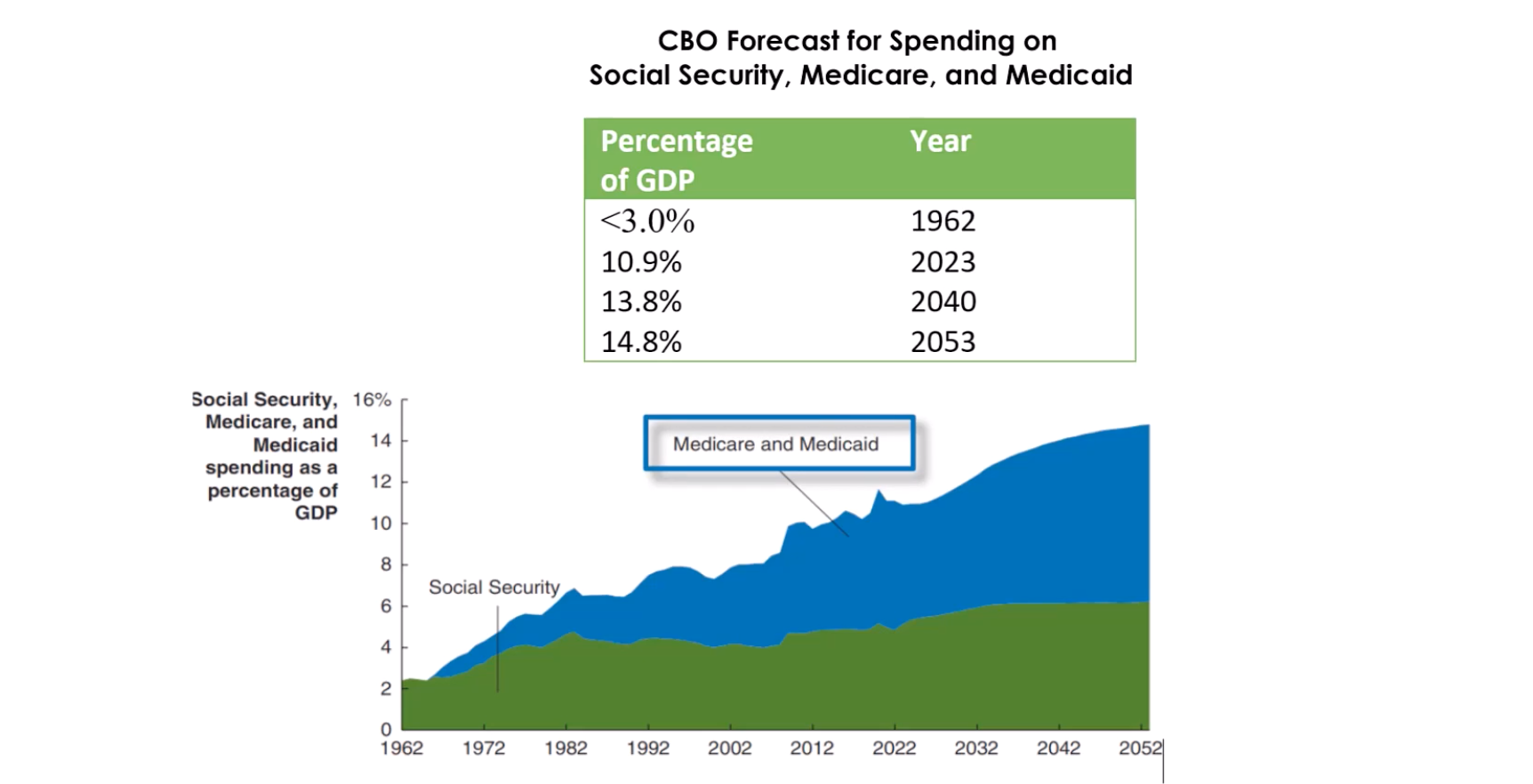
Forecast for soending on social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid programs.
Fiscal policy can aleo be aimed at offsetting the effects of the _____.
Business cycle AND the economy’s long-run growth rate
How are monetery and fiscal policy carried out?
Monetary policy - carried out by the Fed through changes in interest rates
Fiscal policy - carried out by congress and the president through hanges in government purchases, transfer payments, and taxes
Decreases in government purchases or increases in taxes:
can slow the growth of aggregate demand and reduce the inflation rate
When the economy is in a recession,
increases in government purchases or transfer payments or decreases in taxes will increase aggregate demand
Expansionary fiscal policy
involves increasing government purchases or transfer payments or decreasing taxes
Cutting taxes on business income can increase aggregate demand by
increasing investment spending.
The goal of expansionary fiscal policy is
to increase aggregate demand
Expansionary fiscal policy can return real GDP to potential GDP, but only at the expense of _____ in the inflation rate.
an increase
Recessions require
expansionary fiscal policy
Rising inflation requires
contradictory fiscal policy
An attempt to reduce inflation requires _____________ fiscal policy, which causes real GDP to _________ and the price level to __________.
Contradictionary
Fall
Fall
Congress and the president can use fiscal policy to affect aggregate demand,
thereby changing the price level and the level of real GDP.
Over time, potential GDP ________, which is shown by the ________ curve shifting to the right
increases; long-run aggregate supply
In response to the economic effects of the Covid–19 pandemic, Congress and President Trump enacted the
Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act in March 2020.
CARES act and Consolidated Appropriations by Trump and the American Rescue Plan by Biden
The combined $4.7 trillion in spending was by far the largest fiscal policy action in U.S. history; it was equal to about 95 percent of the amount that the federal government spent in 2019 on all programs, including Social Security, Medicare, national defense, and medical research.
The three COVID fiscal policy bills
All three bills included the following: (1) direct payments to individuals as well as supplements to state unemployment benefits; (2) funds to help state and local governments cover the costs of fighting the virus; and (3) funds to local school districts to, among other things, buy improved ventilation systems for school buildings.
Economists refer to the initial increase in government purchases as _____ because it is a result of a decision by the government and is not directly caused by changes in the level of real GDP.
autonomous
Economists use the term _______ to describe the process by which a change in autonomous expenditure leads to a larger change in real GDP.
multiplier effect
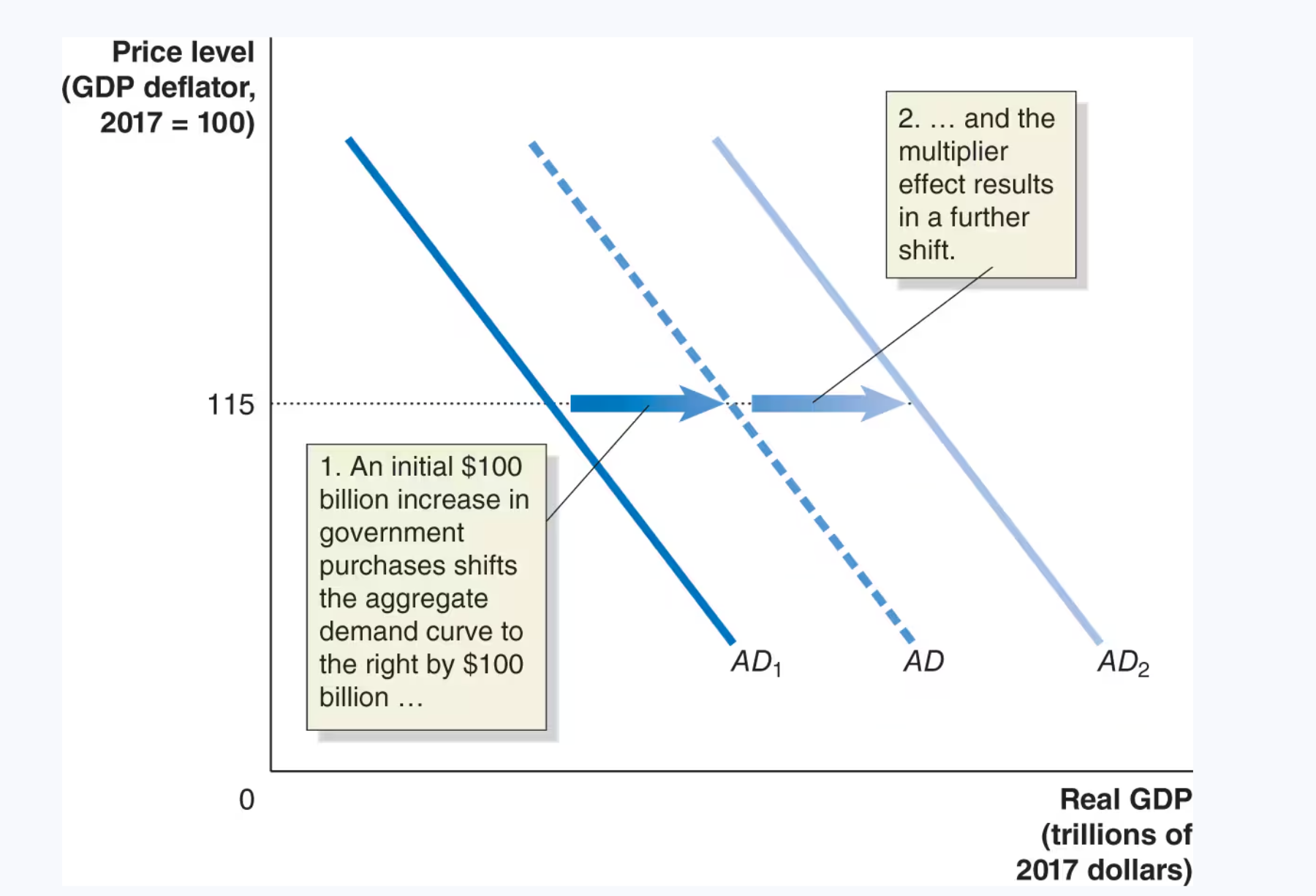
The multiplier effect
The higher the tax rate,
the smaller the multiplier effect. This is because higher taxes reduce consumers' disposable income, which decreases their spending and, therefore, dampens the overall impact of any initial change in spending.
The actual change in real GDP is often
less than what the simple multiplier effect predicts because the simple multiplier assumes no crowding out, no changes in interest rates, prices, or imports. In reality, factors like higher interest rates, inflation, or increased imports can reduce the total impact of fiscal policy.
Expansionary fiscal policy has a ________ multiplier effect on equilibrium real GDP, and contractionary fiscal policy has a ________ multiplier effect on equilibrium real GDP.
positive; negative
Explanation:
Expansionary fiscal policy (like increasing government spending or cutting taxes) increases aggregate demand, leading to a positive multiplier effect on equilibrium real GDP.
Contractionary fiscal policy (like cutting government spending or raising taxes) decreases aggregate demand, leading to a negative multiplier effect on equilibrium real GDP.
Getting the timing right for fiscal policy is difficult for two reasons
The president and a majority of the 535 members of Congress have to agree to change fiscal policy. The delays caused by the legislative process can be very long
It takes time to implement change
Recessions that follow financial crises are:
usually severe
A decline in private expenditure as a result of an increase in government purchases is called _______.
Crowding out
Crowding out occurs because a higher interest rate will cause a decline in
each component of private expenditures.
Crowding out may reduce ______.
the effectiveness of an expansionary fiscal policy.
According to the crowding-out effect, if the federal government increases spending, the demand for money and the equilibrium interest rate will ___________, which will cause consumption, investment, and net exports to ___________.
increase; decrease
Explanation - According to the crowding-out effect, when the federal government increases spending, it boosts aggregate demand, which increases the demand for money. This drives up the equilibrium interest rate, which in turn causes consumption, investment, and net exports to decrease, as borrowing becomes more expensive and the dollar strengthens
What is the long-run effect of a permanent increase in government spending?
The decline in investment, consumption, and net exports exactly offsets the increase in government spending; therefore, real GDP remains unchanged.
Explanation:
In the long run, the economy is at full employment output. A permanent increase in government spending can lead to crowding out of private spending—investment, consumption, and net exports—due to higher interest rates and other factors. This crowding out offsets the increase in government spending, leaving real GDP unchanged in the long run.
Congress and the president can _______ to increase aggregate demand either to avoid a recession or to shorten the length or severity of a recession that is already underway.
increase government purchases and transfer payments and cut taxes
About ________ of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act stimulus package took the form of increases in government expenditures, and about ________ took the form of tax cuts
two-thirds; one-third
Between the beginning of 2009 and the end of 2010, real GDP ________, while employment ________.
increased by 4.0 percent; declined by 3.3 million
Budget deficits automatically __________ during recessions and __________ during expansions
increase; decrease
The cyclically adjusted budget deficit
is measured as if the economy were at potential real GDP
What made the 2020 recession especially severe?
It was caused by a pandemic that forced many businesses to close or operate at reduced capacity.
Why did some typically skeptical economists support fiscal policy during the 2007–2009 recession?
Because the severity of the recession justified increased government spending and tax cuts to boost aggregate demand.
What is a federal budget deficit?
A budget deficit occurs when the federal government's expenditures exceed its tax revenue.
What is a federal budget surplus?
A surplus occurs when the federal government’s tax revenue exceeds its expenditures.
Why is it helpful to measure deficits or surpluses as a percentage of GDP?
Because it puts the size of the deficit or surplus in the context of the overall economy, making it easier to compare across time.
When did the largest budget deficits of the 20th century occur?
During World War I and World War II, due to massive spending increases that weren’t fully offset by higher taxes.
How do recessions affect the federal budget?
Recessions typically cause increased government spending and reduced tax revenues, which widen the deficit.
Why did the federal government return to running deficits after 2001?
Due to recessions, tax cuts, and increased government spending on security and military efforts.
What are two major causes of large federal budget deficits during wartime?
Massive increases in government spending and only partially offsetting increases in taxes.
How does the federal budget act as an automatic stabilizer?
During recessions, the budget deficit increases automatically due to higher spending (like unemployment benefits) and lower tax revenue, which helps stabilize aggregate demand.
Few economists believe the federal government should attempt to balance its budget every year
TRUE
The national debt is best measured as
the total value of U.S. Treasury securities outstanding
What does the Treasury do when the federal government runs a budget deficit?
It borrows funds from investors by selling Treasury securities (bonds).
What happens when the federal government runs a budget surplus?
The Treasury pays off some existing bonds.
Why has the number of Treasury bonds increased over time?
Because the U.S. has had more years of deficits than surpluses.
What does an increase in the debt-to-GDP ratio typically indicate?
That the debt is growing faster than the economy, often due to large budget deficits.
How does a budget surplus affect the national debt?
It allows the Treasury to pay off existing bonds, reducing the federal government debt.
Which of the following statements about the federal debt is correct?
If the debt becomes very large relative to the economy, then the government may have to raise taxes to high levels or reduce other types of spending to make the interest payments on the debt.
The long-run growth rate of real GDP depends primarily on
the growth rate of labor productivity as measured by the growth in real GDP per hour worked
the growth in the number of hours worked.
Economists believe that the smaller the tax wedge for any economic activity, such as working, saving, investing, or starting a business
the more of that economic activity that will occur
What is the main goal of fiscal policy aimed at long-run growth?
To increase incentives to work, save, invest, and start a business by changing tax policy.
How did the Trump administration try to boost long-run economic growth?
By cutting taxes and implementing regulatory reforms to encourage business formation and reduce entry barriers in some occupations.
How did the Biden administration propose improving labor market efficiency?
By reducing occupational licensing and banning non-compete clauses that prevent workers from switching jobs within the same industry.
What are the two main effects of regulatory reform on the labor market?
It can increase the size of the labor force (more people working).
It can increase labor productivity (workers become more efficient).
What is the tax wedge?
The difference between the pretax and posttax return from an economic activity.
What determines the size of the tax wedge?
The marginal tax rate—the portion of each additional dollar of income that must be paid in taxes.
What are tax brackets?
Income ranges within which specific tax rates apply.
Example of a 2023 tax bracket for single taxpayers:
The tax rate was 10% on the first $11,000 earned; higher rates applied to higher income brackets, reaching up to 37%.
Why are marginal tax rates important for economic incentives?
Because higher marginal tax rates reduce the after-tax reward for working, saving, or investing, potentially discouraging economic activity.
What is one way fiscal policy can encourage long-run economic growth without changing taxes?
By implementing regulatory reform to reduce barriers to entry and improve labor market efficiency.
A simplified tax code would reduce economic efficiency by increasing the number of decisions households and firms make solely to reduce their tax payments
FALSE
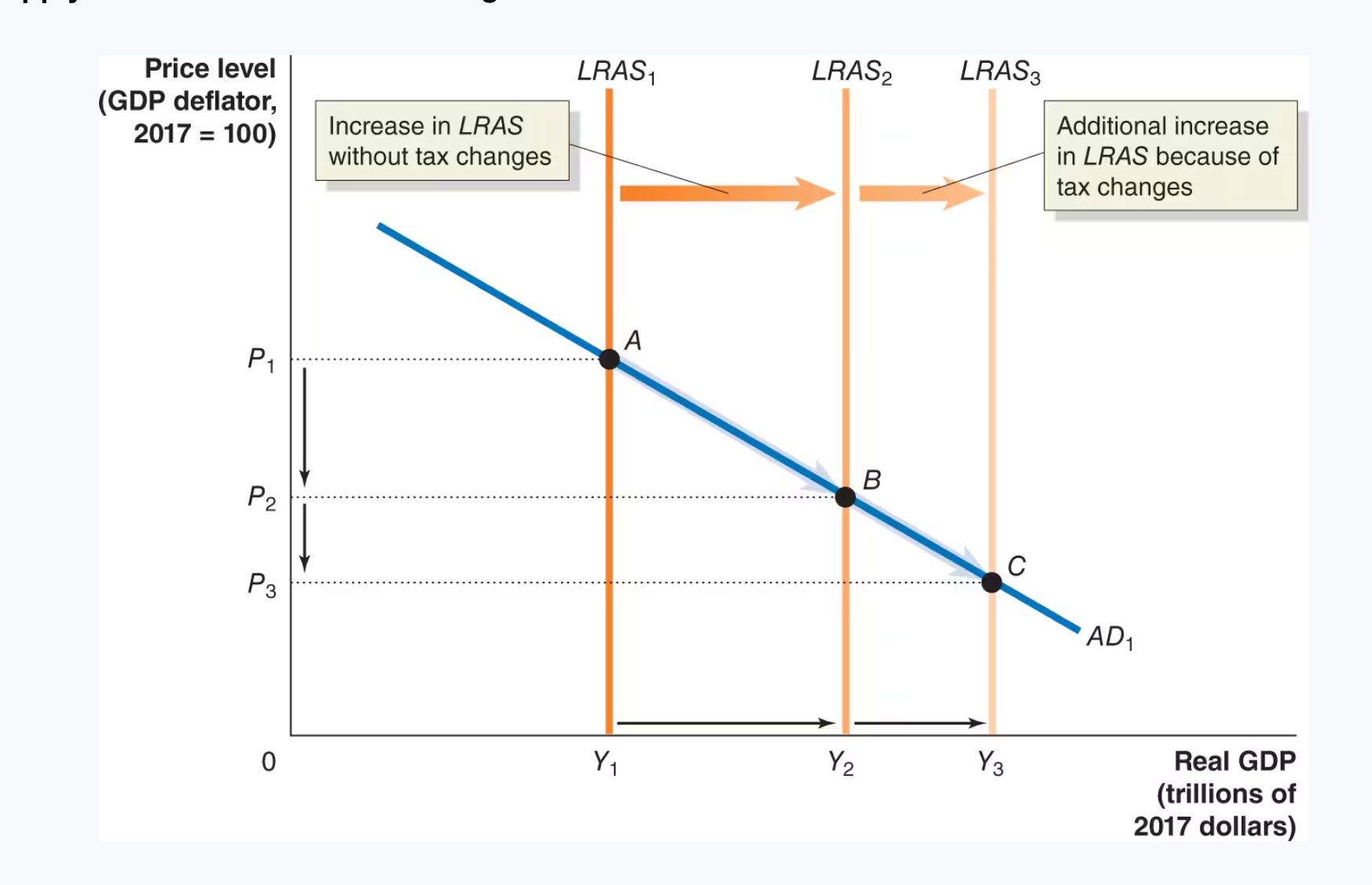
Supply-sode effects of a tax change
The effect on the economy of tax reduction and simplification is
an increase in the quantity of real GDP supplied at every price level, and a shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve.
If a tax cut has supply-side effects, then
it will affect both aggregate demand and aggregate supply.