Imperial Rome
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Barrel Vault
Also known as a “tunnel vault, constructed in the same manner as an arch. Essentially like a sequence of connected arches. The outward pressure exerted by the curving sides required buttressing outside the supporting walls.
Basilica
In ancient Rome, a large oblong hall or building with double colonnades and a semicircular exedra (apse), used in ancient Rome as a court of law or for public assemblies. Later appropriated by Christians as an architectural type dedicated to spaces of worship.
Basilica plan
Building type for early Christian churches that evolved from oblong Roman public buildings with aisles and naves. Longitudinal axes and timber roof, usually terminates with an apse.
Clerestory
Upper register of the main walls of a church, above the nave, pieced by windows.
Coffer
Recessed panel in a ceiling.
Concrete
technological breakthrough in Roman construction that as cheap, light, and easy to transport. Mixture of lime, volcanic sand, and rubble that made taller and more cavernous interior spaces possible.
dome
A rounded vault forming the roof of a building, typically with a circular base called a drum.
Exedra
A semicircular space, like a niche, in a building.
Oculus
A circular opening at the top of a dome.
Porphyry
Greek for “purple.” The term refers to a deep purple hued rock, very hard and difficult to carve. Since purple was the color of royalty in ancient Rome, the use of Porphyry was reserved for the imperial family.
Spolia
Latin for “spoils.” Indicates repurposed building stone or decorative sculpture for new construction. A wide-spread practice since antiquity, where precious building material would be mined from preexisting monuments rather than quarried.
Tetrarchy
A 4-part division of the Roman empire, put in place by the Emperor Diocletian in 293AD. The tetrarchy lasted until 313AD, when Constantine reunified the two halves (Eastern and Western).
Basilica Ulpia
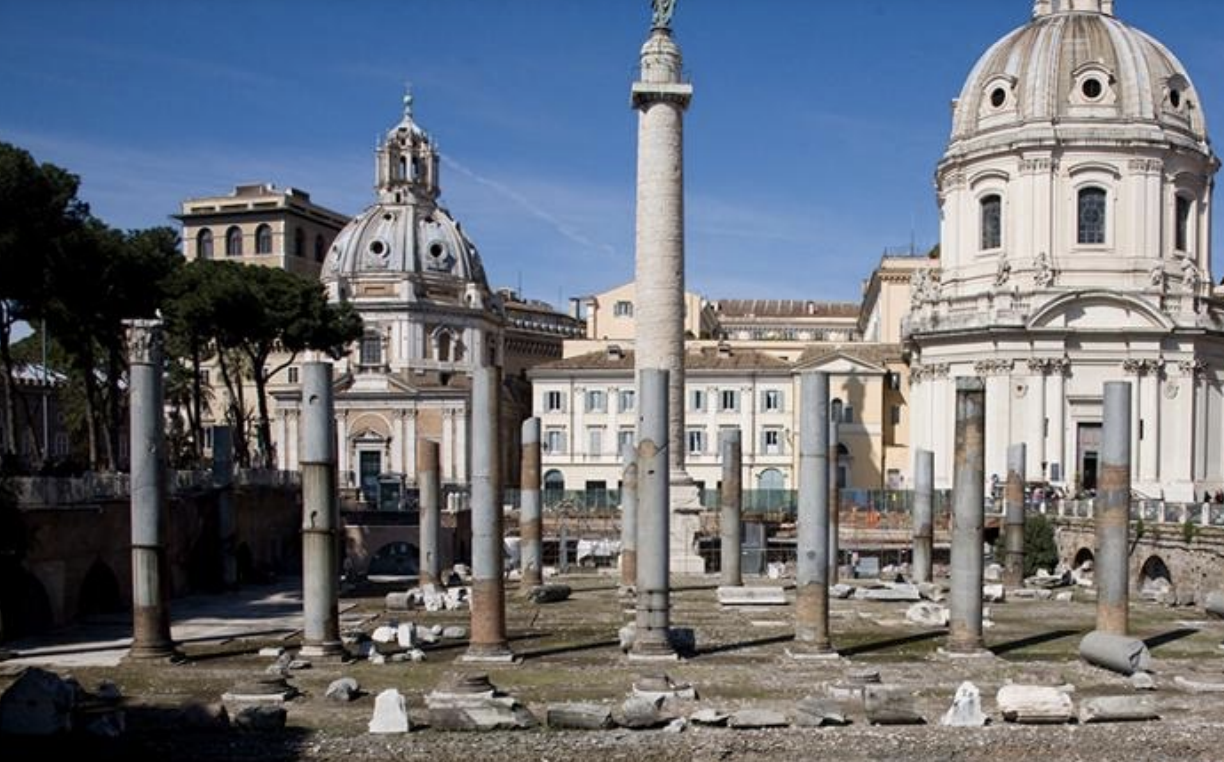

Basilica Ulpia

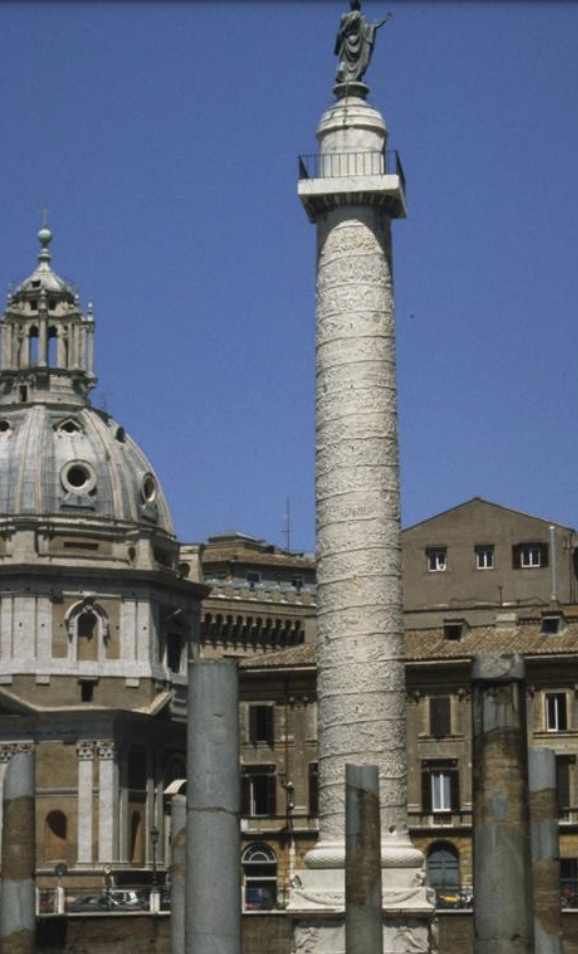
Trajan’s Column

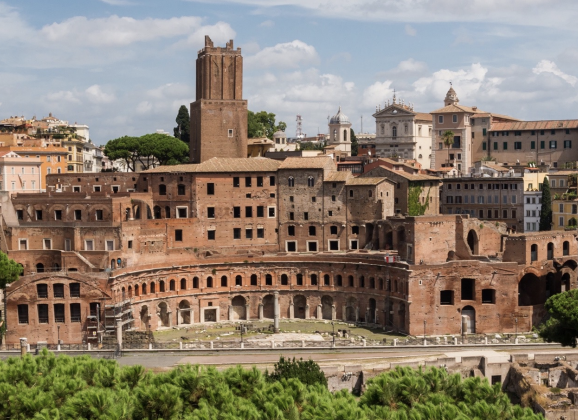
Markets of Trajan
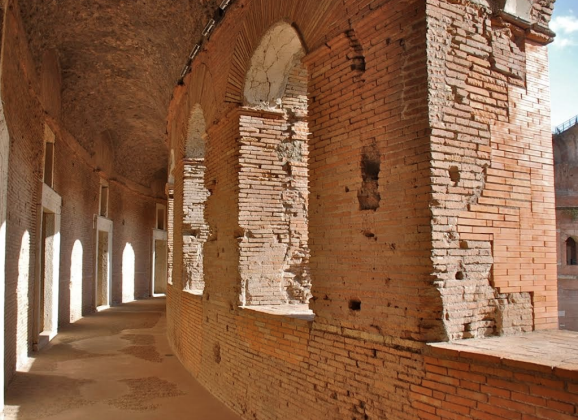

Markets of Trajan

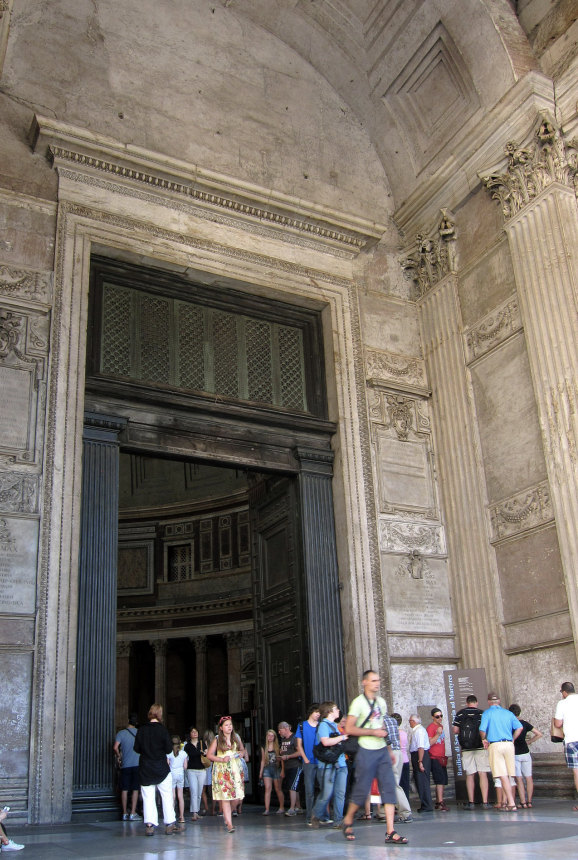
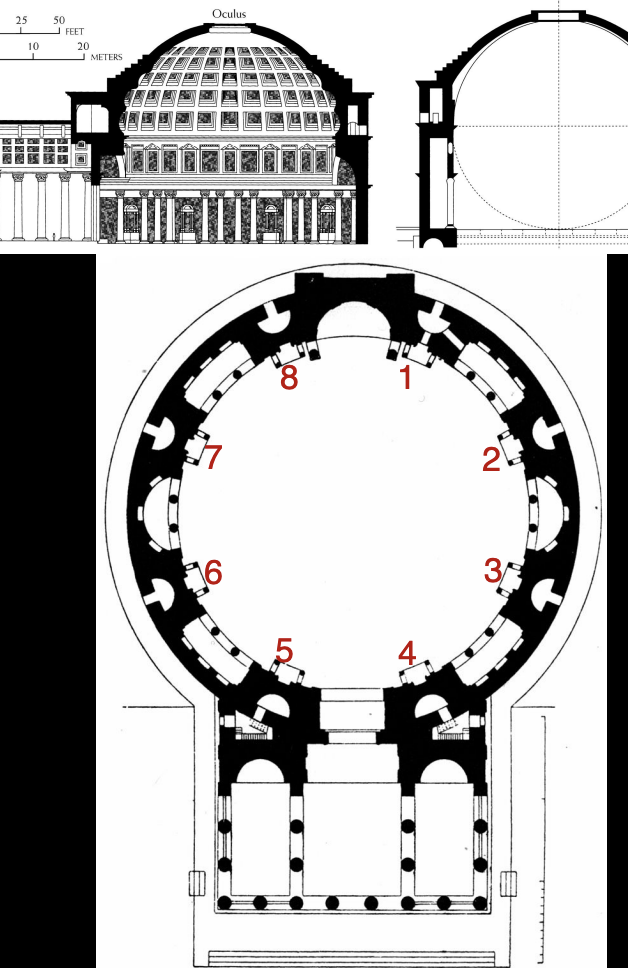
The pantheon

The pantheon
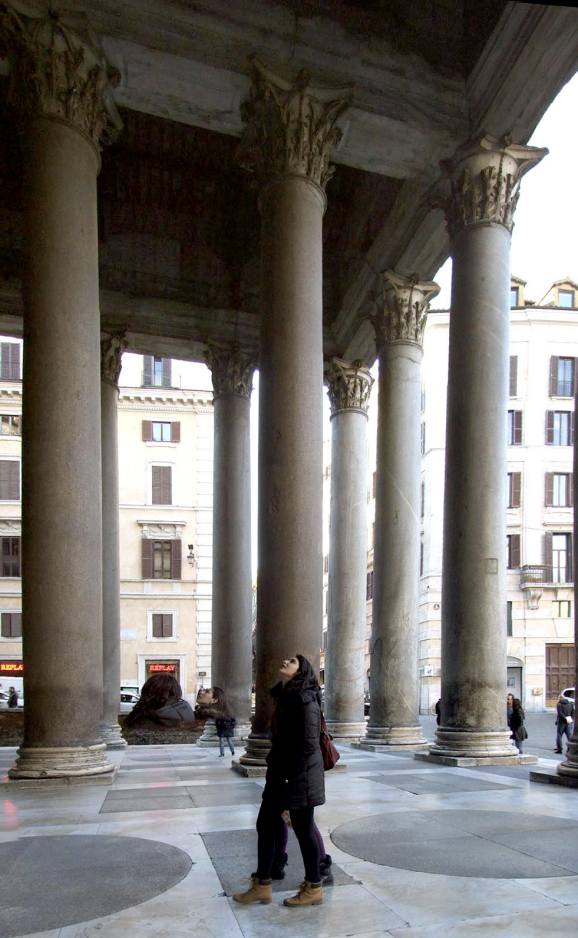

The pantheon
Baths of Caracalla
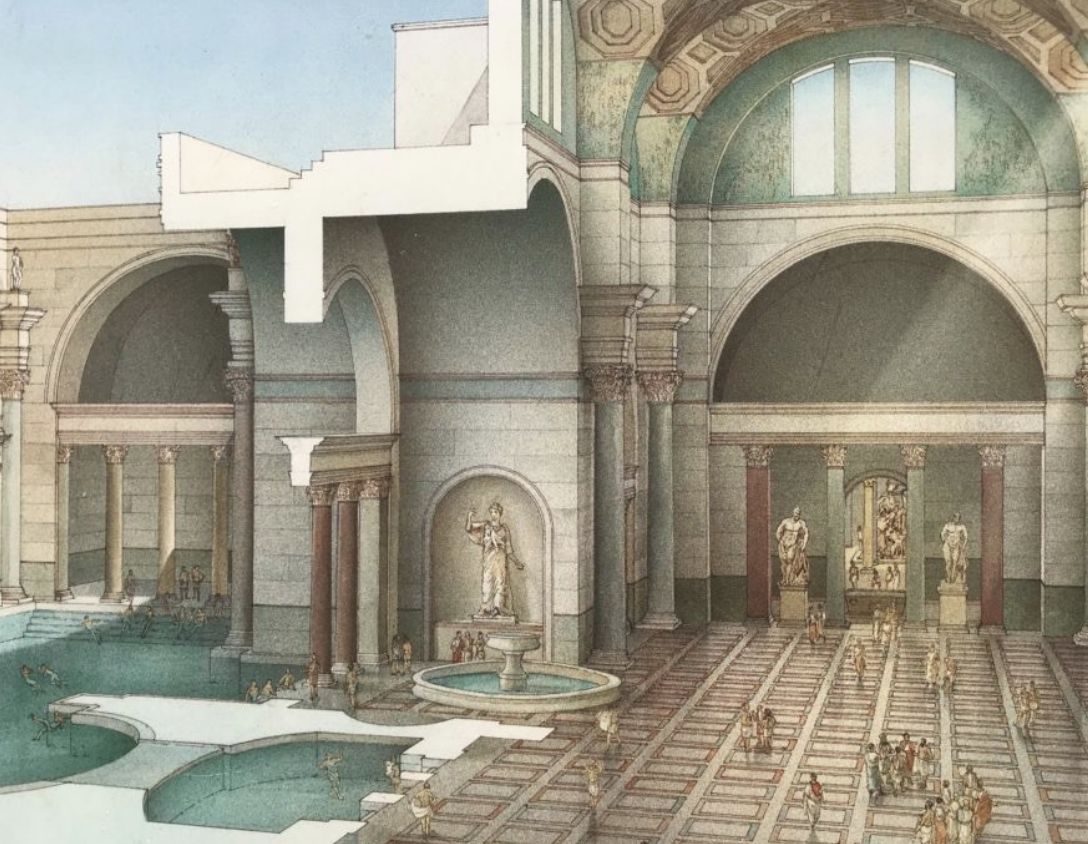
Baths of Caracalla
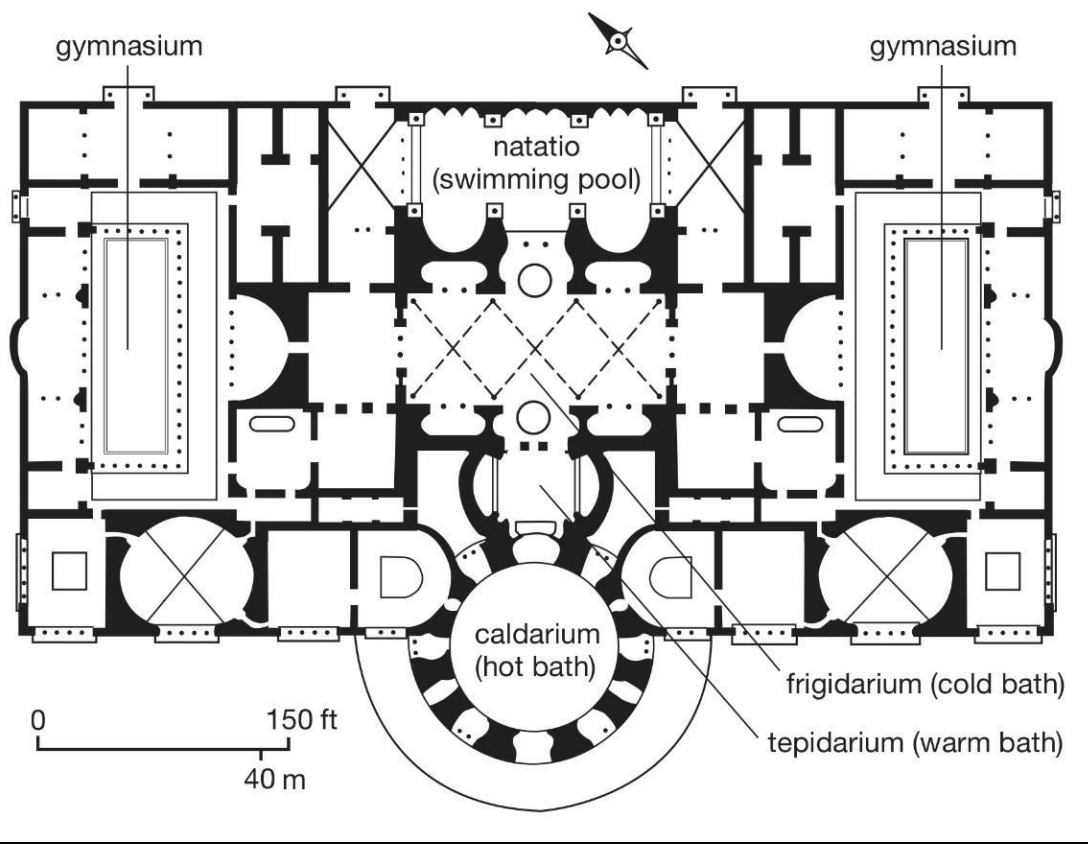
Baths of Caracalla
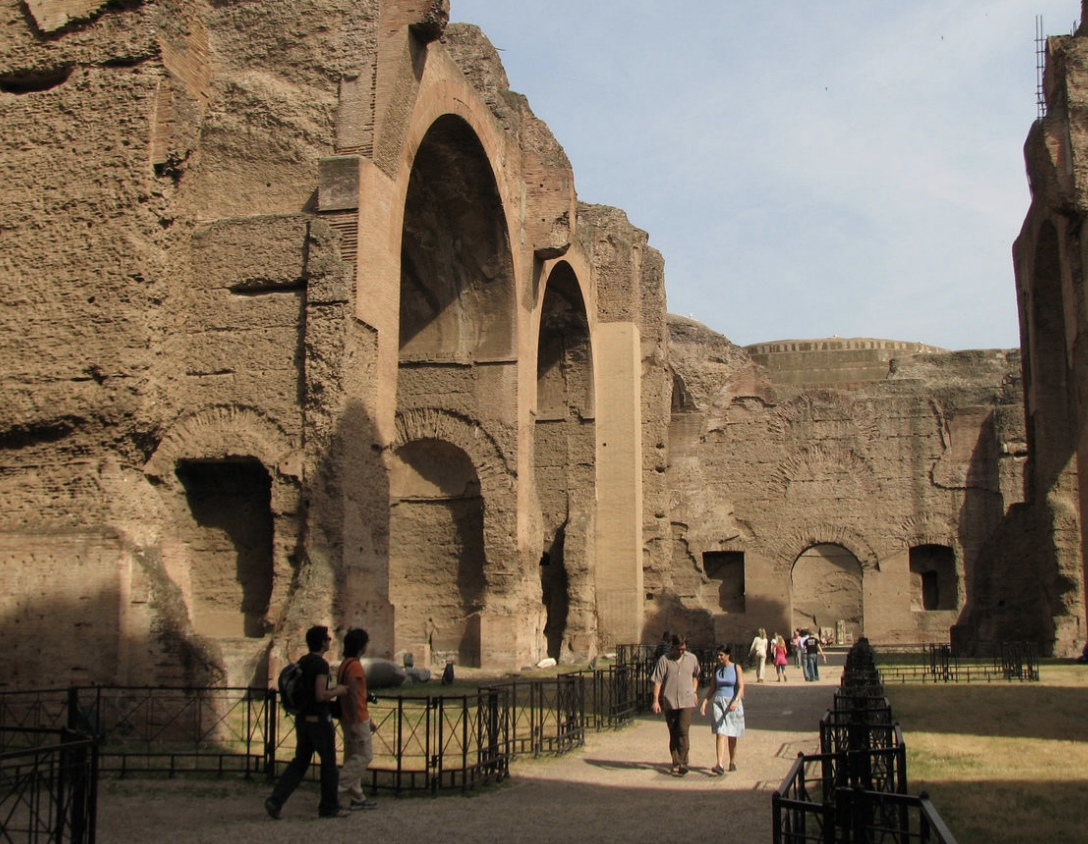

Arch of Constantine
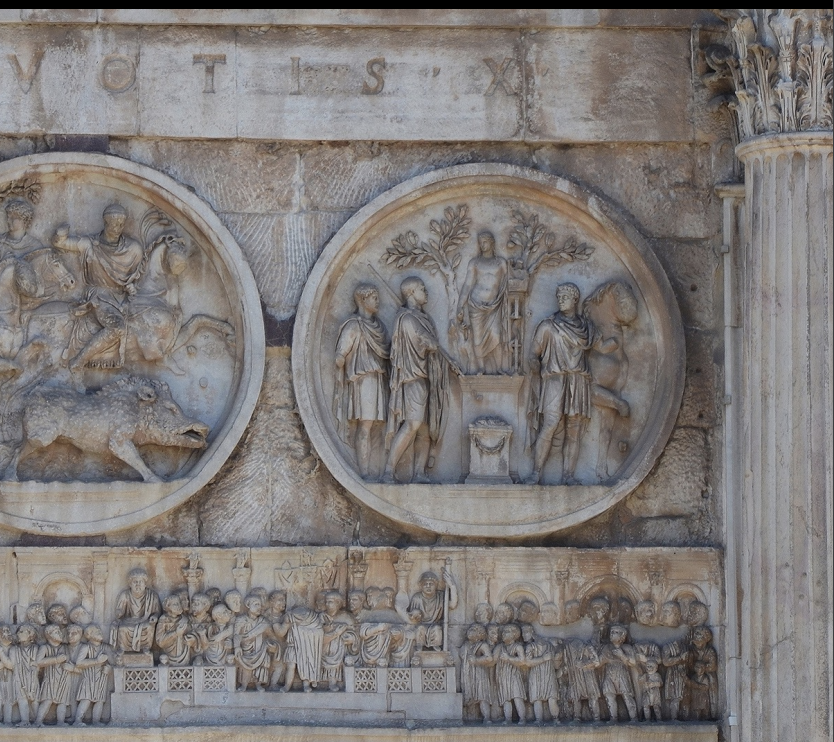

Arch of Constantine

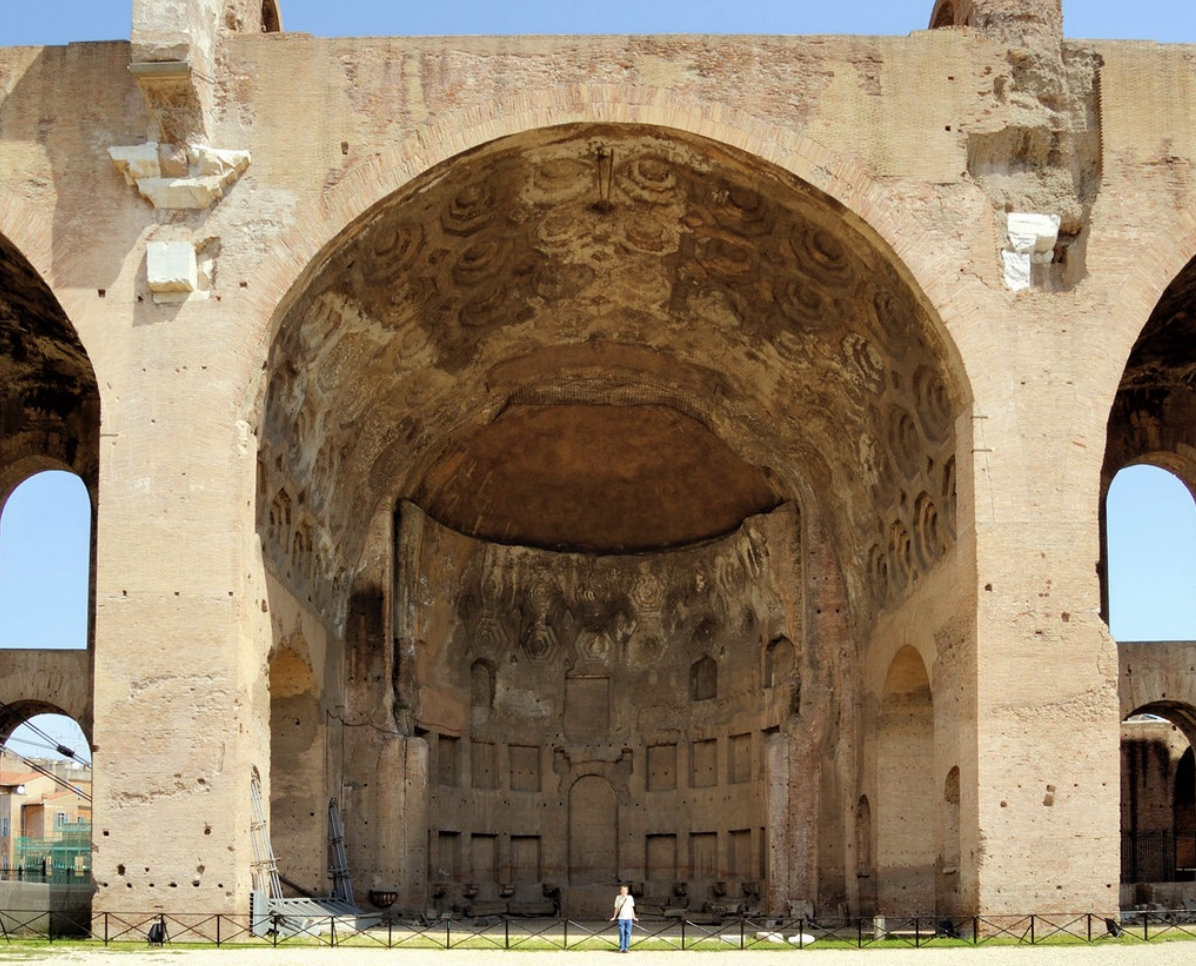
Basilica of Constantine

Basilica of Constantine
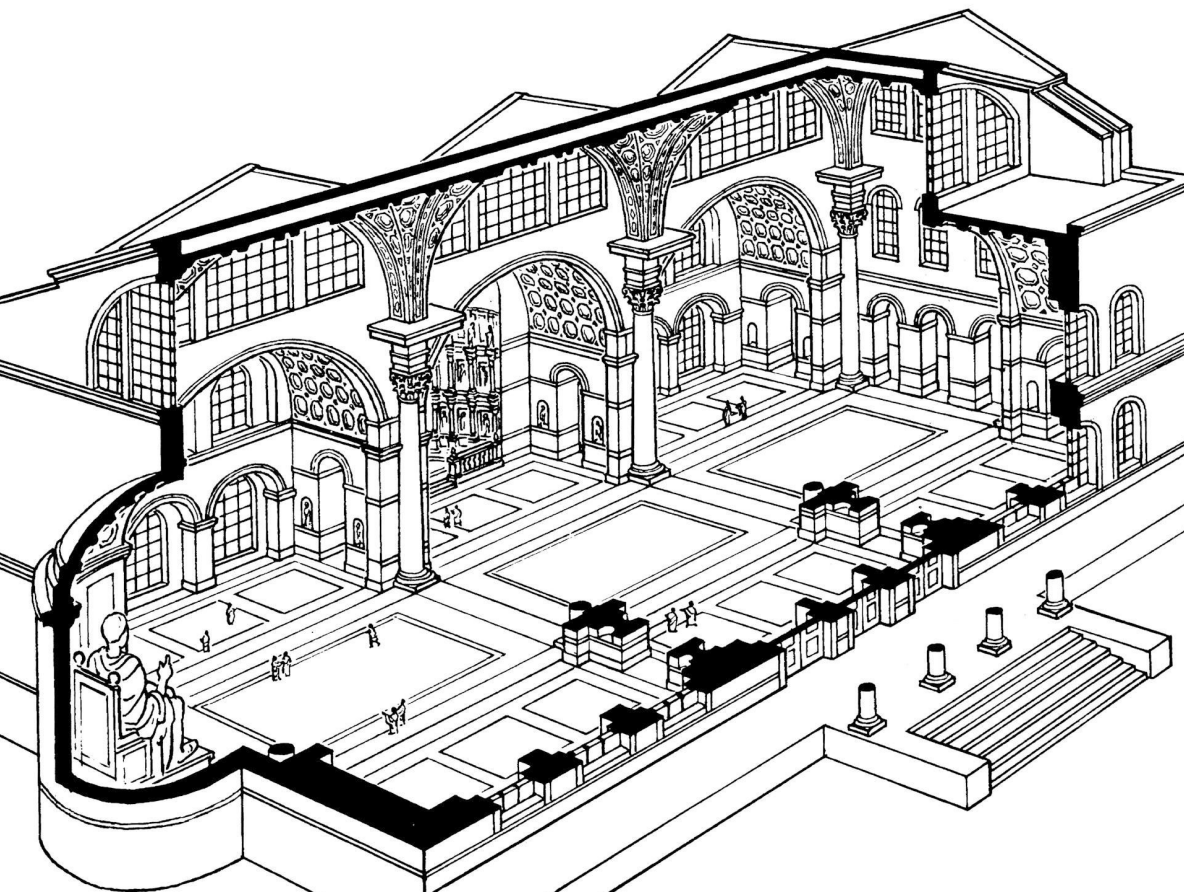
Basilica of Constantine
