Medchem Antifungals: Key Terms & Definitions Study Set
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
ergosterol
cholesterol
fungal cell membrane contains ___________ while mammalian cell membranes contain _______________
ergosterol
This is a picture of
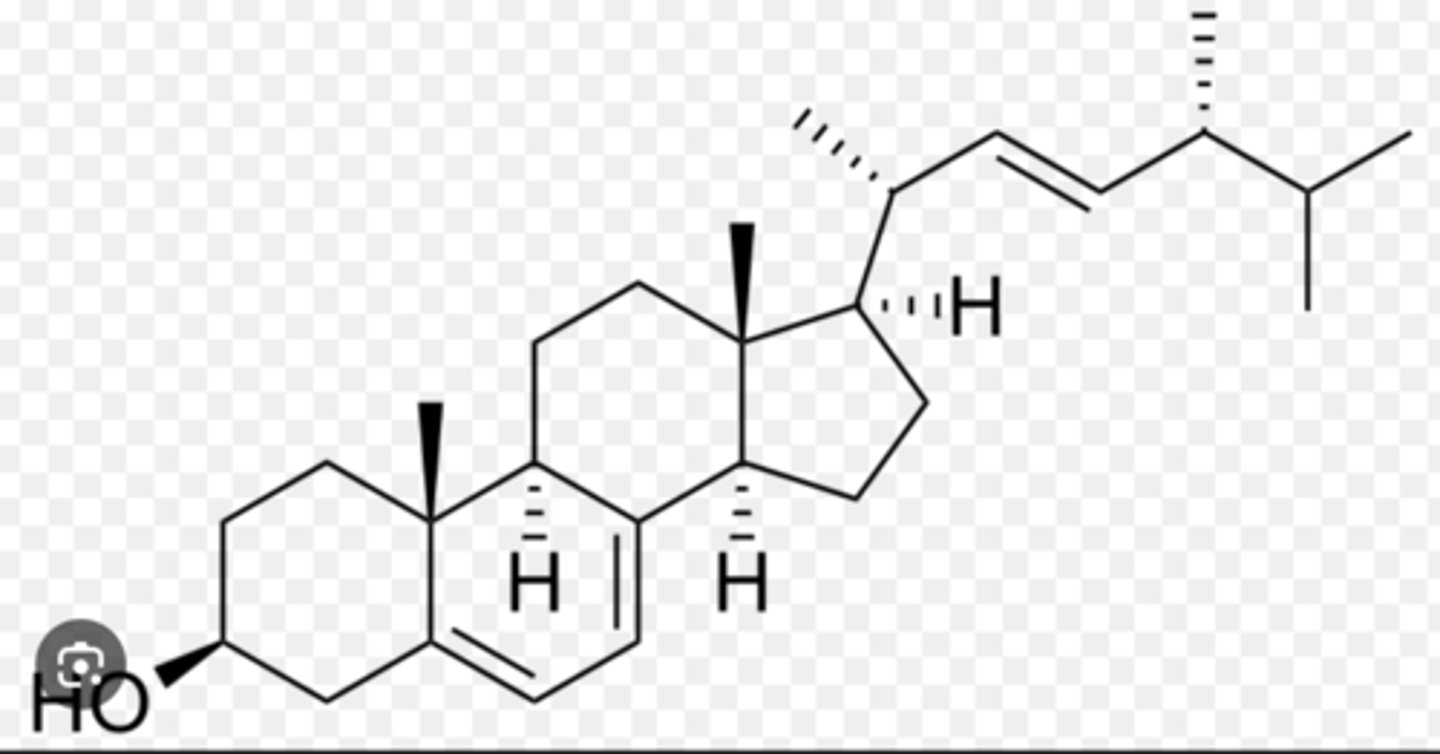
cholesterol
This is a picture of ?
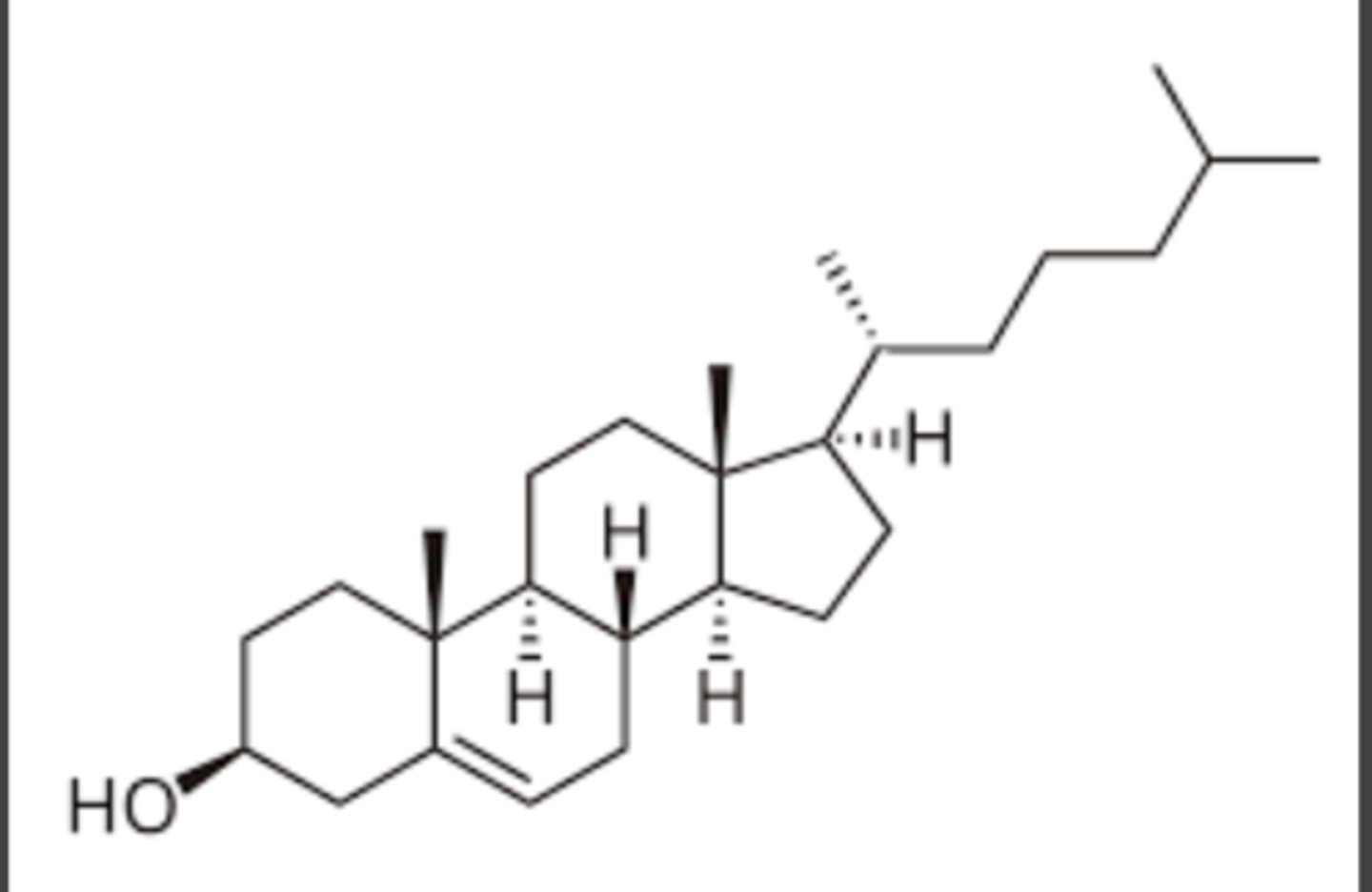
A. cell wall
D. ergosterol
what two things can be targets of antifungal agents with low toxicity to mammalian cells?
A. cell wall
B. cholesterol
C. cell membrane
D. ergosterol
false
True or false: fungal species are generally human pathogens
true
True or false: fungal diseases can be superficial and systemic
amphotericin B
What is this drug
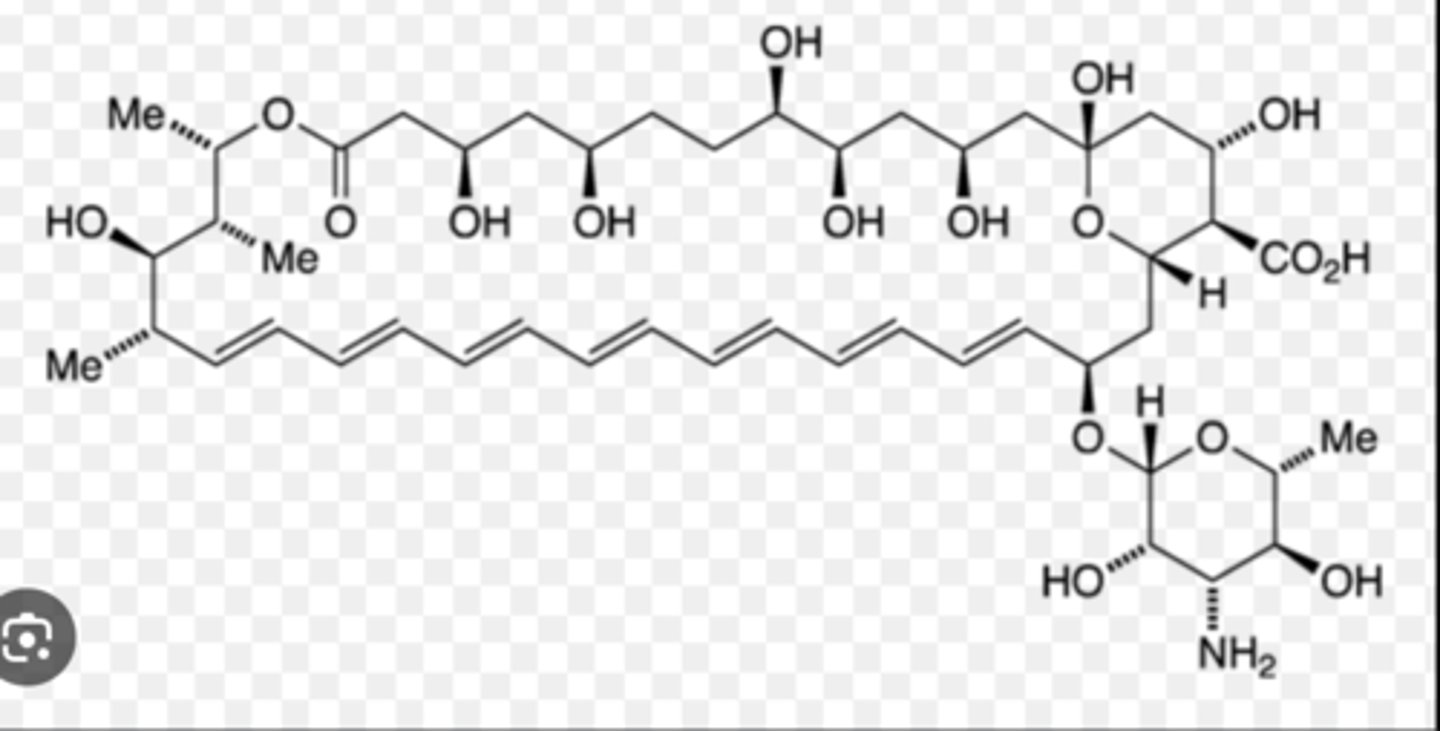
nystatin
What drug is this
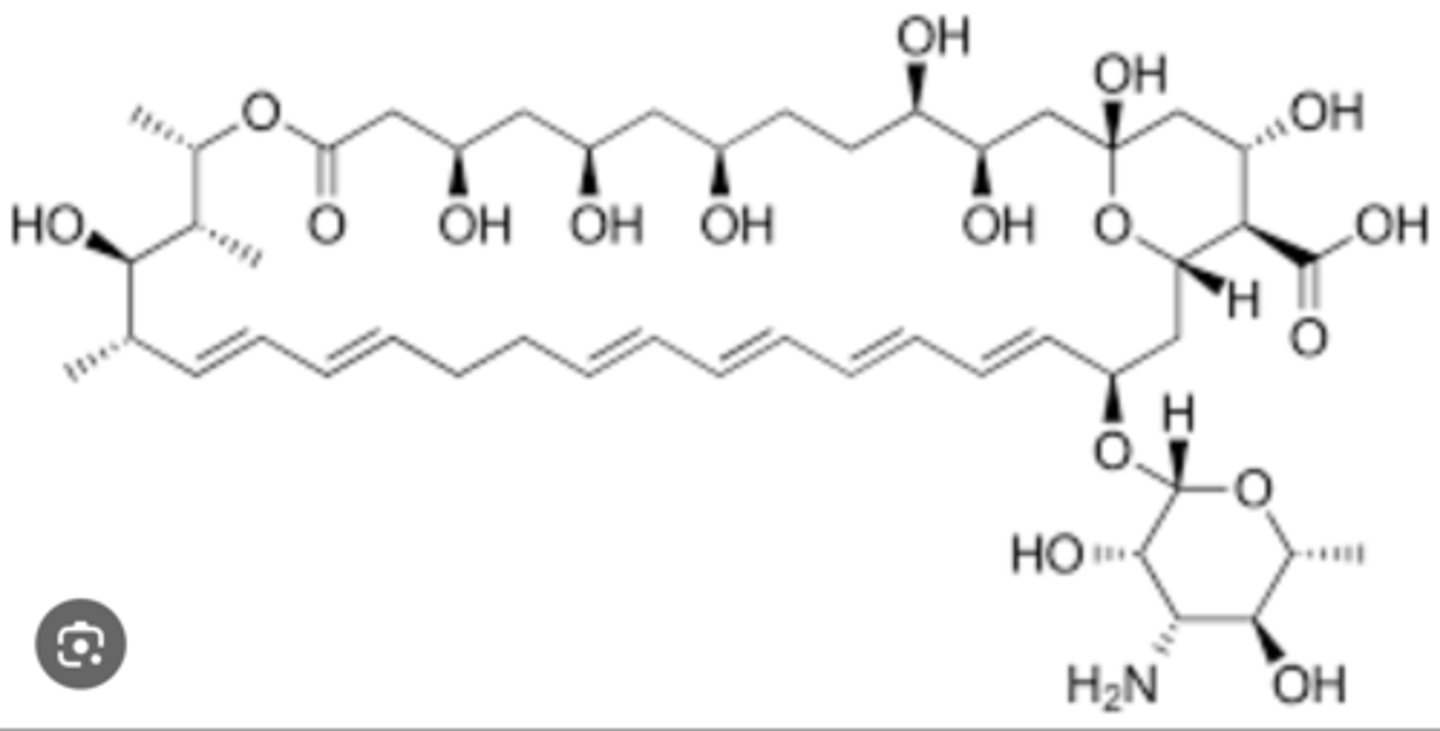
amphotericin B
nystatin
Name two polyenes
hydrophilic
lipophilic (hydrophobic)
the polyenes are macrocyclic lactones with distinct ___________ and _________________ regions
D. alcohols
The hydrophilic region of polyenes contains multiple ____________ and a carboxylic acid group
A. amines
B. amides
C. esters
D. alcohols
B. double
The lipophilic region contains, in part, a chromophore of multiple conjugated ___________ bonds
A. single
B. double
C. triple
D. hydrogen
ergosterol
cholesterol
polyenes favor ____________ over ___________ in the binding
C. polyenes
______________ bind to ergosterol within the fungal cell membrane resulting in the depolarization of the membrane and the formation of pores
A. azoles
B. allylamines
C. polyenes
D. echinocandin
C. polyenes
Which drug class exhibits concentration dependent killing?
A. azoles
B. allylamines
C. polyenes
D. echinocandin
B. amphotericin B analog
____________ was developed to possess potent antifungal activity while avoiding renal toxicity
A. amphotericin B
B. amphotericin B analog
C. nystatin
D. fluconazole
B. 14-A-methyl group
A key step in the conversion of lanosterol to both cholesterol and ergosterol is removal of the _________________ group
A. 13-A-methyl group
B. 14-A-methyl group
C. 15-A-methyl group
D. 16-A-methyl group
C. CYP51
What enzyme converts lanosterol to both cholesterol and ergosterol by removing the 14-A-methyl group
A. CYP 3A4
B. CYP 2D6
C. CYP51
D. CYP50
A. azoles
What antifungal agents target CYP51?
A. azoles
B. allylamines
C. polyenes
D. echinocandin
B. 2
Imidazole rings have _____ nitrogens
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
C. 3
triazole rings have _____ nitrogens
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
C. N3
The basic ______ atom of the azole binds to the heme iron of the CYP450 in the position normally occupied by the substrate: prevents substrate oxidation
A. N1
B. N2
C. N3
D. N4
D. all of the above
The inhibition of CYP51 results in
A. permeability changes
B. leaky membranes
C. malfunction of membrane-imbedded proteins
D. all of the above
A. azoles
The binding pocket of CYP51 is the basis to develop new generation of ____________
A. azoles
B. allylamines
C. polyenes
D. echinocandin
naftitine
terbinafine
Name two allylamines
B. allylamines
____________ occupy substrate binding pocket in squalene epoxidase
A. azoles
B. allylamines
C. polyenes
D. echinocandin
B. allylamines
_____________ are employed only in the treatment of fungal infections of the skin and nails
A. azoles
B. allylamines
C. polyenes
D. echinocandin
D. echinocandins
___________ can only be administered parenterally due to poor oral bioavailability
A. azoles
B. allylamines
C. polyenes
D. echinocandins
D. echinocandins
_______________ interfere with cell wall biosynthesis through inhibition of the enzyme B-1,3-glucan synthase
A. azoles
B. allylamines
C. polyenes
D. echinocandins
D. ibrexafungerp
___________ is an antifungal medication used to treat VVC. it is administered orally
A. tolnaftate
B. caspofungin
C. amphotericin B
D. ibrexafungerp
B. flucytosine
_____________ itself is not cytotoxic but, rather, is a prodrug that is taken up by fungi and metabolized to 5-fluorouracil by fungal cytosine deaminase
A. capsofungin
B. flucytosine
C. ibrexafungerp
D. tolnaftate