Transplantation Immunology
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
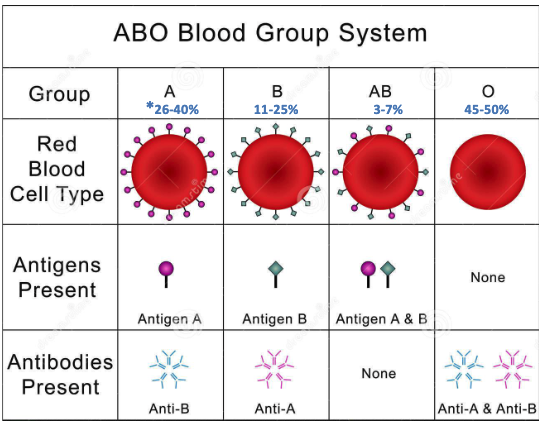
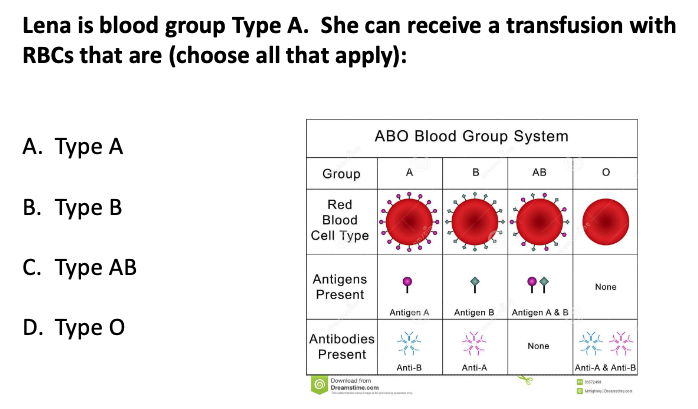
type A
type O
what is an autograft?
Donor & recipient are same person
what is an isograft (syngeneic graft)?
Donor & recipient are genetically identical (between monozygotic twins)
what is an allograft (allogeneic graft)?
Donor & recipient are genetically different
what is an xenograft (xenogeneic graft)?
Donor & recipient are different species
what are the different types of grafts?
autograft
isograft
allograft
xenograft
THE T CELL RESPONSE AGAINST AN ALLOGRAFT IS VERY STRONG, WHY MIGHT THIS BE THE CASE?
Many T cells (both CD4+ and CD8+) will directly recognize foreign MHC (allogeneic or xenogeneic) without regard to a peptide.
Thus, the T-cell immune response attacking allografts (and xenografts) is exceptionally powerful.
how are grafts recognized by recipient T-cells?
2 mechanisms:
Recipient T-cells recognize processed donor MHC peptides being presented by recipient’s antigen-presenting cells
Recipient T-cells directly recognize allogeneic donor MHC molecules on graft antigen presenting cells
what are the mechanisms of allograft rejection?
hyperacute rejection (minutes/hours)
acute rejection (10-14 days)
chronic rejetion (months to years)
hyperacute rejection is due to…?
preformed antibodies in the recipient (primarily to blood group antigens or HLA)
in hyperacute rejection, Preformed antibodies to HLA can be due to
childbirth (anti-father’s HLA)
previous blood transfusion
previous organ transplant recipient
ABO blood group incompatibility
acute rejection is due to…?
T-cells (CMI), especially CD8+ T cells
chronic rejection is due to…?
T cells (CMI), especially CD4+ T-cells producing inflammatory cytokines can also involve:
ADCC (IgG-mediated NK cell attack on the graft)
IgG-mediated complement activation
how can we prevent hyperacute rejection?
Donor and recipient must be matched for ABO blood group the same as would be done for a blood transfusion
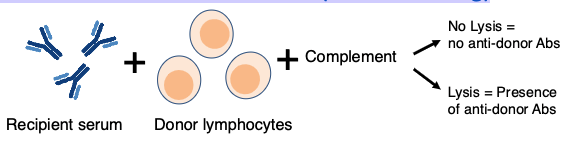
Test recipient’s serum for antibodies to donor (cross-matching)
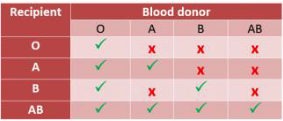
The match list for organ transplants is based on
the number of HLA antigens matching,
the antibody levels of the recipient,
and the length of time a recipient has been on the waiting list.
(children under 18 get extra points)
6-point match is best
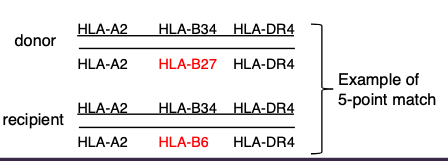
how can we prevent solid organ rejection?
• Match for blood group compatibility
• Test for other pre-formed antibodies (Cross match)
• Match for HLA (as best as possible, especially HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-DR)
• Immunosuppressive drugs (discussed below)
• Live donors give better outcomes than cadaveric donors
what is Hematopoietic Stem Cell (HSC) Transplantation?
clinical procedure to treat intrinsic defects in one or more hematopoietic lineages and more commonly to treat cancers of the blood
patient’s own hematopoietic cells must be eliminated prior
Stem cells used in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation can be obtained from
the peripheral blood
umbilical cord blood
bone marrow
what is the major problem with bone marrow transplantation?
competent T-cells from the donor may be transplanted giving rise to graft versus host disease (GVHD).
what is graft versus host (GVH) disease?
A reaction of donor T-cells against recipient MHC
1) The graft must contain live T-cells
2) The recipient must be immunosuppressed
3) Donor and recipient must have different HLA types
CD4+ T cells in the graft are activated by allogeneic molecules and produce a “cytokine storm”. what does this mean?
recruits other T cells, macrophages and NK cells to create the severe inflammation characteristic of GVHD
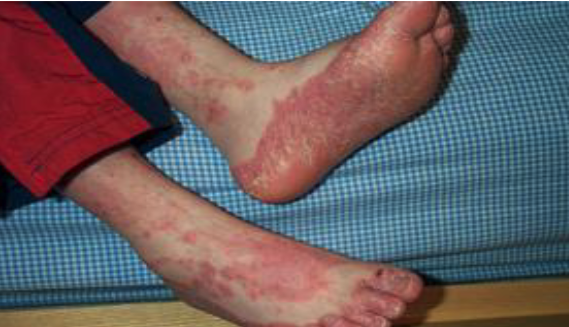
Acute GVHD rash that characteristically involves the palms and soles
t/f: Allograft recipients receive a cocktail of immunosuppressive drugs that must be taken for life
true
what are some immunosuppressive drugs?
cyclosporine (CsA) and tacrolimus
sirolimus
corticosteroids
The problem with all forms of immunosuppressive therapy is that normal immune responses against microorganisms are reduced giving rise to
an increased incidence of infection (recurrent infections)
the best success rates for dental implant bone grafts have been achieved with which type?
autografts
what type of grafts have been used with dental implant bone grafts?
autografts
allografts (mostly cadaver)
xenografts (commonly bovine)
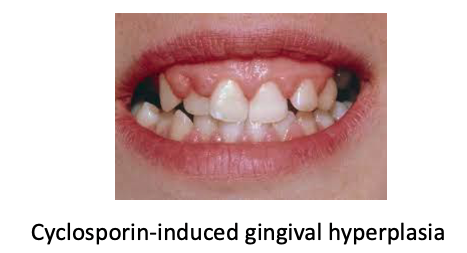
Immunosuppressive agents (specifically cyclosporin), can cause
gingival hyperplasia
poor healing
and infections
Multiple treatments of graft required to prevent allograft bone from eliciting an immune response such as
– Irradiation
– Freeze-drying
– Acid washing
– Chemical treatments
– Donors pre-screened for infectious diseases