Hypotheses to Evaluate Validity
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What are dichotomous variables?
2 categories with no underlying order; nominal
What are dichotomized variables?
Two categories that result from categorizing a measured or ranked variable; ordinal; usefulness of dichotomy relies on nature of underlying distribution
What are polytomous variables?
More than two categories with no underlying order; nominal
What are polytomized variables?
More than two categories that result from categorizing a measured or ranked variable; ordinal; usefulness depends on underlying distribution
What sort of distribution do ranked variables normally produce?
Rectangular or uniform (1 person per category except for occasional tied ranks)
What are some problems of measured variables?
Lack of sensitivity (not enough capability to differentiate range of individual differences that exists in a particular group), can result in floor/ceiling effects (measuring instrument cannot sufficiently differentiate at lower or upper ends of underlying variable), will have problems for measured variables that are assumed to have equal intervals but in fact do not
What is a variate?
Artificial statistical variable obtained by combining a number of measured variables in a specified manner; usually are linear or additive composites (ex. number-correct score on test) but some are weighted linear combinations (ex. GPA) or nonlinear (ex. cross-product terms)
What are some problems with variates?
Implicit weighting in apparently unweighted variates (variables with larger sds have more weight in variates even though appear to be unweighted → need to standardize (z-scores) before variate is created)
Also affected by intercorrelations
What is a dummy variable?
Artificial 0-1 variables created from dichotomous or polytomous variables so can be used for correlational methods that assume linearity
How do dummy polytomous variables work?
Create a series of dummy variables each representing 1 for a specific category and 0 for any other that combine so an individual might have a score of 0100 or 1000
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for 2 dichotomous variables?
Contingency coefficient, phi correlation
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for 2 polytomous variables?
Contingency coefficient
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for 2 dichotomized variables?
Tetrachoric correlation
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for 2 polytomized variables?
Polychoric correlation
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for 2 dichotomous/dichotomized/polytomous/polytomized variables?
Contingency coefficient
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for 1 dichotomous, 1 measured variables?
Point-biserial correlation, t-test
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for 1 dichotomized, 1 measured variables?
Point-biserial correlation, t-test
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for 1 polytomous, 1 measured variables?
Eta (correlation ratio), 1-way ANOVA
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for 1 polytomized, 1 measured variables?
Polyserial correlation, eta, 1-way-ANOVA
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for 2 ranked variables?
Spearman rank-order correlation (rho)
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for 2 measured variables?
Eta (not assuming linearity), Pearson product-moment r (assuming linearity)
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for measured predictors, 1 dichotomous criterion?
Multiple regression with a dichotomous dummy variable
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for measured predictors, 1 polytomous criterion?
Multiple regression with polytomous dummy criterion variables
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for measured predictors, 1 measured criterion?
Multiple regression (linear/nonlinear)
What statistical measures of association/correlation are used for measured predictors, measured criteria?
Canonical correlation analysis
What is the phi correlation?
Pearson product-moment correlation between two dichotomous dummy-coded variables
What is the equation for phi correlation?
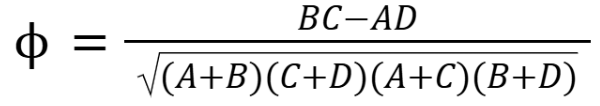
What is a point-biserial correlation?
Pearson product-moment correlation between a measured variable and a dichotomous dummy variable
What is the equation for point-biserial correlation?
M = mean of y variable for each group
Sy = standard deviation of y variable for total group
P = proportion of total group in each group
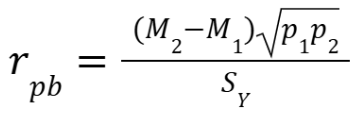
What is the relationship between a point-biserial correlation and t-test?
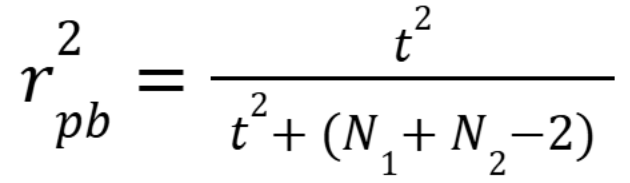
What is a biserial correlation?
Correlation for 1 dichotomized, 1 measured variable; NOT a Pearson correlation—gives an inflated estimate of r, values can exceed 1.0, assumes an underlying normal distribution for dichotomized variable
What is the equation for a biserial correlation?
Z = ordinate of the unit/normal distribution corresponding p1 or p2, whichever is smaller
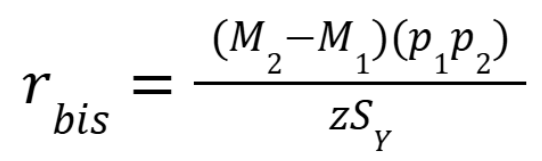
What is a tetrachoric/polychoric correlation?
Correlation for two dichotomized (tetrachoric) or polytomized (polychoric) variables; NOT Pearson-product moment, become unstable as approach 0.0 or 1.0, both assume a normal distribution underlying categorized variables
What is the Spearman rank-order correlation?
Pearson product-moment correlation between two sets of ranks
What is the equation for the Spearman rank-order correlation?
Di = difference between ith person’s ranks on two variables
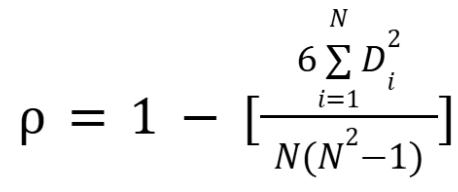
What is the contingency coefficient?
Correlation between 2 dichotomous/dichotomized/polytomous/polytomized variables, NOT a Pearson product-moment correlation, upper limit is a function of k and can be greater than 1.0
What is the equation for contingency coefficient?
O = observed cell frequency
E = expected cell frequency
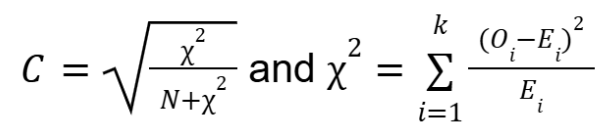
What is the eta coefficient?
General case of the Pearson product-moment correlation, requires 1 polytomous/polytomized variable and one measured, always positive, doesn’t assume anything about nature of relationship between means on measured and categorized variable
What is the equation for eta coefficient?
G = number of categories on polytomous/polytomized variable
Mg = number of persons in group g
Y = total group mean
Yig = score on the measured variable for the ith person in group g
N = total number of people
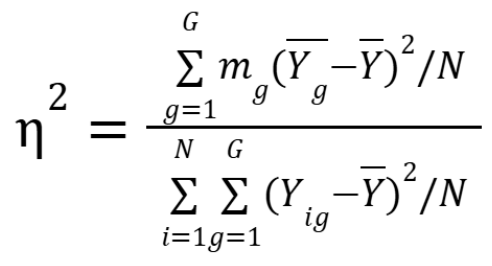
What is the Pearson product-moment correlation?
Special case of the eta coefficient where group means are replaced by “best fit” straight line, ranges from -1.0 to 1.0
What is the equation for the Pearson product-moment correlation?
Zxi = person’s standardized score on one of measured variables
Zyi = person’s standardized score on other measured variable
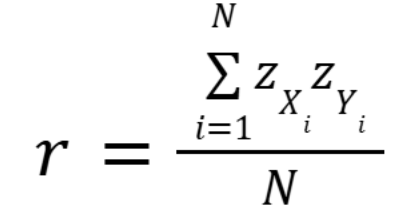
What is r2?
Proportion of variance in one variable that is linearly common with, predictable from, or attributable to the other variable
What is the difference between eta and Pearson’s r?
Eta indicates any form of relationship while r reflects only linear relationship
What is multiple correlation?
Generalization of bivariate Pearson’s r to multiple predictor variable, more than 1 measured predictors and 1 measured criterion, always positive, assumes that all relationships are linear
What are some issues with correlation?
Curvilinearity, restriction of range, moderator variables, outliers, optimization/inflation (regression weights and correlations become sample-specific)
What are the methods for estimating the population correlation?
Compute 2 Rs and select lower of the two
Cross validation (more conservative; highly recommended to use this approach to generalize beyond sample of data in prediction or validation studies)
What is cross-validation?
Method of estimating population correlation
Split sample into Sample 1 and Sample 2, compute multiple correlation and beta weights on one sample, apply beta weights from Sample 1 to scores in Sample 2 to compute a variate of the predictor variables, compute correlation between x variate and y variable in second sample