Bituminous Materials and Testing in Construction
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Bituminous Materials
Materials containing bitumen for construction purposes.
Bitumen
Hydrocarbon material from petroleum distillation.
Paving Grade Bitumen
Composite material for roads and airports.
OXIDIZED BITUMEN
also known as blown bitumen is a bitumen type produced by blowing air into the pure bitumen
LIQUID BITUMEN
s bitumen that is dissolved in a solvent. Typical solvents include naphtha, gasoline and kerosine, white spirit, etc. The type of solvent controls the curing time while the amount determines the viscosity of the liquid bitumen.
NATURAL BITUMEN
naturally occurring deposits of the solid or semi-solid form of petroleum.Extracted from oil sands or derived from natural lakes
PETROLEUM REFINING
- or Oil refining is an industrial process in which crude oil is extracted from the ground and transformed and refined into useful products like Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), kerosene, asphalt base, jet fuel, gasoline, heating oil, fuel oils etc.
Fractional Distillation
crucial process in oil refineries, where crude oil is separated into various hydrocarbon products based on their relative molecular weights
Asphalt
Bitumen mixed with aggregates for pavement.
Natural Asphalt
also referred to as asphaltum or bitumen, is a black, viscous, and semi-solid substance found in nature.
Manufactured Asphalt
is just gravel covered in an oily glue. Asphalt cement or a mixture of chemical solvents is required for these manufactured materials to bond.
Stability
durability
Impermeability
Workability
Skid resistance
Plasticity
Properties of Asphalt
Hamburg Wheel Tracking Test
Test for rutting resistance in asphalt mixtures.
Semi-Circular Bending Test
It's often referred to as a "flexibility index test." It can predict whether the material is resilient enough to meet its intended longevity.
Disc Shaped Compact Tension Test
measures the fracture energy of asphalt pavements.
Marshall Stability Test
Assesses stability of bituminous mixtures under load.
Bituminous Mixture
Combination of bitumen and aggregates for paving.
Light Fractions
Low boiling point products like gasoline and kerosene.
Middle Fractions
Moderate boiling point products, including diesel and jet fuel.
Heavy Fractions
High boiling point products, including bitumen and fuel oils.
Distillation Column
Equipment where crude oil is heated for separation.
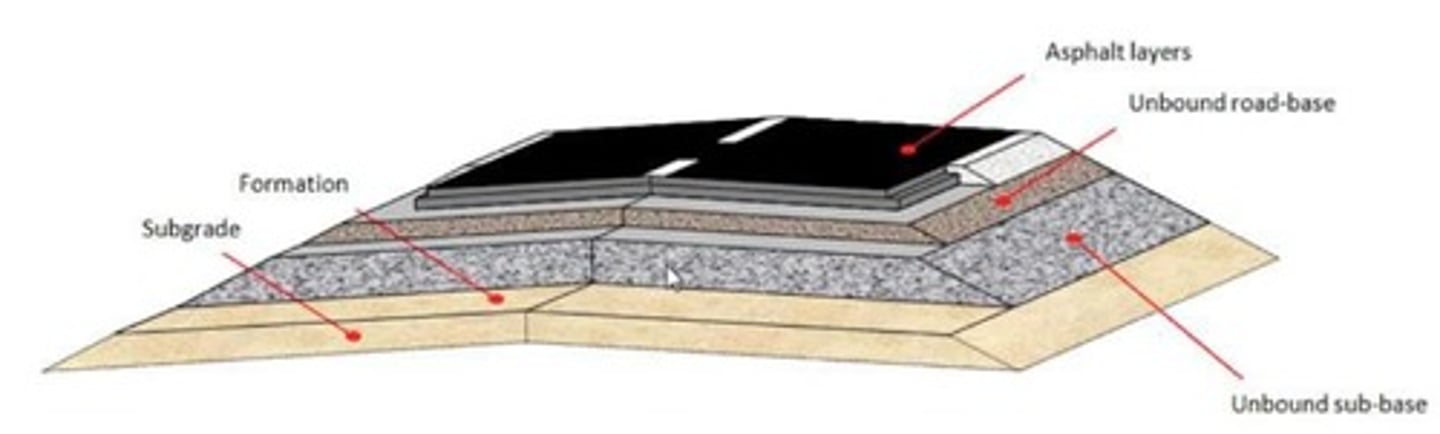
Hot-Mix Asphalt (HMA)
Produced by mixing aggregates and asphalt at high temperature.
Hydroplaning
Loss of tire contact due to water film.
Aggregate
Crushed stones, sand, or gravel in asphalt mixtures.
HMA mixture
Hot Mix Asphalt, used for paving surfaces.
Cold-laid plant mix
Asphalt mix applied at ambient temperature.
Mixed-in-place
Aggregates mixed on-site with asphalt binders.
Penetration macadam
Layers of aggregate treated with asphalt.
Asphaltenes
high-molecular-weight polycyclic hydrocarbons that provide the rigidity and stiffness to bituminous materials
Resins
serve as an intermediate component between asphaltenes and maltenes, maintaining the colloidal stability of bitumen
Aromatics
Hydrocarbons enhancing fluidity and workability.
Saturates
Low molecular weight hydrocarbons improving flexibility.
Viscosity
Resistance of bitumen to flow under stress.
Penetration Value
A higher penetration value indicates softer bitumen, suitable for colder regions, while lower penetration values signify harder bitumen, ideal for hot climates.
Softening Point
the temperature at which bitumen transitions from a solid to a semi-liquid state
Thermal cracking
Cracking due to temperature fluctuations.
Colloidal stability
Maintaining uniform dispersion of components.
Aging characteristics
Changes in material properties over time.
Application efficiency
Effectiveness of applying materials in construction.
High-viscosity bitumen
Preferred for high-temperature applications.
Low-viscosity bitumen
Used for mixing in cold climates.
Penetration Value
Measures bitumen hardness via needle penetration depth.
Higher Penetration Value
Indicates softer bitumen for colder climates.
Lower Penetration Value
Signifies harder bitumen for hot climates.
Softening Point
Temperature where bitumen becomes semi-liquid.
Ductility
Ability to stretch bitumen without breaking.
Elasticity and Cohesion
refers to the ability of bitumen to return to its original shape after deformation, particularly in polymer-modified bitumen.
ensures internal strength, which is vital for withstanding traffic loads and mechanical stresses
Temperature Susceptibility
Behavior changes with temperature extremes in bitumen.
Adhesion to Aggregates
Bitumen's ability to bond with mineral aggregates.
Poor Adhesion
Leads to stripping and pavement failures.
Oxidation Resistance
Resists aging from air and UV exposure.
Oxidative Aging
Increases stiffness and reduces ductility over time.
Solubility in Organic Solvents
Pure bitumen dissolves in carbon disulfide.
Aging and Volatilization
Loss of volatile hydrocarbons increases brittleness.
Polymer-Modified Bitumen (PMB)
Enhances elasticity and durability using polymers.
Crumb Rubber Modification
Improves flexibility using recycled tire rubber.
Anti-Stripping Agents
Enhance adhesion between bitumen and aggregates.
Ductility Test
Measures bitumen's ability to stretch without breaking.
Flash Point
Temperature where vapors ignite upon exposure to flame.
Fire Point
Temperature sustaining combustion for at least 5 seconds.
Float Test
Assesses bitumen's flow characteristics in warm conditions.
Loss on Heating Test
Evaluates volatile component loss at high temperatures.
Penetration Test
Measures depth of needle penetration in bitumen.
Softening Point Test
Temperature where bitumen softens to specified consistency.
Specific Gravity Test
Determines bitumen density compared to water.
Viscosity Test
Measures flow characteristics under specified conditions.
Water Content Test
Determines amount of water present in bitumen.
Temperature for Ductility Test
Conducted at 27°C for accurate results.
Capillary Tube
Used in viscosity test to measure flow time.
Load for Penetration Test
Needle applied under 100 g load for measurement.