UNLV KIN 223 EXAM 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Another name for the intracellular fluid is
A) interstitial fluid.
B) cytosol.
C) cytoplasm.
D) cisternae.
E) intercellular matrix.
B
The phase of mitosis that begins with the arrival of a group of single-stranded chromosomes at each pole of the cell is
A) anaphase.
B) metaphase.
C) telophase.
D) prophase.
E) S phase.
C
The movement of glucose across a plasma membrane is achieved by
A) osmosis.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) receptor-mediated exocytosis.
D) phagocytosis.
E) ion pumps.
B
The organelles responsible for organizing microtubules that are part of the mitotic spindle are called
A) centrioles.
B) cilia.
C) nucleoli.
D) microvilli.
E) vesicles.
A
When fertilization occurs, the sperm recognizes the egg by
A) the strong acidity of the egg's environment.
B) the unique glycocalyx on the egg's surface.
C) the much larger relative size of the egg.
D) the chemical messages the egg secretes into the interstitial space
B
Which of the following is not a component of the cytoplasm?
A) Chromatin
B) Cytosol
C) Organelles
D) Inclusions
A
Pinocytosis is the process in which the cell
A) splits ("pinches") off a small part of itself to secrete into the extracellular space.
B) internalizes ("drinks") a droplet of interstitial fluid.
C) internalizes ("eats") a large solid particle.
D) pumps small solutes against their concentration gradient and out of the cell.
B
Which of the following structures function in holding organelles in place, maintaining cell shape and rigidity, and directing organelle movement?
A) Microtubules
B) Flagella
C) Centrioles
D) Cilia
E) Golgi apparatus
A
The pigment melanin is a(n)
A) triglyceride.
B) non-membrane-bound organelle.
C) inclusion.
D) membrane-bound organelle.
E) nutrient.
C
The term "codon" refers to
A) a three-base sequence of mRNA.
B) the part of a rRNA molecule where a new amino acid is added.
C) a three-nucleotide sequence of DNA that codes for a protein.
D) an amino acid that is coded for by three bases of DNA.
E) the part of tRNA that is a triplet of bases that forms hydrogen bonds with complementary sequences.
A
The replication of a DNA molecule during interphase occurs during the
A) generation "gap" phase.
B) second "gap" phase.
C) S phase.
D) metaphase.
E) first "gap" phase.
C
When a cell is placed in a solution with a very low solute concentration, water diffuses into the cell. Such a solution is called a(n) _________ solution.
A) hypertonic
B) hypotonic
C) isotonic
D) endergonic
B
When a cell surrounds a large particle with pseudopodia and then engulfs it, the process is called
A) phagocytosis.
B) receptor-mediated endopinocytosis.
C) pinocytosis.
D) secondary active transport.
E) exocytosis.
A
Identify the organelle that provides enzymes for autolysis.
A) Lysosomes
B) Smooth ER
C) Mitochondria
D) Golgi apparatus
E) Peroxisomes
A
complete each statement by dragging each label into the appropriate blank.
WORD BANK
hydrostatic pressure, osmosis, filtration, carrier-mediated diffusion, simple diffusion
A) Movement of fluids through a selectively permeable membrane caused by hydrostatic pressure is referred to as _________.
B) The pressure exerted by a fluid on the inside wall of its container (or vessel, in the case of the human body), is called ____________.
C) The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration describes _____________.
D) Movement away from high solvent concentration or towards high solute concentration describes _____.
E) The movement of small, polar molecules across the plasma membrane by a carrier protein is called ________.
A) filtration
B) hydrostatic pressure
C) simple diffusion
D) osmosis
E) carrier-mediated diffusion.
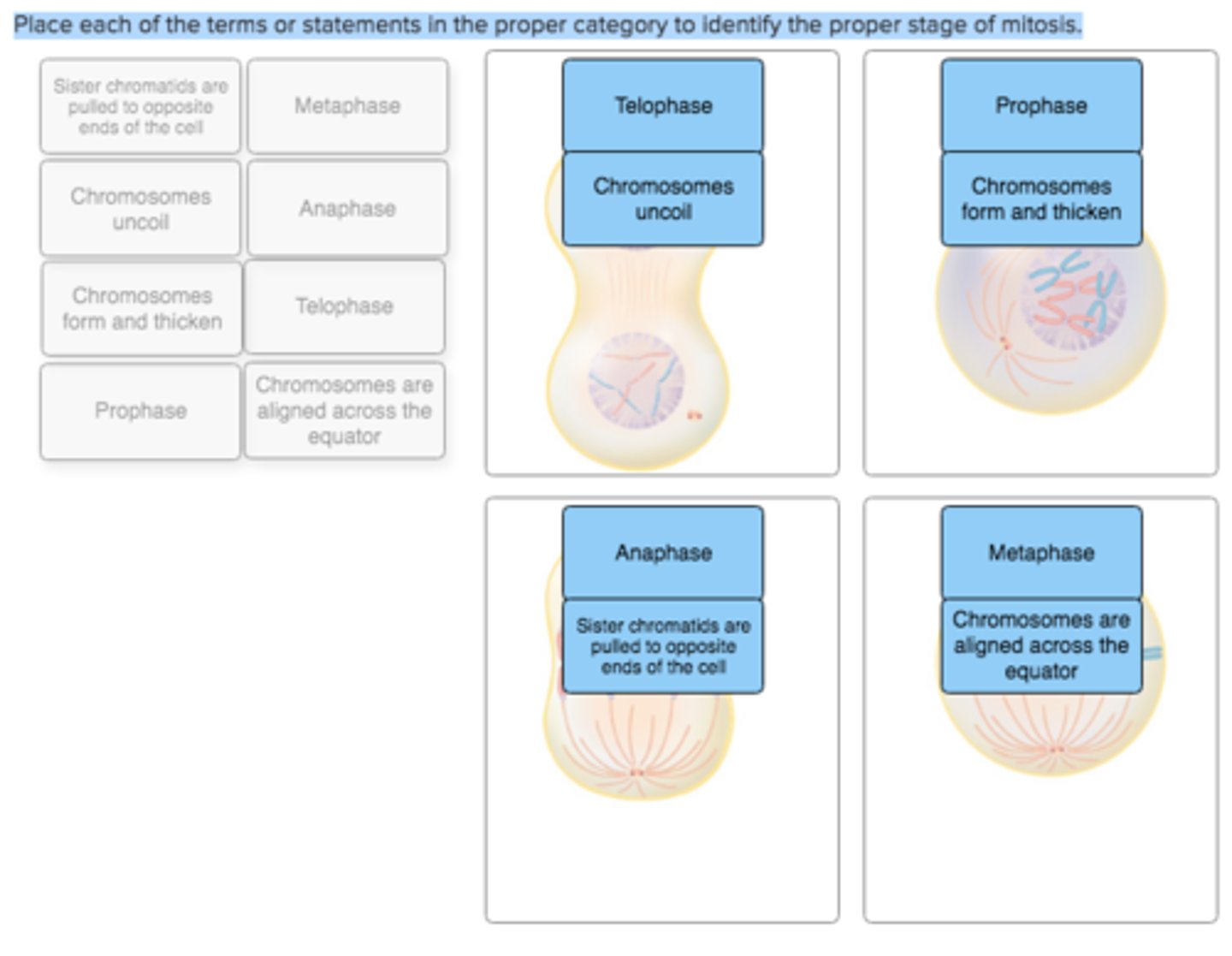
Place each of the terms or statements in the proper category to identify the proper stage of mitosis.
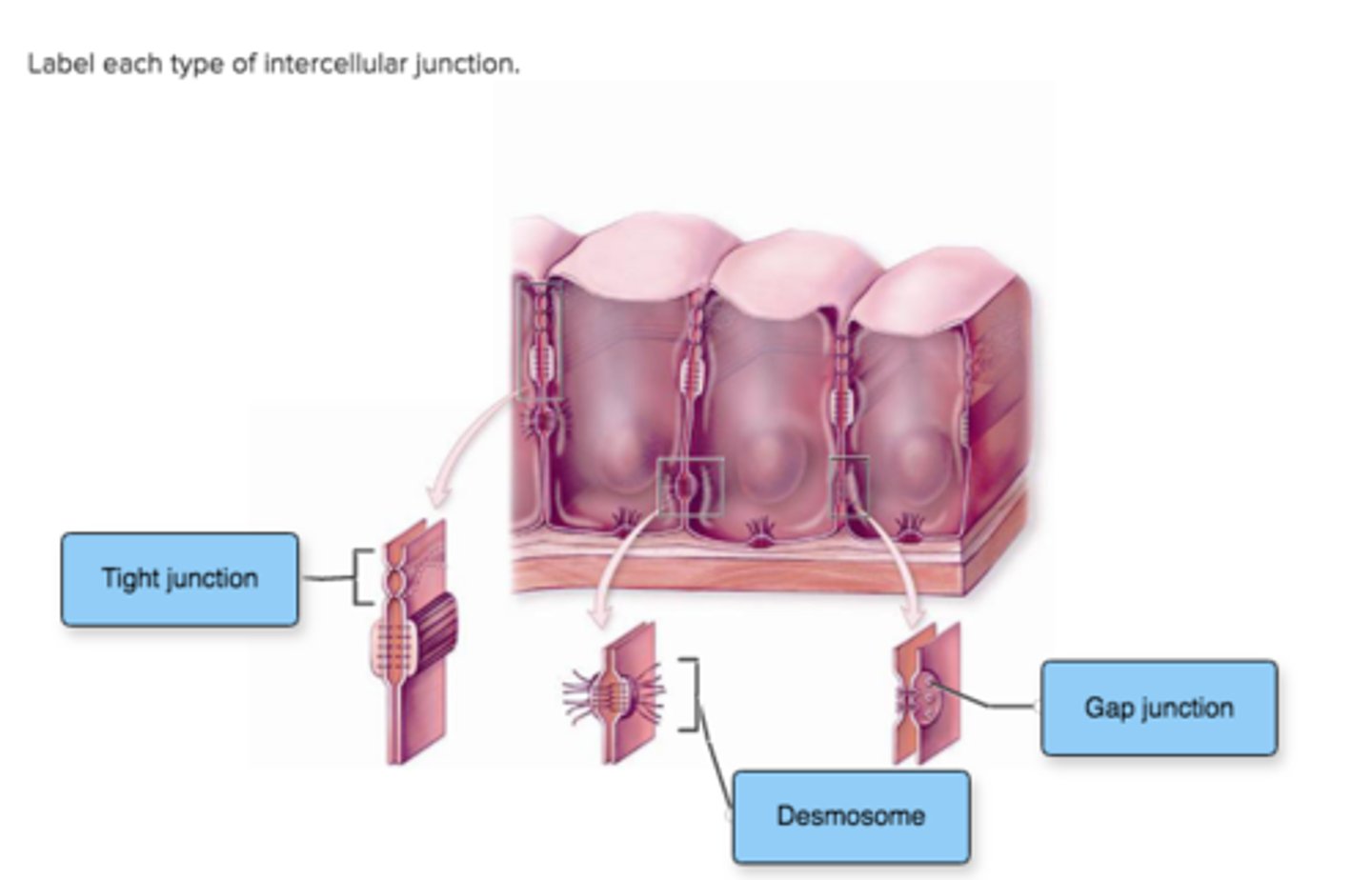
Label each type of intercellular junction.
What feature of your ear accounts for its ability to regain its shape after it has been deformed or compressed?
A) The elastic fibers present in the ear's cartilage
B) The elastic fibers in the ear's skin that contract after being stretched
C) The abundance of reticular fibers forming a dense meshwork
D) The elastic fibers present in the ear's muscles
E) The ear's built-in memory based upon its overall size and shape
A
The primary role of epithelial tissue in the stomach is
A) mixing and propulsion of foodstuffs.
B) secretion of substances for chemical digestion.
C) housing blood vessels and nerves.
D) regulation of contraction.
B
Which type of epithelium is composed of multiple layers, including an apical layer containing tall, slender cells?
A) Stratified columnar
B) Stratified squamous
C) Simple columnar
D) Pseudostratified squamous
E) Simple squamous
A
Which of the following is not lined by nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
A) Oral cavity
B) Small intestine
C) Esophagus
D) Vagina
E) Pharynx
B
Which of the primary tissue types is most widely distributed throughout the body?
A) Connective
B) Muscle
C) Epithelium
D) Nervous
A
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium is found lining
A) ducts of sweat glands.
B) large kidney tubules.
C) portions of the respiratory system.
D) the larger blood vessels.
E) the oviduct.
C
The type of epithelial tissue that is only one cell-layer thick is called __________; the type of epithelial tissue that is two or more cell-layers thick is called _________.
A) stratified; columnar
B) simple; stratified
C) squamous, transitional
D) pseudostratified, cuboidal
B
Which type of connective tissue protein fiber forms a meshlike framework that provides structural support within many organs (within the spleen, for example)?
A) Cartilaginous fibers
B) Elastic fibers
C) Reticular fibers
D) Collagen fibers
E) Mucoid fibers
C
If a gland secretes its products through a duct to the surface of the small intestine epithelium, it must be an
A) exocrine gland.
B) endocrine gland.
A
If you were examining a microscope slide containing a type of muscle tissue and observed a branching network of striated cells, each with one or two central nuclei, you could conclude that you were looking at _____ muscle.
A) skeletal
B) cardiac
C) osseous
D) smooth
E) voluntary
B
Suppose you cut your finger only slightly in what is known as a "paper cut." You observe that the cut hurts but it doesn't bleed. How would you interpret your observation?
A) The paper severed the skin, missing blood vessels, but hitting nerve endings.
B) You probably have some unknown condition related to blood clotting.
C) The paper had some factor that prevented the release of blood but not the sensation of pain.
D) Nerve endings occur in epithelium but blood vessels do not.
E) Very thin cuts never draw blood but do sever nerves.
D
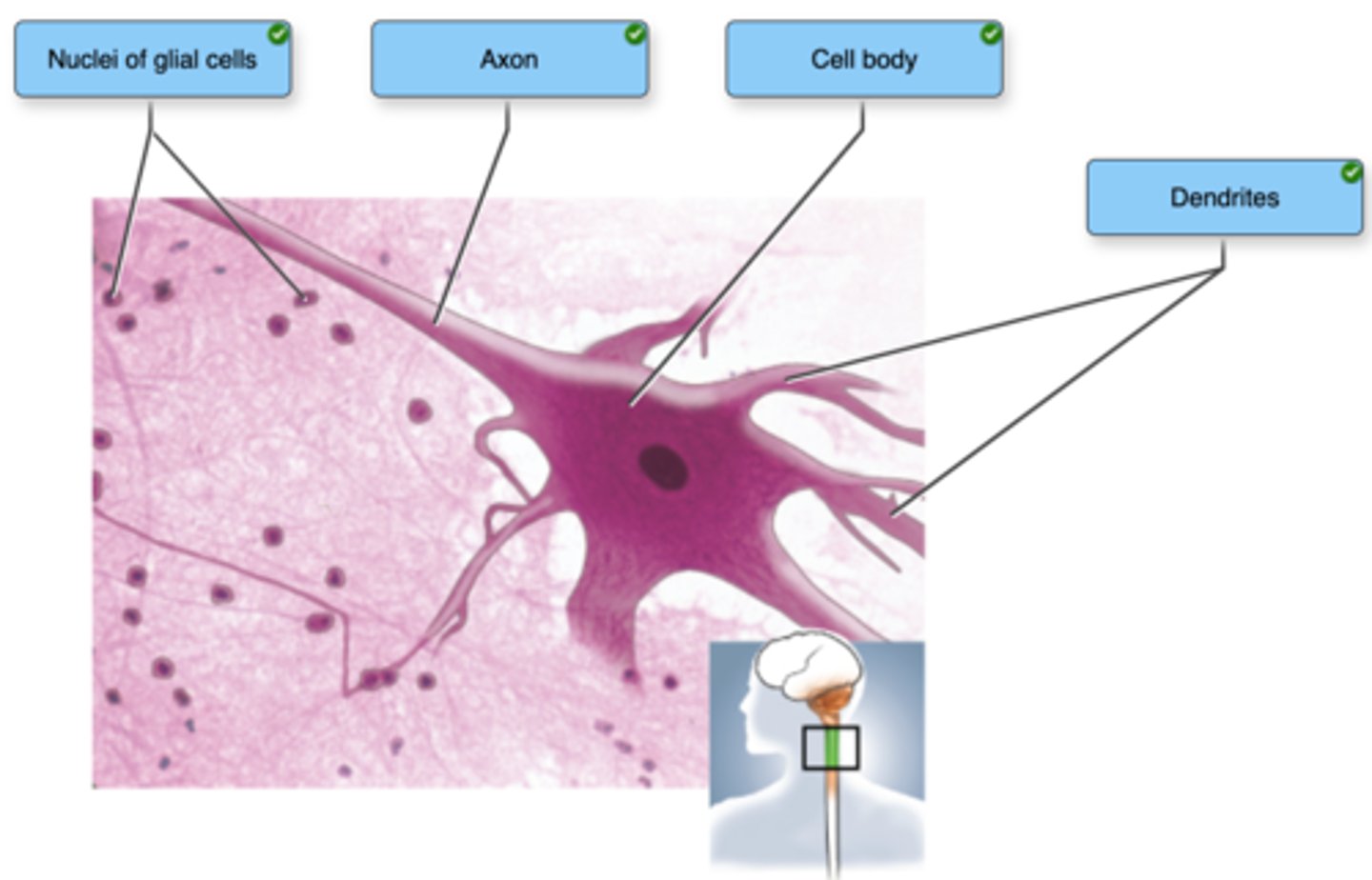
Dendrites
A) transmit signals away from the cell body.
B) transmit signals toward the cell body.
C) manufacture proteins to be used by the neuron.
D) use hormones to transmit information.
E) release neurotransmitter.
B
The heart is confined within a double-walled serous membrane sac. The part of the membrane that is in contact with the heart is the _____ layer.
A) visceral
B) parietal
C) synovial
D) mesothelial
E) serous
A
The internal feature of bone that makes it simultaneously strong and lightweight is the
A) latticework structure of spongy bone.
B) pattern of osteons.
C) areolar connective tissue in the central cavity.
D) arrangement of collagenous fibers.
E) presence of cartilage.
A
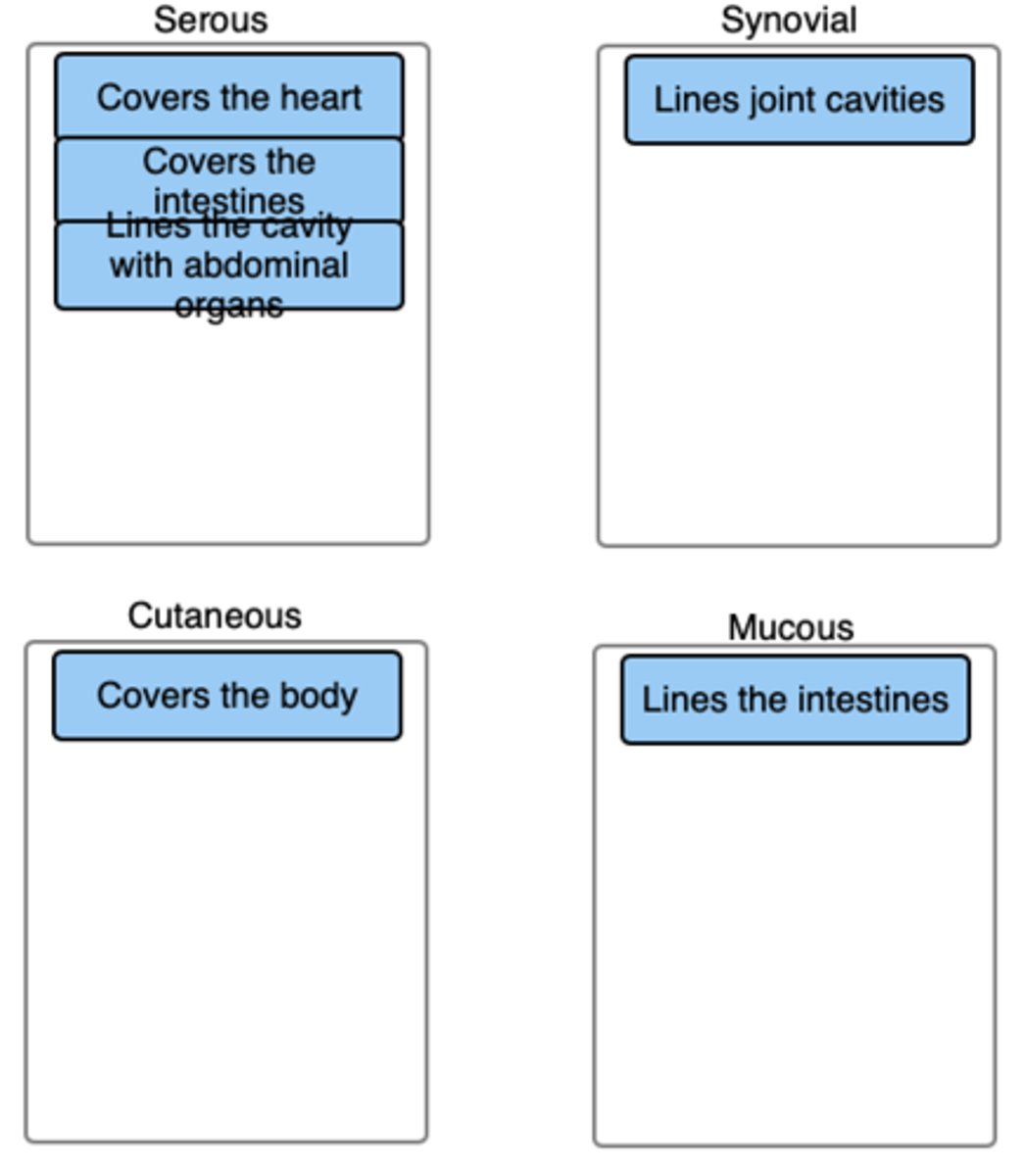
Place the following terms or examples with the correct category.
Correctly label the following areas on a slide of nervous tissue.
What is the greatest risk factor for skin cancer?
A) Using excessive sun block
B) Low skin hydration levels
C) Exposure to UV light rays
D) Advanced age
E) Being a female
C
Tactile (Merkel) cells are sensitive to
A) light.
B) sound.
C) cold.
D) heat.
E) touch.
E
The function of melanin in the skin is to
A) help regulate body temperature.
B) keep the epidermis soft and pliable.
C) prevent infections.
D) protect against UV light.
E) reduce water loss.
D
Select the way in which sweat glands function in homeostasis.
A) Protection
B) Sensory perception
C) Production of vitamin D3
D) Temperature regulation
D
Match the structure with its protective function.
WORD BANK
Glands, Skin, Nails, Hair
1. Protects against abrasion; contains melanin, which absorbs damaging UV light _______
2. Protects against abrasion; acts as a heat insulator, protects the eyes against foreign objects _______
3. Produce secretions that create an environment unsuitable for some microorganisms ________
4. Protect the ends of the fingers and toes from damage; can be used in defense _______
1. Skin
2. Hair
3. Glands
4. Nails
Which of the following is not a type of hair?
A) Lanugo
B) Vellus
C) Keratin
D) Terminal
E) All of these choices are correct.
C
Nails are hard derivatives formed from the stratum ______ of the epidermis.
A) lucidum
B) basale
C) spinosum
D) corneum
E) granulosum
D
What is the composition of the subcutaneous layer?
A) Areolar connective tissue and dense irregular connective tissue
B) Areolar connective tissue and adipose connective tissue
C) Adipose connective tissue
D) Dense irregular connective tissue
E) Areolar connective tissue
B
Epidermal dendritic (Langerhans) cells function as part of the ______ response.
A) sweating
B) tanning
C) heating
D) sensory
E) immune
E
The structure responsible for pulling on the follicle and causing "goose bumps" is the
A) external root sheath.
B) arrector pili muscle.
C) papilla.
D) internal root sheath.
E) epithelial root sheath.
B
Production of this vitamin requires skin exposure to the sun. This vitamin is crucial for regulation of calcium and phosphate.
A) Vitamin B12
B) Vitamin D
C) Vitamin A
D) Vitamin C
E) Vitamin E
B
Which is the actively growing part of the nail?
A) Nail root
B) Nail matrix
C) Nail folds
D) Nail bed
E) Free edge
B
The sweat glands that produce a watery substance and are associated with exercise and stress are the _________ sweat glands, while glands that produce an organic substance that causes body odor are the __________ sweat glands.
A) eccrine, apocrine
B) holocrine, merocrine
C) merocrine, eccrine
D) sebaceous, apocrine
A
Which type of hair forms the beard on the faces of males?
A) Vellus
B) Terminal
C) Pilus
D) Lanugo
E) Nonpigmented
B
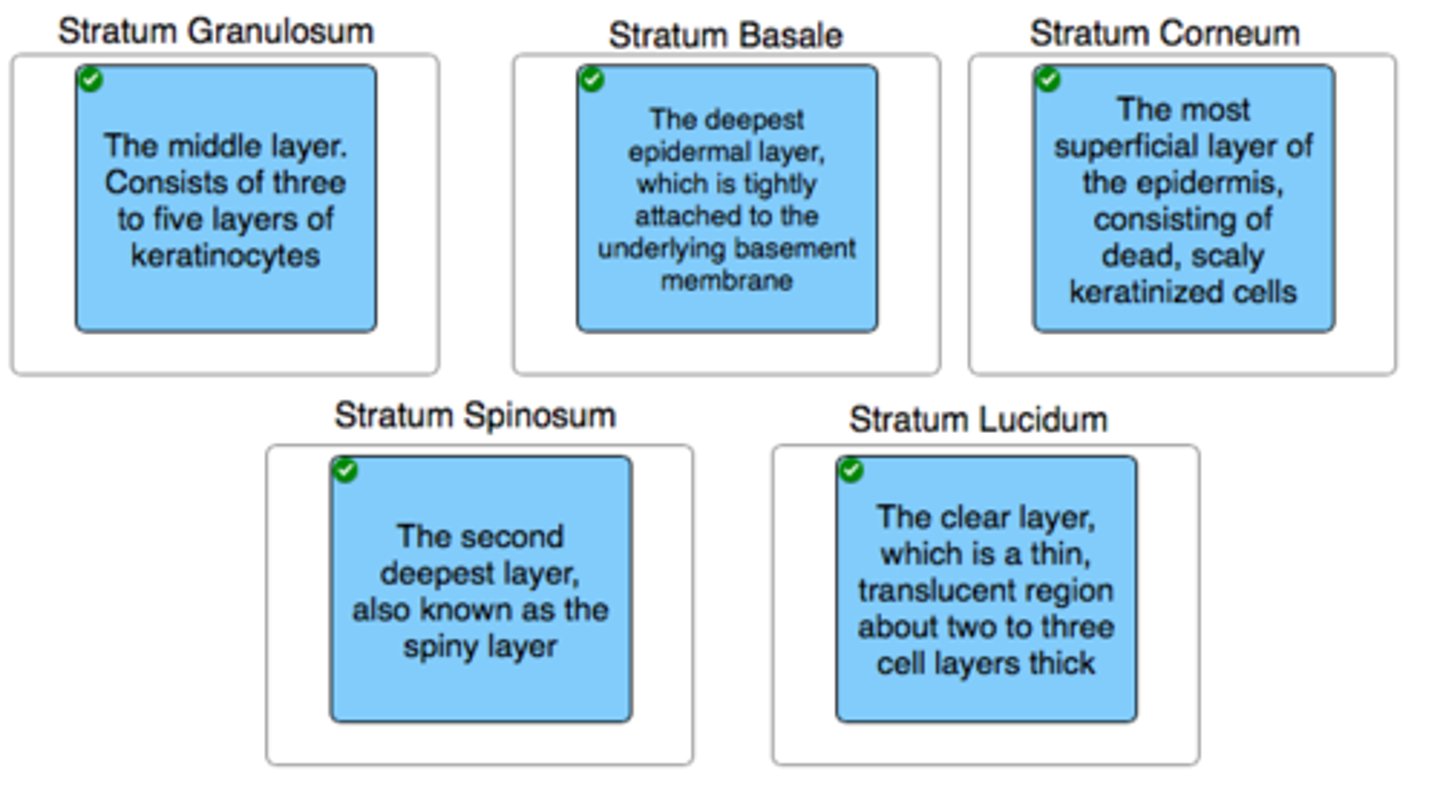
Classify each description with the appropriate layer of the epidermis.
Classify the situations into the correct boxes according to whether they would result in constriction of the dermal blood vessels (vasoconstriction) or dilation of the dermal blood vessels (vasodilation).
vasoconstriction
1. Going outside in a cold day
2. Jumping into a cold pool
vasodilation
1. Sitting in the sun on a warm day
2. Running on the treadmill in the gym
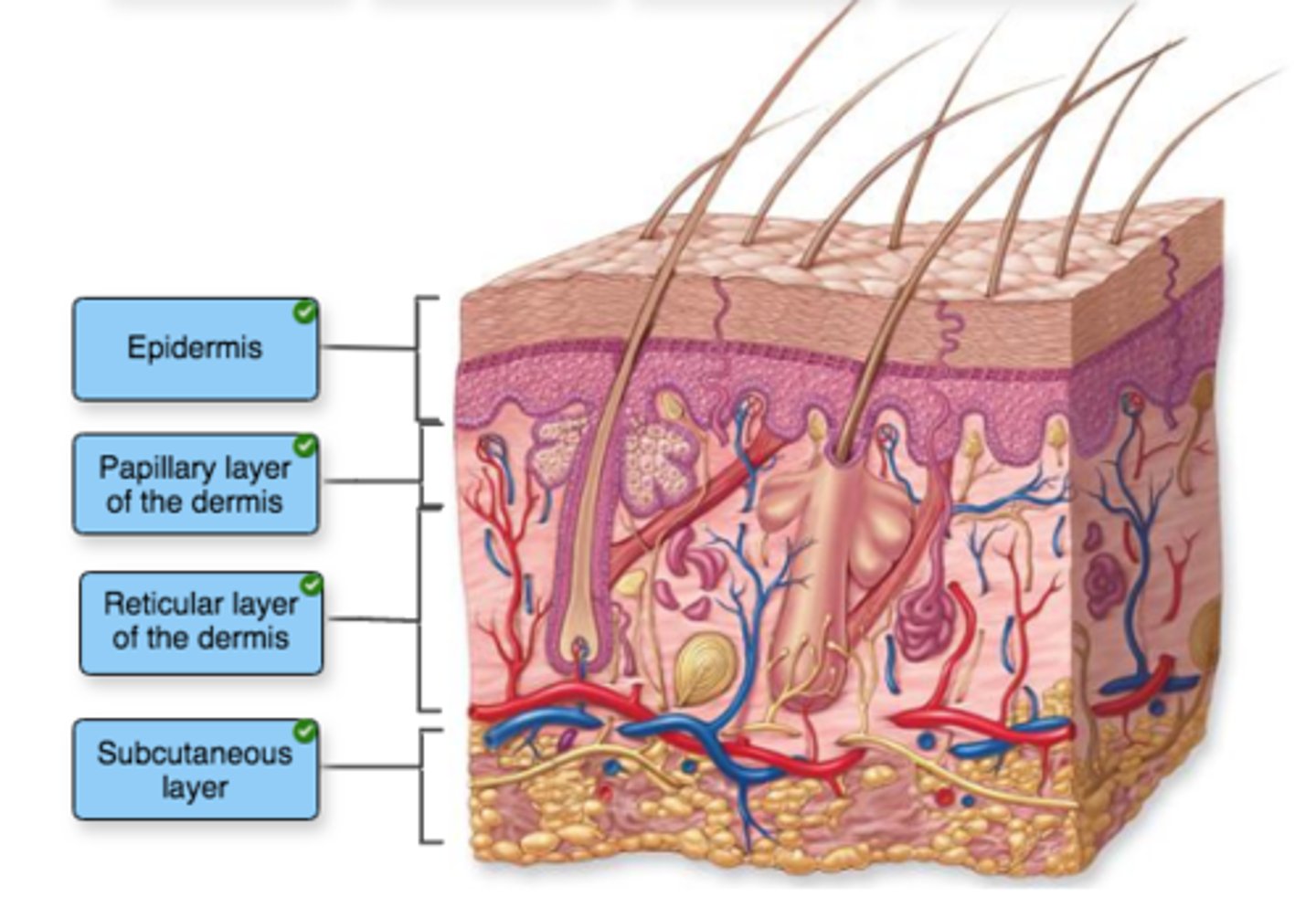
Label the structures of the integument.