Ancient History
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What was the mythological reason for the Trojan War?
- Eris caused discord at wedding of gods/goddesses
- Threw golden apple 'for the fairest'
- Argument between Hera, Athena & Aphrodite
- Asked Zeus to judge but he let Paris judge instead
- Hera = power, Athena = wisdom, Aphrodite = love
- Paris chose Aphrodite, telling him about Helen (who was married to Menelaus in Greece)
- Paris left with/stole Helen back to Troy
- Menelaus was angry and declared war against Troy
Who was Paris?
- Prince of Troy
- Prophesised to destroy Troy
- Took or kidnapped Helen
- Shot Achilles in heel with an arrow guided by Apollo
- Paris himself was killed by arrows of Hercules
Who was Menelaus?
- King of Sparta
- Married to Helen
- Brother of Agamemnon
Who was Odysseus?
- King of Ithaca
- Proposed idea of Trojan Horse
- 10 years to get home (punished by Poseidon for horse & killing his son)
Who was Achilles?
- Greatest Greek warrior
- Murdered Hector to avenge bff Patroclus
- Shot by Paris
Who was Agamemnon?
- King of Mycenae
- Leader of the Greek armies
- Brother of Menelaus
Who was Hector?
- Brother of Paris
- Murdered Patroclus
- Killed by Achilles
Who was Homer?
Author of the Iliad and the Odyssey
What is the Iliad about?
- Trojan War
(parts of story)
What is the Odyssey about?
Odysseus' 10 year journey home (Ithaca) after the Trojan War
What role did the Iliad and Odyssey play in Greek history? Provide examples.
Provided basis of Greek education & culture in Classical age
Define Unitarians regarding Homer
Believed epics composed with such beauty and detail, produced by one creative mind - yes Homer
Define Separatists regarding Homer
Believed parts of epics were inconsistent & analysed as separate individual works - no Homer
Representations of Persepolis: Modern
Fascinates modern visitors, debate over the role of Alexander the Great in its destruction
Cyrus the Great (c. 560 - 530 BC)
founded and expanded the empire. Incorporated the neighbouring kingdoms of the Medes, Libyans and Babylonians
When did Cyrus the Great rule and how did he get into power?
c. 560 - 530 BC. He overthrew his grandfather, the Median emperor
Why is the Achaemenid dynasty called the Achaemenid dynasty?
Because Cyrus claimed to be the descendant of a famous patriarch
Darius I (c. 522-486BC)
Expanded the empire to its greatest extent. Added Thrace and Macedonia. Invaded the Greek mainland but his forces were defeated by the Athenians at the battle of Marathon
When did Darius I rule?
522-486 BCE
Xerxes I (486-465 B.C.)
Darius' son and chosen successor. Suppressed revolts in Egypt and Babylon.
480 BC
Victory over the Greeks at the Battle of Thermopylae
Ecbatana
capital city of the Medes. Lies beneath modern city Hamadan
Pasargade
1st capital of Persian Empire; location of Cyrus' tomb. Constructed to celebrate conquest of Medes. National shrine and used for royal coronation ceremonies
Babylon
Administrative capital of the Persian empire under Cyrus and Darius
Geographical location of Persepolis
70 km NE of modern Shriaz in the Fars province of southern Iran.
Nations in the Persian Empire
Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Turkey, Macedonia, Thrace
224-651 AD (Sasanian period, discovery/excavation)
Rulers started the mythological tradition of trying to explain the presence of the ruins
Early 19th century (excavation + discovery)
First organised excavations of the Persepolis ruins. Included Hebert Weld and Lord Curzon
Gate of All Nations
Formal entrance to Persepolis, accessed through double staircase near the north-west corner of the sites. Built by Xerxes. Establishes the might of the empire
Apadana
Shows appreciation of other cultures, influence of other cultures and the king as mighty.
Influences of the Apadana
Stonework techniques from Lydia and Ionia, influences from Median, Egyptian, Phoenician and Mesopotamian cultures
Hall of Hundred Columns
King Xerxes throne hall in Persepolis. it was the largest roofed area at 250 feet squared. Function changed to a store room because the treasury was too small
Main features of Architecture
Hypostyle halls from the Medians
Columns from the Greeks
Staircases- enabling easy climb
Foreign influence of design and ornamentation
Greece: columns
Media: Hypostyle halls
Lydia: Masonary techniques
Susa: Archers
Babylonia: Sphinxes
Egypt: inlaying precious stones
The role of Persepolis as a centre of Persian power (Ancient)
Venue for Persian NY festival. Used as an administrative hub, central bank, fortress, seat of gov of achaemenid empire. Operated as a symbol centre of Persian power and kingship
Alexander the Great defeated the Persians when and where?
330 BC at the Battle of the Persian gate
Archaeology
The study of human history and prehistory through the excavation of sites and the analysis of artefacts and other physical remains.
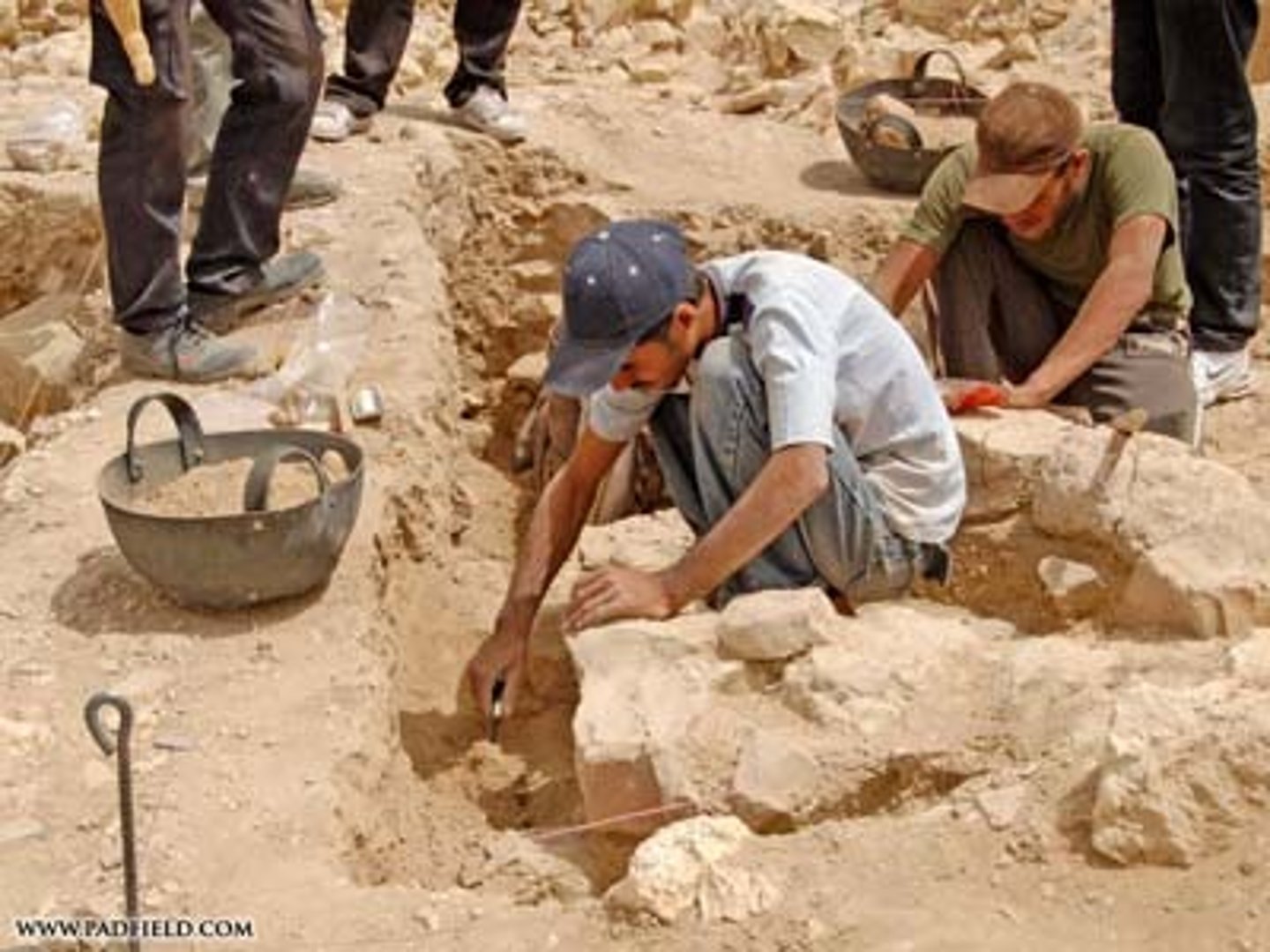

Excavation
The act of digging; "there's an interesting excavation going on near Princeton". The action of excavating something, especially an archaeological site.
Site
The site of an archeological exploration; "they set up camp next to the dig".
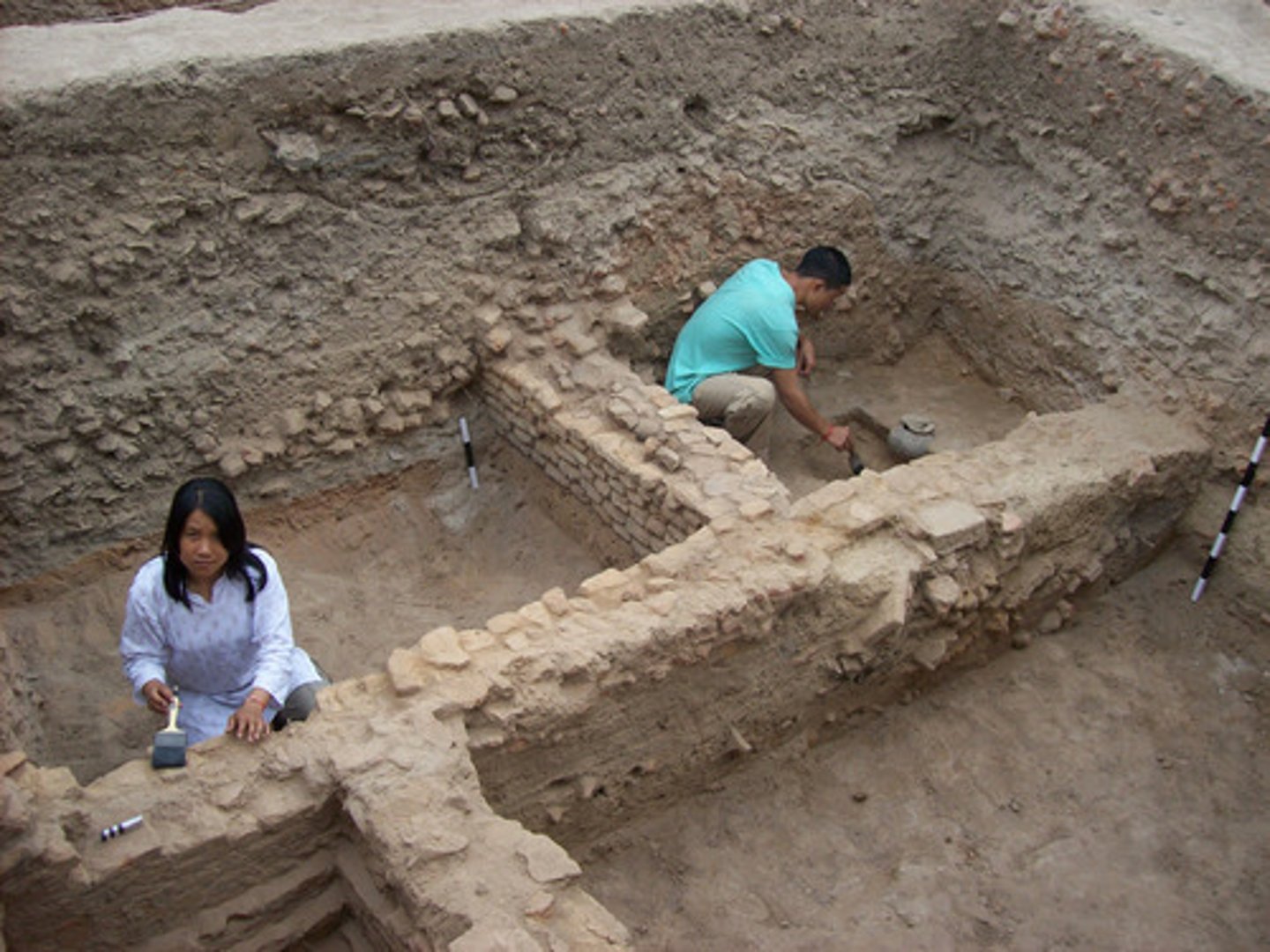

Evidence
The available body of facts or information indicating whether a belief or proposition is true or valid.

Infrared Photography
Photography using film with an emulsion that is sensitive to infrared light, enabling it to be used in misty weather, in darkened interiors, or at night. It has applications in aerial surveys, the detection of forgeries, etc.
Geophysical
A branch of science that deals with the physical movements and forces of the Earth (such as its climate and oceans).

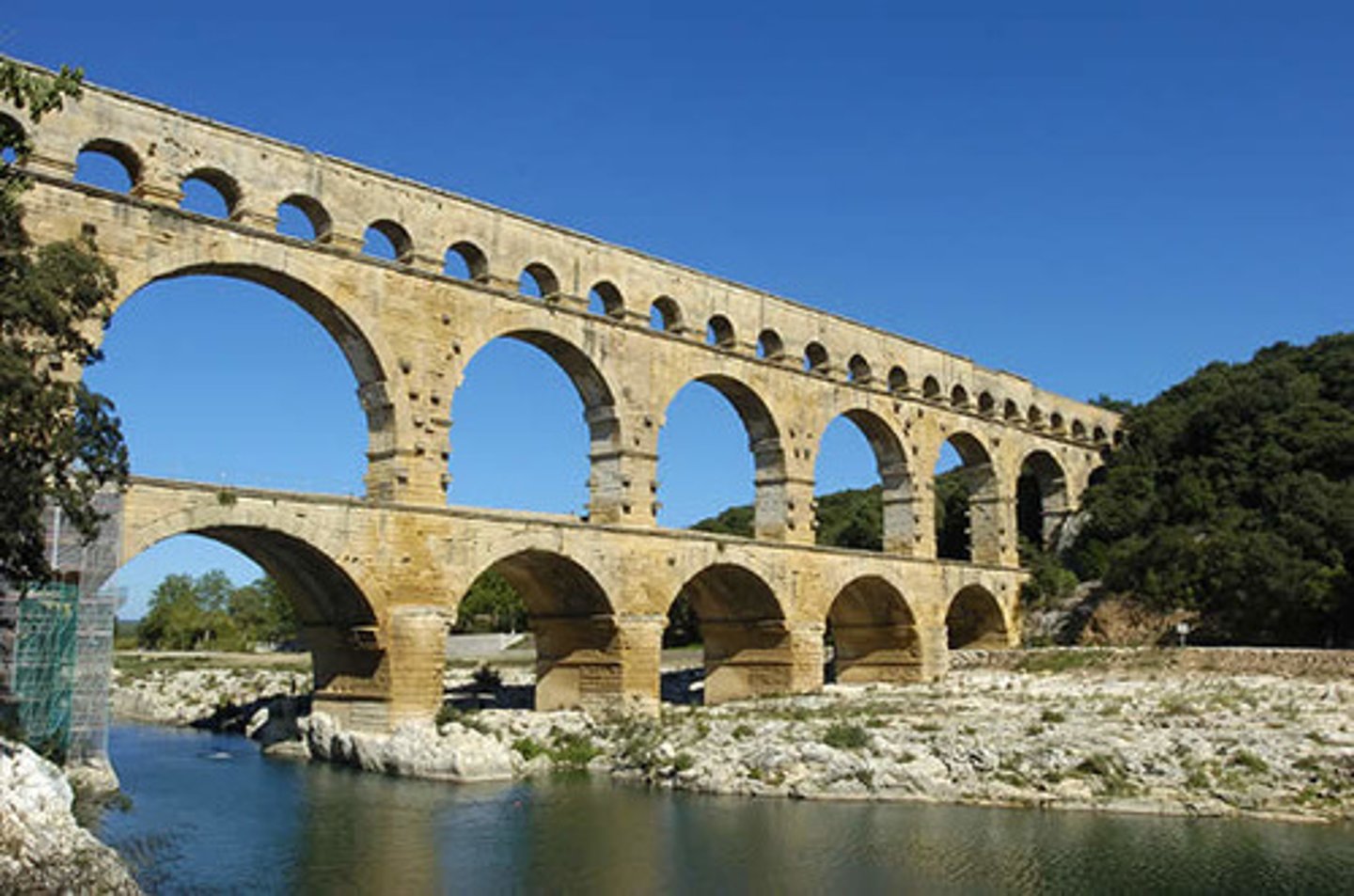
Aqueduct
A bridge or viaduct carrying a waterway over a valley or other gap. An artificial channel for conveying water.

Stratum/Strata
A layer or a series of layers of rock in the ground: a stratum of flint.
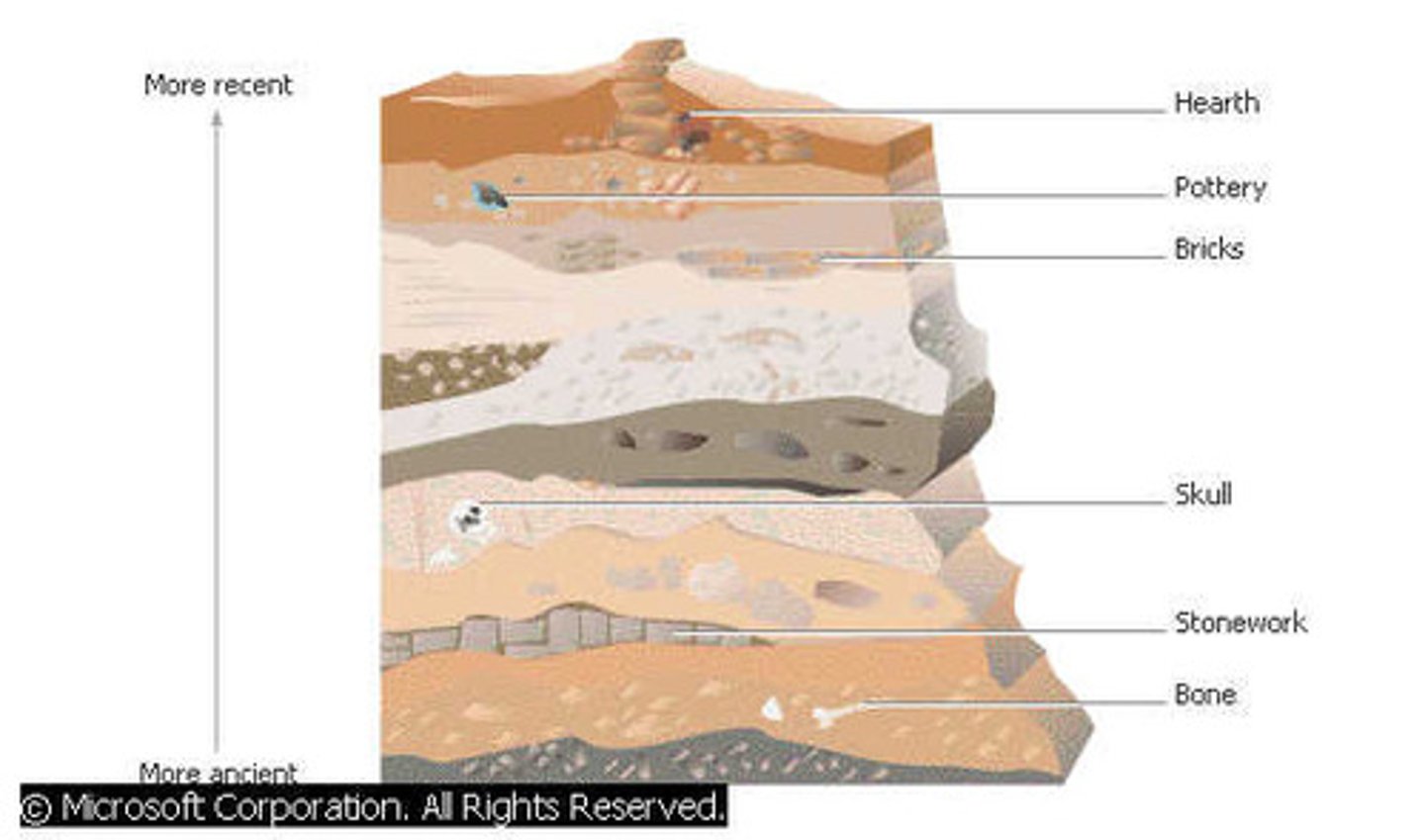
Stratigraphy
The analysis of the order and position of layers of archaeological remains.

Findspot
The place where an object is found.
Provenance
The place of origin or earliest known history of something: an orange rug of Iranian provenance.
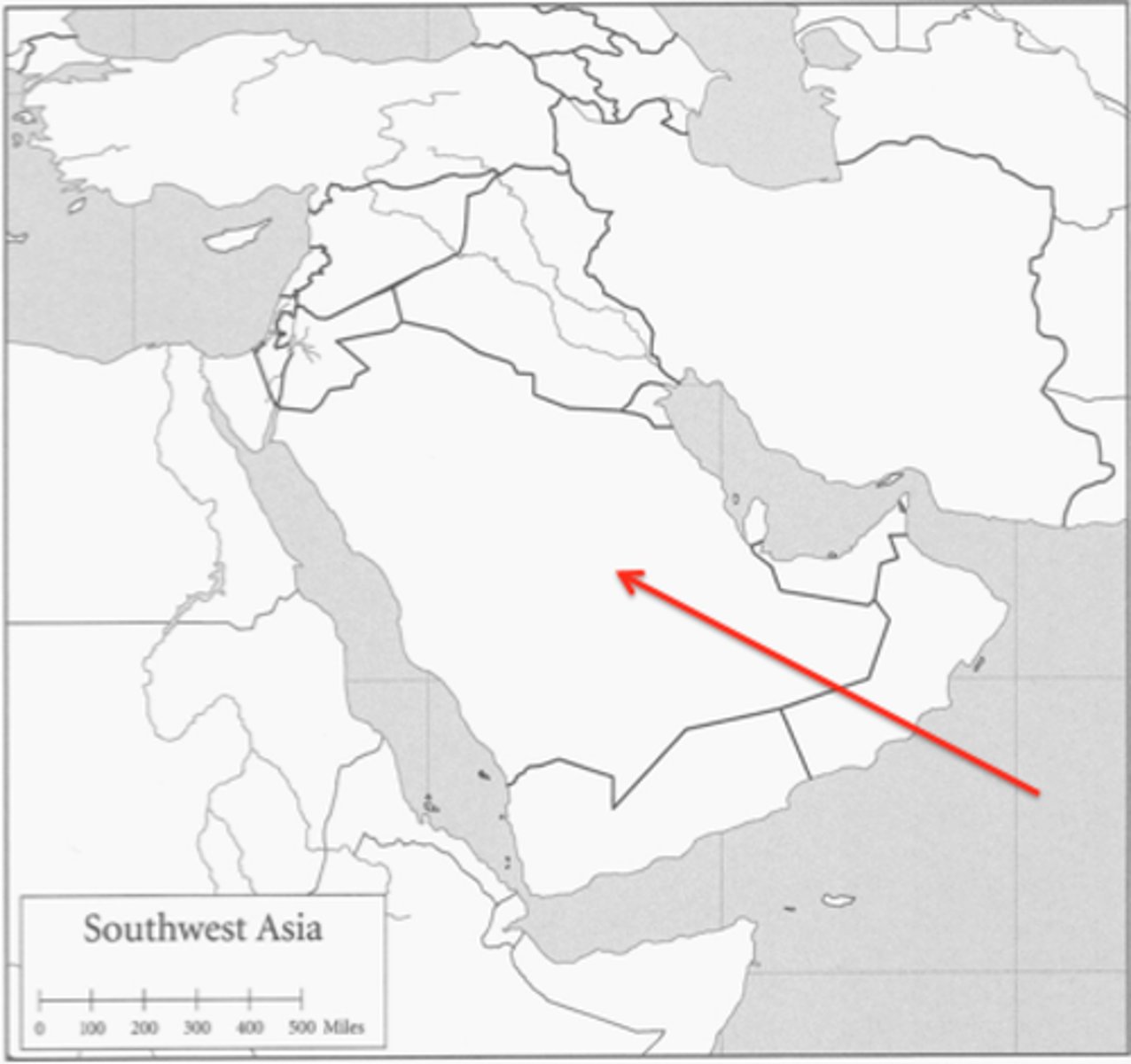
In situ
In the original place: [as adverb]: frescoes have been left in situ [as adjective]: a collection of in situ pumping engines.
![<p>In the original place: [as adverb]: frescoes have been left in situ [as adjective]: a collection of in situ pumping engines.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2b62fb19-4e96-45d2-87e0-07bb10e70b38.jpg)
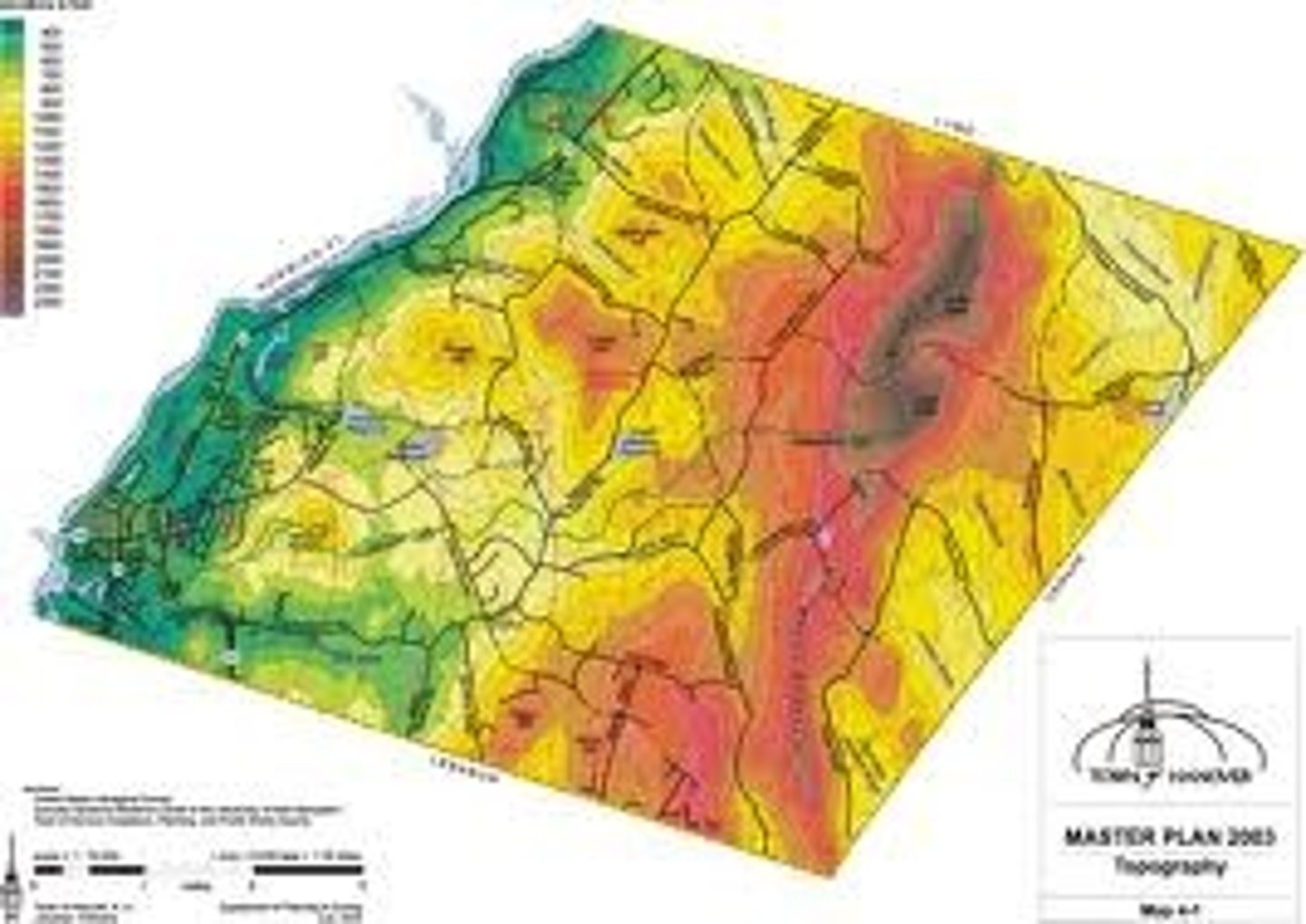
Topography
The arrangement of the natural and artificial physical features of an area: the topography of the island. a detailed description or representation on a map of the physical features of an area.
Methodology
A system of methods used in a particular area of study or activity: a methodology for investigating the concept of focal points [mass noun]: courses in research methodology and practice.
Artefact
An object made by a human being, typically one of cultural or historical interest: gold and silver artefacts.
