Marine Geology
1/32
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
how to track sound in the sea
single-beam sonar: creates a trackline of bottom depth as the ship moves forward
multi-beam sonar: creates a swath of bottom depth as the ship moves forward so you get a 2d image of the sea floor as your move along
towed multi-beam sonar: creates a high-resolution swath of bottom depth as the ship moves forward
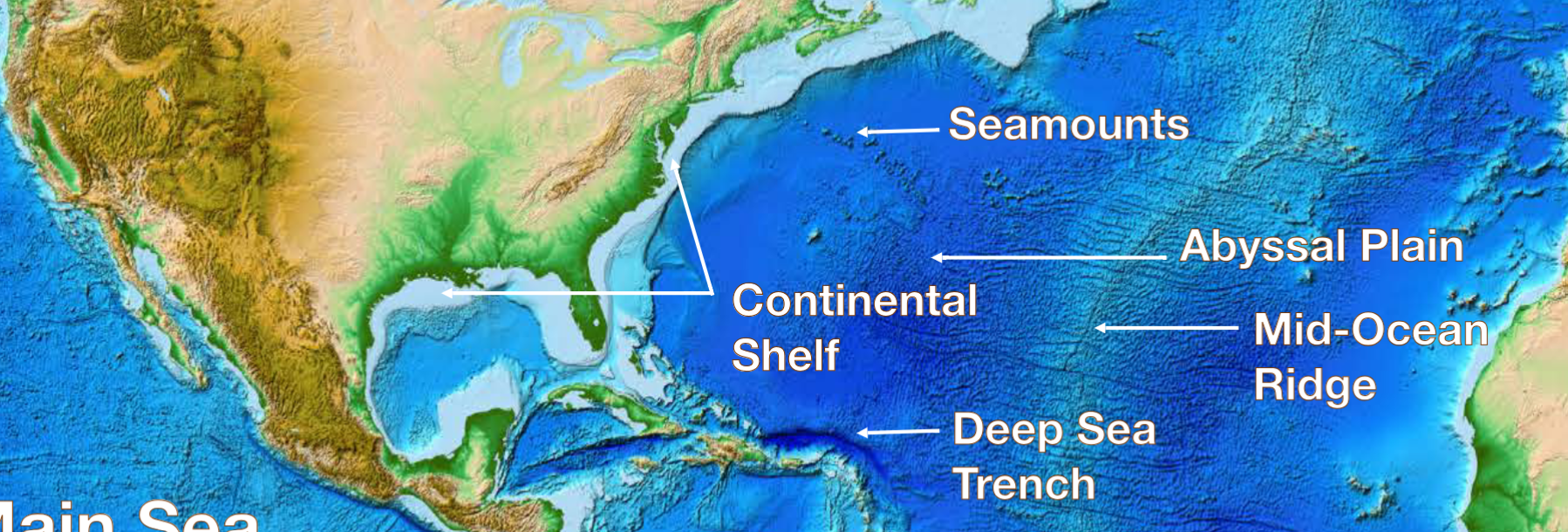
main seafloor features
continental shelf
deep sea trench
mid-ocean
ridge
abyssal plain seamounts
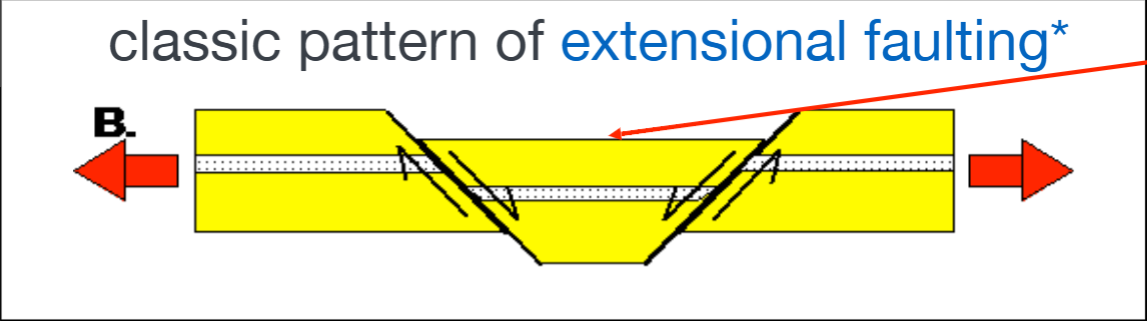
proof for plate tectonic theory
sea floor subduction → at mid-ocean mountain ranges, there is a drop on the ride (extensional faulting) ->
magnetic anomaly patterns: earth magnetic field is moving 35 miles per years and has gone through many reversals (seen through how minerals lined up opposite)
parts of the earth
rigid outer crust
thin and rigid and floats on the higher density mantle below
plastic upper mantle
although solid, the high temperatures cause the material to be sufficiently ductile to flow on very long timescales
molten outer core
solid inner core
different crusts of the earth
oceanic
thin (~5km), higher density, younger, mainly made of basalt
continental
thick (~70km), lower density, older, mainly granite
what is the driving mechanism of plate tectonic movements
hot molten rock rises to divergent boundaries via convection and solidifies to form new oceanic crust
oceanic crust spreads laterally, cools over time and gets more dense, sinks and is pulled by gravity back into the mantle at subduction
what does a tectonic plate consist of
a lithosphere (solid ridge upper mantle that is topped by either an oceanic, continental crust or both)
what happens when a tectonic plate moves
continent that is part of the plate also moves
what really sealed the deal that the continents were once pangaea
discovery of deep sea trenches and associated seismic activity helped to explain the eventual loss of ocean crust that was initially formed at mid-ocean ridges
types of boundaries
divergent, convergent and transform
what crusts are involved at a divergent boundary
continent-continent
ocean-ocean
what crusts are involved at a convergent boundary
ocean-continent
ocean-ocean
continent-continent
what is the rate of sediment accumulation
very slow and a 10-meter sediment core can represent a record of up to a million years of earth history
divergent plate boundaries
two plates moving apart
most are mid-ocean ridges
less commonly they are also continental rift zones → east africa rift zone
examples: cocos plate and nazca plate, eurasion and caribbean and african plate
what is the process that caused pangaea to break up
wilson rock cycle
convergent plate boundaries - oceanic and continental crust
since ocean crust is more dense than continent crust, it subducts under continent and is pushed into the mantle
generates deep ocean trench and forms very explosive volcanoes → it is SiO2 rich and very viscous, rich in H2O → water is derived from subducting oceanic crust
example: north cascade mountains mountains in washington and andes mountains in chile; mount saint helens (explosive volcano caused from o-c colliding)
convergent plate boundaries - ocean and ocean
plate subducted is often furthest from its respective spreading and thus older, colder and denser
creates deep oceanic trench (sometimes filled with sediments)
chain of volcanoes an “island arc”
examples: aleutian islands in japan and idnonesia
convergent plate boundaries - continental and continental
neither want to subduct so mountain building often happens because both plate boundaries are largely equal density
forms large mountain ranges
example: india’s collision with asia to form mt everest
transform plate boundaries
plates slide laterally relative to one another
example: san andreas fault
example of stationary mantle plume underlying a moving tectonic plate
hawaii
what is the range of material raining down in sediment accumulation
wide-range: river-born sediments, continental dust, biological material
what are the biological marine sediment types
calcareous and siliceous ooze that sink to the bottom of the ocean
what is the sediment thickness near the coast
high due to river runoff of terrigenous sediment and high productivity that leads to high rain rate of biological material
where is red clay ooze found in
open ocean due to the slow rain of continental dust (and very low biological addition) which creates red clay
where are calcareous/siliceous sediments usually found in
high biological productivity regions (and absence of river outflows containing terrigenous material)
how can sediments tell us the ocean’s temperature in the past
many microorganisms’ shells found in sediment cores are constructed of calcite
all oxygen atoms have 8 protons → most have 8 neutrons but some have 10
indirect (proxy) estimates of the temperature of seawater can be obtained from calcite fossils using the isotope ratio 18O:16O preserved in the oxygen atoms of their shell
how many mass extinction events have there been
5, a 6th one caused by humans may happen
are the oceanic and continental crusts denser or less dense than the underlying mantle material
less dense
how did alfred wegener theorize that the continents used to make up pangaea
apparent good fit of continental boundaries
distribution of fossil and mineral belts made sense if the continents were joined together in the past
how did naturalists first theorize about pangaea (before alfred wegener)
the apparent fit of continents
age of ocean crust at ridges and off-axis
ocean crust at ridges are younger and symmetrically older off-axis
what can the remains of planktonic organisms be a proxy measurement for
reveal information about growth conditions of the overlying ocean
such as: surface water temperatures level of biological productivity
what is an example of reconstructing earth history using sediment core analysis
mass extinction event