2.2.1 - Sleep/Wake Cycle & Circadian Rhythm
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
The state of being able to perceive one's thoughts, feelings, sensations, wakefulness, and surroundings is:
Consciousness
- It involves various levels, from alert wakefulness to altered states such as sleep or meditation
Circadian Rhythm is:
the natural, internal process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle

What is your sleep-wake cycle?
relatively self-explanatory:
your body's pattern of sleep and wakefulness, regulated by sleep homeostasis and circadian rhythms
- influenced by internal mechanisms and external light-dark cycles.

The circadian rhythm repeats every . . . (time interval?)
24 hours
What does the circadian rhythm influence? (4)
- patterns of alertness
- hormone release
- body temperature
- other physiological processes
Jet Lag is:
a disruption of the body's circadian rhythm due to rapid travel across time zones.

Is Jet Lag temporary or longer lasting?
temporary
What are the results of experiencing jet lag?
- fatigue
- sleep disturbances
- difficulty concentrating
Shift Work is:
Employment schedules that require working outside of typical daylight hours, often interrupting the body's natural circadian rhythm.

Is Shift Work temporary or longer lasting?
Longer lasting
What are the results of doing Shift Work?
- sleep disturbances
- fatigue
- increased risk of health problems because of mismatched work hours-internal clock relationship

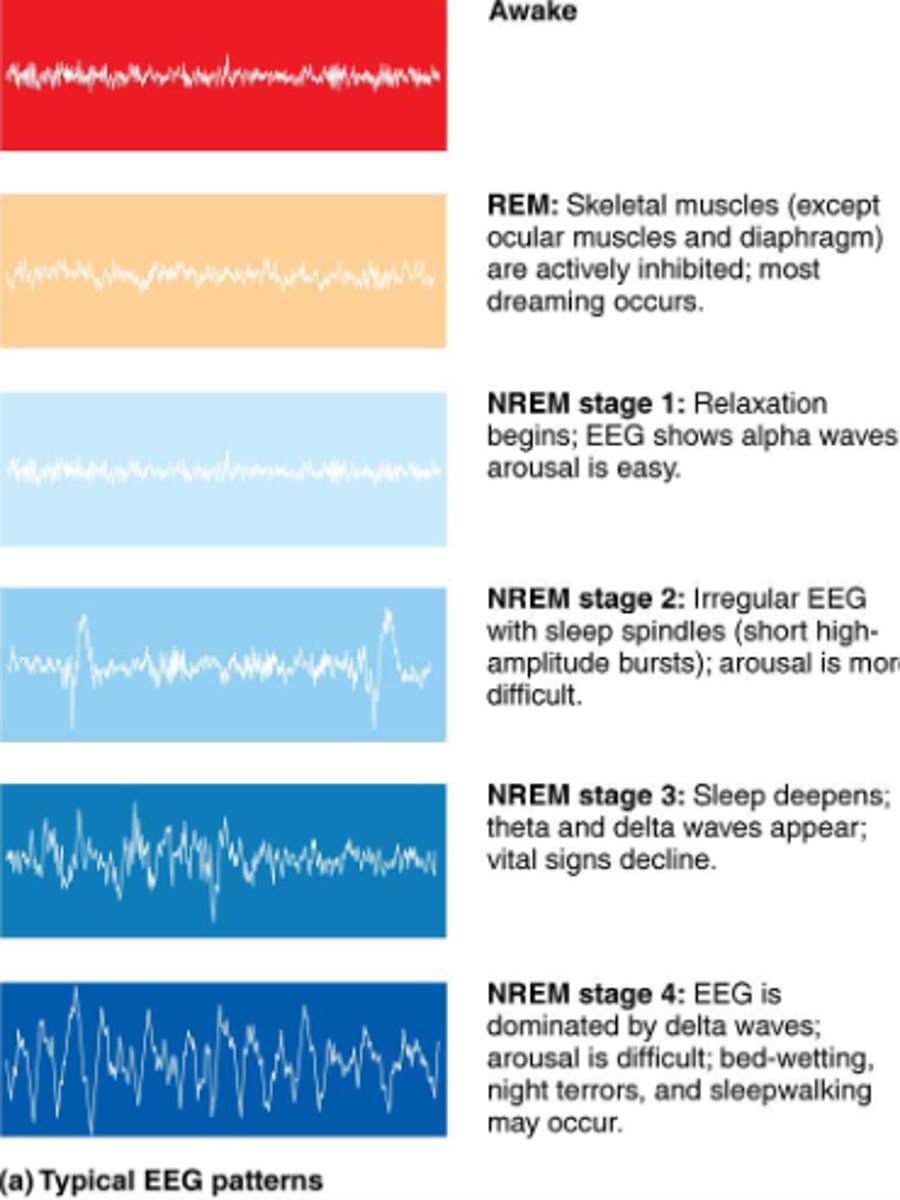
NREM Stage I:
...
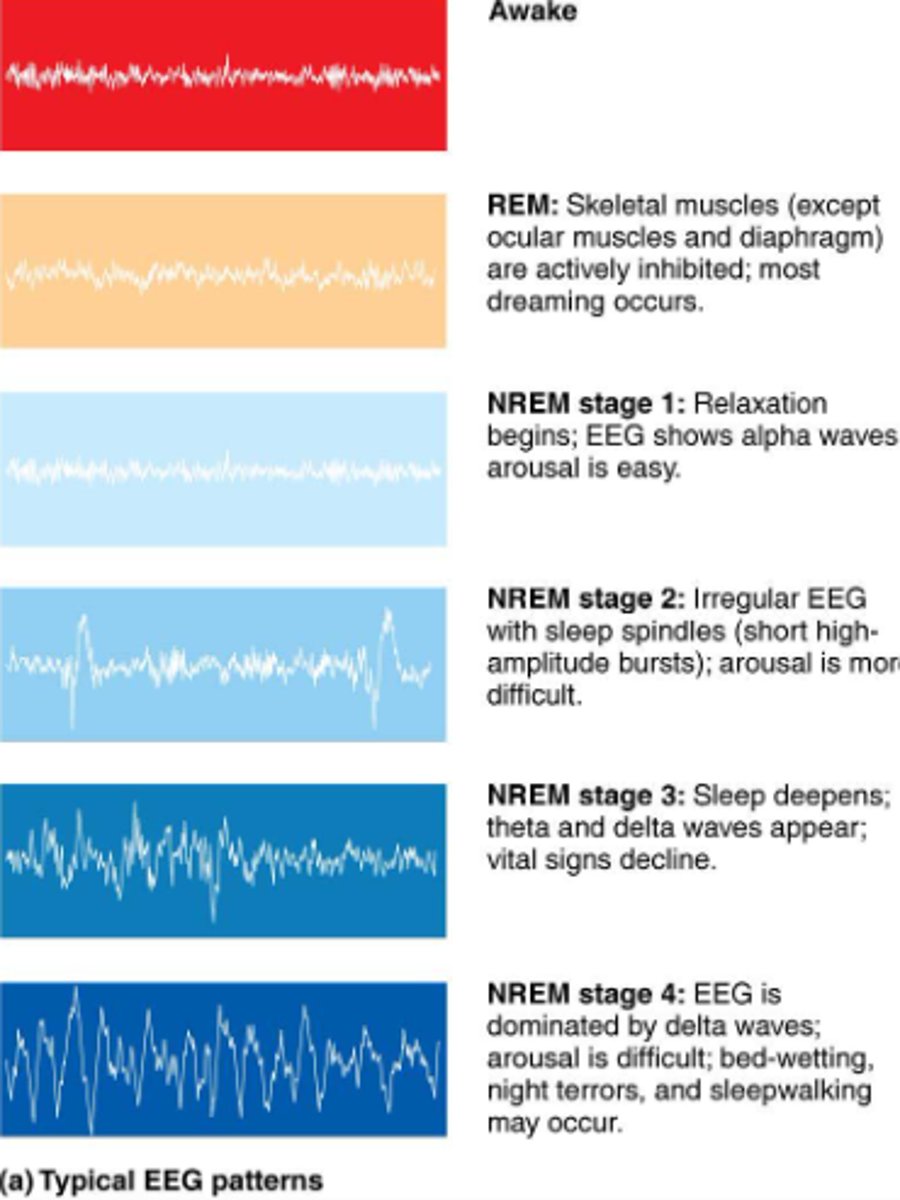
VOLTAGE:
NREM Stage 2:
...
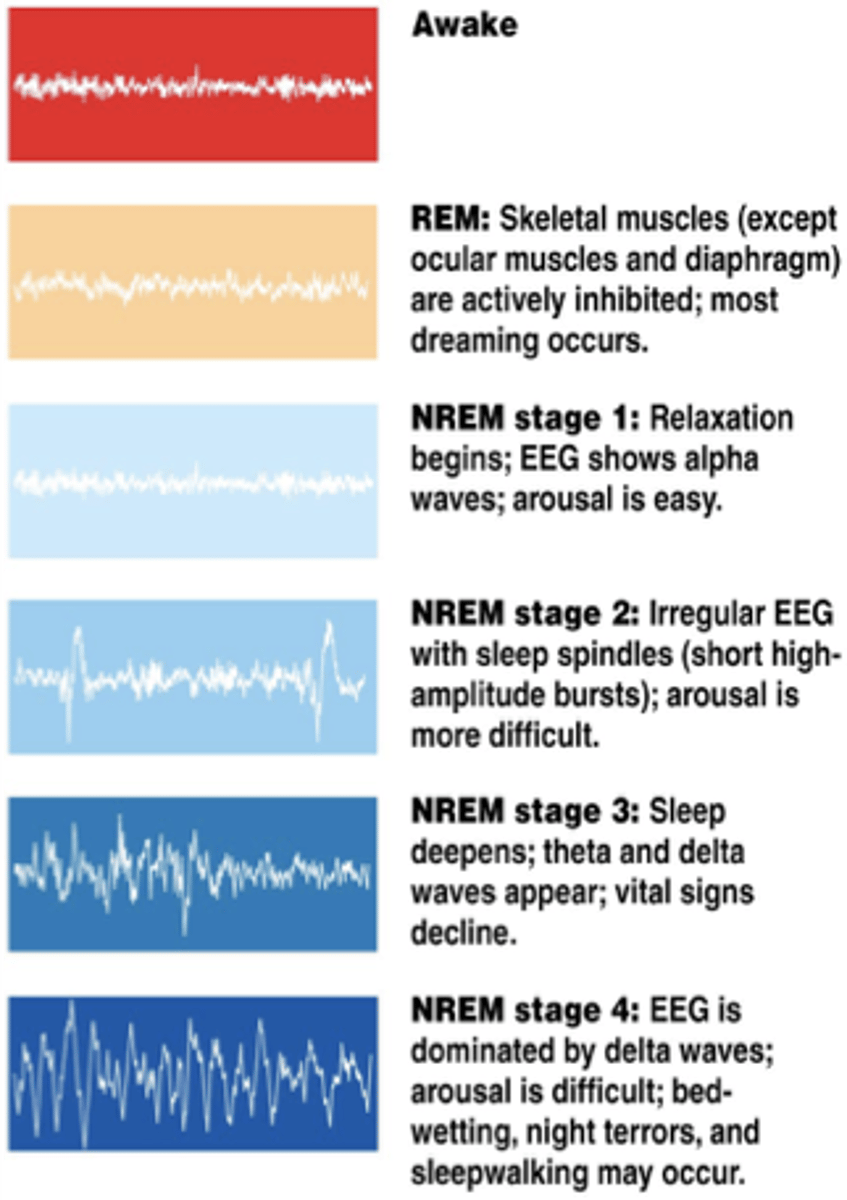
How long does NREM Stage 2 last?
about 20 minutes
What are sleep spindles?
short bursts of brain activity
What are K-complexes?
sudden, sharp waveforms in brain voltage
NREM Stage 3
a). what kind of waves are predominant?
the deepest stage of non-rapid eye movement; predominantly delta waves

Restoration of Resources:
a). when does it occur?
b). what happens?
- the process during sleep where the body and brain replenish energy
- the body and brain together repair tissues, remove waste products, promoting physical + mental well-being.
What is REM sleep?
a). what are the characteristics?
A stage of sleep characterized by rapid eye movements, vivid dreams, and muscle paralysis
- active brainwaves, increased heart rate and blood pressure, limp muscle state
- 80% of REM is dream sleep
- Alternates on 90 minute cycles
REM sleep is associated with what in the brain?
- increased brain activity
- dreaming
- a role in memory consolidation
- emotional processing
REM Rebound:
a). why does this occur?
1). what kind of sleep does this rebound result in?
the phenomenon where the body increases the time spent in REM sleep after a period of REM deprivation
- occurs as a response to the lack of REM sleep
- often results in more intense + frequent REM sleep episodes

What are the two primary theories involving the role/reason for dreams?
1). Activation Synthesis
2). Consolidation Theory
1
2

2
1

Insomnia:
a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restorative sleep

Narcolepsy:
a sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplexy, and hallucinations during sleep onset or awakening.
What is cataplexy?
sudden episodes of muscle weakness

Sleep Apnea:
a sleep disorder characterized by temporary cessations of breathing / shallow breathing during sleep and repeated momentary awakenings
- leads to disrupted sleep patterns, daytime fatigue, and other health problems

REM Sleep Behavior Disorder:
A sleep disorder where individuals physically act out their dreams during REM sleep, potentially causing injury to themselves or others due to loss of muscle paralysis