Water Cycle Study Quizlet
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Label the water cycle
Evaporation, Transpiration, Condensation, Precipitation, Runoff, Infiltration
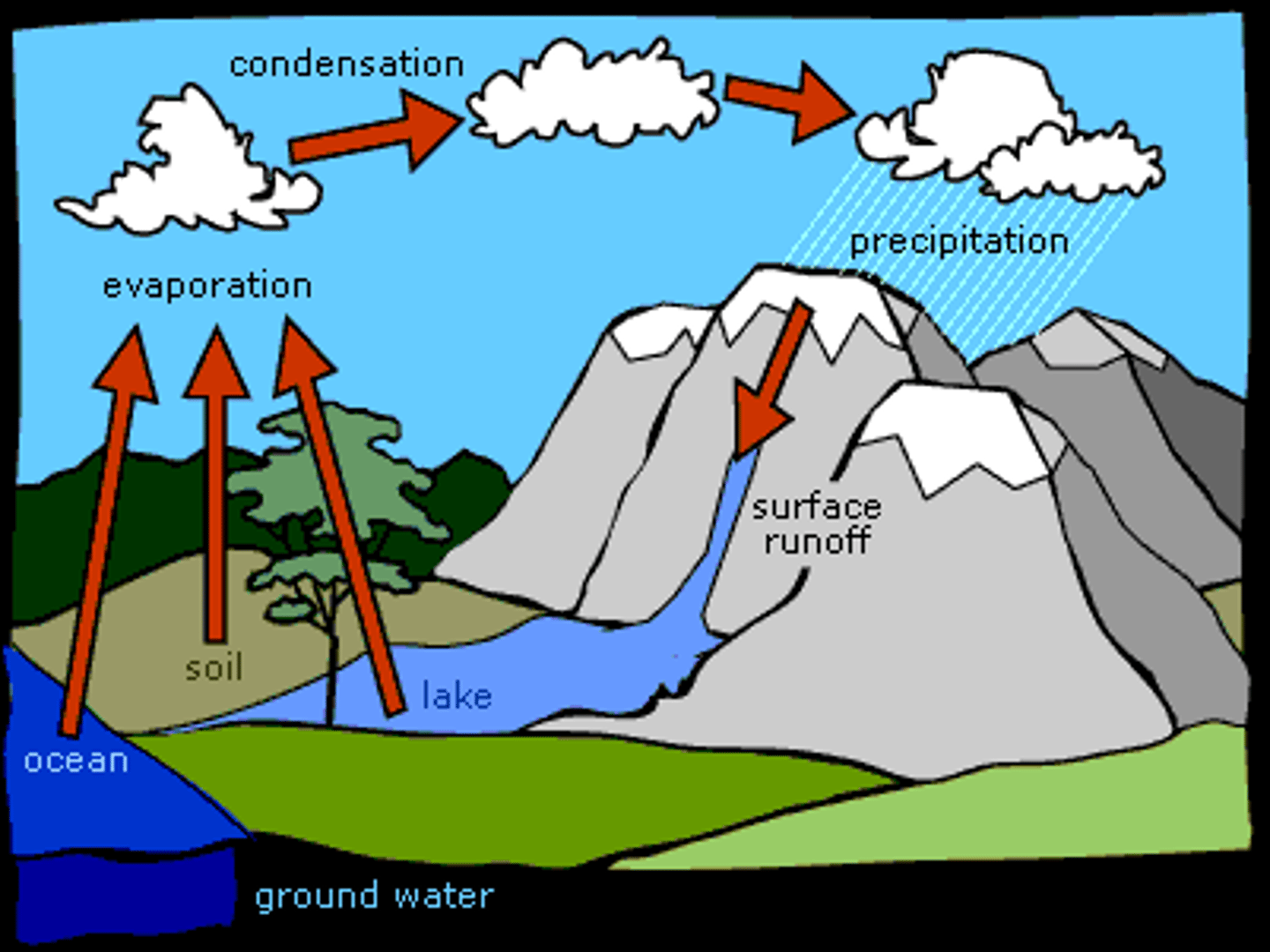
Water Cycle
The continuous process of water moving through Earth's atmosphere, land, and bodies of water, changing from liquid, solid, or gas states powered by the sun's heat energy.
Key stages: evaporation (water turning into vapor)
transpiration (water release from plants)
condensation (vapor forming clouds)
precipitation (water falling to Earth)
runoff (water moving across the ground)
infiltration (water moving into the ground)
infiltration
the process where water soaks into the ground and becomes groundwater
transpiration
the process in which plants give off water vapor through their leaves
evaporation
the process where water transforms into water vapor by absorbing heat energy from the sun
condensation
the process where water vapor in the atmosphere cools down and changes back into a liquid state
precipitation
freshwater returns to the Earth's surface in the form of rain, sleet, snow, or hail
runoff
the flow of water that does not soak into the ground but runs across the land to larger bodies of water such as rivers and lakes.
groundwater
water that is naturally stored underground
aquifer
a rock unit that can transfer water through its pore space
porosity
is the measure of empty spaces, or pores, within a material
permeability
the quality of a material to allow liquids to pass through it
How does sunlight drive the water cycle?
Energy from the Sun causes water in the oceans and other parts of Earth's surface to enter the atmosphere through evaporation.
What role does water vapor play in the water cycle?
Water vapor is created by evaporation and transpiration. As it rises and cools, it changes into a liquid again through condensation and forms clouds. The condensation in clouds can release precipitation returning to the Earth's surface.
What is the difference between runoff and infiltration?
Runoff does not soak into the ground but runs into rivers and lakes. Infiltration soaks into the ground and creates groundwater.