Pulmonary Exam 2: Pathology II (Dr. Menon)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Which respiratory tract infections are more minor and transient: Upper or Lower?
Upper respiratory tract infections

Which respiratory tract infections are a significant cause of morbidity and mortality: Upper or Lower?
Lower respiratory tract infections

What has the following characteristics?
- Any infection of lung
- Viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites
pneumonia

list 4 different causes of pneumonia:
- Viruses
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Parasites

If a pathogen cannot be identified, how can you classify it?
By clinical setting

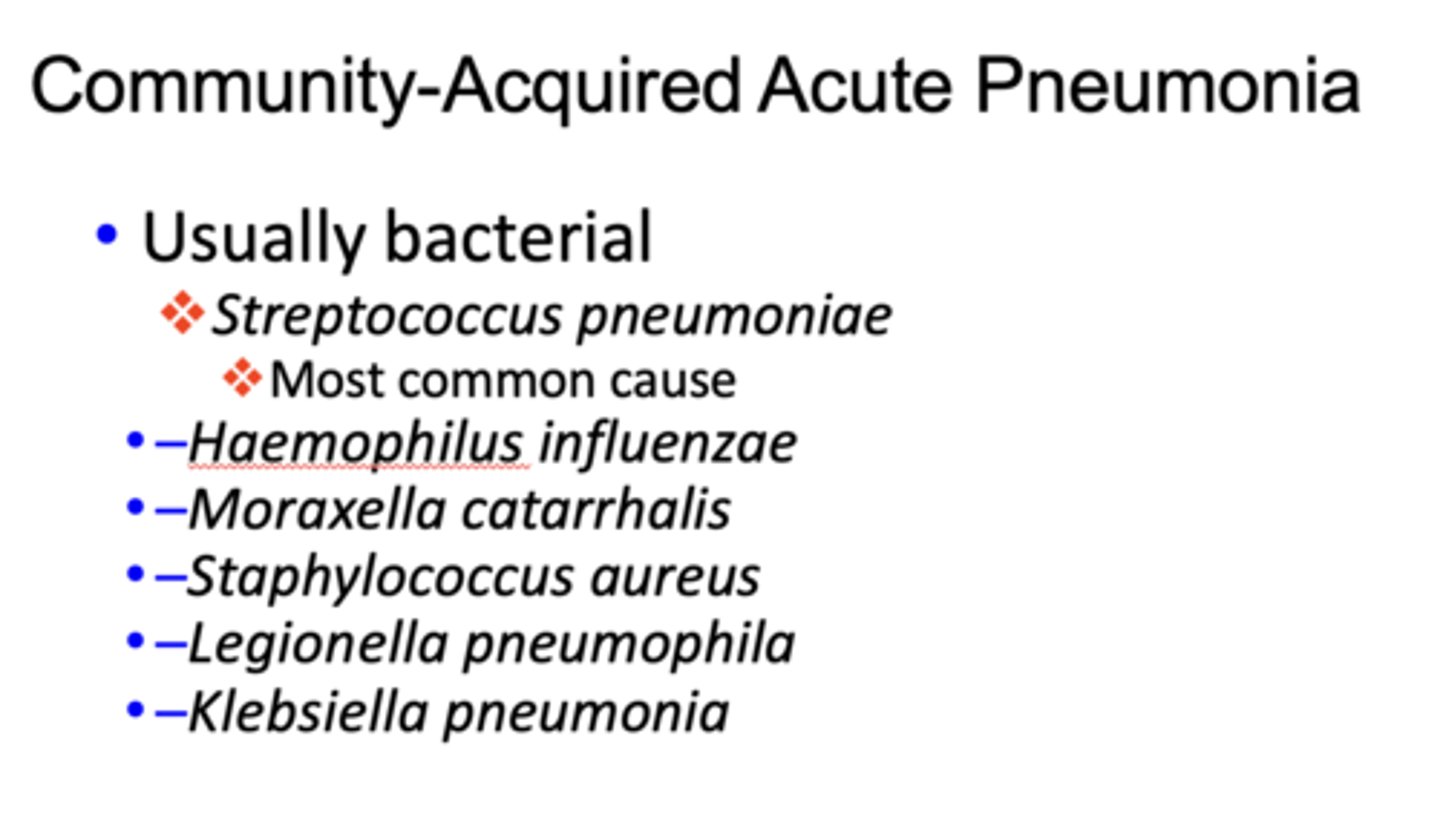
Most common cause of pneumonia:
Streptococcus pneumoniae

All of the following are usually bacterial causes of ___________:
– Haemophilus influenzae
– Moraxella catarrhalis
– Staphylococcus aureus
– Legionella pneumophila
- Klebsiella pneumonia
Community-Acquired Acute Pneumonia
What is a common cause of community-acquired atypical pneumonia?
mycoplasma

All of the following are causes of ___________:
- Mycoplasma
- Rhinovirus
- Influenza types A and B
- Parainfluenza
- Respiratory syncytial virus
- Human metapneumovirus
- Adenovirus
Community-Acquired Atypical Pneumonia

What has the following characteristics?
- Pulmonary infections acquired during hospital stay
- Common in patients with severe underlying disease, immunosuppression, H/O prolonged antibiotic regimens
- Usually gram-negative rods (S. pneumoniae is not a common pathogen)
nosocomial pneumonia

What has the following characteristics?
- Abnormal gag and swallowing reflexes facilitate aspiration
- Infection partly chemical and partly bacterial
- Abscess formation common in survivors
Aspiration pneumonia

What has the following characteristics?
- Most often localized when in otherwise healthy patients, disseminated when in immunocompromised
- Granulomatous inflammation due to bacteria or fungi
- Tuberculosis causes 6% of all deaths worldwide
Chronic pneumonia

What has the following clinical features?
– Rare oral lesions typically present as painless ulcers
- 0.5-5.0% of infected patients have clinically evident lesions
- Most cases represent secondary infection
- Rare primary cases
- Bone involvement may be seen
Tuberculosis

What type of pneumonia has organisms that often have typical geographic distribution?
fungal pneumonia

what is the typical geographic distribution of Histoplasma capsulatum (fungal pneumonia)?
Ohio and Mississippi river valley

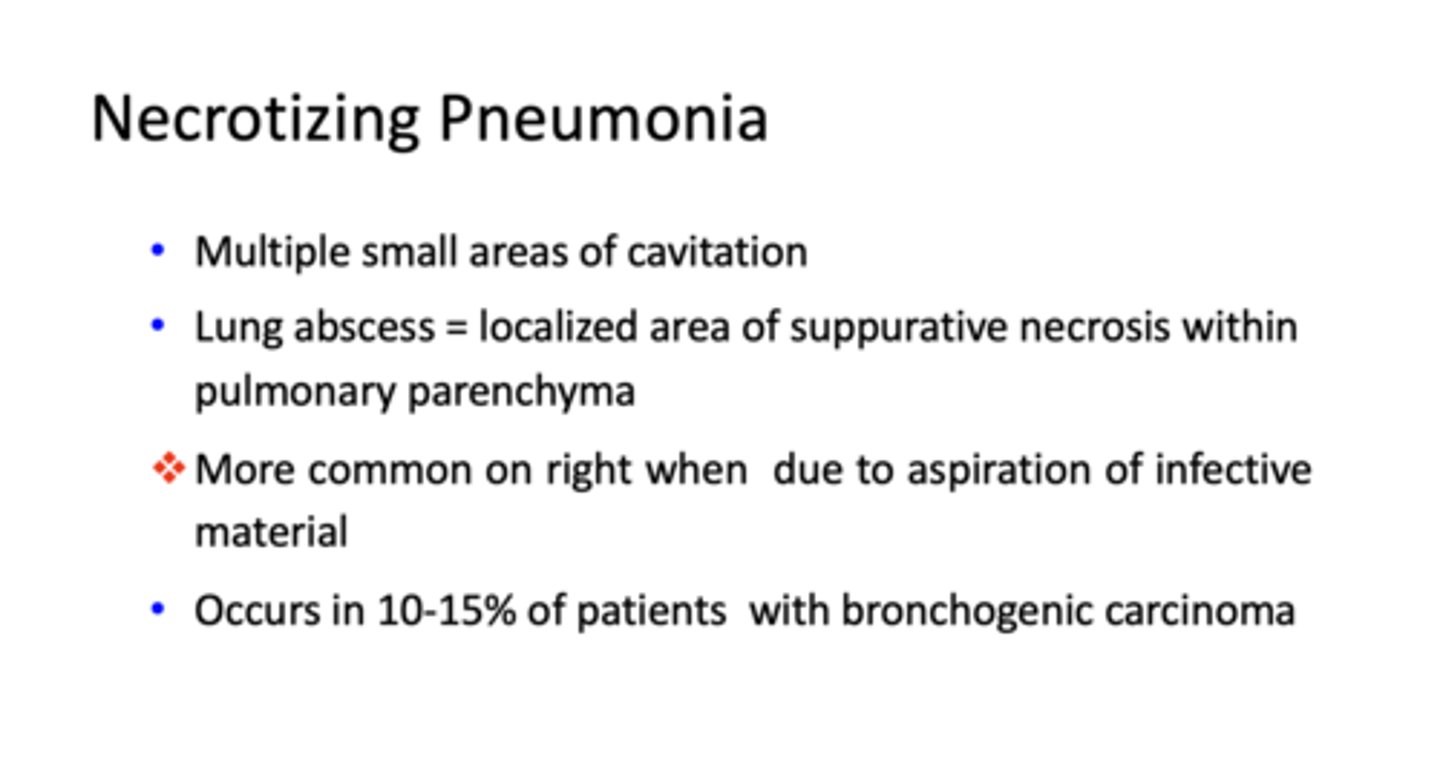
Type of pneumonia
- More common on right lung when due to aspiration of infective material
- Multiple small areas of cavitation
- Lung abscess = localized area of suppurative necrosis within pulmonary parenchyma
- Occurs in 10-15% of patients with bronchogenic carcinoma
necrotizing pneumonia
This fungi is associated with: opportunistic infections, often seen with hematologic malignancy or diabetes:
Mucormycosis

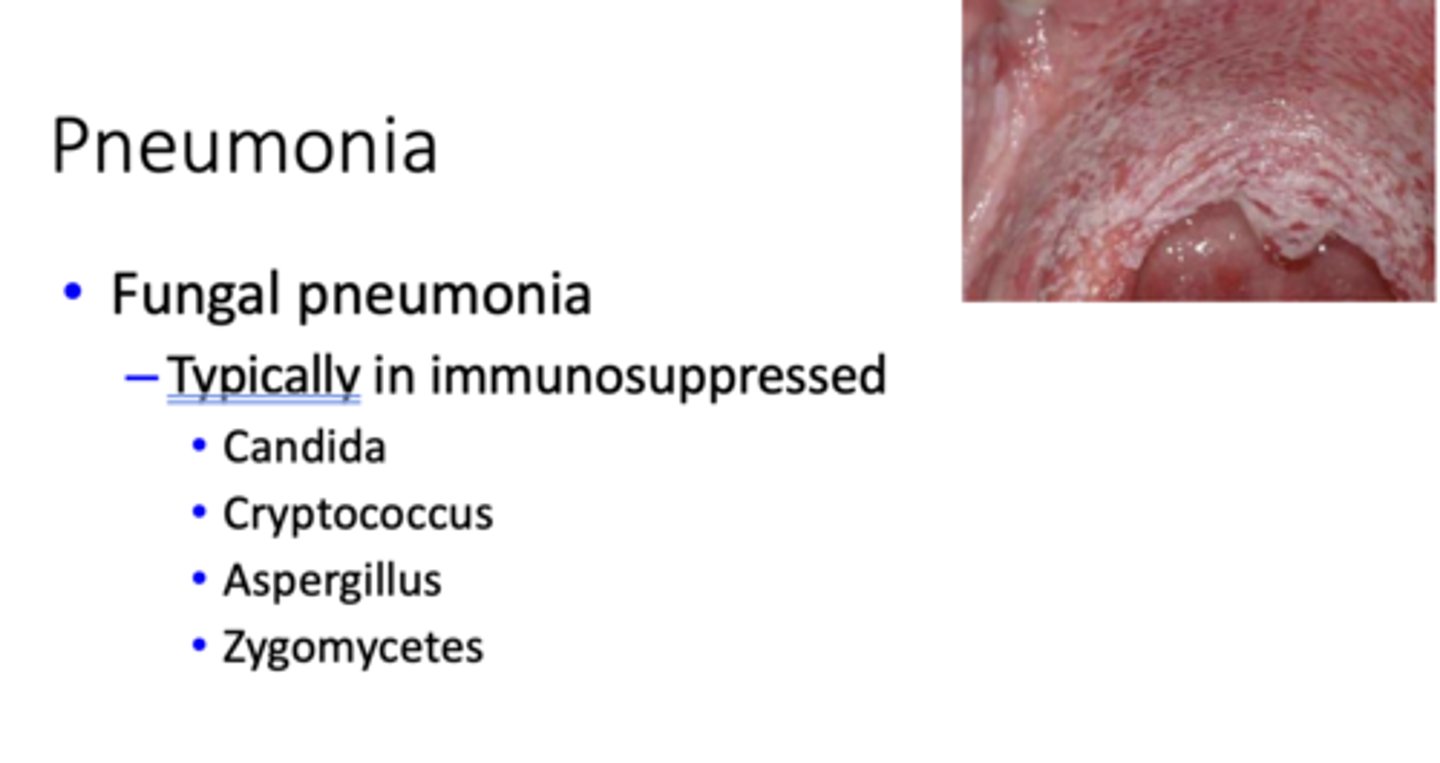
The following are fungal pneumonia typically found in ___________:
- Candida
- Cryptococcus
- Aspergillus
- Zygomycetes
immunosuppressed
the most common form of lung cancer (95%) is _______
bronchogenic carcinomas

Which of the following statements is false?
A. Increased smoking in developing countries associated with decreased lung cancer incidence
B. Cessation for 10 years reduces risk but never to control levels
C. Passive smokers have 2x risk of developing lung cancer
D. Also associated with carcinoma of oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, pancreas, uterine cervix, kidney and urinary bladder
A. Increased smoking in developing countries associated with decreased lung cancer incidence (should be INCREASED lung cancer incidence)

The incidence of ____________ has been declining since 1980s for men, since mid 2000s for women
Bronchogenic carcinoma

___________ incidence directly related to cigarette smoking and environmental factors (Radioactive material, asbestos, nickel, chromium, iron oxides, coal gas plants, and natural radioactive gas)
Bronchogenic carcinoma

Which histopathologic type of bronchogenic carcinoma occurs 38% of the time?
adenocarcinoma
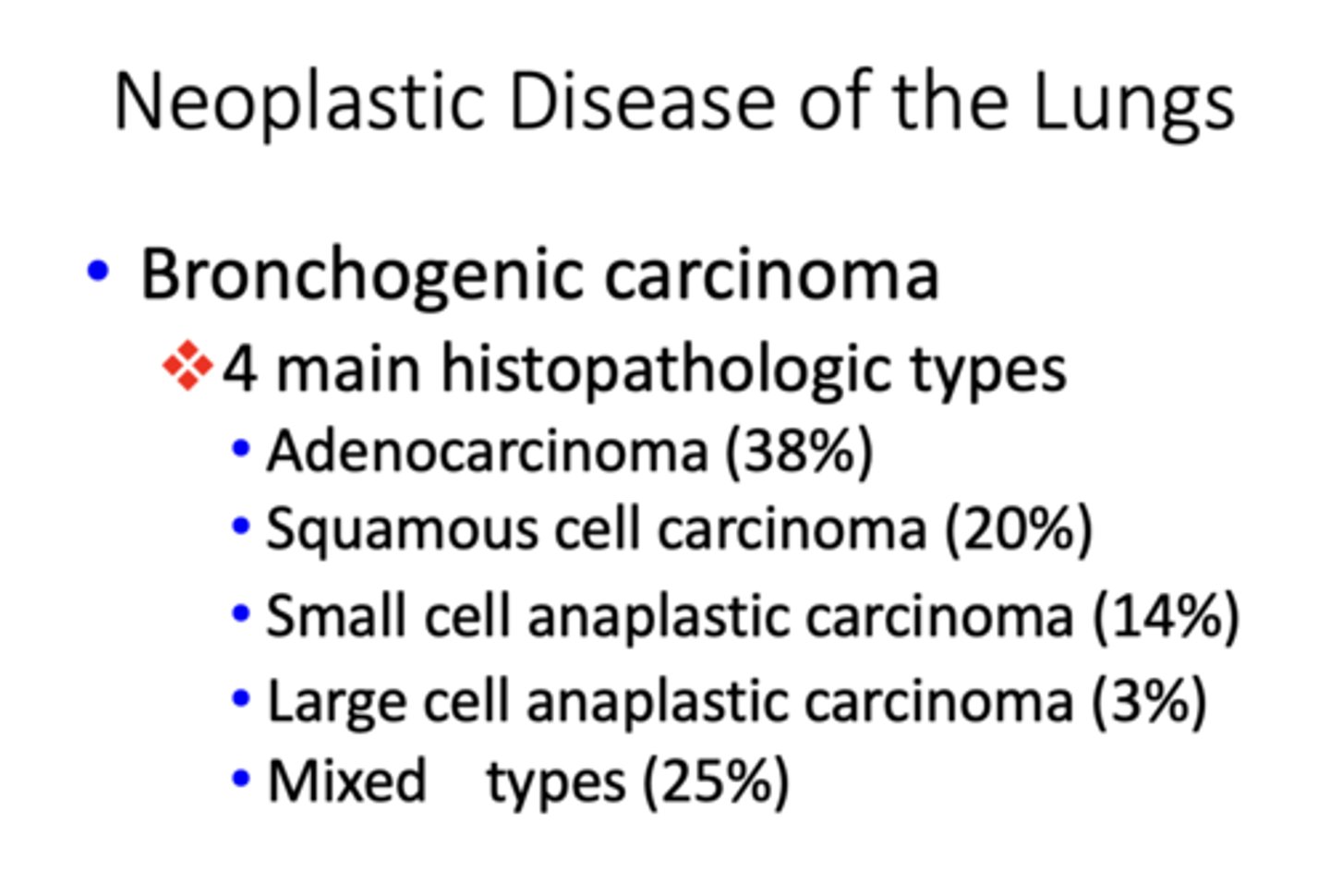
Which histopathologic type of bronchogenic carcinoma occurs 20% of the time?
squamos cell carcinoma
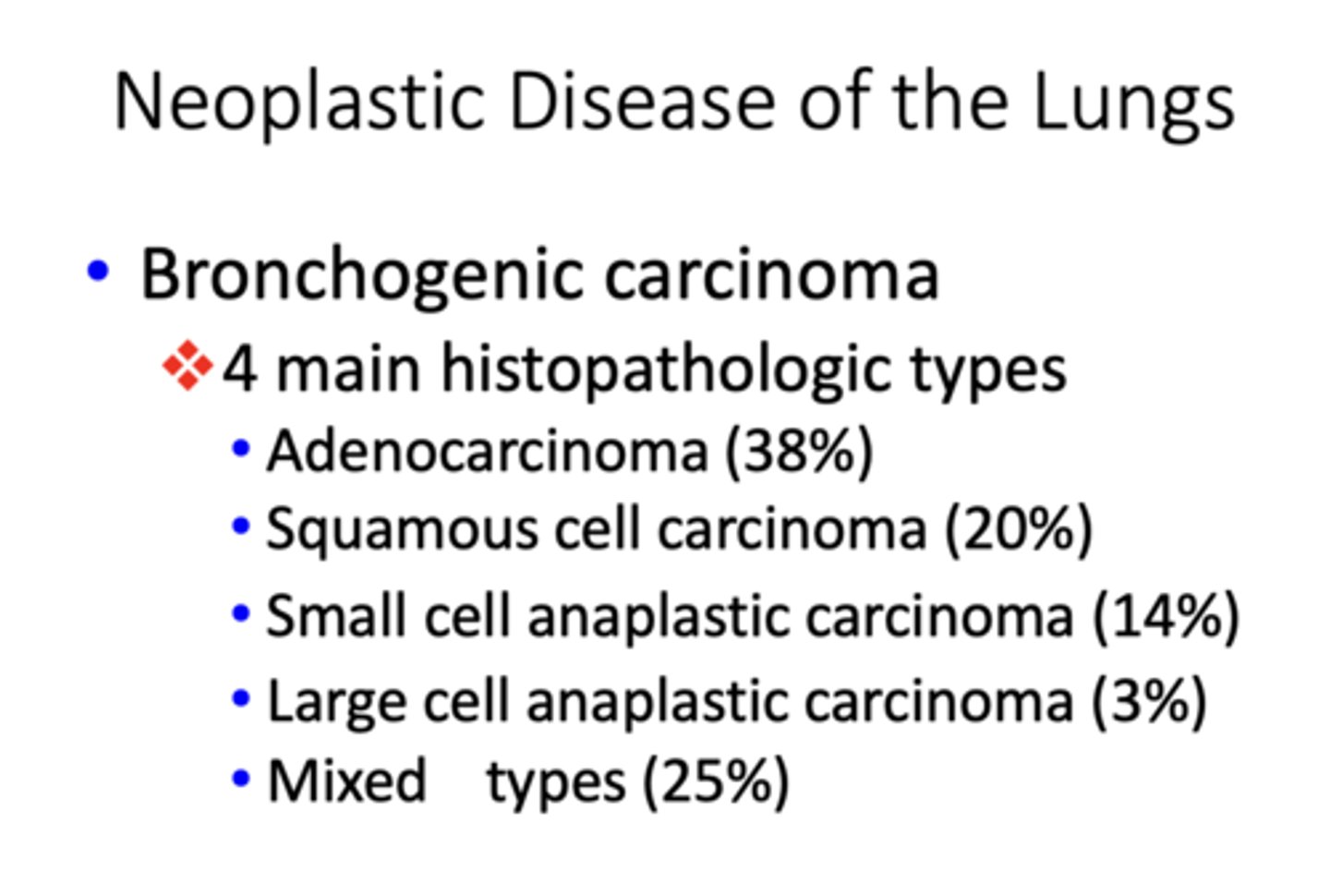
Which histopathologic type of bronchogenic carcinoma occurs 14% of the time?
small cell anaplastic carcinoma
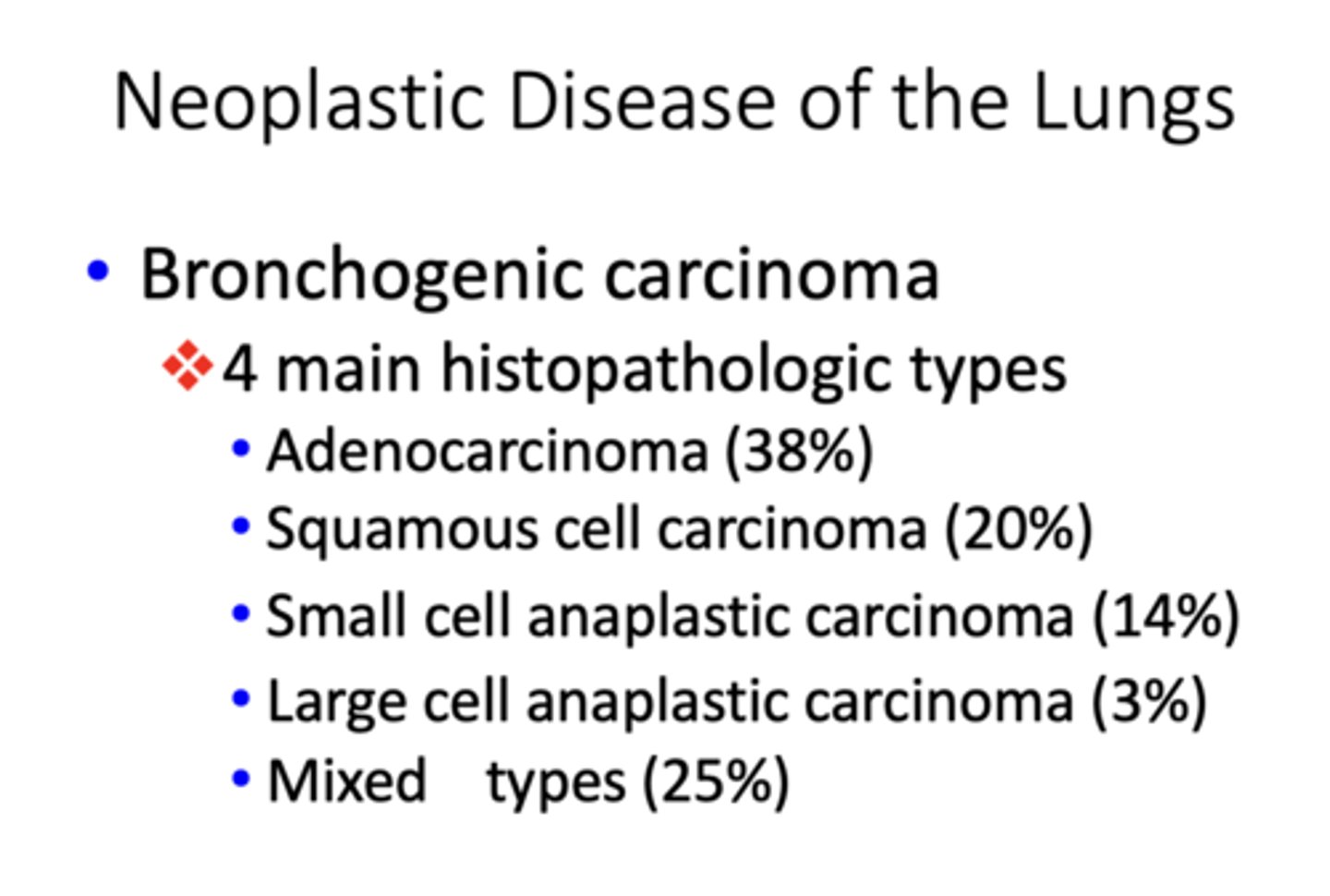
Which histopathologic type of bronchogenic carcinoma occurs 3% of the time?
Large cell anaplastic carcinoma
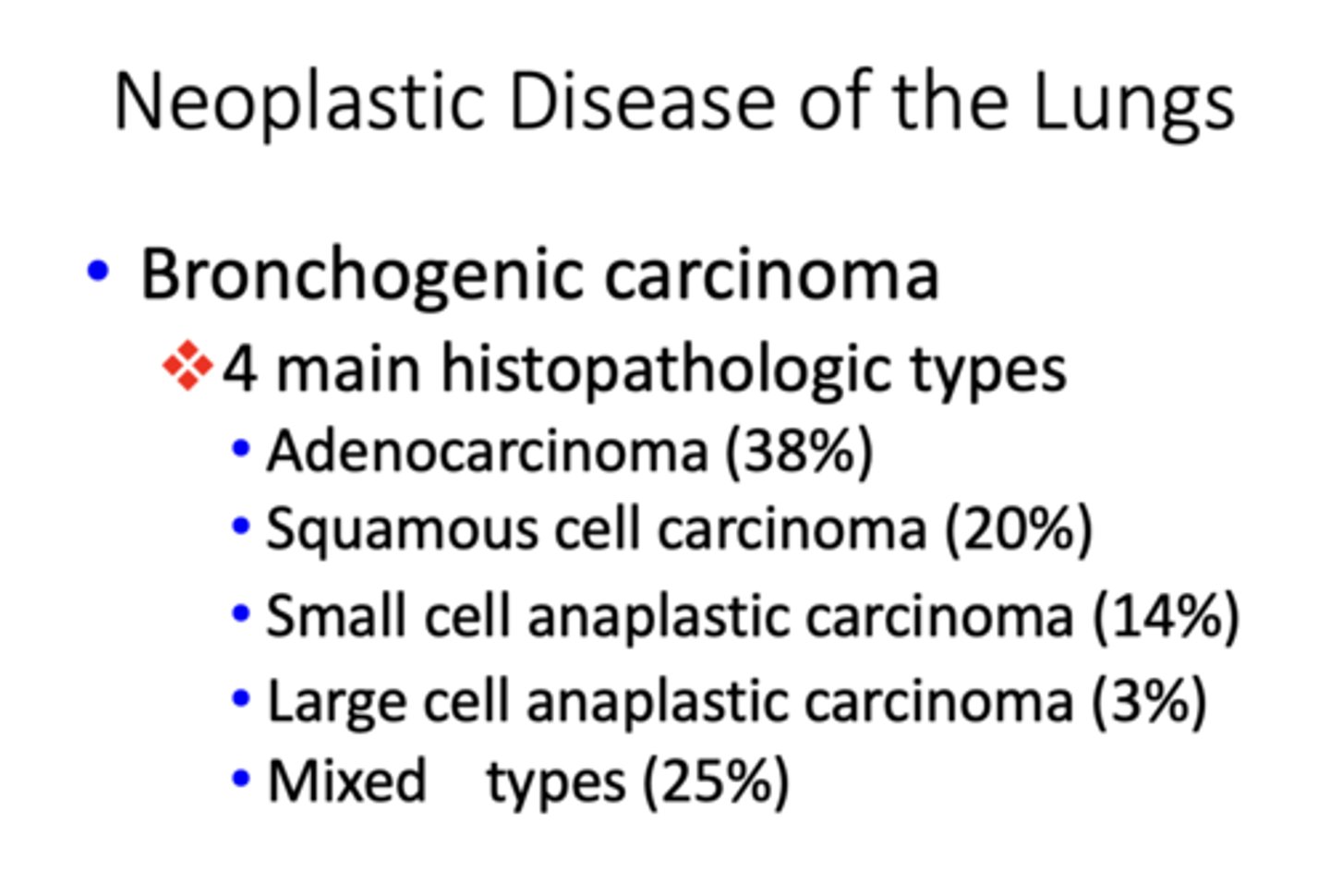
Which histopathologic type of bronchogenic carcinoma has the greatest incidence?
adenocarcinoma
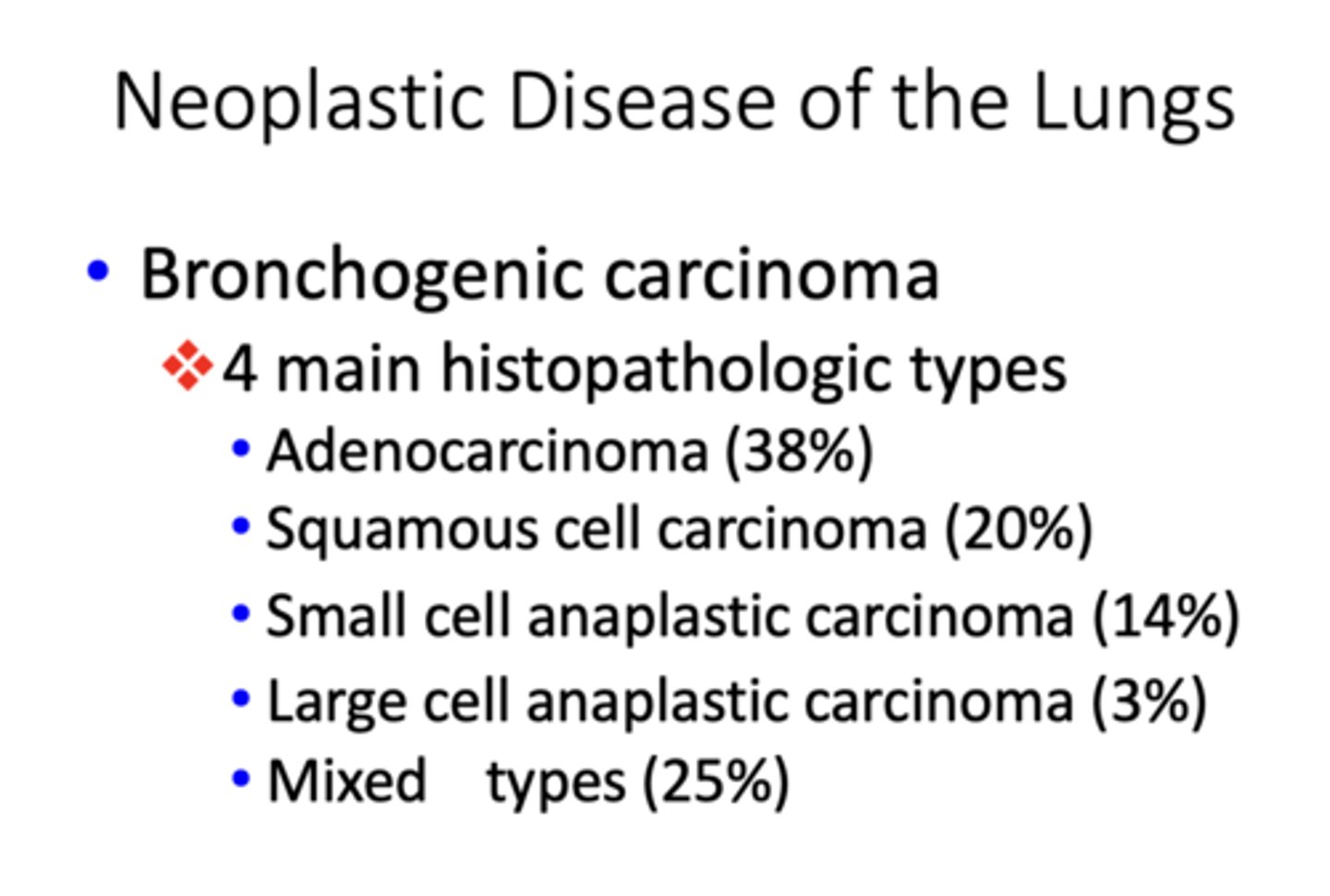
Which histopathologic type of bronchogenic carcinoma has the lowest incidence?
large cell anaplastic carcinoma
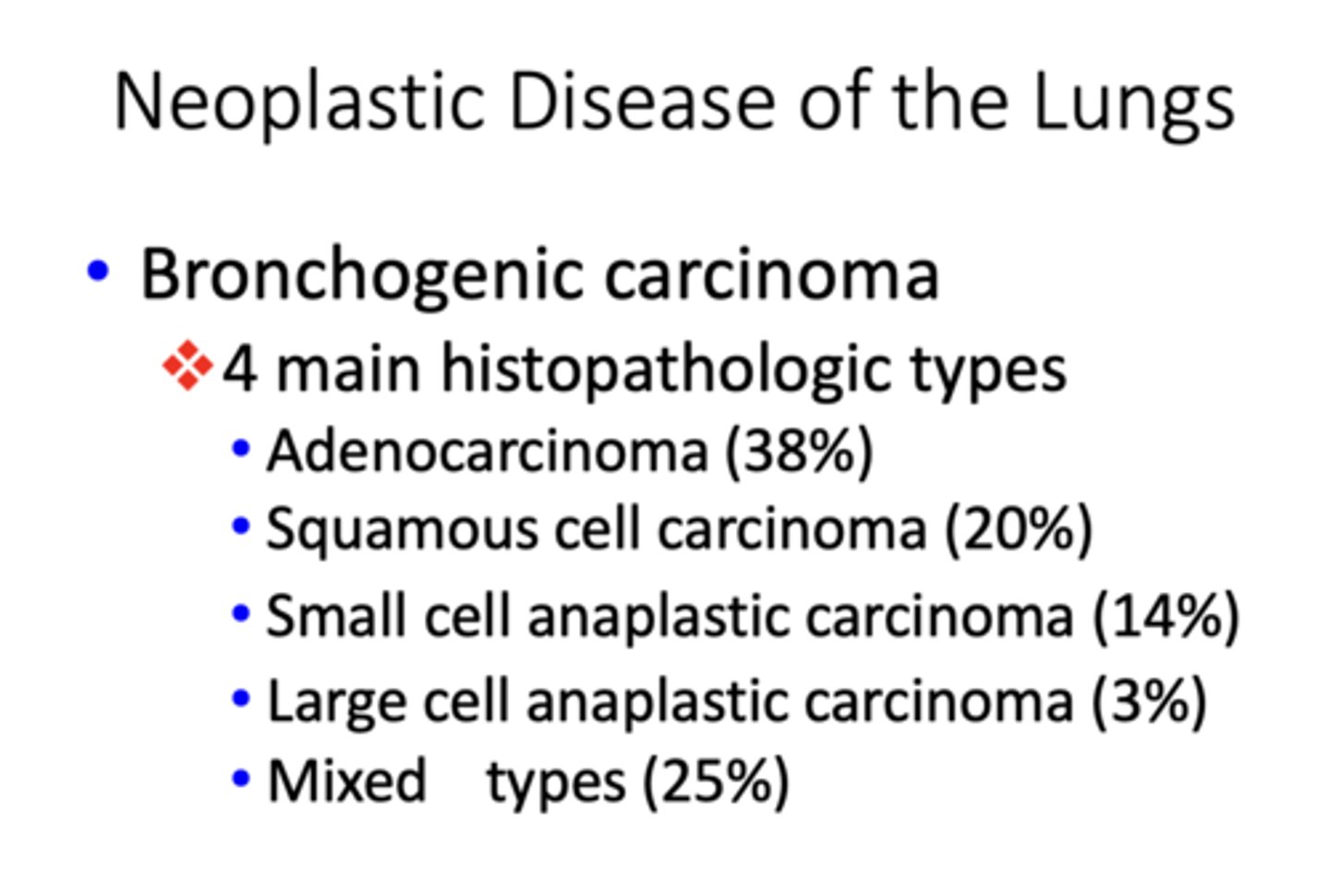
What type of bronchogenic carcinoma?
- Equal gender incidence, but most common type in women
- Not as closely linked to cigarette smoking as other types
- Usually develop peripherally
- Acinar, papillary, solid, and mucinous patterns
adenocarcinoma
What type of bronchogenic carcinoma?
- Male predilection
- Closely correlated with smoking history
- Arise centrally in major bronchi
squamous cell carcinoma

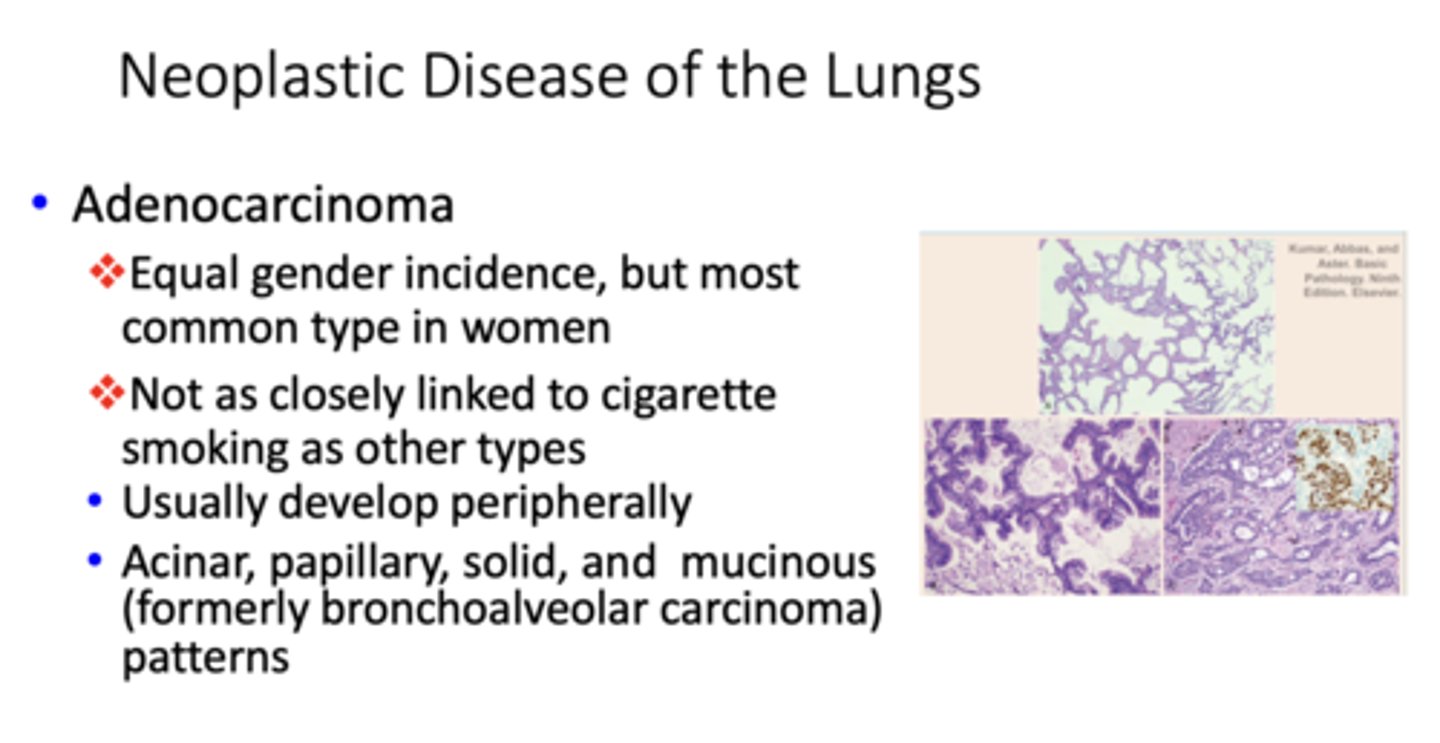
What type of bronchogenic carcinoma?
women non-smokers
adenocarcinoma

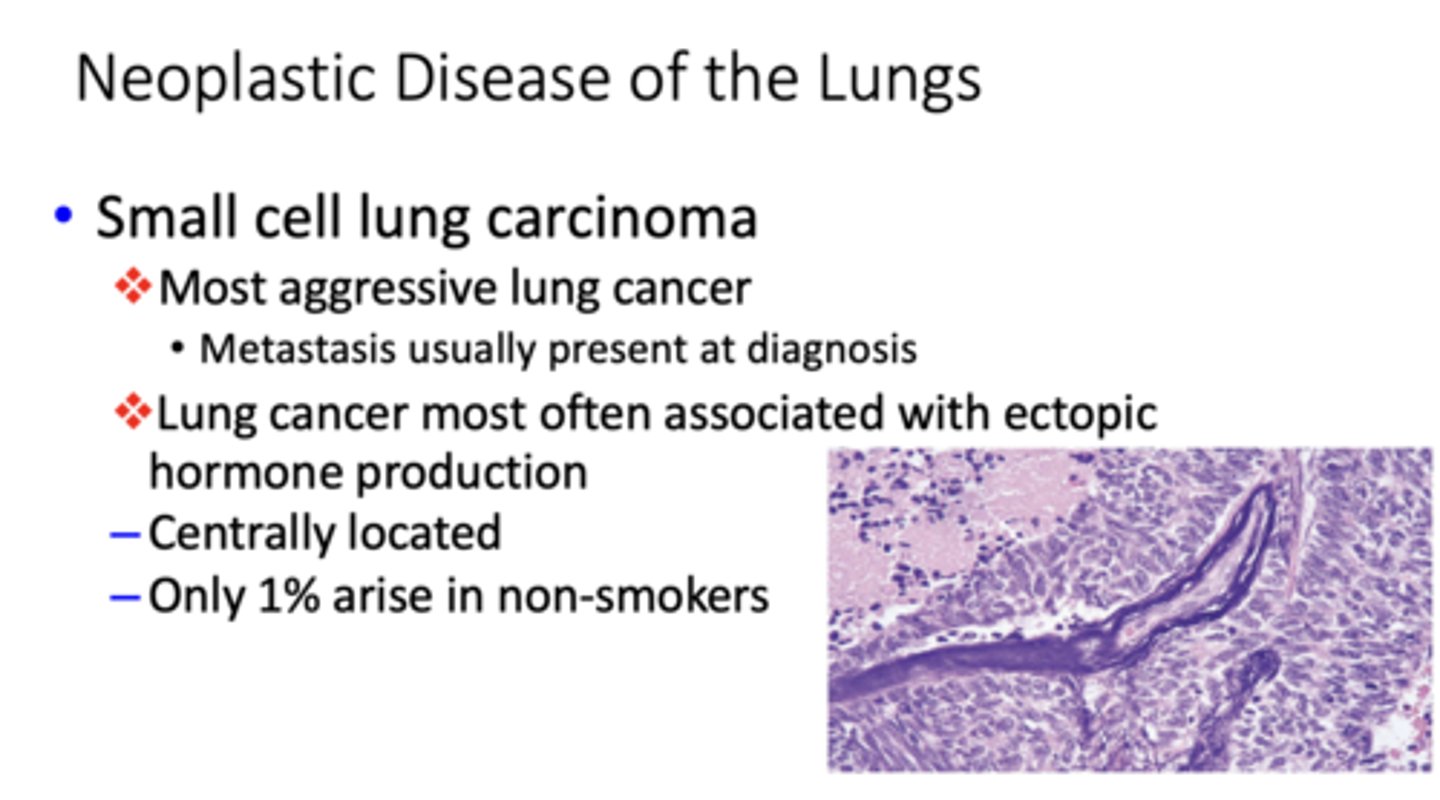
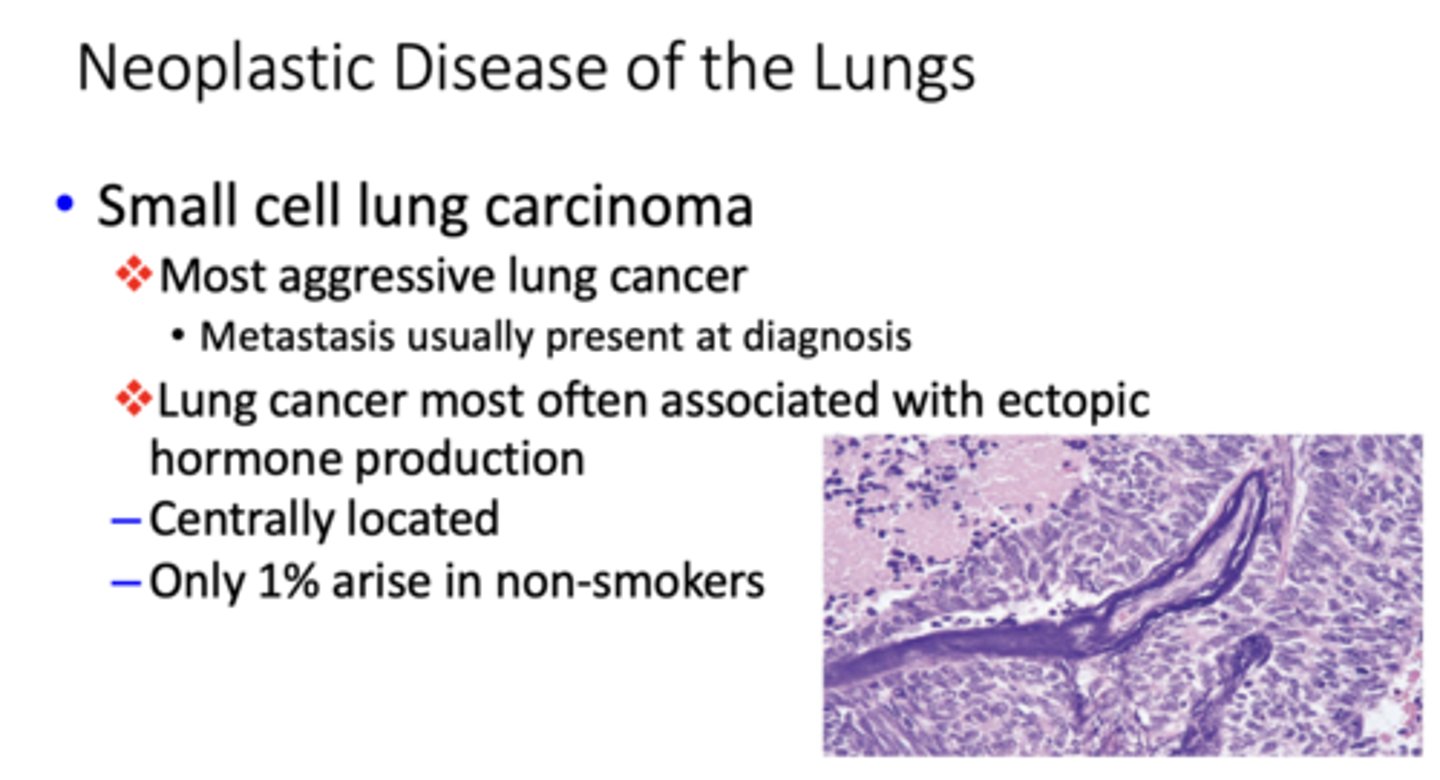
What type of bronchogenic carcinoma?
- Most aggressive lung cancer
- Metastasis usually present at diagnosis
- Arise centrally in major bronchi
small cell lung carcinoma
What type of bronchogenic carcinoma?
– Undifferentiated tumors that lack glandular, squamous, or endocrine features
– Central or peripheral location
– Poor prognosis
– Frequently widely disseminated at time of diagnosis
Large cell carcinoma

What type of bronchogenic carcinoma?
-Lung cancer most often associated with ectopic hormone production
small cell lung carcinoma
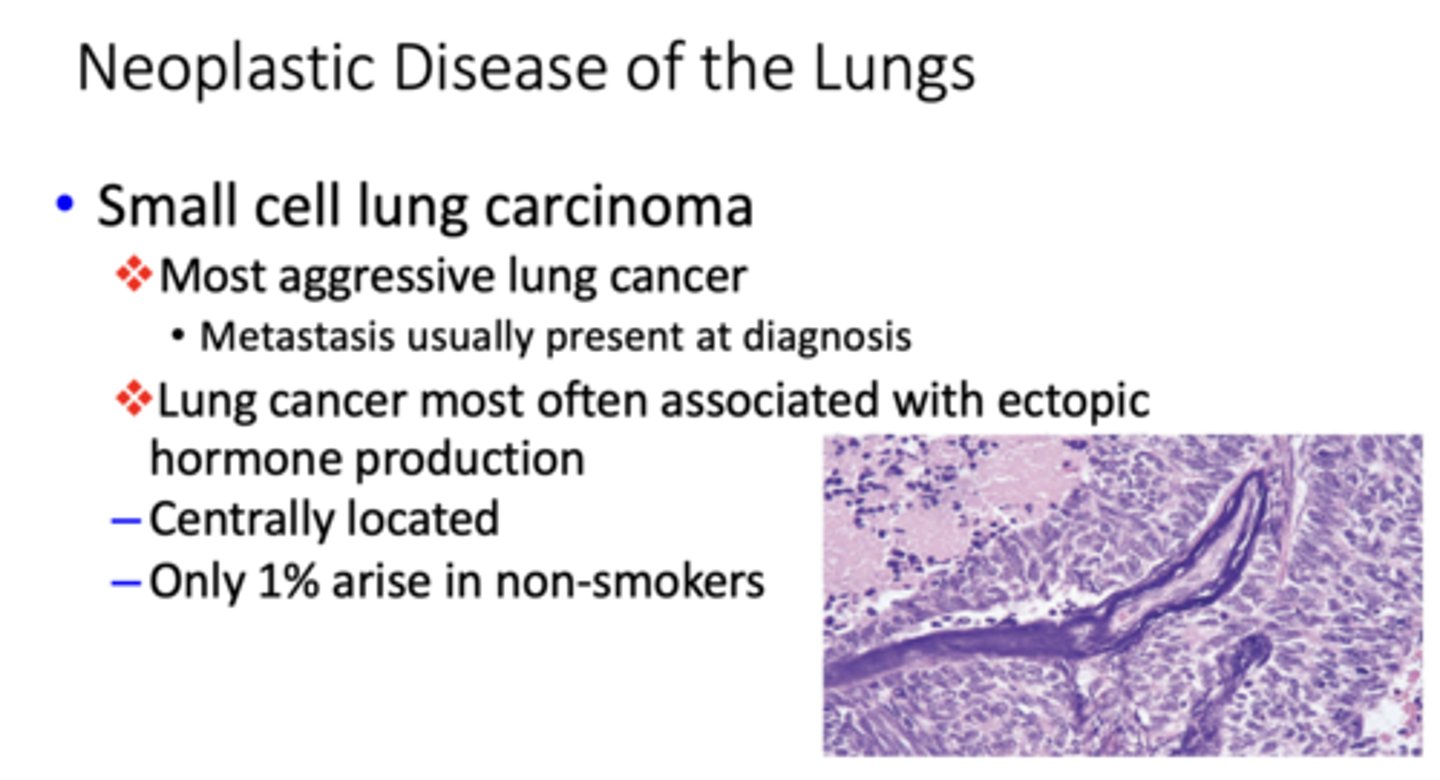
What is the most aggressive lung cancer (metastasis usually present at diagnosis)?
small cell lung carcinoma
________ is a presenting feature in 70% of cases of neoplastic diseases of the lungs
lung cancer metastasis

What are three things to use for diagnosis of neoplastic disease of the lungs?
- Clinical features
- Imaging
- Histopathology
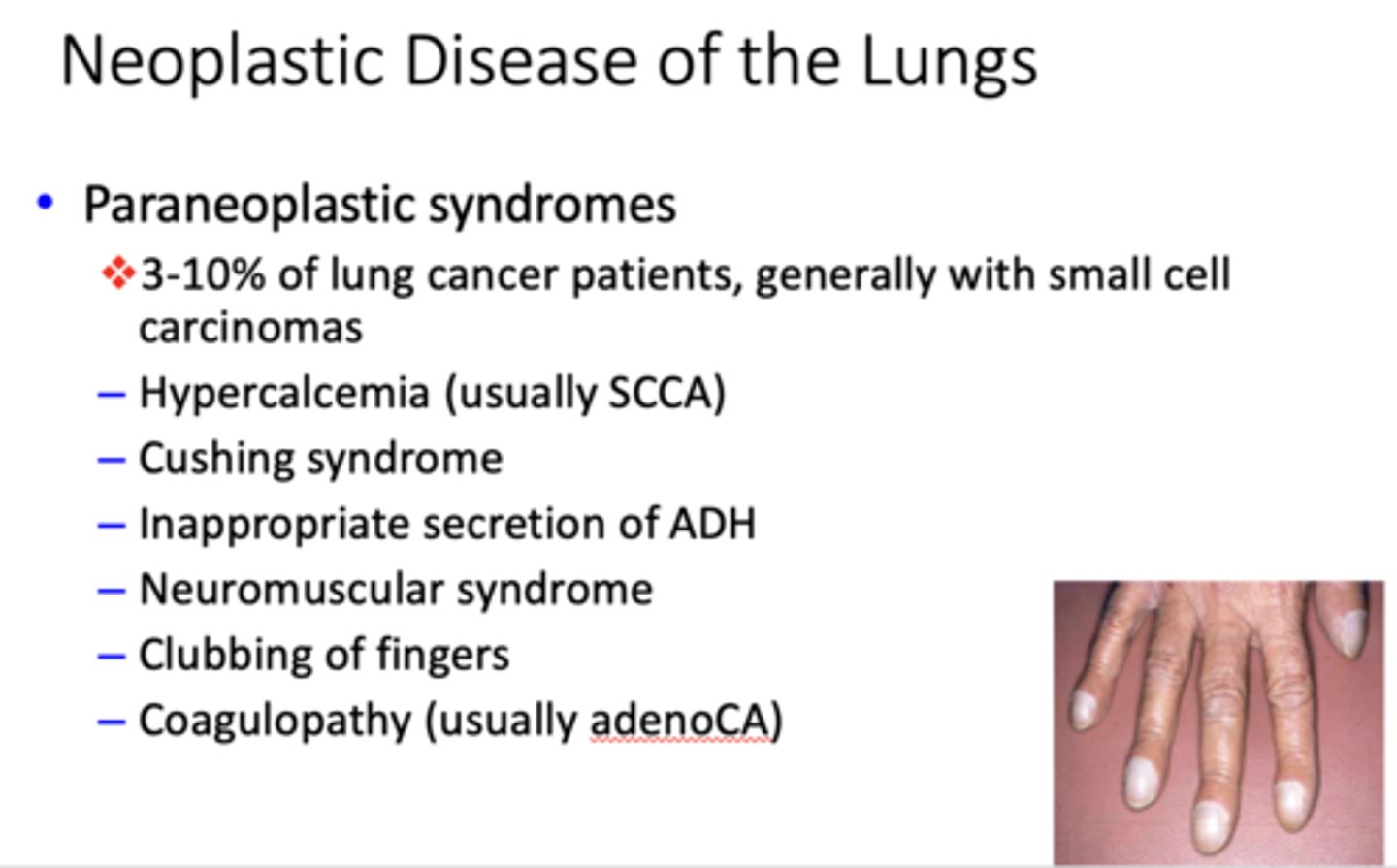
this presentation is common in 3-10% of lung cancer patients, generally with small cell carcinomas
paraneoplastic syndromes
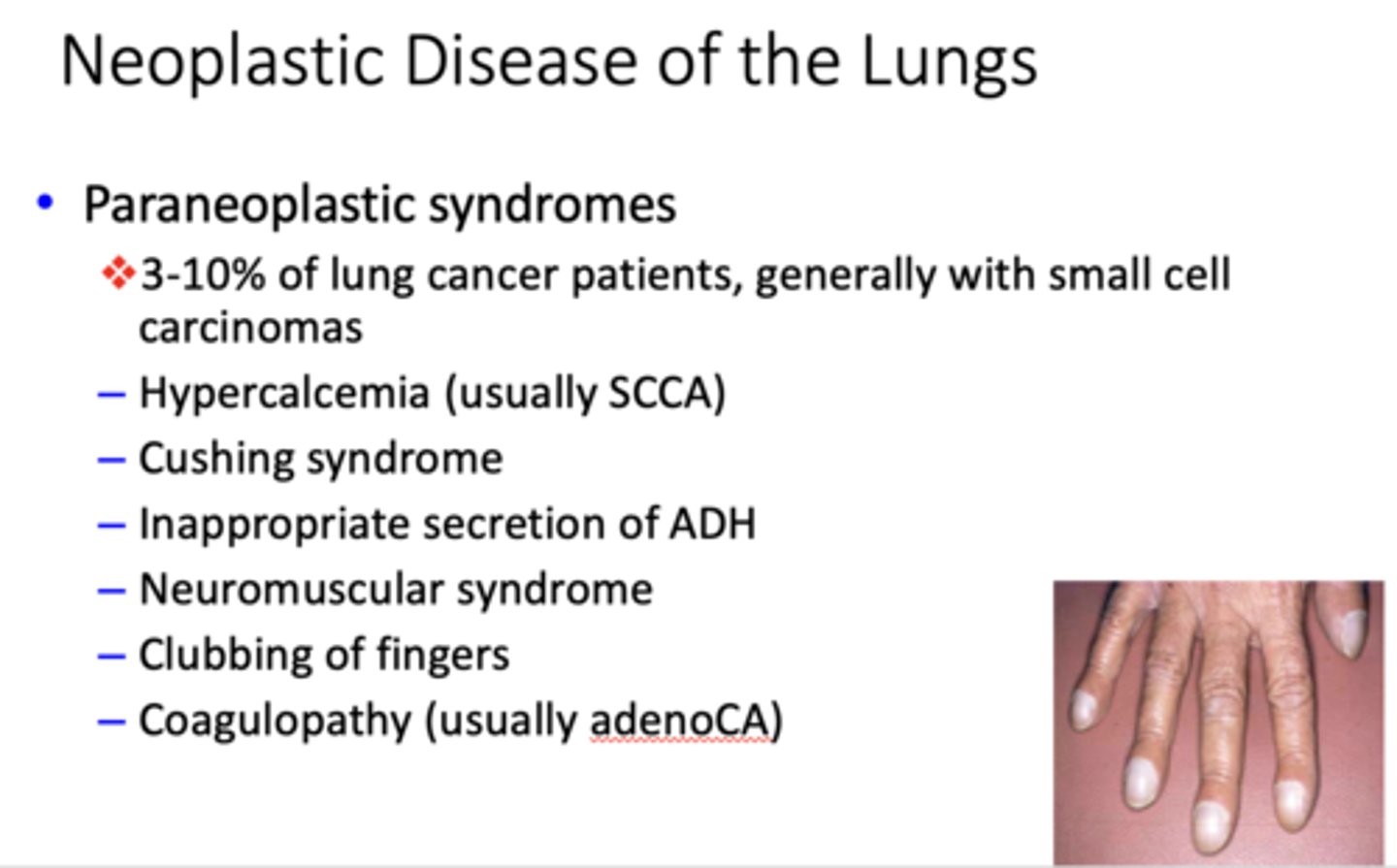
These are examples of what?
- Hypercalcemia (usually SCCA)
- Cushing syndrome
- Inappropriate secretion of ADH
- Neuromuscular syndrome
- Clubbing of fingers
- Coagulopathy (usually adenoCA)
paraneoplastic syndromes
What is the 5 year survival rate of bronchogenic carcinomas?
16%

Which bronchogenic carcinoma has the worst prognosis?
small cell lung carcinoma
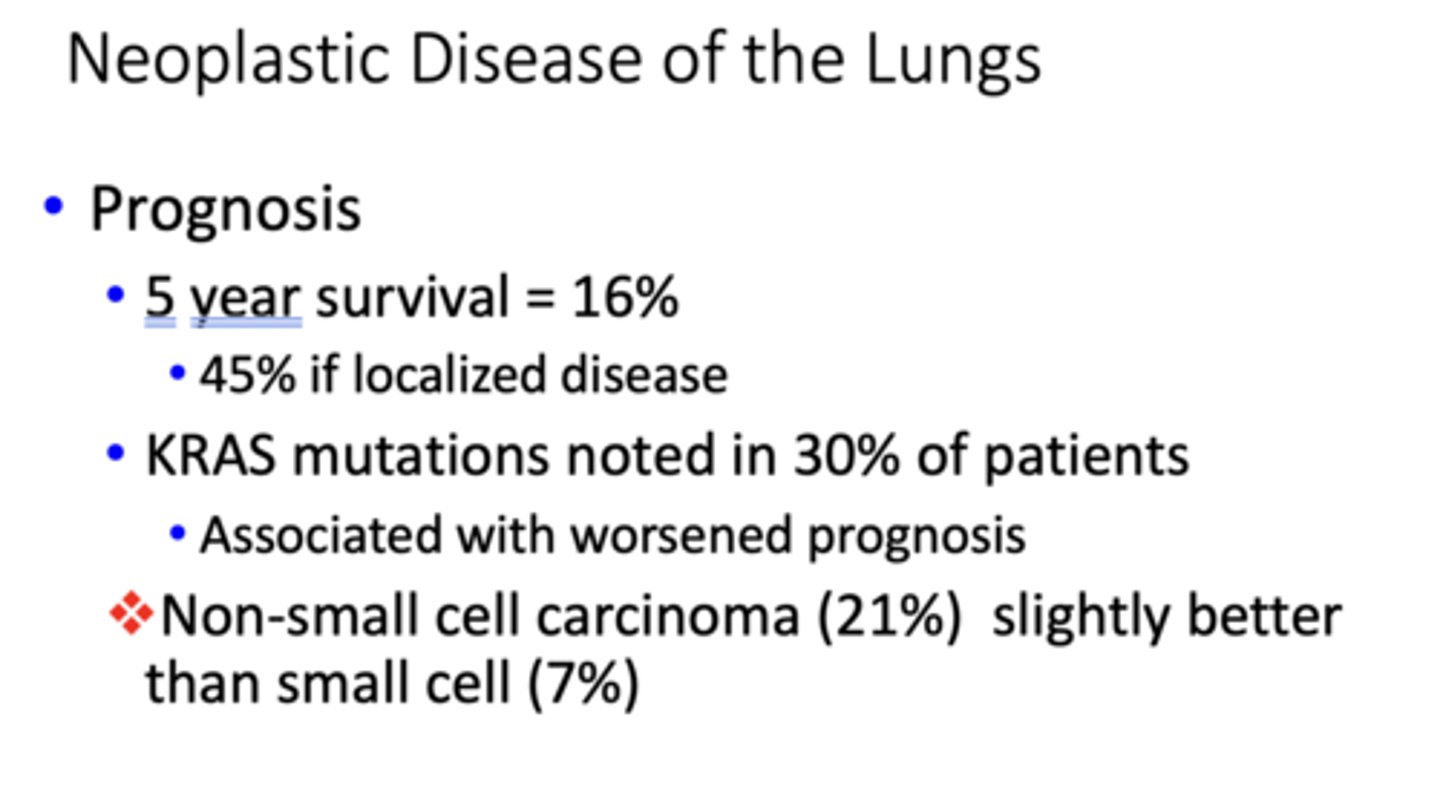
T/F: Non-small cell carcinomas have a slightly better prognosis than small cell
true
What has the following characteristics?
- Common benign neoplasm
- <3-4 cm in diameter
- Mostly cartilage with fat and muscle
- Discovered as incidental findings on chest radiograph as rounded radio- opacities ("coin lesions")
Lung hamartomas

What are the two types of pleural fluid types?
- Transudate
- Exudate

What CHF is the most common cause of pleural effusions?
Transudate

Congestive heart failure causing pleural effusion is an example of transudate or exudate?
transudate

What is the most common cause of pleural effusions?
congestive heart failure (CHF)

Most common neoplasms of pleura:
metastatic tumors (esp. lung/breast)

What has the following characteristics?
- Rare but strongly associated with asbestos exposure
up to 90% asbestos related
- Long latent period up to 40 years
- No increased risk among smokers
Mesothelioma

Most common primary neoplasm of the pleura with following symptoms:
- Pleural effusion
- Breathlessness
- Chest pain
Mesothelioma

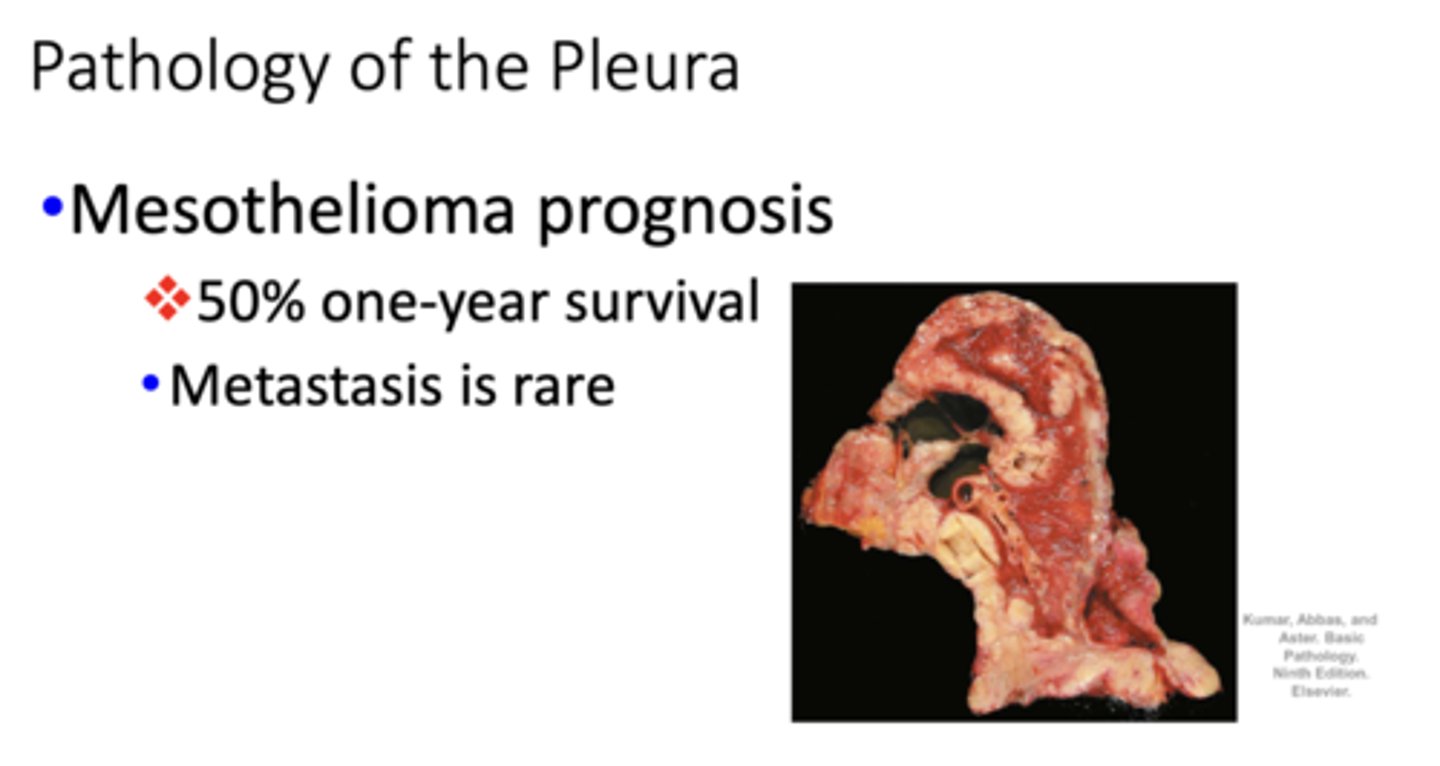
prognosis for Mesothelioma:
50% one-year survival
What has the following characteristics?
- Hyaline membrane disease
- Due to deficiency of surfactant in the lungs
– Primarily affects premature infants
Respiratory distress syndrome of the newborn (RDS)
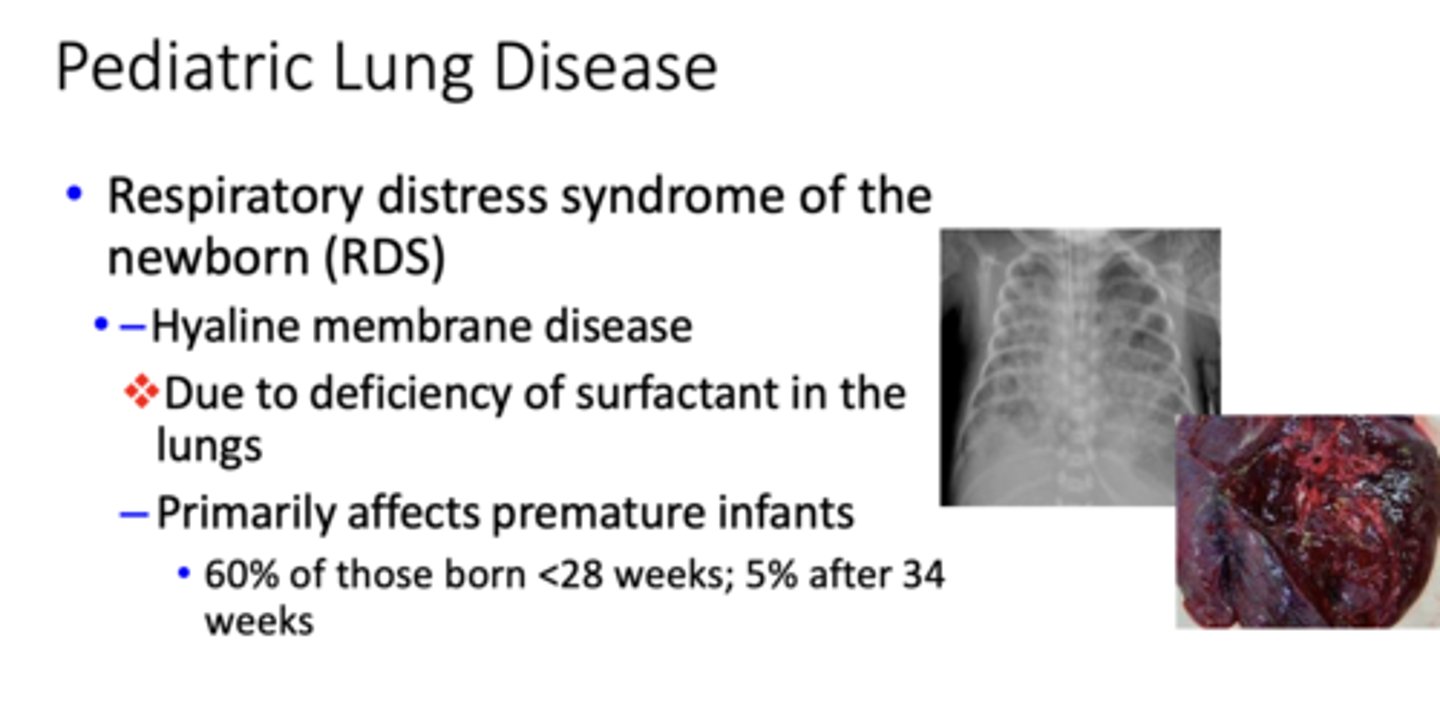
What is RDS caused by?
deficiency of surfactant
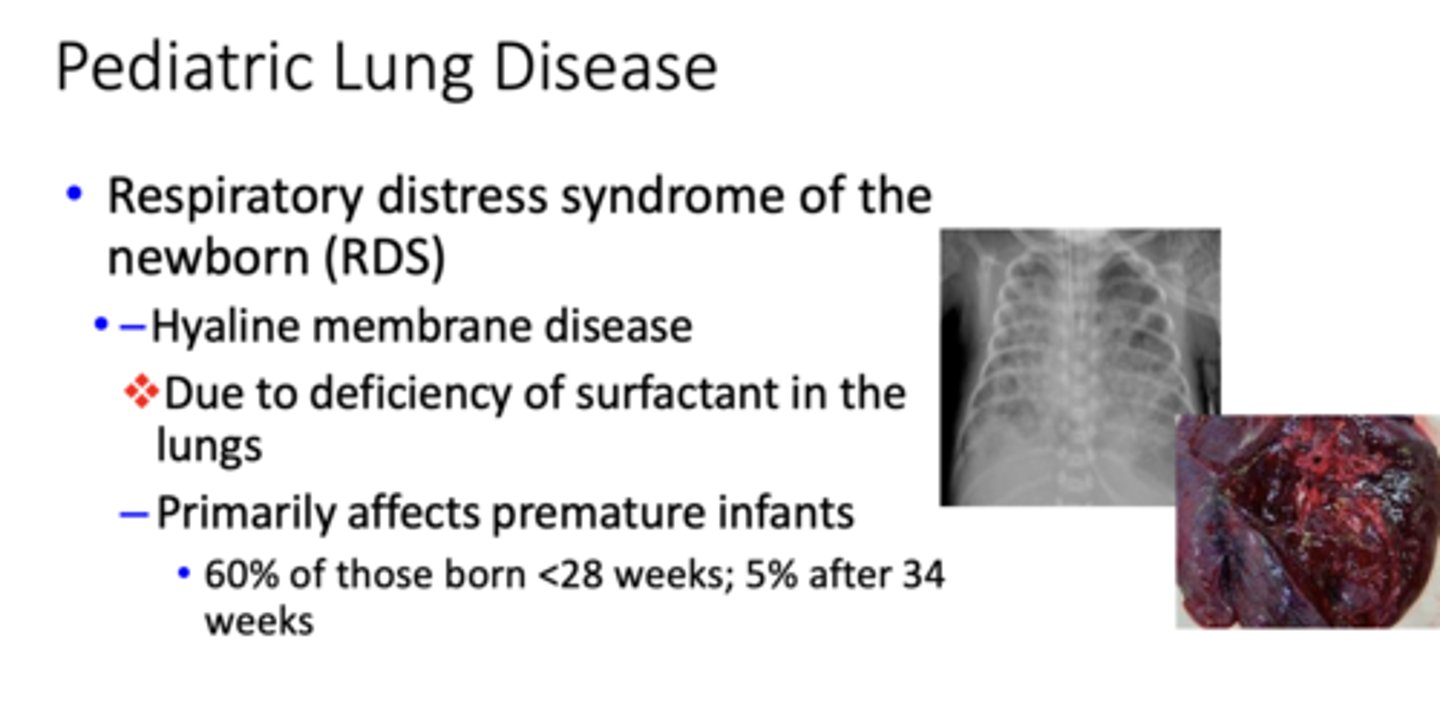
What has the following characteristics?
- Lungs fail to inflate after birth
- Hyaline membranes (necrotic epithelial cells and plasma proteins) line airways
- Treatment includes surfactant therapy, prophylactic administration of steroids, and ventilation techniques
Respiratory distress syndrome

What has the following characteristics?
- Most common lethal genetic disease in Caucasians
- - 1 in 2500 live births
- Autosomal recessive transmission
- Disorder of epithelial transport caused by mutations of CFTR gene
Cystic fibrosis

What has the following characteristics?
- Associated with pancreatic exocrine dysfunction
- Caused by production of abnormally viscous mucus
- - Cannot be cleared from the lungs
- - Blocks main pancreatic ducts
Cystic fibrosis
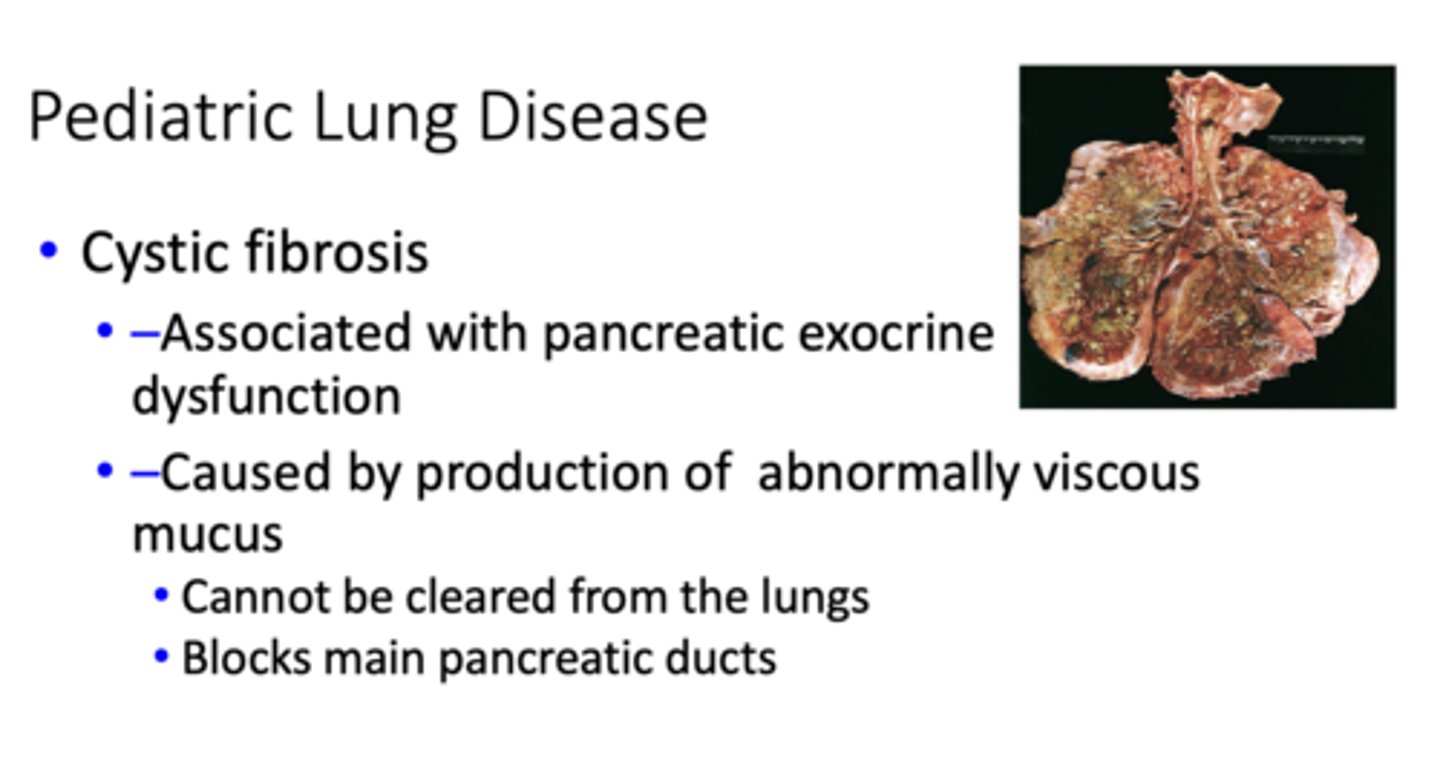
Pulmonary changes are most significant complications of this Pediatric Lung Disease:
Cystic fibrosis

What is the most significant complication of cystic fibrosis?
pulmonary changes

What has the following characteristics?
- Pulmonary changes are most significant complications
- 85-90% have pancreatic insufficiency
- 10% develop liver disease, recurrent nasal polyps, or sinusitis
- Median life expectancy now age 40
Cystic fibrosis
