Thromboembolic Disorders
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
A blood clot that forms in a vein, deep in the body/ most deep vein clots occur in the lower leg, thigh or pelvis/ if it can break loose it can cause PE -
its blood clots can be caused by: injury to a vein, surgery, Limited movement or Inactivity
a clot that has originally formed in the deep vein of the leg that usually breaks off and travels up through the circulation
injury; clot risk
overweight; hypoxia; Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1 (PAI1)
family history of DVT; smoking; nicotine
seated
CA, CHF
(DVT) risk factors:
__ that damages the vein (bone fx) (Damages to veins often occur during bone fractures or surgery. Postsurgery bed rest increases __)
__ (Fatty acids cause __ (decreased oxygenation), affecting tissues, Increase in __ due to fat deposits impairs fibrinolysis, Impaired fibrinolysis disrupts normal clot breakdown, increases pressure, and affects circulation)
__ - __ (__depletes blood circulation, promoting clot formation)
staying __ for a long time
__, __
venous capacitance
under/beneath
standing
pregnancy; hypercoagulability
delivery
(DVT) Risk during pregnancy:
__ (Degree of active constriction of veins affects blood return to heart and cardiac output. Increased during pregnancy, raising risk of DVT.) & venous pressure in the legs are increased resulting in stasis (stoppage of blood flow) (hypostasis: “hypo” (__) and “statis” (__)— prolonged standing or sitting leads to blood pooling, reducing circulation, and increasing clot risk)
__ causes a degree of __ (Thrombophilia or hypercoagulability refers to a higher tendency for blood to form clots)
__ (due to vascular trauma)
thrombophilia
hypercoagulability
a more specific term referring to inherited or acquired conditions that predispose to thrombosis
a broader term encompassing any state that increases clotting risk
foot, ankle, leg (usually on one side)
cramping pain; calf
foot; ankle
warmer
reddish-bluish
(DVT) Sx:
swelling of __, __, __
__ (due to blood pooling) in the affected leg that usually begins in the __
severe, unexplained __ and __ pain
an area of skin that feels __ than the skin on the surrounding areas
skin over the affected area turning pale or __ color
neck
shoulder
arm or hand
bluish-tinted
arm; forearm
UPPER EXTREMITY DVT
__ pain
__ pain
swelling in the __ or __
__ skin color (indicating poor
circulation)
pain that moves from the __ to
the __ weakness in the hand
doppler ultrasonography
(DVT) Diagnosis:
__ (non-invasive test estimating blood flow through vessels using high- frequency sound waves, utilizes a transducer to bounce sound waves off blood cells in the affected area, aiding in the detection of thrombosis) (used to assess specific areas, such as legs)
CT scan with contrast
__ (used to provide detailed images of veins and detect clots, contrast material helps enhance the visibility of blood vessels during imaging, uses a dye/contrast to highlight specific body areas for detailed examination) (contraindicated for pregnant women due to teratogenic sound waves)
venogram; 30 to 90 mins; OGG dye
white
gray
black
__ (an x-ray test that uses contrast material to visualize veins) (duration: __) (uses __ to visualize clots during x-ray) (appearance: bones (__), soft tissues (__), air in veins (__) (can affect renal functioning and creatinine levels)
0.9-1 mg/dl
0.7-1.2 mg/dl
48-72
Normal Creatinine Values:
Females: __
Males: __
(monitor creatinine levels closely for __ post-procedure to assess for CIN)
Contrast-Induced Nephropathy (CIN)
An impairment of kidney function due to dye, indicated by increased serum creatinine
sodium bicarbonate
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC)
dehydration therapy/ forced diuretics
Medications counteracting CIN:
__: decreases renal perfusion, expands intravascular volume to maintain renal blood flow, prevents hypoxemia)
__: enhances elimination of contrast from the body
__: helps to eliminate contrast taken during procedures
heparin; 6
warfarin
Treatment: (anticoagulant)
1. __ (throughout pregnancy & for _ weeks PP)
2. __ (non-pregnant patient)
(both are blood thinners used to prevent clot formation by inactivating thrombin and antithrombin, prevents conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, thus inhibiting clot formation)
lifestyle changes
healthy diet
compression stocking;
compression therapy
surgical thrombectomy
Management:
1. __ (avoid smoking and alcohol consumption)
2. __ (high fiber, low fat, increased fluid intake for
better circulation)
3. __- are elastic compression garments worn around the leg, compressing the limb. This reduces the diameter of distended veins and increases venous blood flow velocity and valve effectiveness.
4. __ - helps decrease venous pressure, prevents venous stasis and impairments of venous walls, and relieves heavy and aching legs.
__ (incision of the affected blood vessel and removal of the clot)
Thrombectomy
Removal of clot through incision
Catheter aspiration thrombectomy
Blood clot is removed using suction
Mechanical thrombectomy
Blood clot is broken up into small pieces and removed
foot pumps
knee pulls
ankle circles
DVT exercises (FKA)
pulmonary embolism
A Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) that causes blockage in 1 of the blood vessels (arteries) in the lungs - usually due to a blood clot.
thrombus
a blood clot
thrombosis
formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel/ a blockage of a blood vessel by a blood clot
embolism
occurs when a part or all of the thrombus dislodges from where it formed and travels in the blood vessel, elsewhere in the body
embolus
broken thrombus travelling in the blood that causes embolism
fatty material
foreign material
AF
air bubble
tumor
Mycotic emboli
(DVT) Causes:
__ from the marrow of a broken bone
__ from an impure injection (drug misuse)
__ from a pregnancy or child birth
A large __ in a vein
A small piece of cancerous material (__) that has broken off from a larger tumor in the body.
7. __- a material from a fungal infection
1. Breathlessness (mild to obvious
SOB)
2. Chest pain (sharp pain felt when
breathing in/the blood clot may
irritate the lining layer (pleura)
3. Hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
4. Fever
5. Tachycardia
6. No symptoms at all (common)
(DVT) Symptoms:
BCHFTN
Very Important
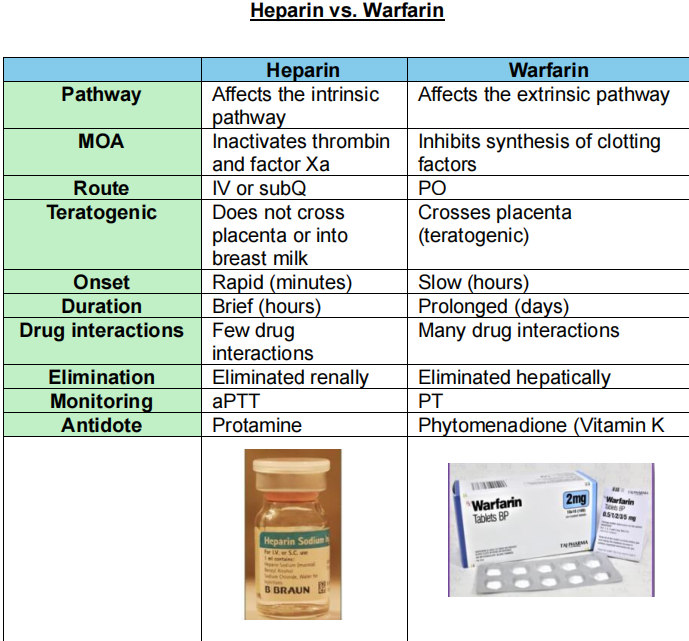
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT)
test to evaluate blood clot formation ability.
Works alongside PT (prothrombin time) for clot evaluation.
anticoagulant
oxygen; 0-2
thrombolysis; Streptokinase/
Urokinase
embolectomy
(DVT) Treatment:
1. __ (blood thinner, it alters certain chemicals in the blood to stop clots from forming)
2. __ (to reduce breathlessness) (__ LPM)
3. __ (clot-dissolving injection) (__/__) (more powerful than anticoagulant but with SE of unwanted bleeding--- Intracerebral Hemorrhage)
4. __ (surgical removal of embolus--a last resort for very ill patients
duplex doppler
(DVT) Diagnosis:
a type of UTZ used to show blood flow in the leg veins & any blockage to blood flow
blood test for D-dimer
(DVT) Diagnosis)
it detects fragments of breakdown products of a blood clot
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Stroke
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Why is D-Dimer done?
(DPSD)
catheter embolectomy
balloon embolectomy
METHODS:
1. __
2. __ Typically this is done by inserting a catheter with an inflatable balloon attached to its tip into an artery, passing the catheter tip beyond the clot, inflating the balloon, and removing the clot by withdrawing the catheter.
aspiration embolectomy
is also used for aspiration embolectomy, where the thrombus is removed by suction rather than pushing with a balloon. It is a rapid and effective way of removing thrombi in thromboembolic occlusions of the limb arteries below the inguinal ligament, as in leg infarction.
surgical embolectomy
is the simple surgical removal of a clot following incision into a vessel by open surgery on the artery
left lateral position
supine position
supine with neck extended
POSITIONS DURING 2D ECHO
__ - Classic position for 2d echo
__ - sometimes you may be asked to assume this position. Better for subcoastal view
__ - you may be asked to assume this position for assessment of aorta (grear artery of the body)
V1
4th intercostal space to the right of the sternum
V2
4th intercostal space to the left of the sternum
V3
Directly between the leads V₂ and V4
V4
5th intercostal space at midclavicular line
V5
Level with V₁ at left anterior axillary line
V6
Level with Vs at midaxillary line (directly
under the midpoint of the armpit
abrasion
A cut or scrape in the skin
contusion
A bruise or hematoma of tissue commonly caused by damaged capillaries
protamine
antidote for heparin
phytomenadione (vit. K)
antidote for warfarin